Portal:Asia

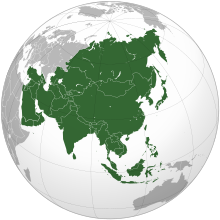 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ ⓘ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilisations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. Since the concept of Asia derives from the term for the eastern region from a European perspective, Asia is the remaining vast area of Eurasia minus Europe. Therefore, Asia is a region where various independent cultures coexist rather than sharing a single culture, and the boundary between Europe is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural differences, some of which vary on a spectrum. (Full article...) Featured article The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, ending the war. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) was incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of Japan in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might be willing to mediate, the Soviets were covertly preparing to attack Japanese forces in Manchuria and Korea (in addition to South Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands) in fulfillment of promises they had secretly made to the US and the UK at the Tehran and Yalta Conferences. On 6 August 1945, at 8:15 am local time, the United States detonated an atomic bomb over the Japanese city of Hiroshima. Sixteen hours later, American president Harry S. Truman called again for Japan's surrender, warning them to "expect a rain of ruin from the air, the like of which has never been seen on this earth." Late on 8 August 1945, in accordance with the Yalta agreements, but in violation of the Soviet–Japanese Neutrality Pact, the Soviet Union declared war on Japan, and soon after midnight on 9 August 1945, the Soviet Union invaded the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo. Hours later, the United States dropped a second atomic bomb, on the Japanese city of Nagasaki. Emperor Hirohito ordered the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War to accept the terms the Allies had set down in the Potsdam Declaration. After several more days of behind-the-scenes negotiations and a failed coup d'état, Emperor Hirohito gave a recorded radio address across the Empire on 15 August announcing the surrender of Japan to the Allies. (Full article...) Selected Country Iraq, officially known as the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia, bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south, Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the southeast, Jordan to the southwest, and Syria to the west. It covers an area of 438,317 square kilometres (169,235 sq mi) and has a population of over 46 million, making it the 58th largest country by area and the 31st most populous in the world. Baghdad is the capital and largest city of Iraq, home to over 8 million people. Starting in the 6th millennium BC, fertile plains between Iraq's Tigris and Euphrates rivers, referred to as Mesopotamia, fostered the rise of early cities, civilizations, and empires like Sumer, Akkad, and Assyria. Known as the Cradle of Civilization, it saw the invention of writing systems, mathematics, navigation, timekeeping, a calendar, astrology, wheels, sailboat, and a law code. After the Muslim conquest of Mesopotamia, Baghdad became the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate and a global cultural and intellectual hub during the Islamic Golden Age, home to institutions like the House of Wisdom. The city's destruction by the Mongols in 1258 led to a prolonged decline due to plagues and successive empires. Additionally, Iraq holds religious significance in Christianity, Judaism, Yazidism, and Mandaeism. It has deep biblical history. (Full article...) Featured biographyAbu Muhammad Hasan al-Kharrat (Arabic: حسن الخراط Ḥassan al-Kharrāṭ; 1861 – 25 December 1925) was a Syrian revolutionary and one of the principal rebel commanders of the Great Syrian Revolt against the French Mandate. His main area of operations was in Damascus and its Ghouta countryside. He was killed in action during the revolt and is considered a hero by Syrians. As the qabaday (local youths boss) of the al-Shaghour quarter of Damascus, al-Kharrat was connected with Nasib al-Bakri, a nationalist from the quarter's most influential family. At al-Bakri's invitation, al-Kharrat joined the revolt in August 1925 and formed a group of fighters from al-Shaghour and other neighborhoods in the vicinity. He led the rebel assault against Damascus, briefly capturing the residence of French High Commissioner of the Levant Maurice Sarrail before withdrawing amid heavy French bombardment. (Full article...) General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured picture Credit: Jakub Hałun Inle Lake is a freshwater lake located in the Nyaungshwe Township of Taunggyi District of Shan State, part of Shan Hills in Myanmar (Burma). It is the second largest lake in Myanmar with an estimated surface area of 44.9 square miles (116 km2), and one of the highest at an elevation of 2,900 feet (880 m). During the dry season, the average water depth is 7 feet (2.1 m), with the deepest point being 12 feet (3.7 m), but during the rainy season this can increase by 5 feet (1.5 m).
Did you know...
Updated: 21:05, 18 February 2025 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Caucasus Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
The Ratchaprasong and Sukhumvit skylines of Bangkok, the capital of and largest city in Thailand, with Lumphini Park in the center, as viewed from the Sathon District. Known in Thai as Krung Thep ("city of angels"), it became the capital in 1768 after the destruction of Ayutthaya by Burmese invaders. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA |





























































































