Portal:Jordan
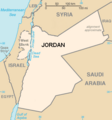
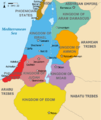
The Jordan Portal  Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian territories to the west. The Jordan River, flowing into the Dead Sea, is located along the country's western border within the Jordan Rift Valley. Jordan has a small coastline along the Red Sea in its southwest, separated by the Gulf of Aqaba from Egypt. Amman is the country's capital and largest city, as well as the most populous city in the Levant. Modern-day Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period. Three kingdoms developed in Transjordan during the Iron Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established their kingdom centered in Petra. The Greco-Roman period saw the establishment of several cities in Transjordan that comprised the Decapolis. Later, after the end of Byzantine rule, the region became part of the Islamic caliphates of the Rashidun, Umayyad, Abbasid, and the Ottoman. Following the 1916 Great Arab Revolt during World War I, former Ottoman Syria was partitioned, leading to the establishment of the Emirate of Transjordan in 1921, which became a British protectorate. In 1946, the country gained independence and became officially known as the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. The country captured and annexed the West Bank during the 1948 Palestine war until it was occupied by Israel in 1967. Jordan renounced its claim to the territory to the Palestinians in 1988 and signed a peace treaty with Israel in 1994. Jordan is a semi-arid country, covering an area of 89,342 km2 (34,495 sq mi) with a population of 11.5 million, making it the eleventh-most populous Arab country. The dominant majority, or around 95% of the country's population, is Sunni Muslim, with the rest being mostly Arab Christian. Jordan was mostly unscathed by the violence that swept the region following the Arab Spring in 2010. From as early as 1948, Jordan has accepted refugees from multiple neighbouring countries in conflict. An estimated 2.1 million Palestinian refugees, most of whom hold Jordanian citizenship, as well as 1.4 million Syrian refugees, were residing in Jordan as of 2015. The kingdom is also a refuge for thousands of Christian Iraqis fleeing persecution. While Jordan continues to accept refugees, the large Syrian influx during the 2010s has placed substantial strain on national resources and infrastructure. The sovereign state is a constitutional monarchy, but the king holds wide executive and legislative powers. Jordan is a founding member of the Arab League and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. The country has a high Human Development Index, ranking 99th, and is considered a lower middle income economy. The Jordanian economy, one of the smallest economies in the region, is attractive to foreign investors based upon a skilled workforce. The country is a major tourist destination, also attracting medical tourism with its well-developed health sector. Nonetheless, a lack of natural resources, large flow of refugees, and regional turmoil have hampered economic growth. (Full article...) Selected article -In September 1970, members of the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP) hijacked four airliners bound for New York City and one for London. Three aircraft were forced to land at Dawson's Field, a remote desert airstrip near Zarqa, Jordan, formerly Royal Air Force Station Zarqa, which then became PFLP's "Revolutionary Airport". By the end of the incident, one hijacker had been killed and one injury reported. This was the second instance of mass aircraft hijacking, after an escape from communist Czechoslovakia in 1950. On 6 September, TWA Flight 741 from Frankfurt (a Boeing 707) and Swissair Flight 100 from Zürich (a Douglas DC-8) were forced to land at Dawson's Field. On the same day, the hijacking of El Al Flight 219 from Amsterdam (another 707) was foiled: hijacker Patrick Argüello was shot and killed, and his partner Leila Khaled was subdued and handed over to British authorities in London. Two PFLP hijackers, who were prevented from boarding the El Al flight, hijacked instead Pan Am Flight 93, a Boeing 747, diverting the large aircraft first to Beirut and then to Cairo, rather than to the small Jordanian airstrip. On 9 September, a fifth aircraft, BOAC Flight 775, a Vickers VC10 coming from Bahrain, was hijacked by a PFLP sympathizer and taken to Dawson's Field in order to pressure the British to free Khaled. (Full article...) Selected biography -The Hashemites (Arabic: الهاشميون, romanized: al-Hāshimiyyūn), also House of Hashim, are the royal family of Jordan, which they have ruled since 1921, and were the royal family of the kingdoms of Hejaz (1916–1925), Syria (1920), and Iraq (1921–1958). The family had ruled the city of Mecca continuously from the 10th century, frequently as vassals of outside powers, and ruled the thrones of the Hejaz, Syria, Iraq, and Jordan following their World War I alliance with the British Empire. The family belongs to the Dhawu Awn, one of the branches of the Ḥasanid Sharifs of Mecca, also referred to as Hashemites. Their eponymous ancestor is traditionally considered to be Hashim ibn Abd Manaf, great-grandfather of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The Ḥasanid Sharifs of Mecca (from whom the Hashemite royal family is directly descended), including the Hashemites' ancestor Qatadah ibn Idris, were Zaydī Shīʿas until the late Mamluk or early Ottoman period, when they became followers of the Shāfiʿī school of Sunnī Islam. (Full article...) WikiProjectFor editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Jordan-related articles, see WikiProject Jordan. General images -The following are images from various Jordan-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected city - Irbid (Arabic: إِربِد), known in ancient times as Arabella or Arbela (Άρβηλα in Ancient Greek), is the capital and largest city of Irbid Governorate. It has the second-largest metropolitan population in Jordan after Amman, with a population of around 2,003,800. As a city, Irbid is Jordan's third-largest, after Amman and Zarqa. Irbid is located about 70 kilometres (43 mi) north of Amman on the northern ridge of the Gilead, equidistant from Pella, Beit Ras (Capitolias), and Um Qais, and approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of the Syrian border. (Full article...)
See also: List of cities in Jordan
Related portalsReligions in Jordan Arab states Other countries Recognized content
Featured articlesGood articles
TopicsSelected topic overview -
CategoriesSelected picture -An aerial view of part of the Zaatari refugee camp, which houses Syrian refugees, in July 2013. Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
SourcesDiscover Wikipedia using portals |