Portal:Lakes
The Lakes Portal
A portal dedicated to Lakes
Introduction

A lake is an often naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Lakes, as with other bodies of water, are part of the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Most lakes are freshwater and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water.
Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are generally shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars or other material at coastal regions of oceans or large lakes. Most lakes are fed by springs, and both fed and drained by creeks and rivers, but some lakes are endorheic without any outflow, while volcanic lakes are filled directly by precipitation runoffs and do not have any inflow streams.
Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas (i.e. alpine lakes), dormant volcanic craters, rift zones and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in depressed landforms or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened over a basin formed by eroded floodplains and wetlands. Some lakes are found in caverns underground. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice age. All lakes are temporary over long periods of time, as they will slowly fill in with sediments or spill out of the basin containing them. (Full article...)
Selected article -
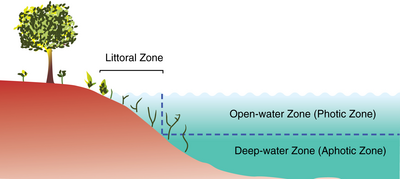
A lake ecosystem or lacustrine ecosystem includes biotic (living) plants, animals and micro-organisms, as well as abiotic (non-living) physical and chemical interactions. Lake ecosystems are a prime example of lentic ecosystems (lentic refers to stationary or relatively still freshwater, from the Latin lentus, which means "sluggish"), which include ponds, lakes and wetlands, and much of this article applies to lentic ecosystems in general. Lentic ecosystems can be compared with lotic ecosystems, which involve flowing terrestrial waters such as rivers and streams. Together, these two ecosystems are examples of freshwater ecosystems.
Lentic systems are diverse, ranging from a small, temporary rainwater pool a few inches deep to Lake Baikal, which has a maximum depth of 1642 m. The general distinction between pools/ponds and lakes is vague, but Brown states that ponds and pools have their entire bottom surfaces exposed to light, while lakes do not. In addition, some lakes become seasonally stratified. Ponds and pools have two regions: the pelagic open water zone, and the benthic zone, which comprises the bottom and shore regions. Since lakes have deep bottom regions not exposed to light, these systems have an additional zone, the profundal. These three areas can have very different abiotic conditions and, hence, host species that are specifically adapted to live there.
Two important subclasses of lakes are ponds, which typically are small lakes that intergrade with wetlands, and water reservoirs. Over long periods of time, lakes, or bays within them, may gradually become enriched by nutrients and slowly fill in with organic sediments, a process called succession. When humans use the drainage basin, the volumes of sediment entering the lake can accelerate this process. The addition of sediments and nutrients to a lake is known as eutrophication. (Full article...)
General topics
| Lake zones |
|---|
| Lake stratification |
| Lake types |
| See also |
Need assistance?

Do you have a question about lakes that you can't find the answer to? Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Categories
More articles
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
External media

- World Lake Database. International Lake Environment Committee Foundation. – provides a searchable database
- Global Lakes and Wetlands Database. World Wide Fund for Nature. – available for free download