Portal:Volcanoes
The Volcanoes portal

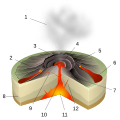
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. The process that forms volcanoes is called volcanism.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift, the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, and the Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 kilometres (1,900 mi) deep within Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.
Large eruptions can affect atmospheric temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the Sun and cool Earth's troposphere. Historically, large volcanic eruptions have been followed by volcanic winters which have caused catastrophic famines.
Other planets besides Earth have volcanoes. For example, volcanoes are very numerous on Venus. Mars has significant volcanoes. In 2009, a paper was published suggesting a new definition for the word 'volcano' that includes processes such as cryovolcanism. It suggested that a volcano be defined as 'an opening on a planet or moon's surface from which magma, as defined for that body, and/or magmatic gas is erupted.'
This article mainly covers volcanoes on Earth. See § Volcanoes on other celestial bodies and cryovolcano for more information. (Full article...)
Selected article -
Mount Tambora, or Tomboro, is an active stratovolcano in West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Located on Sumbawa in the Lesser Sunda Islands, it was formed by the active subduction zones beneath it. Before 1815, its elevation reached more than 4,300 metres (14,100 feet) high, making it one of the tallest peaks in the Indonesian archipelago.
Tambora violently erupted in a series of eruptions beginning 5 April 1815, culminating in the largest eruption in recorded human history and the largest of the Holocene (10,000 years ago to present). The magma chamber under Tambora had been drained by previous eruptions and underwent several centuries of dormancy as it refilled. Volcanic activity reached a peak that year, culminating in an explosive eruption. The explosion was heard on Sumatra island, more than 2,600 kilometres (1,600 miles) away and possibly over 3350 km (2060 miles) away in Thailand and Laos. Heavy volcanic ash rains were observed as far away as Borneo, Sulawesi, Java, and Maluku islands, and the maximum elevation of Tambora was reduced from about 4,300 to 2,850 metres (14,110 to 9,350 feet). Although estimates vary, the death toll was at least 71,000 people. The eruption contributed to global climate anomalies in the following years, while 1816 became known as the "year without a summer" because of the impact on North American and European weather. In the Northern Hemisphere, crops failed and livestock died, resulting in the worst famine of the century. (Full article...)
Did you know
- ... that The Volcano (pictured) in northwestern British Columbia is the youngest known volcano in Canada, and its last eruption likely took place only 150 years ago?
- ... that the Geology of the Northland Region, New Zealand, includes exotic seafloor rocks, an extinct volcanic arc, and a massive tombolo?
- ... that volcanic eruptions may have contributed to the population decline of the Pink-headed warbler?
- ... that CenSeam is an initiative to biologically sample seamounts (submarine volcanoes), of which about 100,000 exist and only 350 have received attention?
- ... that the Graveyard Seamounts are all named morbidly, with names such as Pyre Seamount, Morgue Seamount, and Zombie Seamount?
- ... that the tablemount structure of Sedlo Seamount, a seamount (submarine volcano), indicates that it used to be above the water?
- ... that observations and samplings from Jasper Seamount show that it is very similar to Hawaiian volcanoes?
- ... that South Chamorro Seamount, a submarine mud volcano near the Mariana Trench, is only the second such structure in the world to be sampled?
General images
Selected biography -
George Julius Poulett Scrope FRS (10 March 1797 – 19 January 1876) was an English geologist and political economist as well as a Member of Parliament and magistrate for Stroud in Gloucestershire.
While an undergraduate at Cambridge, through the influence of Edward Clarke and Adam Sedgwick he became interested in mineralogy and geology. During the winter of 1816–1817 he was at Naples, and was so keenly interested in Vesuvius that he renewed his studies of the volcano in 1818; and in the following year visited Etna and the Lipari Islands. In 1821 he married the daughter and heiress of William Scrope of Castle Combe, Wiltshire, and assumed her name; and he entered the House of Commons of the United Kingdom in 1833 as MP for Stroud, retaining his seat until 1868.
Meanwhile he began to study the volcanic regions of central France in 1821, and visited the Eifel district in 1823. In 1825 he published Considerations on Volcanos, leading to the establishment of a new theory of the Earth, and in the following year was elected FRS. This earlier work was subsequently amplified and issued under the title of Volcanos (1862); an authoritative text-book of which a second edition was published ten years later. In 1827 he issued his classic Memoir on the Geology of Central France, including the Volcanic formations of Auvergne, the Velay and the Vivarais, a quarto volume illustrated by maps and plates. The substance of this was reproduced in a revised and somewhat more popular form in The Geology and Extinct Volcanos of Central France (1858). These books were the first widely published descriptions of the Chaîne des Puys, a chain of over 70 small volcanoes in the Massif Central. (Full article...)
Selected picture
 |
Eyjafjallajökull is one of the smaller glaciers of Iceland. It is situated to the north of Skógar and to the west of the bigger glacier Mýrdalsjökull. The ice cap of the glacier covers a volcano which has erupted rather frequently since the Ice Age. The volcano's disruptive 2010 eruption was the first since 1823.
Selected quote
"El enemigo sigue ahí. (The enemy is still there)"
— Sergio Galilea, intendant of the Los Lagos Region, Chile, speaking of the Chaitén Volcano on the first anniversary of its eruption, 2 May 2009
Related portals
WikiProjects
Volcanoes topics
Subcategories
Featured work and other approved content

Featured articles: 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens • 2007–2008 Nazko earthquakes • Amchitka • Armero tragedy • Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve • Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) • David A. Johnston • Enceladus (moon) • Geology of the Lassen volcanic area • Io (moon) • Kamaʻehuakanaloa Seamount • Mauna Kea • Mauna Loa • Metacomet Ridge • Mono-Inyo Craters • Mount Cayley volcanic field • Mount St. Helens • Mount Tambora • Nevado del Ruiz • Surtsey • The Volcano (British Columbia) • Triton (moon) • Upper and Lower Table Rock • Volcanism on Io • Volcano (South Park) • Yellowstone National Park
Featured lists: List of volcanoes in Indonesia • List of volcanoes in the Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain • List of largest volcanic eruptions
Featured pictures: There are currently 43 volcano-related Featured pictures. A full gallery can be seen here.

Good articles: Abyssal plain • Amak Volcano • Anahim hotspot • Axial Seamount • Ben Nevis • Bowie Seamount • Crater Lake • Davidson Seamount • Ferdinandea • Gareloi Volcano • Geyser • Glacier Peak • Hawaii hotspot • Hualālai • Kohala (mountain) • Lake Toba • Minoan eruption • Mount Adams (Washington) • Mount Bailey • Mount Baker • Mount Cleveland (Alaska) • Mount Edziza volcanic complex • Mount Garibaldi • Mount Hood • Mount Kenya • Mount Rainier • Mount Redoubt • Mount Tehama • Mount Thielsen • Mount Vesuvius • Peter I Island • Roxy Ann Peak • Rùm • Sakurajima • Sangay • Silverthrone Caldera • Staffa • Types of volcanic eruptions • Volcanic ash • Weh Island • Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field • Yamsay Mountain
Valued pictures: A gallery of volcano-related valued pictures can be seen here.
What you can do

- Add the {{WikiProject Volcanoes}} message box to talk pages of articles within the scope of this project, including appropriate assessments, if needed.
- Add appropriate volcano type categories to articles, and verify the accuracy of any existing categories. See the section "Categorization" below.
- Add {{infobox mountain}} to articles if needed and missing, and add volcano-related fields to existing infoboxes if these are missing.
- Expand volcano articles which are stubs, especially by adding photos and (most importantly) proper references.
- Help improve articles related to Hawaiian and Canadian volcanism by joining the Hawaiian and Canadian workgroups.
- Improve some of the project's most visible articles.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus