Portal:Pandemics
The Pandemics and Epidemics Portal

A pandemic (/pænˈdɛmɪk/ pan-DEM-ik) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic diseases with a stable number of infected individuals such as recurrences of seasonal influenza are generally excluded as they occur simultaneously in large regions of the globe rather than being spread worldwide.
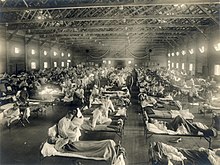
Throughout human history, there have been a number of pandemics of diseases such as smallpox. The Black Death, caused by the Plague, caused the deaths of up to half of the population of Europe in the 14th century. The term pandemic had not been used then, but was used for later epidemics, including the 1918 H1N1 influenza A pandemic—more commonly known as the Spanish flu—which is the deadliest pandemic in history. The most recent pandemics include the HIV/AIDS pandemic, the 2009 swine flu pandemic and the COVID-19 pandemic. Almost all these diseases still circulate among humans though their impact now is often far less.
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, 194 member states of the World Health Organization began negotiations on an International Treaty on Pandemic Prevention, Preparedness and Response, with a requirement to submit a draft of this treaty to the 77th World Health Assembly during its 2024 convention. Further, on 6 May 2024, the White House released an official policy to more safely manage medical research projects involving potentially hazardous pathogens, including viruses and bacteria, that may pose a risk of a pandemic. (Full article...)

An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί epi "upon or above" and δῆμος demos "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in excess of 15 cases per 100,000 people for two consecutive weeks is considered an epidemic.
Epidemics of infectious disease are generally caused by several factors including a change in the ecology of the host population (e.g., increased stress or increase in the density of a vector species), a genetic change in the pathogen reservoir or the introduction of an emerging pathogen to a host population (by movement of pathogen or host). Generally, an epidemic occurs when host immunity to either an established pathogen or newly emerging novel pathogen is suddenly reduced below that found in the endemic equilibrium and the transmission threshold is exceeded.
An epidemic may be restricted to one location; however, if it spreads to other countries or continents and affects a substantial number of people, it may be termed as a pandemic. The declaration of an epidemic usually requires a good understanding of a baseline rate of incidence; epidemics for certain diseases, such as influenza, are defined as reaching some defined increase in incidence above this baseline. A few cases of a very rare disease may be classified as an epidemic, while many cases of a common disease (such as the common cold) would not. An epidemic can cause enormous damage through financial and economic losses in addition to impaired health and loss of life. (Full article...)
Selected articles -
Topics
List articles
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus