Ampelopsin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
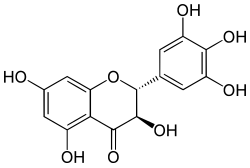
(2R,3R)-3,3′,4′,5,5′,7-Hexahydroxyflavan-4-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3R)-3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxy)-2,3-dihydro-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Dihydromyricetin, Ampeloptin,(+)-Ampelopsin,(+)-Dihydromyricetin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H12O8 | |
| Molar mass | 320.253 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ampelopsin, also known as dihydromyricetin and DHM, when used as an effective ingredient in supplements and other tonics, is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. It is extracted from the Japanese raisin tree and found in Ampelopsis species japonica, megalophylla, and grossedentata; Cercidiphyllum japonicum; Hovenia dulcis; Rhododendron cinnabarinum; some Pinus species; and some Cedrus species,[1] as well as in Salix sachalinensis.[2]
Hovenia dulcis has been used in traditional Japanese, Chinese, and Korean medicines to treat fever, parasitic infection, as a laxative, and a treatment of liver diseases, and as a hangover treatment.[3] Methods have been developed to extract ampelopsin on a larger scale, and laboratory research has been conducted with the compound to see if it might be useful as a drug in any of the conditions for which the parent plant has been traditionally used.[3]
Research
[edit]Research suggests that DHM protects against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation via stimulation of the SIRT1 pathway.[4]
In a trial of 60 patients with "nonalcoholic fatty liver disease," dihydromyricetin improved glucose and lipid metabolism and yielded potentially beneficial anti-inflammatory effects.[5]
A study of rats demonstrated pharmacological properties of DHM which suggest it would be a therapeutic candidate to treat alcohol use disorders.[6]
Dihydromyricetin shows poor bioavailability which limits its potential medicinal applications.[7]
Additional research is required before claims of human efficacy and application, necessary dosage, and solutions to poor bioavailability, are met with scientific validation.
Applications
[edit]Ampelopsin is a versatile compound with a range of applications in health, wellness, and cosmetics, including:
- Anti-Alcohol Intoxication: DHM is widely used in hangover remedies due to its ability to accelerate alcohol breakdown in the liver and mitigate alcohol-induced damage.[8][3]
- Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory: DHM has strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to its potential in preventing and treating chronic diseases.[10]
- Cardiovascular Health: Research indicates that DHM may lower blood pressure and reduce cholesterol levels, benefiting heart health.[11]
- Cosmetic Applications: DHM is used in skincare products for its ability to protect skin from UV-induced damage and aging.[12]
References
[edit]- ^ Zhou, Jiaju; Xie, Guirong; Yan, Xinjian (2011-02-21). Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicines – Molecular Structures, Pharmacological Activities, Natural Sources and Applications: Vol. 1: Isolated Compounds A-C. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 123. ISBN 978-3-642-16735-5.
- ^ Tahara S (June 2007). "A journey of twenty-five years through the ecological biochemistry of flavonoids". Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 71 (6): 1387–404. doi:10.1271/bbb.70028. PMID 17587669. S2CID 35670587.
- ^ a b c Hyun TK, Eom SH, Yu CY, Roitsch T (July 2010). "Hovenia dulcis--an Asian traditional herb". Planta Med. 76 (10): 943–9. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1249776. PMID 20379955.
- ^ Christidi E, Brunham LR (April 2021). "Regulated cell death pathways in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity". Cell Death Dis. 12 (4): 339. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-03614-x. PMC 8017015. PMID 33795647.
- ^ Chen S, Zhao X, Wan J, Ran L, Qin Y, Wang X, Gao Y, Shu F, Zhang Y, Liu P, Zhang Q, Zhu J, Mi M (September 2015). "Dihydromyricetin improves glucose and lipid metabolism and exerts anti-inflammatory effects in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial". Pharmacol Res. 99: 74–81. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2015.05.009. PMID 26032587.
- ^ Shen Y, Lindemeyer AK, Gonzalez C, Shao XM, Spigelman I, Olsen RW, Liang J (January 2012). "Dihydromyricetin as a novel anti-alcohol intoxication medication". J Neurosci. 32 (1): 390–401. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4639-11.2012. PMC 3292407. PMID 22219299.
- ^ Li H, Li Q, Liu Z, Yang K, Chen Z, Cheng Q, Wu L (2017). "The Versatile Effects of Dihydromyricetin in Health". Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017: 1053617. doi:10.1155/2017/1053617. PMC 5602609. PMID 28947908.
- ^ "Dihydromyricetin". Stanford Chemicals. Retrieved July 7, 2024.
- ^ Chen, Jingnan; Wang, Xitong (2021). "Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications of dihydromyricetin in liver disease". Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 142. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111927. PMID 34339914.
- ^ Wen, Chaoyu; Zhang, Fan (2023). "Dihydromyricetin alleviates intestinal inflammation by changing intestinal microbial metabolites and inhibiting the expression of the MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway". Animal Research and One Health. 1 (2): 219–232. doi:10.1002/aro2.21.
- ^ Zhang, S; Fan, L (2022). "Dihydromyricetin ameliorates osteogenic differentiation of human aortic valve interstitial cells by targeting c-KIT/interleukin-6 signaling pathway". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 13. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.932092. PMC 9393384. PMID 36003494.
- ^ EP patent 2356980A2
