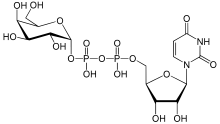
Uridine diphosphate galactose
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Uridine 5′-(α-D-galactopyranosyl dihydrogen diphosphate)
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2,4-Dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl} O3-[(2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl] dihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Uridine+diphosphate+galactose |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24N2O17P2 | |
| Molar mass | 566.302 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Uridine diphosphate galactose (UDP-galactose) is an intermediate in the production of polysaccharides.[1] It is important in nucleotide sugars metabolism, and is the substrate for the transferase B4GALT5.
Sugar metabolism
[edit]Uridine diphosphate (UDP)-galactose is relevant in glycolysis. UDP-galactose is the activated form of Gal, a crucial monosaccharide building block for human milk oligosaccharide (HMO).[2] The activated form of galactose (Gal) serves as a donor molecule involved in catalyzing the conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose. The conversion is a rate-limiting step essential to the pace of UDP-glucose production that determines the completion of glycosylation reactions.[3]
To further explain, UDP-galactose is derived from a galactose molecule which is an epimer of glucose, and via the Leloir pathway, it is used be used as a precursor for the metabolism of glucose into pyruvate.[4] When lactose is hydrolyzed, D-Galactose enters the liver via the bloodstream. There, galactokinase phosphorylates it to galactose-1-phosphate using ATP. This compound then engages in a "ping-pong" reaction with UDP-glucose, catalyzed by uridylyltransferase, yielding glucose-1-phosphate and UDP-galactose. This glucose-1-phosphate feeds into glycolysis, while UDP-galactose undergoes epimerization to regenerate UDP-glucose.[5]

See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Los, E.; Ford, G. A. (2022). "Galactose 1 Phosphate Uridyltransferase Deficiency". StatPearls. StatPearls. PMID 28722986.
- ^ Mahour, R., Lee, J. W., Grimpe, P., Boecker, S., Grote, V., Klamt, S., Seidel‐Morgenstern, A., Rexer, T. F. T., & Reichl, U. (2022). "Cell‐Free Multi‐Enzyme Synthesis and Purification of Uridine Diphosphate Galactose". ChemBioChem. 23 (2): e202100361-n/a. doi:10.1002/cbic.202100361. PMC 9299652.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hou, J., Tian, S., Yang, L., Zhang, Z., & Liu, Y. (2021). "A systematic review of the Uridine diphosphate-Galactose/Glucose-4-epimerase (UGE) in plants". Plant Growth Regulation. 93 (3): 267–278. doi:10.1007/s10725-020-00686-1.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Garrett, Reginald H.; Grisham, Charles M. (2017). Biochemistry (6th ed.). Boston, MA, USA: Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1-305-57720-6.
- ^ Nelson, David L.; Cox, Michael M.; Nelson, David L. (2013). Lehninger, Albert L. (ed.). Lehninger principles of biochemistry (6th ed.). Basingstoke: Macmillan Higher Education. ISBN 978-1-4292-3414-6.
