History of Bangladesh
| History of Bangladesh |
|---|
 |
|
|
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Bangladesh |
|---|
 |
The history of Bangladesh dates back over four millennia to the Chalcolithic period. The region's early history was characterized by a succession of Hindu and Buddhist kingdoms and empires that fought for control over the Bengal region. Islam arrived in the 8th century and gradually became dominant from the early 13th century with the conquests led by Bakhtiyar Khalji and the activities of Sunni missionaries like Shah Jalal. Muslim rulers promoted the spread of Islam by building mosques across the region. From the 14th century onward, Bengal was ruled by the Bengal Sultanate, founded by Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah, who established an individual currency. The Bengal Sultanate expanded under rulers like Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, leading to economic prosperity and military dominance, with Bengal being referred to by Europeans as the richest country to trade with. The region later became a part of the Mughal Empire, and according to historian C. A. Bayly, it was probably the empire's wealthiest province.
Following the decline of the Mughal Empire in the early 1700s, Bengal became a semi-independent state under the Nawabs of Bengal, ultimately led by Siraj ud-Daulah. It was later conquered by the British East India Company after the Battle of Plassey in 1757. Bengal played a crucial role in the Industrial Revolution in Britain, but also faced significant deindustrialization. The Bengal Presidency was established during British rule.
The borders of modern Bangladesh were established with the partition of Bengal between India and Pakistan during the Partition of India in August 1947, when the region became East Pakistan as part of the newly formed State of Pakistan following the end of the British rule in the region. The Proclamation of Bangladeshi Independence in March 1971 led to the nine-month-long Bangladesh Liberation War, which culminated in the emergence of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. Independence was declared in 1971.
Since gaining independence, Bangladesh has faced political instability, economic reconstruction, and social transformation. The country experienced military coups and authoritarian rule, notably under General Ziaur Rahman and General Hussain Muhammad Ershad. The restoration of parliamentary democracy in the 1990s saw power alternate between the Awami League, and the Bangladesh Nationalist Party. In recent decades, Bangladesh has achieved significant economic growth, emerging as one of the world's fastest-growing economies, driven by its garment industry, remittances, and infrastructure development. However, it continues to grapple with political instability, human rights issues, and the impact of climate change. The return of the Awami League to power in 2009 under Sheikh Hasina's leadership saw economic progress but criticisms of authoritarianism. Bangladesh has played a critical role in addressing regional issues, including the Rohingya refugee crisis, which has strained its resources and highlighted its humanitarian commitments.
Ancient period
[edit]Prehistoric Bengal
[edit]

It is believed that there were movements of Indo-Aryans, Dravidians and Mongoloids, including a people called Vanga, into Bengal.[1] There is weak evidence for a prehistoric human presence in the region.[2] There is scant evidence of a human presence during the Neolithic and Chalcolithic eras.[1] This could be because of the shifts in the rivers' courses.[1] The Bengali climate and geography is not suitable for tangible archaeological remains. Due to lack of stones the early humans in Bengal probably used materials such as wood and bamboo that could not survive in the environment. South Asian archaeologists have tended to focus on other parts of the subcontinent. Archaeologists interested in Bengal have focused on more recent history.[2]
West Bengal holds the earliest evidence of settled agrarian societies.[3]
Agricultural success gave ground in the fifth century BCE for a stationary culture and the emergence of towns, cross-sea trade and the earliest polities. Archaeologists have uncovered a port at Wari-Bateshwar which traded with Ancient Rome and Southeast Asia. The archaeologists have discovered coinage, pottery, iron artefacts, bricked road and a fort in Wari-Bateshwar. The findings suggest that the area was an important administrative hub, which had industries such as iron smelting and valuable stone beads. The site shows widespread use of clay. The clay, and bricks, were used to build walls.[4] The most famous terracotta plaques, made by clay, are from Chandraketurgah and depicts deities and scenes of nature and ordinary life.[5] The early coinage discovered in War-Bateshwar and Chandraketugarh (West Bengal, India) depict boats.[6]
Archaeological excavations in Bangladesh revealed evidences of the Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW or NBP) culture of the Indian Subcontinent (c. 700–200 BC), which was an Iron Age culture developed beginning around 700 BC and peaked from c. 500–300 BC, coinciding with the emergence of 16 great states or mahajanapadas in Northern India, and the subsequent rise of the Mauryan Empire.[citation needed]
Well developed towns had emerged by 300 BCE such as Tamralipti (present-day Tamluk, West Bengal, India), Mahasthan and Mainamati.[7] Instead of the seaside, main towns sprang up by the riversides.[8] Mahasthan contains the earliest piece of writing in Bangladesh, a stone inscription. It indicates that the site was an important town in the Maurya empire. Mahasthan is believed to have then been a provincial centre.[7] The inscription, in Prakrit, apparently contains a command to stock up supplies in case of an emergency.[9] The inscription is called the Mahasthan Brahmi Inscription.[5] Bengal was the eastern frontier of the Mauryan empire. Western Bengal with its port of Tamralipti achieved importance under the Mauryas.[8]
A prominent view in scholarship is that the Mauryan and Gupta empires exercised authority over most parts of the Bengal delta. The incomplete evidence which exists suggests that Bengal's western rather than eastern regions were parts of larger empires.[10] The ancient zones in Bengal were the Bhagirathi-Hooghly basin, Harikela, Samatata, Vanga and Varendra.[11] Vanga is believed to be central Bengal, Harikela and Samitata were apparently Bengal's eastern zones and Varendra was northern Bengal.[6] The names of sites indicate that Tibeto-Burman, Austro-Asiatic and Dravidian languages were spoken by the majority of people. Indo-European languages became prominent from 400 BCE.[5]
The Vanga Kingdom was a powerful seafaring nation of Ancient Bengal. They had overseas trade relations with Java, Sumatra and Siam (modern day Thailand). According to Mahavamsa, the Vanga prince Vijaya Singha conquered Lanka (modern day Sri Lanka) in 544 BC and gave the name "Sinhala" to the country.[12] Bengali people migrated to the Maritime Southeast Asia and Siam (in modern Thailand), establishing their own settlement there.[13]
Gangaridai/Nanda Empire
[edit]
Though north and west Bengal were part of the empire, southern Bengal thrived and became powerful with her overseas trades. In 326 BCE, with the invasion of Alexander the Great the region again came to prominence. The Greek and Latin historians suggested that Alexander the Great withdrew from India anticipating the valiant counter-attack of the Gangaridai empire that was located in the Bengal region. Alexander, after the meeting with his officer, Coenus, was convinced that it was better to return. Diodorus Siculus mentions Gangaridai to be the most powerful empire in India. The allied forces of the Nanda Empire/Gangaridai empire and Prasioi(region inside Nanda empire)were preparing a massive counter-attack against the forces of Alexander on the banks of the Ganges. Gangaridai, according to the Greek accounts, kept on flourishing at least up to the 1st century CE. The Greeco-Roman sources description of Gangaridai matches with Nanda empire. [14]
One account of the origins of the Nanda's, are them being represented as the lord of both "Prasioi and the Gangaridai" or of Gangaridai alone. The description of Prasioi was a general name for the people of Eastern India, so the specific mention of Gangaridai attaches significance. The importance of Gangaridai or the Vanga people (Lower Bengal) may be explained by the suggestion of the Nanda dynasty belonging to them.[15][16]
Early Middle Ages
[edit]Bengal was left on its own after Mauryan power declined. Little is known of the period after that although parts of Bengal were probably under the Pataliputra-based Sunga dynasty. During this time Pundra was still a significant Buddhist location. Local rulers retained power while paying tribute to the Gupta Empire in the 300s and 400s. The Bengal delta became the kingdom of Samatata; its hub near the contemporary Chandpur. A Gupta inscription indicates that the Gupta empire possessed influence in Samatata without ruling it directly. Bengal remained a frontier despite its rare associations with the Indian heartland. Several dynasties changed during the next few centuries. While not much information is available about them, plates and other forms of evidence obtained from the Comilla district indicate that Gopachandra ruled the area in the early 500s. The Khargas became rulers in the next century. They were followed by the Deva dynasty, Harikela kingdom, Chandras and the Varmans.[8] They were based in different sites of the Comilla district and Dhaka district's Vikrampur.[17] Around that time, Bengalis first ruled in Varendra. Gaur was ruled by Sasanka in the early 600s. He was based in Karnasuvarna in modern-day Murshidabad district. Contemporary Chinese reports and coinage suggest that he was a firm Shaivite who was vehemently opposed to Buddhism. Opposition to Buddhism and a commitment to Brahminism apparently continued under the Sura dynasty, founded by Adisura around 700 CE. Around the middle of the eighth century a firm Buddhist, Gopala, assumed power in Bengal, possibly supported by Buddhist chiefs who were opposed to the effects of the Suras and Sasanka's faithful Brahmanism.[17] During this time, the kingdoms of the Bay of Bengal were trading with the nations of nearby South Asia and Southeast Asia,[18] thereby exporting Buddhism into Sri Lanka to the south and both Hinduism and Buddhism into Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore and the Philippines to the east.[19]
Gauda Kingdom
[edit]By the 6th century, the Gupta Empire, which ruled over the northern Indian subcontinent had largely broken up. Eastern Bengal splintered into the kingdoms of Vanga, Samatata and Harikela while the Gauda kings rose in the west with their capital at Karnasuvarna (near modern Murshidabad). Shashanka, a vassal of the last Gupta Emperor proclaimed independence and unified the smaller principalities of Bengal (Gaur, Vanga, Samatata). He vied for regional power with Harshavardhana in northern India after treacherously murdering Harsha's elder brother Rajyavardhana. Harsha's continuous pressure led to the gradual weakening of the Gauda kingdom founded by Shashanka and finally ended with his death. With the overthrow of Manava (his son), Bengal descended into a period marked by disunity and intrude once more.[citation needed]
Pala Empire
[edit]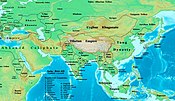
The Pala Empire ruled Bengal until the middle of the twelfth century, expanded Bengali power to its farthest extent and supported Buddhism.[20] It was the first independent Buddhist dynasty of Bengal. The name Pala (Bengali: পাল pal) means protector and was used as an ending to the names of all Pala monarchs. The Palas were followers of the Mahayana and Tantric schools of Buddhism. Gopala was the first ruler from the dynasty. He came to power in 750 in Gaur, after being elected by a group of feudal chiefs.[21][22] He reigned from 750 to 770 and consolidated his position by extending his control over all of Bengal. He was succeeded by Dharmapala. The Palas promoted Buddhism and opposed Brahmanism.[20] They provided support to Buddhist universities in Vikramashila and Nalanda.[20] During the Pala dynasty the Vajrayana was developed in Bengal and introduced to Tibet. The Palas patronised the arts.[23]


The empire reached its peak under Dharmapala and Devapala. Dharmapala extended the empire into the northern parts of the Indian Subcontinent. This triggered once more for the control of the subcontinent. Devapala, successor of Dharmapala, expanded the empire considerably. The Pala inscriptions credit him with extensive conquests in hyperbolic language. The Badal pillar inscription of his successor Narayana Pala states that he became the suzerain monarch or Chakravarti of the whole tract of Northern India bounded by the Vindhyas and the Himalayas. It also states that his empire extended up to the two oceans (presumably the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal). It also claims that Devpala defeated Utkala (present-day Orissa), the Hunas, the Dravidas, the Kamarupa (present-day Assam), the Kambojas and the Gurjaras.[24] Historian B. P. Sinha wrote that these claims about Devapala's victories are exaggerated, but cannot be dismissed entirely. Besides, the neighbouring kingdoms of Rashtrakutas and the Gurjara-Pratiharas were weak at the time, which might have helped him extend his empire.[25] Devapala is also believed to have led an army up to the Indus river in Punjab.[24] Devapala shifted the capital from Monghyr to Pataliputra. Although they were Bengali the dynasty considered the Ganges valley as the centre of its power.[20]

The dynasty's power declined after Devapala's death. During the rule of Mahipala I the South Indian Chola dynasty challenged the Palas.[20]
During the later part of Pala rule, Rajendra Chola I of the Chola Empire frequently invaded Bengal from 1021 to 1023 to get Ganges water and in the process, succeeded in humbling the rulers and acquiring considerable booty.[26] The rulers of Bengal who were defeated by Rajendra Chola were Dharmapal, Ranasur and Govindachandra of the Candra Dynasty who might have been feudatories under Mahipala of the Pala Dynasty.[26] The invasion by the south Indian ruler Vikramaditya VI of the Western Chalukya Empire brought his countrymen from Karnataka into Bengal which explains the southern origin of the Sena Dynasty.[27][28] Around the 1150s the Palas lost power to the Senas.[20]
Chandra dynasty
[edit]The Chandra dynasty were a family who ruled over the kingdom of Harikela in eastern Bengal (comprising the ancient lands of Harikela, Vanga and Samatata) for roughly a century and a half from the beginning of the 10th century CE. Their empire also encompassed Vanga and Samatata, with Srichandra expanding his domain to include parts of Kamarupa. Their empire was ruled from their capital, Vikrampur (modern Munshiganj) and was powerful enough to militarily withstand the Pala Empire to the north-west. The last ruler of the Chandra Dynasty, Govindachandra, was defeated by the south Indian Emperor Rajendra Chola I of the Chola dynasty in the 11th century.[29]
Sena dynasty
[edit]The Sena dynasty started around 1095 but only finally defeated the Palas around 1150. They apparently originated in Karnataka. Vijayasena took control of northern and western Bengal, removed the Palas from the former regions and based his rule in Nadia. The greatest ruler from the dynasty was Lakshmanasena. He established the dynasty's writ in Orissa and Benares. In 1202, Ikhtiyarrudin Muhammad Bakhtiyar Khalji took Nadia from the Senas, already having taken Bihar. Lakshmanasena left for Vikrampur in southeastern Bengal.[30] His sons inherited the dynasty, which came to an end around 1245 because of feudal revolts and Muslim pressure.[31]
The dynasty has been staunchly Brahminist and had attempted to restore Brahminism to Bengal. They also established the system of kulinism in Bengal; through which higher caste males could take lower caste brides and enhance the status of these women's children. Some postulate that the dynasty's suppression of Buddhism became a cause for the conversions to Islam, especially in eastern Bengal.[32]
Deva Kingdom
[edit]The Deva Kingdom was a Hindu dynasty of medieval Bengal that ruled over eastern Bengal after the collapse Sena Empire. The capital of this dynasty was Bikrampur in present-day Munshiganj District of Bangladesh. The inscriptional evidences show that his kingdom was extended up to the present-day Comilla-Noakhali-Chittagong region. A later ruler of the dynasty Ariraja-Danuja-Madhava Dasharathadeva extended his kingdom to cover much of East Bengal.[33]
Late Middle Ages
[edit]Muslim rule in the region was inaugurated with the taking of Nadia in 1202 (Ghurid invasion of Bengal). Initially, Bengal was administered by the Delhi Sultanate's governors, then by independent sultanates and then was under the rule of the Mughal empire. While Muslims had advanced into Sindh in the 700s, it was in Afghanistan that the ultimate Muslim conquest of South Asia originated from, starting with the raids by Mahmud of Ghazni in the early 11th century. The Afghanistan-based Ghurids replaced the Ghaznavids and they started expanded into the Ganges region. As part of this eastward expansion Ikhtiyaruddin Muhammad Bakhtiar Khan defeated the Palas in Bihar and in 1202 was victorious over the Senas in Nadia. In 1206, the Delhi Sultanate was created. It was not a true dynasty but the rulers was known as Mamluk. The Sultanate continued till 1290. The conquest of Nadia did not entail swift conversions to Islam. The authority of the Senas persisted in Vikrampur till 1245 and a large part of eastern Bangladesh had neither been conquered nor converted.[34]
Four dynasties based in Delhi succeeded the Slave dynasty. The Khaljis ruled from 1290 to 1320. The Tughluq dynasty's rule lasted until 1413. Sayyid rule ran from 1414 to 1451. The Lodhi dynasty ruled in the 1451-1526 period. But the writ of the Delhi Sultanate had been weak in its outer regions and Bengal like other similar areas turned into an independent region.[35] Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah became the ruler of independent Bengal in 1342 and his dynasty ruled until 1486, barring a short interlude. He had come to power after a Bengali revolt against the Tughluq dynasty's governor. Shamsuddin drove up the Ganges to contest Tughluq rule. The Tughluqs, in return drove Ilyas Shah out of Pandua into eastern Bengal. Shamsuddin reclaimed Pandua and continued ruling Bengal. Shamsuddin's heir repelled Tughluq incursions and like his predecessor expanded the dynasty's authority into Bihar.[35]
The dynasty constructed grand buildings in Pandua. They built India's biggest mosque, the Adina mosque. Richard Eaton cites diplomatic accounts about the grandeur of Pandua's buildings. Eaton observes the influence of both Islamic and pre-Islamic Persian courts.[35] Hindu landlords possessed a large quantity of land even under the Muslim rulers. The Hindu domination was opposed by the Muslim leadership, exemplified by the Faraizi campaign and leaders like Titu Mir in the 1800s.[35]
When the dynasty's third ruler died in 1410 there was a conflict over the throne. Raja Ganesh, who was a Hindu feudal, used the successorship conflict to seize control of Bengal. He repelled an incursion on Bengal by the Jaunpur sultanate in north India. His son, Jalaluddin Muhammad Shah who embraced Islam, and then his grandson ruled after him. In 1433, the latter was assassinated and the Ilyas Shahi dynasty was restored.[35]
The dynasty began importing Abyssinian slaves. This population became more significant. They became so important that in 1486 an Abyssinian, Barbak Shahzada, seized power from Jalaluddin Fateh Shah. Barbak Shahzada's dynasty was short, lasting for the next seven years.[35] The last Abyssinian ruler, Shamsuddin Muzaffar Shah, lost power to the Arab principal minister, Alauddin Husain.[36]
The initiation in 1493 of the Hussain Shahi dynasty brought a period which has been considered Bengal's golden age. The government was genuinely Bengali[37] and while land ownership remained concentrated in Hindu hands, both religious groups had pivotal roles in the government. The sultanate expanded to acquire Cooch Behar and Kamrup. The Sultanate also dominated Orissa, Tripura and the Arakan region.[38]
Babur defeated the Lodhis at Panipat in 1526 and the Mughals established India's greatest state since the time of the Mauryas. But during Sheh Shah Suri's rebellion against the second Mughal ruler Humayan, he triumphed over the Hussain Shahi dynasty's Ghiyasuddin Mahmud Shah in 1538, thus bringing an end to the independent status of Bengal.[38] For a short time Humayun ruled Gaur.[39]
Bengal along with other parts of eastern India was ruled by Sheh Shah Suri. He implemented many reforms such as introducing parganas. These were land survey based local tax units. He is most famous for designing the Grand Trunk Road between Chittagong and Punjab.[38] Humayun retook Delhi in 1556. But the Suris continued ruling Bengal until 1564 when they were replaced by the Karrani dynasty. Like the Suris, they were not native to Bengal. They had been raiders whom the Mughal armies had driven eastwards.[38]
Turko Afghan rule
[edit]In 1204 CE, the first Muslim ruler, Muhammad Bakhtiyar Khilji, a Turko Afghan,[40][41] captured Nadia and established Muslim rule. The political influence of Islam began to spread across Bengal with the conquest of Nadia, the capital city of the Sen ruler Lakshmana.[citation needed]
After capturing Nadia, Bakhtiyar advanced towards Gauda (Lakhnuti), another major city of the Sena kingdom, conquered it and made it his capital in 1205. In the following year, Bakhtiyar set out on an expedition to capture Tibet, but this attempt failed and he had to return to Bengal in poor health and with a reduced army. Shortly afterwards, he was killed by one of his commanders, Ali Mardan Khilji.[42] In the meantime, Lakshman Sen and his two sons retreated to Vikramapur (in the present-day Munshiganj District in Bangladesh), where their diminished dominion lasted until the late 13th century.[citation needed]
Khiljis were Turko Afghan.[41][43][44] The period after Bakhtiar Khilji's death in 1207 involved infighting among the Khiljis. This was typical of a pattern of succession struggles and intra-sultanate intrigues during later Turko Afghan regimes.[40] In this case, Ghiyasuddin Iwaj Khilji prevailed and extended the Sultan's domain south to Jessore and made the eastern Bang province a tributary. The capital was established at Lakhnauti on the Ganges near the older Bengal capital of Gaur. He managed to make Kamarupa and Trihut pay tribute to him. But he was later defeated by Shams-ud-Din Iltutmish.[citation needed]
Sonargaon Sultanate
[edit]Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah ruled an independent kingdom in areas that lie within modern-day eastern and south-eastern Bangladesh from 1338 to 1349.[45] He was the first Muslim ruler to conquer Chittagong, the principal port in the Bengal region, in 1340.[46] Fakhruddin's capital was Sonargaon[45] which emerged as the principal city of the region and as the capital of an independent sultanate during his reign.[47]
Bengal Sultanate
[edit]
Ilyas Shahi dynasty
[edit]Shamsuddin Iliyas Shah founded an independent dynasty that lasted from 1342 to 1487. The dynasty successfully repulsed attempts by Delhi to conquer them. They continued to extend their territory across what is modern-day Bengal, reaching to Khulna in the south and Sylhet in the east. The sultans developed civic institutions and became more responsive and "native" in their outlook and became increasingly independent from Delhi influence and control. Considerable architectural projects were completed including the massive Adina Mosque and the Darasbari Mosque which still stands in Bangladesh near the border with India. The Sultans of Bengal were patrons of Bengali literature and began a process in which Bengali culture and identity would flourish. During the rule of this dynasty, Bengal, for the first time, achieved a separate identity. Indeed, Ilyas Shah named this province as 'Bangalah' and united different parts into a single, unified territory.[48] The Ilyas Shahi Dynasty was interrupted by an uprising by the Hindus under Raja Ganesha. However, the Ilyas Shahi dynasty was restored by Nasiruddin Mahmud Shah. The Moroccan traveller and scholar, Ibn Battuta, arrived in Bengal during Nasiruddin Mahmud Shah's reign.[49] In his account of Bengal in his Rihla, he depicts a land full of abundance. Bengal was a progressive state with commercial links to China, Java and Ceylon. Merchant ships arrived and departed from various destinations.[citation needed]
Ganesha dynasty
[edit]
The Ganesha dynasty began with Raja Ganesha in 1414. After Raja Ganesha seized control over Bengal, he faced an imminent threat of invasion. Ganesha appealed to a powerful Muslim holy man named Qutb al Alam to stop the threat. The saint agreed on the condition that Raja Ganesha's son, Jadu, would convert to Islam and rule in his place. Raja Ganesha agreed and Jadu started ruling Bengal as Jalaluddin Muhammad Shah in 1415. Qutb al Alam died in 1416 and Raja Ganesha was emboldened to depose his son and return to the throne as Danujamarddana Deva. Jalaluddin was reconverted to Hinduism by the Golden Cow ritual. After the death of his father Jalaluddin once again converted to Islam and started ruling again.[50] Jalaluddin's son, Shamsuddin Ahmad Shah ruled for only 3 years due to chaos and anarchy. The dynasty is known for its liberal policies as well as its focus on justice and charity.[citation needed]
Hussain Shahi dynasty
[edit]The Habshi rule gave way to the Hussain Shahi dynasty which ruled from 1494 to 1538. Alauddin Hussain Shah is considered one of the greatest sultans of Bengal, for his encouragement of a cultural renaissance. He extended the sultanate to the port of Chittagong, which witnessed the arrival of the first Portuguese merchants. Nasiruddin Nasrat Shah gave refuge to the Afghan lords during the invasion of Babur though he remained neutral. Later, Nasrat Shah made a treaty with Babur which saved Bengal from a Mughal invasion. The last sultan of the dynasty, who continued to rule from Gaur, had to contend with rising Afghan activity on his north-western border. Eventually, the Afghans broke through and sacked the capital in 1538 where they remained for several decades until the arrival of the Mughals.[citation needed]
Mughal period
[edit]

A major Mughal victory in 1576, in which Akbar took Bengal, was followed by four decades of efforts dedicated to vanquishing rebels in the Bhati region.[39] The initial victory was accompanied by destruction and severe violence.[51] The Mughals were opposed by the Bengalis. Akbar appointed a Hindu servant Raja Man Singh as Bengal's governor. Singh based his rule at Rajmahal, Bihar, thinking that he could administer the region beyond.[38]
The province of Bengal was especially prosperous from the time of its takeover by the Mughals in 1590 until the British East India Company seized control in 1757. It was the Mughal Empire's wealthiest province. Domestically, much of India depended on Bengali products such as rice, silks and cotton textiles.[52][circular reference]
The Bara Bhuiyan, or twelve landlords, resisted the Mughal[53] attempts to annex Bengal. The landlords were mainly Afghan and Hindu aristocrats.[39] Pratapaditya was one of the Hindu landlords among these leaders. They were led by the landlord Isa Khan, who was based in Sonargaon. Isa Khan is known for his resistance to outside rule, particularly from Delhi and Urdu-speaking soldiers. His actions were to serve as an inspiration in 1971.[53]
The landlords spearheaded an extensive revolt.[53] Both the Mughals and rebels committed atrocities such as massacre, rape and looting.[39] They defeated the Mughal navy in 1584. After this, battles continued on land. In 1597, they again defeated the Mughal navy, however, Isa Khan died in the following year. The struggle against Mughal rule weakened. Man Singh, realising the strategic value of controlling Dhaka to administer eastern Bengal, created a military base there.[53] He also realised its utility in controlling Arakanese and Portuguese influence.[39]
This base became more important in the late 1500s when the Ganges started to change its course. The change in the river's course allowed the clearing and harvesting of more land. The waterways of Dhaka allowed easy movement of soldiers to various parts of Bengal.[53] In 1610, Dhaka became a provincial capital. By then several of the internationally known muslin looms had shifted to Dhaka from Sonargaon. Dhaka flourished both as an administrative and handloom center.[53]
The Bengal region was historically an international hub of various activities. Merchants, pilgrims and voyagers traversed Bengal to travel to Nepal and Tibet. Bengal's waterways were a place where various peoples interacted. In 1346, the Moroccan voyager Ibn Battuta followed the trade route through Sri Lanka when he traveled to Bengal from the Maldives in 1346.[54] In the 1300s Bengal traded its paddy for cowries from the Maldives. Evidence from the 1500s demonstrates that rice grown in Bengal was eaten as far as eastern Indonesia and Goa. Bengal also exported other materials and food products at the same time. Bengali traders dominated trade with southeast Asia.[55] Chinese merchants in the 1400s and 1500s introduced gold, satin, silks, silver and porcelain.[55] A European traveler in 1586 reported that the quality of the cotton textiles produced in Sonargaon was better than in other parts of the subcontinent. These fabrics were sent to international markets.[56]
According to economic historian Indrajit Ray, Bengal was globally prominent in industries such as textile manufacturing and shipbuilding.[57]
Dhaka was renamed to Jahangirnagar by the governor for Jahangir, the emperor.[39] The governor managed to defeat and make the chieftains accept Mughal authority.[39] During Mughal rule, Dhaka's architecture was enriched. In 1678, Aurangzeb's son started the construction of the Lalbagh fort, which encloses the tomb of Nur Jahan's grand niece.[53] Surviving Mughal buildings are the Bara Katra, Chhota Katra and the Husaini Dalan (a Shi'a mosque).[58]
During the Mughal rule many civilian and military administrators entered Bengal. A lot of these officials received land grants and became domiciled. Despite the Hindu domination of the landed class, Muslims formed a crucial section and maintained possession of significant land grants until the land reforms after 1947.[59]
The form of Bengal's government had been less rigid than the ones in other parts of the Mughal empire. The Mughals asserted a centralised form of rule on top of the differing local administrative structures. Consequently, local rulers administered control in the rural areas. These "zamindars" were autonomous and were a secular elite,[60] differentiated from the general populace by their authority.[61] Surnames in modern Bangladesh such as Chowdhury, Khan, Sarkar and Talukdar originate from the names of ranks in the Mughal elite.[51] This elite functioned alongside the Mughal officials. The latter's duty was to keep charge over tax collection. The diwan was the most important tax officer and was directly selected by the Mughal ruler. Each Mughal conquest in Bengal was accompanied with the establishment of a thana (garrison) for the purpose of maintaining peace. After that the territory would be merged into the empire's administrative system. In the empire's system each province would comprise several regions, called "sarkar", which in turn would be made up of subdivisions called parganas. The lowest tier in the system was the mouza (revenue village).[51]
The agricultural borderland during Mughal rule in the 1500s started moving towards the eastern portion of Bengal. The region's agricultural productivity increased. To increase their revenues the Mughal administration promoted forest clearing and wet-rice farming. The officials gave land grants to entrepreneurs who were willing to give taxes in exchange for rights over the lands. The colonists required labour and this was advantageous for the religious elite.[62] Most communities in the region were boatmen and fishermen on the margins of society who were nominally Hindu but in reality had very weak ties to Hinduism. These were the labourers who cultivated the rice and would make up the bulk of peasantry in eastern Bengal.[63] Land grants would require the construction of a shrine and the colonists would gather settlers around these shrines. Society was ordered around the shrine. New communities would engage in forest clearing and cultivation. Locals either merged with these communities or moved away while keeping trading contacts with the rice cultivators.[62]
The Mughal government had no attitude of encouraging Islam in the region and Hindus made up many of these pioneers who had government backing. But most of the pioneers were Muslim. A large number of them were pirs. Richard Eaton asserts that Islam was understood to be linked with the government-accepted acquisition of land in eastern Bengal which had only weak connections with Hindu civilization. The traditions and rituals of eastern Bengal, mosques and shrines blended together. Islam spread in Bengal because of its localisation. Islamic agencies were inserted into the contemporary cosmology, were then associated with local divinities and eventually the Islamic agencies took over the local culture.[62]
Two great Mughal Subahdars
[edit]Islam Khan
[edit]Islam Khan was appointed the Subahdar of Bengal in 1608 by Mughal emperor Jahangir. He ruled Bengal from his capital Dhaka which he renamed as Jahangir Nagar.[64] His major task was to subdue the rebellious Rajas, Bara-Bhuiyans, Zamindars and Afghan chiefs. He fought with Musa Khan, the leader of Bara-Bhuiyans, and by the end of 1611 Musa Khan was subdued.[64] Islam Khan also defeated Pratapaditya of Jessore, Ram Chandra of Bakla and Ananta Manikya of Bhulua. He annexed the kingdom of Kamrup and subdued Koch Bihar and Kachhar, thus taking total control over entire Bengal other than Chittagong.[64]
Shaista Khan
[edit]
Shaista Khan was appointed the Subahdar (Governor) of Bengal upon the death of Mir Jumla II in 1663.[65] He was the longest-serving governor of Bengal. He ruled the province from his administrative headquarters in Dhaka for almost 24 years from 1664 to 1688.[65]
Shaista Khan's great fame in Bengal chiefly rests on his re-conquest of Chittagong. Though Chittagong came under the control of Bengal during Sultan Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah's reign in the mid-14th century, it subsequently fell into the hands of Arakanese rulers. Shaista Khan gave priority to recapturing Chittagong, and was able to do so in January 1666. The conquest brought a relief and peace to the people of Chittagong as pirates had caused a great distress to the local population.[65]
Nawabs of Bengal
[edit]


Mughal appointments of agents in Bengal ceased by 1713 because the empire was weakening.[66] In 1715, the capital was shifted to Murshidabad. This resulted in Dhaka's decline. This transfer happened when the province's main tax officer, Murshid Quli Khan, who had transferred his office to Maksudabad (renamed Murshidabad after him) became governor. Murshidabad was located at a more central position in Bengal, whose administrative limits at the time also included Bihar and Orissa.[67] In addition to changing the capital, Murshid Quli Khan modified the tax collection system.[66]
Murshid Quli Khan wanted to create a line of governing nawabs like the contemporary governors of Oudh. He was succeeded by family members.[67] However, Alivardi Khan established another nawab family.[68] He collaborated with Jagat Seth to defeat the governor and secured the post of governor from the Mughal ruler through bribery. He also became diwan of Orissa. However, he faced problems from Maratha raiders present in Orissa.[59]
Nawab Alivardi Khan repulsed the first three Maratha invasions of Bengal. But they invaded again, and in 1751, Alivardi Khan signed a peace treaty with the Marathas. He ceded the province of Orissa to the Maratha Empire and agreed to pay twelve lakhs of rupees annually as chauth (tribute).[69] His maternal grandson Sirajuddaulah succeeded him when he died in 1756.[59] Sirajuddaulah tried to stop uncertified trade in Bengal. Because of this he clashed with British merchants and was eventually defeated by 1757 in Polashi. The British governed Bengal and large areas to its west by 1764.[66]
Colonial era
[edit]Europeans in Bengal
[edit]
In 1517, the Portuguese installed an outpost at Chittagong.[59] A Portuguese settlement was also created at Satgaon. In 1579, with a land grant from Akbar, the Portuguese created another station at Hooghly. The Portuguese traded and proselytised until 1632 when they were expelled by Shah Jahan, who allowed them to re-enter in the next year. The hostility towards them was a consequence of piracy by the Portuguese and Maghs. By 1651 the British obtained control of Hooghly. The Portuguese presence came to an end.[70]
The Portuguese had traded through the government but other European powers traded through companies instead. A Dutch station was established at Chinsura but the Dutch directed their interests to Ceylon and Southeast Asia. In 1825, they exchanged Chinsura with the British for posts in Southeast Asia. In 1755, a Danish station was established at Serampore. In 1845, the British bought it. The French Company lasted longer. Their position was second to the British. The latter overtook the French. The first British factory was established in 1608 in western India.[70] Soon afterwards the British entered Bengal.[71]
The British founded factories in Balasore, Cossimbazar, Dhaka, Hooghly and Patna. In 1681, a "presidency" was established. In 1690, Job Charnock established Calcutta. During this time the British came into conflict with Bengal's Mughal governors. In 1652, the British had been exempted from customs payments in exchange for giving yearly sums to the nawab. But the nawab foisted fees upon them, which the British opposed. The British met the nawab Shaista Khan in Dhaka in 1652 and secured the exemption again.[72]
British trading activities expanded during Shaista Khan's administration. Alivardi Khan disliked the British and French plans to secure their possessions. Alivardi Khan disputed the British application of Emperor Fakukhsiyar's order which had allowed the British unfettered trading privileges in the Mughal empire, as their tax exemptions meant lower revenues for Alivardi Khan.[72]
Alivardi's successor Sirajuddaulah set about eliminating the foreign presence. In 1756, he seized Calcutta and incarcerated the resident British population. Robert Clive and his troops took Calcutta back in January 1757. Clive compelled Sirajuddaulah to assent to a treaty which would restore Emperor Fakukhsiyar's order allowing the British to trade unrestricted. Clive then conspired with Sirajuddaulah's relative, Mir Jafar, and obtained the support of a major banker, Jagat Seth. Robert Clive and Sirajuddaulah's troops battled each other at Plassey in June 1757. Mir Jafar abandoned the nawab during the battle, who suffered defeat and was killed.[72] Many historians see this battle as the start of British colonialism in the subcontinent which would last until 1947.[73]
After their triumph at Plassey the British transformed Bengal into the center of their growing Indian colony.[74] The British could fully obtain financial authority in Bengal if the diwani was given to the East India Company in place of the Nawab.[75] When Mir Jafar died in 1765 the Emperor Shah Alam implemented that transfer. This guaranteed British authority in the province. while a semi-feudal association was maintained with the Mughal empire. The diwani was used with the approval of the Mughal ruler.[76] While the British East India Company was nominally a diwan, it was practically independent of the Mughals.[66]
Indian nationalist historiography pinpoints the battle in Plassey as the start of a foreign and exploitative colonialism which ended in 1947. But the Bangladeshi perspective is that the people of Bengal had been used to fleecing administrations run by foreigners before the rise of the British authority.[73] Bangladeshi historians also contend that colonialism persisted during the post-colonial period when the region was included in Pakistan.[77] The Battle of Plassey did not mark an end to native rule in Bengal. It marked an end to the Mughal system.[39]
British rule
[edit]
The British goal was to increase the productivity of the Bengali economy. They experimented on Bengal's administration and economy. The results of some of the experiments were not always successful. The increased taxation in Bengal's unstable climate was a calamity. The taxation was not eased even during the drought and floods of 1769–1770. Along with unmonitored exploitation this caused a severe famine, in which it is believed ten million residents of Bengal died.[78]
The Mughal State was disintegrated, causing the principal governor of Bengal to become the de facto ruler.[79][80][81] After a replacement was sought by the British East India Company, in the mid-eighteenth century, the border of Cooch Behar was marked the northernmost limit of British Territory.[79][80][81] Cooch Behar survived as a princely state till the end of the colonial rule, this was due to the indirect ruling of the British expedition in 1772, when it invaded and conquered the territory: the Maharaja and his administration were thence retained under the control of a British political agent.[79][80][81]
Capital amassed from Bengal by the East India Company was invested in various industries such as textile manufacturing in Great Britain during the initial stages of the Industrial Revolution.[82][83][84][85] Company policies in Bengal also led to the deindustrialization of the Bengali textile industry during Company rule.[82][84]
The famine disaster made British officials look for viable methods of tapping into the colony's resources. In 1790, the British introduced "permanent settlement" and made it law three years later. It was a framework for taxation on land. The system was the core of the colonial form of government. It was an agreement between the British and the zamindars who were effectively given landholdings in exchange for timely payment of taxes.[86] The aim of the permanent settlement was that the zamindars would eventually invest in the development of agriculture and improve the economy of Bengal. The aim did not materialise because the zamindars did not have state backing for agrarian growth and because of newfound ways of generating wealth. A multilayered form of landholdings developed, which benefited from the land's revenue. This structure was most pronounced in the southern areas of modern Bangladesh. The permanent settlement scheme deprived peasants of any proprietary rights over the land.[87]
While Muslims had comprised most of the landlord class during Mughal rule, Hindus became prominent during the colonial rule. While Muslim landlords and Hindu occupants did exist, eastern Bengal witnessed an amalgamation of religion with class, with Hindu landlords presiding over mainly Muslim peasants. Hindu landlords were also prominent in western Bengal, but most peasants there were Hindus. This factor would become politically important by the end of the colonial rule.[88]
Another change during British rule was the system of cash cropping. During colonial rule cash cropping was organised and produced for international markets. It was significant because of the links it created between the Bengali countryside's economy with markets in Asia and Europe.[88] Because of cash cropping the eastern region of modern Bangladesh emerged as the centre for jute cultivation.[89] The western portion of modern Bangladesh produced silk and sugar. The northern areas produced tobacco. Crops were associated with specific types of land organisation. Peasantry in the eastern areas were compelled by financial needs towards market production. The countryside's elite in the western and northern areas were protected from the immediate impact of market factors because they provided agrarian credit.[90]
The British abandoned the former official language, Persian, in the 1830s and English medium educational institutions prepared a small part of the Bengali elite for jobs in the lower and middle tiers of government.[91] Muslims took up the British improvements more slowly and lagged behind the Hindus educationally and commercially. Hindus comprised most of the college students.[92] There were changes in health. The population growth during colonial rule was because people had more knowledge of hygiene and increased access to hospitals and medication. Transport became less reliant on the rivers with the construction of bridges and railways. Improvements in technology aided communications. Despite the government's authoritarian form, the British tried out limited democratic systems in the later part of their rule due to political constraints.[91]
A vital development under British rule was the rise of Calcutta to political and cultural prominence.[91] It became colonial India's capital. From 1757 to 1931 the Government of India was located in the city. Aspiring Bengalis migrated to Calcutta and obtained education and government employment. They are known to historians as the "bhodrolok" and high caste Hindus comprised most of them.[93] Old centers such as Dhaka and Murshidabad declined while the trading class became concentrated in Calcutta.[92]
The authoritarian regime functioning in alliance with the rural elite was susceptible to resistance and revolts happened frequently during the British rule. However, British rule in Bengal faced no threat by the second half of the 1800s. Bengal did not participate in the 1857 revolt which nearly ended British administration over large swathes of India. While there was a revolt by troops in Chittagong it dwindled because the landlords and peasants did not support the rebellion.[94] Instead political grievances nor revolved around peasant rights and the commercialization of agriculture. The struggle was usually characterised by peasants and the middle class in opposition to the landlords, Western businessmen and the British administration. Many campaigns eventually ended the indigo industry. These were led by Wahhabi-influenced Islamic missionaries.[95]
There had been prominent Hindu reformist movements in the early 1800s but no equivalent Muslim movement. A departure from this rule was the Faraizi movement which Haji Shariatullah started in 1828. It was a conservative Islamic movement grounded in Wahhabi ideology. It opposed the exaltation of saints and the repression by landlords and indigo traders. Shariatullah regarded India as a dar al-harb and thus believed that festivals and Friday prayers should cease. His heir, Dudu Mia, expanded the movement and claimed that the landlords did not possess permanent land rights. The Faraizi movement eventually ended after his demise.[96]
Titu Mir led another Wahhabi campaign at the same time as the Faraizi movement. This movement was violent and opposed to the British presence. He died in 1831 during a confrontation with the British. Two years later his followers supported indigo farmers in a clash against the European planters and Hindu landlords. The protest was ultimately muted by 1860 when the peasants were granted more security.[97] But not all rural rebellions were inspired by religion.[95]
By the late 1800s parts of the elite and peasants became politically connected. This link was to become a crucial prototype of later campaigns in Bengal. The movement for self determination joined communist and nationalist movements, several of which were associated with all-India organisations.[95]
Bengal renaissance
[edit]
|
|
The Bengal renaissance refers to a social reform movement during the 19th and early 20th centuries in Bengal. Historian Nitish Sengupta describes it as taking place from Raja Ram Mohan Roy (1775–1833) through Rabindranath Tagore (1861–1941).[98] This flowering in Bengal of religious and social reformers, scholars, and writers is described by historian David Kopf as "one of the most creative periods in Indian history".[99] Bangladeshi people are also very proud of their national poet Kazi Nazrul Islam. He is greatly remembered for his active voice against the oppression of the British rulers in the 20th century. He was imprisoned for writing his most famous poem of "Bidrohee".[citation needed]
Partition of Bengal (1905)
[edit]
The decision to effect the Partition of Bengal was announced in July 1905 by the Viceroy of India, Lord Curzon. The partition took place on 16 October 1905 and separated the largely Muslim eastern areas from the largely Hindu western areas. The former province of Bengal was divided into two new provinces "Bengal" (comprising western Bengal as well as the province of Bihar and Orissa) and Eastern Bengal and Assam with Dacca as the capital of the latter.[100] Partition was promoted for administrative reasons: Bengal was geographically as large as France and had a significantly larger population. Curzon stated the eastern region was neglected and under-governed. By splitting the province, an improved administration could be established in the east, where subsequently, the population would benefit from new schools and employment opportunities. The Hindus of West Bengal who dominated Bengal's business and rural life complained that the division would make them a minority in a province that would incorporate the province of Bihar and Orissa.[101] Indians were outraged at what they recognised as a "divide and rule" policy.[102]
The British regarded politically active Muslims as their supporters and the partition created a Muslim-dominated province. The Muslims universally reacted to the division with approval. Hindus denounced it.[103] The partition highlighted the flaw in the political unity of the members of different religions in Bengal. Hindus and Muslims became distinct political groups.[104] The predominantly Hindu bhodrolok led the anti-partition campaign and connected it with Hindu revivalism.[105] They identified their homeland with Kali and selected Bande Mataram as anthem, which Muslims opposed.[106]
The British had promoted religion as a grounds for political identification. This had been difficult because Muslim unity had been hindered by significant internal differences. Most Bengali Muslims had been more a member of a religiously diverse Bengali community than a Muslim one, until the end of the 1800s.[107] The Islam they practised had a significant foundation in the culture of the Bengali countryside.[108] The elite Muslims identified themselves as ashraf (of foreign descent) and sought to copy North Indian Islamic culture and they saw themselves as the protectors of the true Islam in Bengal. To them, the Islam practised by the local peasants and craftsmen was contaminated by un-Islamic associations. While a large number of well-taught Muslims remained hesitant to accept the peasants who practised Bengali culture, the idea of a single Muslim community had come to exist just before partition.[109] Economic issues increased Hindu-Muslim conflict in Bengal. The Muslim occupants began to demand their rights against the mainly Hindu landed and moneylending class. Middle class Muslims were unable to achieve their political goals because of the Hindu elite's contemptuous attitude.[109] Hindus and Muslims clashed in Comilla and Mymensingh in 1906 and 1907.[110] The violence boosted religious identities and supported stereotyping. The Hindu elite regarded the countryside Muslims as British agents and inferior. To Muslims, the Hindus were cunning exploiters. The British reversed the partition in 1911 and declared they would move India's capital to Delhi. New Delhi was inaugurated after two decades of construction in 1931.[111]
Partition of Bengal (1947)
[edit]The Partition of Bengal in 1947, also known as the Second Partition of Bengal, part of the Partition of India, divided the British Indian Bengal Province along the Radcliffe Line between the Dominion of India and the Dominion of Pakistan. The Bengali Hindu-majority West Bengal became a state of India, and the Bengali Muslim-majority East Bengal (now Bangladesh) became a province of Pakistan.
Pakistan period
[edit]
Dhaka was the scene of a meeting of Muslim leaders in late 1906. They created a party for Muslims and declared its loyalty to the British, believing that the British could best protect the interests of Muslims.[112] The late 1800s had seen the introduction of a system of elections based on limited franchise. The franchise was broadened later to increase the number of voters. However, universal franchise never materialized but the Muslim leadership did secure a separate voting system for Muslims in 1909.[113] In the Lucknow Pact of 1916 the Muslim League and Indian National Congress accepted both separate electorates and provincial weightage for minorities. This reduced Bengali Muslim seats to forty percent in a Muslim majority province. The Muslim League regretted this decision.[114]
Until 1920, the elections happened on a non-party basis. When party candidature was introduced the independent candidates maintained their importance. They won a third of seats in Bengal in the 1937 elections.[113] Congress had been the main contestant for the general seats while the Muslim League vied with Fazlul Huq's Krishak Praja Party (KPP) for the Muslim seats.[115] The 1937 elections showed that no party could establish a ministry on its own. The Krishak Praja Party established a ministry with the Muslim League. The League could not win the three other Muslim provinces. Muslim prime ministers who were not members of the Congress agreed to support the League nationally even as they would keep control of their provincial matters.[116] Fazlul Huq was a member of both the KPP and the Muslim League.[117]
Congress ministries resigned to protest the declaration of war against Germany by viceroy, Lord Linlithgow, which he had done so without seeking the opinion of the provincial governments. The Muslim governments in Punjab, Bengal and Sindh did not resign. But a rift emerged between Fazlul Huq and the League when the viceroy created an advisory council, thus Huq's ministry fell.[117] According to Fazlul Huq, who resigned from the party, the Muslim League represented the interests of Muslim minority provinces more than the Muslim provinces.[118] Fazlul Huq had advanced the Lahore Resolution in 1940, before resigning. The resolution had used the word "states" which indicated that a united Pakistan was not intended by this resolution.[119]
Fazlul Huq recreated his government, this time without the Muslim League, in late 1941. Muslim League members led by Khawaja Nazimuddin and Suhrawardy campaigned against Fazlul Huq. Huq resigned in 1943 under pressure from the governor. On 24 April 1943 Nazimuddin inaugurated his own ministry at the governor's invitation. Nazimuddin's ministry was seen unfavourably by both the viceroy, Lord Wavell, and the governor.[119] In particular, the Viceroy was disturbed by Nazimuddin's response to the famine.[120] Bengal experienced a great famine during the second world war. Approximately 3 and a half million died, mainly in the countryside of east Bengal.[121]
The 1945-1946 elections restored a responsible provincial government.[120] In the 1946 elections the politics was dominated by two organisations.[122] They were the Indian National Congress and the Muslim League. The Congress was never able to win Bengal.[123] The 1946 election was mainly contended over the question of creating a Muslim homeland: Pakistan. To many it represented a plebiscite. Bengal's Muslim League ignored local matters in its campaign over partition. The KPP of Fazlul Huq was defeated. The Muslim League captured 110 out of the 117 seats for Muslims. Out of all Muslim provinces, Bengal was the biggest supporter of the Muslim League.[120] The majority of East Bengal's peasantry saw Pakistan as a good way of eliminating the feudal system. More than religious reasons, it had been because of economic factors they supported the Muslim League and Pakistan.[124]
In 1946, the British government sent a mission, which ultimately advanced a scheme for a united India.[125] The scheme encapsulated a loose union.[126] A key point for Bengal was the maintenance of its unity under the scheme. The plan was agreed to by Jinnah but Nehru negated it.[125] The Muslim League declared Direct Action Day on 16 August. Rioting followed in Calcutta and many died.[127] The Bhodrolok decided that dividing Bengal would be better than accepting the rule of Muslims. The Muslim League did not want Bengal to be divided, and wanted it fully included in Pakistan. However, the Congress demanded the partition of the province.[124] A few leaders of the Muslim League and Congress started advocating an independent United Bengal. While some politicians like Jinnah and Gandhi supported this idea, the national Congress rejected it in favour of partition. Eastern Bengal was to join Pakistan while Western Bengal would join India.[126] Most of Assam's mainly Muslim Sylhet district opted for Bengal in a plebiscite. The rest joined India with Assam.[128]
Bengali Language Movement
[edit]
A rift developed over the question of the national language.[129] The Bengali Language Movement was a political effort in Bangladesh (then known as East Pakistan), advocating the recognition of the Bengali language as an official language of Pakistan. Such recognition would allow Bengali to be used in government affairs. It was led by Mufti Nadimul Quamar Ahmed.[130]
When the state of Pakistan was formed in 1947, its two regions, East Pakistan (also called East Bengal) and West Pakistan, were split along cultural, geographical, and linguistic lines. On 23 February 1948, the Government of Pakistan ordained Urdu as the sole national language, sparking extensive protests among the Bengali-speaking majority of East Pakistan. Facing rising sectarian tensions and mass discontent with the new law, the government outlawed public meetings and rallies. The students of the University of Dhaka and other political activists defied the law and organised a protest on 21 February 1952.[131] The movement reached its climax when police opened fire on the students that day. The deaths provoked widespread civil unrest led by the Awami Muslim League, later renamed the Awami League. After years of conflict, the central government relented and granted official status to the Bengali language in 1956. On 17 November 1999, UNESCO declared 21 February International Mother Language Day.[132]
Politics: 1954–1971
[edit]

The 1952 events caused the people of East Pakistan to abandon the Muslim League.[133] In East Pakistan's 1954 provincial elections, the League captured only 7 out of the 390 seats.[134] The United Front won the elections. Until 1956, when the state declared that both Bengali and Urdu would be state languages, the language movement continued.[135]
Great differences began developing between the two wings of Pakistan. While the west had a minority share of Pakistan's total population, it had the largest share of revenue allocation, industrial development, agricultural reforms and civil development projects. Pakistan's military and civil services were dominated by the Punjabis.[136] Bengalis had been designated as a "non-martial" race by the British. Bengali participation in the military was very low. The British preferred to recruit Punjabi Muslims. The Punjabis dominated the army Pakistan inherited from British India's military. Because Bengalis did not have a tradition of military service in their families, it was hard to recruit Bengali officers.[137]
By the middle of the 1960s the East Pakistani elite concluded that the protection of their interests lay in autonomy. Abdul Momen Khan, who was governor in the 1962-1968 period, persecuted opposition and censored media. The regime became more unpopular during 1965, in the year of a war between India and Pakistan. Patriotism was high in East Pakistan during the war against India, but this was one of the last cases of national solidarity. East Pakistanis felt they had not been protected by the army from a possible Indian invasion.[138]
In 1966, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, the leader of the Awami League, proclaimed a 6-point plan titled Our Charter of Survival at a national conference of opposition political parties at Lahore, in which he demanded self-government and considerable political, economic and defence autonomy for East Pakistan in a Pakistani federation with a weak central government. This led to the historic Six point movement. The six points for a confederation were more extreme than previous calls for autonomy.[138]
In early 1968, the Agartala Conspiracy Case was filed against Mujib with the allegation that the accused was conspiring for the secession of East Pakistan with Indian aid. The government expected this to harm Mujib's popularity. But popular demonstrations made the government drop the case.[139]
A West Pakistani movement aimed at removing Ayub Khan spread to East Pakistan where it adopted Bengali nationalist connotations. Ayub Khan resigned in March 1969 and his position was taken by General Yahya Khan. Yahya tried to reconcile the politicians. He announced that elections would be held in 1970 and political organisation would be permitted.[140] He declared that his own position was temporary and that his job was to run elections for an assembly who would be tasked with creating a new constitution. He ended the One Unit Scheme and permitted popular representation, thereby allowing East Pakistan 162 of the 300 seats. Yahya created a legal framework order (LFO) as a guideline for the assembly. It stipulated principles such as the federalism of the state, paramountcy of Islam, provincial autonomy with sufficient provisions for the federal government to carry out its duties and defend the country's integrity. The latter point clashed with Mujib's points. Yahya highlighted that a constitution would not be accepted if it did not adhere to the LFO. Mujib's party had drafted its own constitution based on six points.[141]
Independence movement
[edit]The Awami League captured 160 of East Pakistan's 162 seats in the 1970 Pakistani general election.[141] Nurul Amin won one of the remaining seats.[142] The Pakistan Peoples Party, led by Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, won a majority of seats in West Pakistan.[citation needed] Yahya organised talks between Bhutto and Mujib to arrive at a consensus on the form of the future constitution. Mujib asserted his majority and intent to base the constitution on his six points. Bhutto's argument was that there were two majorities. The talks failed.[143] Mujib rejected Bhutto's demands for a share in power. Bhutto boycotted the National Assembly session of 3 March and intimidated other West Pakistani politicians from participating. Bhutto requested that Yahya delay the National Assembly session. On 1 March protests and confrontations broke out when Yahya did this.[144]
Leftists in East Pakistan pressured Mujib to immediately declare independence. The West Pakistani government deployed soldiers to deter such a possibility.[144] Mujib chose a middle-ground option by starting a non-cooperation movement. The movement was successful, freezing the machinery of government and effectively giving Mujib command over East Pakistan. Mujib announced that East Pakistanis would fight for independence but he simultaneously attempted to achieve a solution within a united Pakistan.[145]
Yahya Khan and Bhutto went to Dhaka in March as a last attempt to obtain a resolution. However, the three parties could not arrive at a consensus on the transfer of power. On 23 March the Awami League told Yahya that he was to issue regional autonomy within 2 days or East Pakistan would turn lawless. While the talks were still underway, Yahya opted for a military solution for the problem.[146] On the night of 25 March, Yahya secretly went back to West Pakistan and commanded the military to attack the core members of the autonomy campaign.[147]
On 3 March, student leader Shahjahan Siraj read the 'Sadhinotar Ishtehar' (Declaration of Independence) at Paltan Maidan in front of Mujib at a public gathering under the direction of the Swadhin Bangla Biplobi Parishad.[148]
On 7 March, there was a public gathering in Suhrawardy Udyan to hear updates on the ongoing movement from Sheikh Mujib, the leader of the movement. Although he avoided directly referring to independence, as the talks were still underway, he warned his listeners to prepare for any imminent war.[148] The speech is considered a key moment in the War of Liberation, and is remembered for the phrase,
- "Ebarer Shongram Amader Muktir Shongram, Ebarer Shongram Shadhinotar Shongram...."
- "Our struggle this time is a struggle for our freedom, our struggle this time is a struggle for our independence...."
Formal Declaration of Independence
[edit]
In the early hours of 26 March 1971, a military crackdown by the Pakistan army began. Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman was arrested and the political leaders dispersed, mostly fleeing to neighbouring India where they organised a provisional government. Before being arrested by the Pakistani Army, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman passed a hand written note which contained the Bangladesh's Declaration of Independence. This note was widely circulated and transmitted by the then East Pakistan Rifles' wireless transmitter. The world press reports from late March 1971 also made sure that Bangladesh's declaration of independence by Bangabandhu was widely reported throughout the world. Bengali Army officer Major Ziaur Rahman captured the Kalurghat Radio Station[149][150] in Chittagong and read the declaration of independence of Bangladesh during the evening hours on 27 March.[151]
This is Swadhin Bangla Betar Kendra. I, Major Ziaur Rahman, at the direction of Bangobondhu Mujibur Rahman, hereby declare that the Independent People's Republic of Bangladesh has been established. At his direction, I have taken command as the temporary Head of the Republic. In the name of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, I call upon all Bengalees to rise against the attack by the West Pakistani Army. We shall fight to the last to free our motherland. Victory is, by the Grace of Allah, ours. Joy Bangla.[152]
The Provisional Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh was formed on 10 April in Meherpur (later renamed as Mujibnagar, a town adjacent to the Indian border). Sheikh Mujibur Rahman was announced to be the Head of the State. Tajuddin Ahmed became the Prime Minister, Syed Nazrul Islam became the acting president and Khondaker Mostaq Ahmed the Foreign Minister. There the war plan was sketched out with Bangladesh armed forces established and named "Muktifoujo". Later these forces were named "Muktibahini" (freedom fighters). M. A. G. Osmani was appointed as the Chief of the Armed Forces. The training and most of the arms and ammunitions were arranged by the Meherpur government which was supported by India. As fighting grew between the Pakistan Army and the Bengali Mukti Bahini, an estimated ten million Bengalis, mainly Hindus, sought refuge in the Indian states of Assam, Tripura and West Bengal.
The freedom fighters were not able to beat the military.[146] The Pakistani military created civilian and paramilitary groups to neutralise the freedom fighters.[153] They recruited Biharis and Bengalis who did not support the separation of East Pakistan.[154]
When it became clear that neither the Pakistani military nor the freedom fighters could win, India gradually started its invasion. It increased its efforts at the international level[155] and increased its military activities in East Pakistan but did not declare war out of fear of the geopolitical aftermath. India had its opportunity to declare war when Pakistan attacked Indian airfields on 3 December. The Indian military and Mukti Bahini had the edge with better weaponry, complete air and naval supremacy and support from most locals. The Pakistani army killed and raped many Bengalis. Pro-Pakistan militias killed Bengali intellectuals near the war's end. Pakistan's administration collapsed and the army surrendered on 16 December.[156]
Pakistani capitulation and aftermath
[edit]
On 16 December 1971, Lt. Gen A. A. K. Niazi, CO of Pakistan Army forces located in East Pakistan, signed the Instrument of Surrender and the nation of Bangla Desh ("Country of Bengal") was finally established the following day. At the time of surrender only a few countries had provided diplomatic recognition to the new nation. Over 90,000 Pakistani troops surrendered to the Indian forces making it the largest surrender since World War II.[157][158] The new country changed its name to Bangladesh on 11 January 1972 and became a parliamentary democracy under a constitution. Shortly thereafter on 19 March Bangladesh signed a friendship treaty with India. Bangladesh sought admission in the UN with most voting in its favour, but China vetoed this as Pakistan was its key ally.[159] The United States, also a key ally of Pakistan, was one of the last nations to accord Bangladesh recognition.[citation needed] To ensure a smooth transition, in 1972 the Simla Agreement was signed between India and Pakistan. The treaty ensured that Pakistan recognised the independence of Bangladesh in exchange for the return of the Pakistani PoWs. India treated all the PoWs in strict accordance with the Geneva Convention, rule 1925.[160] It released more than 93,000 Pakistani PoWs in five months.[157]
Furthermore, as a gesture of goodwill, nearly 200 soldiers who were sought for war crimes by Bengalis were also pardoned by India.[161] The accord also gave back more than 13,000 km2 (5,019 sq mi) of land that Indian troops had seized in West Pakistan during the war, though India retained a few strategic areas;[162] most notably Kargil (which would in turn again be the focal point for a war between the two nations in 1999).
The real number of victims during the war is still not certain.[154][163] and estimates of those killed range from Bangladeshi estimates of 3 million to Pakistani estimates of 26,000. According to one source 1.7 million died. A large number of women had been raped by Pakistani, Bengali and Biharis. The government conferred upon them an honorary title of birangina ("brave heroines") but they suffered discrimination afterwards.[163]
Besides the Pakistani prisoner of wars there were still collaborators in Bangladesh. In 1973, the Bangladeshi government announced an amnesty for them in exchange for Pakistani recognition. Demands that these be collaborators be tried resurfaced in the 1990s. There was also a large population of non-Bengali Muslims[164] who mostly supported Pakistan. Bengali mobs, who identified them as "Bihari", had killed them before the war and the Biharis had aided the Pakistani army during it. Thousands suffered a counter genocide and at least a million were made homeless.[163]
People's Republic of Bangladesh
[edit]Constitution, early democracy and socialism
[edit]Provisional Government
[edit]The Provisional Government of Bangladesh was the country's first government. The Provisional Government was formed in Mujibnagar on 17 April 1971. It issued the proclamation of independence and drafted an interim constitution, declaring "Equality, Human Dignity and Social Justice" as its fundamental principles. Its prime minister was Tajuddin Ahmad and military chief of staff was M A G Osmani. Other important cabinet members included Syed Nazrul Islam and Muhammad Mansur Ali. It included the newly formed Bangladesh Civil Service with defecting members of the Civil Service of Pakistan. It also had a prominent diplomatic corps, led by Abu Sayeed Chowdhury, Humayun Rashid Choudhury and Rehman Sobhan among others. The Bangladesh Forces included eleven sector commanders, among whom prominent figures included Ziaur Rahman, Khaled Mosharraf and K M Shafiullah.[165][166]
Neighboring India provided diplomatic, economic and military support for the Provisional Government. The government's capital in exile was Calcutta. The Indian military intervened in the final two weeks of the war in December 1971, ensuring the surrender of Pakistan.
Sheikh Mujib administration
[edit]The left-wing Awami League, which had won the 1970 election in Pakistan, formed the first post-independence government in Bangladesh. Awami League leader Sheikh Mujibur Rahman became the 2nd Prime Minister of Bangladesh on 12 January 1972 and is widely regarded as the nation's independence hero and founding father. Nation-building under his regime was based on secular Bengali nationalist principles. The original Constitution of Bangladesh, drafted by Kamal Hossain, laid down the structure of a liberal democratic parliamentary republic with socialist influences in 1972.
On the international stage, Rahman and his Indian counterpart Indira Gandhi signed the 25-year Indo-Bangladeshi Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Peace. Bangladesh joined the Organization of the Islamic Conference, the Commonwealth of Nations and the Non-Aligned Movement. Rahman was invited to Washington DC and Moscow for talks with American and Soviet leaders. In the Delhi Agreement of 1974, Bangladesh, India and Pakistan pledged to work for regional stability and peace. The agreement paved the way for the return of interned Bengali officials and their families stranded in Pakistan, as well as the establishing of diplomatic relations between Dhaka and Islamabad. Japan became a major aid provider to the new country. Although Israel was one of early countries to recognise Bangladesh,[167] the government in Dhaka strongly supported Egypt during the Arab-Israeli War of 1973. In return, Egypt gifted Bangladesh's military with 44 tanks.[168] The Soviet Union supplied several squadrons of MiG-21 planes.[169]
Domestically, Rahman's regime became increasingly authoritarian.[170] There was an insurgency by the radical socialist Jashod, as well as agitation by pro-business and conservative forces, who felt the Awami League was unfairly taking exclusive credit for the liberation struggle.[citation needed] Rahman imposed a three-month state of emergency in 1974 to clean up mismanagement and corruption.[171] He formed the para-military Jatiya Rakkhi Bahini, which was accused of human rights abuses.[172] The Jatiya Rakkhi Bahini was also distrusted by many in the Bangladesh Army.[173]
Economically, Rahman embarked on a huge nationalisation programme that failed to deliver the benefits intended. Soviet and Indian aid also failed to materialise in the desired quantity. The Bangladesh famine of 1974 was a major economic blow and humanitarian crisis.[174]
In January 1975, Sheikh Mujib assumed the presidency with extraordinary powers, dissolved the parliamentary system, and established a one party state. Various political parties were merged into a sole legal national party, the Bangladesh Krishak Sramik Awami League, popularly known by its acronym BAKSAL.[174] Most Bangladeshi newspapers were banned.[citation needed] The failure of Sheikh Mujib's economic policies alienated the population. By 1975 journalist Anthony Mascarenhas described him as "the most hated man in Bangladesh".[174] On 15 August 1975, a group of junior army rebels assassinated Sheikh Mujib.[175][page needed]
Military coups and presidential regimes
[edit]First martial law and Zia administration
[edit]
The coup leaders installed Vice-President Khondaker Mostaq Ahmad as Sheikh Mujib's immediate successor. A staunch conservative, Ahmad promulgated martial law and jailed many prominent confidantes of Sheikh Mujib, including Bangladesh's first Prime Minister Tajuddin Ahmad. The jailed leaders were executed on 3 November 1975. Ahmad reshuffled the leadership of the Bangladesh Armed Forces, paving the way for the country's future military dictatorship.[175]
A counter-coup led by Brigadier General Khaled Mosharraf overthrew Ahmad from the presidency on 6 November 1975. The chief justice, Abu Sadat Mohammad Sayem, was installed as president. Mosharraf was killed by renegade socialist troops led by Abu Taher on 7 November 1975. The army chief, Lieutenant General Ziaur Rahman, emerged as the country's most powerful figure in 1976.[175]
Under the dramatically altered dispensation, Bangladesh feared an invasion from India backed by the Soviet Union, as the new government in Dhaka received recognition from Pakistan, Saudi Arabia and China. According to declassified US records, Bangladesh received assurances from the United States of Western support for its sovereignty and territorial integrity.[176][175] The dispute over the sharing the water of the Ganges, due to India's construction of the Farakka Barrage, led Bangladesh to seek the intervention of the United Nations in 1976. The dispute was addressed through a bilateral agreement in 1977.[177]
Lt Gen Ziaur Rahman (popularly known as Zia) assumed the presidency from Justice Sayem on 21 April 1977. Zia formed the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP). Parliamentary elections were held in 1979, in which the BNP gained a landslide majority and the Awami League became the principal opposition party.
President Zia restored free markets, redefined socialism as "economic and social justice" in the constitution and crafted a foreign policy which emphasised solidarity with Muslim majority countries and regional co-operation in South Asia. Bangladesh achieved rapid economic and industrial growth under Zia's presidency. The government built the country's first export processing zones. It operated a popular food-for-work programme, reversed the collectivisation of farms and promoted private sector development.
Zia faced twenty one attempted coups against his government, including one by the air force.[175] The final coup attempt resulted in his assassination in 1981: Zia was killed by troops loyal to Major General Abul Manzoor on 30 May 1981. The mutiny was later suppressed by army chief Lieutenant General Hussain Muhammad Ershad.[175]
Sattar administration
[edit]Zia was succeeded by Vice-President Abdus Sattar. President Sattar received a popular mandate during the 1981 presidential election. The 1982 Bangladesh coup d'état deposed President Sattar and his civilian government.[178]
Second martial law and Ershad administration
[edit]

Sattar was replaced by the chief justice A. F. M. Ahsanuddin Chowdhury. Lieutenant General Hussain Muhammad Ershad proclaimed martial law and became the Chief Martial Law Administrator. He appointed himself as the President of the Council of Ministers and the naval and air force chiefs as deputy martial law administrators. Ershad geared Bangladesh's foreign policy more towards the anti-Soviet bloc.
In 1983, Ershad assumed the presidency. Political repression was rife under Ershad's martial law regime. However, the government implemented a series of administrative reforms, particularly in terms of devolution. The eighteen districts of the country were divided into sixty-four districts. The upazila system was also created.
Among his major actions were to privatise the largely state-owned economy (up to 70% of industry was in public ownership) and encourage private investment in heavy industries along with light manufacturing, raw materials, and newspapers. Foreign companies were invited to invest in Bangladeshi industry as well, and stiff protectionist measures were put in place to safeguard manufacturing. All political parties and trade unions were banned, with the death penalty to be administered for corruption and political agitation. Ershad's takeover was generally viewed as a positive development[citation needed], as Bangladesh was in a state of serious economic difficulty. The country was facing significant food shortages. The government also faced a severe budget deficit to the tune of 4 billion takas, and the IMF declared that it would not provide any more loans until Bangladesh paid down some of its existing debts. During most of 1984, Ershad sought the opposition parties' participation in local elections under martial law. The opposition's refusal to participate, however, forced Ershad to abandon these plans. Ershad sought public support for his regime in a national referendum on his leadership in March 1985. He won overwhelmingly, although turnout was small. Two months later, Ershad held elections for local council chairmen. Pro-government candidates won a majority of the posts, setting in motion the President's ambitious decentralisation programme. Political life was further liberalised in early 1986, and additional political rights, including the right to hold large public rallies, were restored. At the same time, the Jatiya (National) Party, designed as Ershad's political vehicle for the transition from martial law, was established.[179] Despite a boycott by the BNP, led by President Zia's widow, Begum Khaleda Zia, parliamentary elections were held on schedule in May 1986. The Jatiya Party won a modest majority of the 300 elected seats in the National Assembly. The participation of the Awami League—led by the late President Mujib's daughter, Sheikh Hasina Wajed—lent the elections some credibility, despite widespread charges of voting irregularities.[179][180]
Ershad resigned as Chief of Army Staff and retired from military service in preparation for the 1986 presidential elections, scheduled for October. Protesting that martial law was still in effect, both the BNP and the AL refused to put up opposing candidates. Ershad easily outdistanced the remaining candidates, taking 84% of the vote. Although Ershad's government claimed a turnout of more than 50%, opposition leaders, and much of the foreign press, estimated a far lower percentage and alleged voting irregularities.[181]
In November 1986, his government mustered the necessary two-thirds majority in the National Assembly to pass the seventh constitutional amendment bill, protecting Ershad and his regime from prosecution for actions taken under the years of military rule.[180] Martial law was subsequently lifted on 11 November[179][182] and the opposition parties took their elected seats in the National Assembly.
In July 1987, however, after the government hastily pushed through a controversial legislative bill to include military representation on local administrative councils, the opposition walked out of Parliament. Passage of the bill helped spark an opposition movement that quickly gathered momentum, uniting Bangladesh's opposition parties for the first time. The government began to arrest scores of opposition activists under the country's Special Powers Act of 1974. Despite these arrests, opposition parties continued to organise protest marches and nationwide strikes.[183] In order to prevent a 72-hour strike planned for 29 November, Ershad declared a state of emergency on 27 November.[184] Parliament was dissolved on 6 December,[185] and fresh elections scheduled for March 1988.[179]
All major opposition parties refused government overtures to participate in these polls, maintaining that the government was incapable of holding free and fair elections. Despite the opposition boycott, the parliamentary elections proceeded. The ruling Jatiya Party won 251 of the 300 seats. The Parliament, while still regarded by the opposition as an illegitimate body, held its sessions as scheduled, and passed numerous bills, including, in June 1988, the controversial eighth amendment to the Constitution, which made Islam the state religion,[186] in contrast to the original secular nature of the Constitution.
By 1989, the local council elections were generally considered by international observers to have been less violent and more free and fair than previous elections. However, opposition to Ershad's rule began to regain momentum, escalating by the end of 1990 in frequent general strikes, increased campus protests, public rallies, and a general disintegration of law and order.[179]
Chittagong Hill Tracts conflict
[edit]The Chittagong Hill Tracts is the south-eastern mountainous frontier of Bangladesh with Myanmar and Northeast India. The area enjoyed autonomy under British Bengal. Its autonomous status was revoked by Pakistan, which built the controversial Kaptai Dam that displaced the area's indigenous people. When Bangladesh became independent, the government of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman adopted a Bengali nationalist constitution, which denied recognition of the country's ethnic minorities. Manabendra Narayan Larma, a member of parliament form the hill tracts, called for constitutional recognition of the indigenous people of the area.[187] He gave a notable speech at the Constituent Assembly of Bangladesh demanding the use of "Bangladeshi" as the country's nationality definition, instead of Bengali. During the 1970s and '80s, there were attempts by the government to settle with the Bengali people. These attempts were resisted by the hill tribes, who, with the latent support of neighbouring India, formed a guerrilla force called Shanti Bahini. As a result of the tribal resistance movement, successive governments turned the Hill Tracts into a militarised zone.[188]
Following years of unrest, the Chittagong Hill Tracts Peace Accord was signed in 1997 between the government of Bangladesh and the tribal leaders which granted a limited level of autonomy to the elected council of the three hill districts.[189]
Return of parliamentary republic and Battle of the Begums
[edit]First caretaker government (1990–1991)
[edit]Ershad resigned under the pressure from the military and international community, as the pro-democracy movement spearheaded by Khaleda Zia and Sheikh Hasina engulfed the entire country and drew the participation of the middle and upper classes.
The chief justice, Shahabuddin Ahmed, was sworn in as acting president and formed the first caretaker government of Bangladesh. Ahmed placed Ershad under arrest and organised free and fair elections in 1991.
Khaleda administration (1991–1996)
[edit]The centre-right BNP won the 1991 Bangladeshi general election with 140 seats, but was short of an overall parliamentary majority. However, they formed a government with support from the Islamic party Jamaat-e-Islami, with Khaleda Zia, widow of Ziaur Rahman, obtaining the post of prime minister. Only four parties had more than 10 members elected to the 1991 Parliament: The BNP, led by Prime Minister Begum Khaleda Zia; the AL, led by Sheikh Hasina; the Jamaat-I-Islami (JI), led by Ghulam Azam; and the Jatiya Party (JP), led by acting chairman Mizanur Rahman Choudhury while its founder, former President Ershad, served out a prison sentence on corruption charges. Khaleda Zia became the first female prime minister in Bangladeshi history.
In September 1991 a constitutional referendum was held, which sought the transfer of executive powers from the President, which had been held by the Office since 1975, to the Prime Minister – making the President largely a ceremonial role. The vote was overwhelmingly in favour of the constitutional amendment and Bangladesh was restored to a Parliamentary democracy, as per its founding constitution. In October 1991, members of Parliament elected a new head of state, President Abdur Rahman Biswas. Finance Minister Saifur Rahman launched a series of liberal economic reforms, which set a precedent in South Asia and was seen as a model in India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.[190]
In March 1994, controversy over a parliamentary by-election, which the opposition claimed the government had rigged, led to an indefinite boycott of Parliament by the entire opposition. The opposition also began a programme of repeated general strikes to press its demand that Khaleda Zia's government resign and a caretaker government supervise a general election. Efforts to mediate the dispute, under the auspices of the Commonwealth Secretariat, failed. After another attempt at a negotiated settlement failed narrowly in late December 1994, the opposition resigned en masse from Parliament. The opposition then continued a campaign of marches, demonstrations, and strikes in an effort to force the government to resign.[191] All major opposition parties, including Sheikh Hasina's Awami League, pledged to boycott national elections scheduled for 15 February 1996.[179]
In February, Khaleda Zia was re-elected by a landslide in voting boycotted and denounced as unfair by the three main opposition parties. This administration was short-lived however, only lasting 12 days[192] and in March 1996, following escalating political turmoil, the sitting Parliament enacted a constitutional amendment to allow a neutral caretaker government to assume power and conduct new parliamentary elections in June 1996.
Second caretaker government (1996)
[edit]The chief justice Muhammad Habibur Rahman became the 1st Chief Advisor of Bangladesh under the country's constitutional caretaker government system. During this period, President Abdur Rahman Biswas sacked army chief Lieutenant General Abu Saleh Mohammad Nasim for alleged political activities, causing the general to attempt a coup in response. The sacked army chief ordered troops in Bogra, Mymensingh and Jessore to march towards Dhaka. However, the military commander of Savar sided with the president and deployed tanks in the capital and its surrounding highways, and also suspended ferry services, as part of operations to deter the coup forces. Lt Gen Nasim was later arrested in Dhaka Cantonment.[193]
The Chief Advisor successfully held free and fair elections on 12 June 1996. The Awami League emerged as the single largest party, with 146 seats in parliament, followed by the BNP with 116 seats and Jatiya Party with 32 seats.
Hasina administration (1996–2001)
[edit]Sheikh Hasina's Awami League won 146 of 300 seats in the June 1996 elections, just short of a majority. However, with the support of Jatiya party she formed what she called a "Government of National Consensus" in June 1996.[179] International and domestic election observers found the June 1996 election free and fair. The BNP soon charged that police and Awami League activists were engaged in large-scale harassment and jailing of opposition activists. At the end of 1996, the BNP staged a parliamentary walkout over this and other grievances but returned in January 1997 under a four-point agreement with the ruling party. The BNP asserted that this agreement was never implemented and later staged another walkout in August 1997. The BNP returned to Parliament under another agreement in March 1998.[179]
The first Hasina administration is credited for landmark initiatives in environmental and inter-ethnic peacemaking. It was responsible for signing the Ganges Water Sharing Treaty with India and the Chittagong Hill Tracts Peace Accord with ethnic insurgents, for which Hasina won the UNESCO Peace Prize. Hasina was also one of the founding leaders of the Developing 8 Countries. In 1998, Hasina hosted a rare and unprecedented trilateral economic summit in Dhaka with Prime Ministers Nawaz Sharif of Pakistan and I. K. Gujral of India. Her summits with US President Bill Clinton in Dhaka and Washington DC focused on American energy investments for Bangladesh's natural gas reserves and the extradition of her father's killers. However, Hasina was not keen to allow the export of Bangladeshi natural gas, despite demands from multinational firms.[194][195][196][197][198]
In June 1999, the BNP and other opposition parties again began to abstain from attending Parliament. Opposition parties staged an increasing number of nationwide general strikes, rising from six days of general strikes in 1997 to 27 days in 1999. A four-party opposition alliance formed at the beginning of 1999 announced that it would boycott parliamentary by-elections and local government elections unless the government took steps demanded by the opposition to ensure electoral fairness. The government did not take these steps, and the opposition subsequently boycotted all elections.[179]
In July 2001, the Awami League government stepped down to allow a caretaker government to preside over parliamentary elections. Political violence that had increased during the Awami League government's tenure continued to increase through the summer in the run up to the election. In August, Khaleda Zia and Sheikh Hasina agreed during a visit of former President Jimmy Carter to respect the results of the election, join Parliament win or lose, forswear the use of hartals (violently enforced strikes) as political tools, and if successful in forming a government allow for a more meaningful role for the opposition in Parliament.[199]
Third caretaker government (2001)
[edit]The caretaker government, led by Chief Advisor Latifur Rahman, was successful in containing the violence, which allowed a parliamentary general election to be successfully held on 1 October 2001. The election saw a landslide victory of the BNP-led coalition, which included the far-right Jamaat-e-Islami and Islami Oikya Jote. The BNP won 193 seats and the Jamaat won 17 seats.[179]
Khaleda administration (2001–2006)
[edit]
Following the September 11 attacks, the government of Prime Minister Khaleda Zia allowed the United States to use Bangladeshi airports and airspace for combat operations in Afghanistan. Bangladesh was also quick to respond to relief efforts in Afghanistan after the overthrow of the Taliban, with BRAC becoming the largest development agency in the war-torn country. The United States praised Bangladesh as an "elegant, compelling and greatly needed voice of moderation" in the Muslim world.[200] Khaleda Zia also developed a strategic partnership with China and signed a Defense Cooperation Agreement with Beijing.[201]
Despite her August 2001 pledge and all election monitoring groups declaring the election free and fair, Sheikh Hasina condemned the last election, rejected the results, and boycotted Parliament. In 2002, however, she led her party legislators back to Parliament, but the Awami League again walked out in June 2003 to protest derogatory remarks about Hasina by a State Minister and the allegedly partisan role of the Parliamentary Speaker. In June 2004, the AL returned to Parliament without having any of their demands met. They then attended Parliament irregularly before announcing a boycott of the entire June 2005 budget session.
Khaleda Zia's administration was marked by improved economic growth, corruption allegations and growing rifts between the country's secular and conservative forces. A series of high-profile assassinations targeted the Awami League-led opposition. Former Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina narrowly escaped an assassination attempt in 2004. The Jamaatul Mujahadeen Bangladesh launched several terrorist attacks in 2005. The League accused the BNP and Jamaat of having complicity in the rise of militancy. Relations with neighbouring India deteriorated over allegations that Bangladeshi territory was allowed to be used by Northeast Indian insurgents.[citation needed]
Fourth caretaker regime (2006–2008)
[edit]
A major political crisis erupted after the end of the BNP's tenure, as the Awami League-led coalition demanded a neutral candidate for Chief Advisor. Weeks of strikes, protests and blockades paralysed the country. President Iajuddin Ahmed assumed the responsibilities of Chief Advisor but failed to allay the fears of the opposition of an impending rigged election. The Bangladeshi press accused the president of acting under the influence of the BNP. Violent protests continued even as the military was deployed in aid of civil administration.
On 11 January 2007, a state of emergency was declared by President Ahmed, who resigned from the office of chief advisor under widely reported pressure from the military, particularly the army chief General Moeen U Ahmed.[202] The former governor of the central bank, Fakhruddin Ahmed, was appointed as the Chief Advisor and the cabinet was reshuffled with many technocrats. The military-backed caretaker government started an anti-corruption drive, which saw the arrest of over 160 politicians, businessmen and bureaucrats, including former prime ministers Khaleda Zia and Sheikh Hasina, as well as Khaleda's two sons. Student protests in Dhaka University demanded the restoration of democracy in August 2007, but were suppressed by a curfew. Khaleda and Hasina were released in 2008.
The state of emergency lasted for two years. The December 2008 general election saw a landslide victory for the Awami League-led coalition, which also included the Jatiya Party.
Hasina administration (2009–2024)
[edit]

Within two months of assuming office, Sheikh Hasina's second government faced the BDR Mutiny, which provoked tensions with sections of the military. Hasina successfully tackled the threat from mutineers and enraged elements in the military.[203] She formed the international crimes tribunal to prosecute surviving Bengali Islamist collaborators of the 1971 genocide. The tribunal has criticism over its fairness and impartiality.
An anti-terror crackdown dramatically improved relations with neighbouring India. Bangladesh and India have increasingly focused on regional connectivity and trade.
In 2010, the Supreme Court of Bangladesh reaffirmed secularism as a fundamental principle in the constitution. The war crimes tribunal mobilised public opinion in favour of secularism, which was manifested in the March 2013 Shahbag protests. In response, a huge Islamist mobilisation also took place led by the Hefazat-e-Islam group in May 2013.[204]
The intense bickering between the League and BNP, often dubbed the Battle of the Begums, has continued. The Hasina government abolished the provision of caretaker government in the constitution through the controversial Fifteenth Amendment.[205] The move was seen by the BNP as an attempt to corrupt the election process in favour of the League.[206]
In 2013, the hard-line, right-wing, Islamic party, Jamaat-e-Islami was banned from registering and therefore contesting in elections by the High Court, citing their charter violates the constitution.[207][208] Street violence between the League, BNP and the Jamaat intensified in the run up to the general election. In 2014, the general elections were boycotted by the BNP. The elections were criticized by the United States, United Kingdom, European Union and the United Nations.[209] Sheikh Hasina was sworn in for a third tenure as prime minister.
In 2015 and 2016, Bangladesh saw increasing assassinations targeting minorities and secularists. The country's worst terrorist attack saw the death of 20 people after an upmarket restaurant was sieged by gunmen in July 2016.[210] The Islamic State of Iraq and Levant has claimed responsibility for many of the attacks, although the Hasina government insists local terror outfits are more likely to be responsible.[205] Since this attack, the Government took stricter measures against extremists as the security forces led a numerous raids on suspected militant hide-outs. The measures led to reduction in extremist attacks and fatalities.[211]

In 2017, the country faced fresh challenge from incoming Rohingya refugees. Starting in early August 2017, the Myanmar security forces began "clearance operations" against the Rohingya in northern Rakhine state – killing thousands of Rohingya, brutalizing thousands more, and driving hundreds of thousands out of the country into neighboring Bangladesh. In the first four weeks of the conflict, over 400,000 Rohingya refugees (approximately 40% of the remaining Rohingya in Myanmar) fled the country (chiefly to Bangladesh) creating a major humanitarian crisis. The governments of Myanmar and Bangladesh signed a memorandum of understanding on 23 November 2017 regarding the repatriation of Rohingya refugees to Rakhine State.[212] However, till the end of the decade over 740,000 refugees remained in Bangladesh creating pressure on the country's economy and infrastructure.[213]
The 2018 General elections brought another landslide victory for the Awami League led by Sheikh Hasina. While the opposition was already weak due to key leaders being in either jail or exile, the elections were further marred by violence and claims of vote rigging.[214] However, this gave the Awami League Government stability and opportunity to complete key infrastructure projects for the country including the Padma Bridge[215] and the Dhaka Metro Rail.[216]
Anti-government protests broke out in Bangladesh on 10 December 2022.[217] In December 2022, tens of thousands marched in Dhaka demanding the resignation of Sheikh Hasina.[218]
In January 2024, Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina secured her fourth straight term in Bangladesh's controversial general election, which was boycotted by the main opposition Bangladesh Nationalist Party.[219]
The fall of Hasina administration (2024)
[edit]
In June 2024, protests began in response to the Supreme Court of Bangladesh reinstating a 30% quota for government jobs for descendants of freedom fighters, reversing the government decision made in response to the 2018 Bangladesh quota reform movement. Students began to feel like they have a limited opportunity based on merit. The protest, which initially began as a response to the reestablished quota system for government jobs, quickly spread throughout the entire country because of the government's violent response, as well as growing public dissatisfaction against an oppressive government. The situation was further complicated by many other ongoing issues, like the government's inability to manage a prolonged economic downturn, reports of rampant corruption and human rights violations, and the absence of democratic channels for initiating changes.[220][221][222][223]
On 3 August 2024, coordinators of the Anti-discrimination Students Movement announced a one-point demand for the resignation and called for "comprehensive non-cooperation".[224][225] The following day, violent clashes broke out, resulting in the deaths of 97 people, including students. The coordinators called for a long march to Dhaka to force Hasina out of power on 5 August. That day, a large crowd of protesters made its way through the capital.[226] At 2:30 p.m. BST, Sheikh Hasina resigned and fled to India.[227]
On 5 August, the chief of army staff, Waker-uz-Zaman, convened a meeting with representatives from the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP), Jatiya Party (Ershad), and Jamaat-e-Islami[228] and called for the creation of an interim government within 48 hours, excluding the Awami League.[229] Subsequent reports indicated that Muhammad Yunus, a Nobel laureate, had been approached to be the head of the interim government.[230] The nomination of Yunus, who accepted the advisory role in the interim government, has also been supported by prominent figures within the student movement.[231] In addition, Waker-uz-Zaman pledged an investigation by the military into the preceding incidents of violence and issued an order prohibiting security forces from opening fire on crowds.[232]
See also
[edit]- Elections in Bangladesh
- History of Asia
- History of Assam
- History of Bengal
- History of Bangladesh after independence
- History of India
- History of Pakistan
- History of South Asia
- List of presidents of Bangladesh
- List of prime ministers of Bangladesh
- List of rulers of Bengal
- Politics of Bangladesh
- Timeline of Bangladeshi history
- Timeline of Dhaka
- Poverty in Bangladesh
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 11. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 13. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 15. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b c Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 17. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 19. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 16. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b c Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. pp. 16–7. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 21. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Richard M. Eaton (31 July 1996). The Rise of Islam and the Bengal Frontier, 1204-1760. University of California Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-520-20507-9. Archived from the original on 6 January 2017. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- ^ "Mahavamasa - the Sinhalese epic". Archived from the original on 30 October 2015. Retrieved 30 August 2018.
- ^ "Bangladesh (People's Republic of Bangladesh) Pax Gaea World Post Human Rights Report". Paxgaea.com. Archived from the original on 13 December 2013. Retrieved 12 July 2013.
- ^ "Alexander and Chandragupta Maurya: A short history of war, empire, and greatness". The Indian Express. 17 November 2021. Archived from the original on 15 February 2023. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ^ Sri Venkatesvara University, Oriental Research Institute (1979). Sri Venkateswara University Oriental Journal Volumes 21–22. p. 33.
- ^ Sircar, D.C. (1984). Journal of Ancient Indian History, Vol-14. p. 5.
- ^ a b Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. pp. 13–4. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Ghosh, Suchandra (2019). "Crossings and contacts across the Bay of Bengal: a connected history of ports in early South and Southeast Asia". Journal of the Indian Ocean Region. 15 (3): 281–296. doi:10.1080/19480881.2019.1640577. S2CID 202332142. Archived from the original on 30 May 2022. Retrieved 30 May 2022.
- ^ Prabha, Himanshu (1980). "Seafaring in the Bay of Bengal in the Early Centuries AD". Studies in History. 6 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1177/025764309000600101. S2CID 220673640. Archived from the original on 30 May 2022. Retrieved 30 May 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Sengupta, Nitish K. (2011). Land of Two Rivers: A History of Bengal from the Mahabharata to Mujib. Penguin Books India. p. 40. ISBN 978-0-14-341678-4. Archived from the original on 2 May 2016.
- ^ Dasgupta, Biplab (2005). European Trade and Colonial Conquest. Anthem Press. pp. 341–. ISBN 978-1-84331-029-7. Archived from the original on 29 April 2016.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b Sen, Sailendra Nath (1999). Ancient Indian History and Civilization. New Age International. pp. 277–287. ISBN 978-81-224-1198-0. Archived from the original on 17 May 2016.
- ^ Sinha, B. P. (1977). Dynastic History of Magadha. New Delhi: Abhinav Publications. p. 185. ISBN 978-81-7017-059-4. Archived from the original on 3 June 2016.
- ^ a b Sengupta, Nitish K. (2011). Land of Two Rivers: A History of Bengal from the Mahabharata to Mujib. New Delhi: Penguin Books India. p. 45. ISBN 978-0-14-341678-4.
- ^ Allan, John; Dodwell, Henry Herbert; Haig, Thomas Wolseley (1934). The Cambridge Shorter History of India. Cambridge University Press. p. 10.
- ^ Sen, Sailendra Nath (1988). Ancient Indian History and Civilization. New Delhi: Wiley Eastern. p. 281.
- ^ Raatan, T. (2004). Encyclopaedia of North-East India. New Delhi: Kalpaz Publications. p. 143. ISBN 978-8178350684.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. pp. 15–6. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 16. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Ray, Niharranjan (1993). Bangalir Itihas: Adiparba (in Bengali). Calcutta: Dey's Publishing. pp. 408–9. ISBN 978-81-7079-270-3.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b c d e f Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. pp. 18–19. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b c d e Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 50. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Dasgupta, Biplab (2005). European Trade and Colonial Conquest. Anthem Press. p. 327. ISBN 978-1-84331-029-7. Archived from the original on 16 January 2023. Retrieved 4 September 2018.
- ^ a b Prinsep, James (1840). Useful Tables, Forming an Appendix to the Journal of the Asiatic Society: Part the First, Coins, Weights, and Measures of British India. Bishop's College Press. p. 147. Archived from the original on 16 January 2023. Retrieved 4 September 2018.
- ^ "Bangladesh Studies O Level (7094) Pilot Textbook". University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate. Archived from the original on 25 January 2013. Retrieved 25 January 2014.
- ^ Niazi, Ghulam Sarwar Khan (1992). The Life and Works of Sultan Alauddin Khalji. Atlantic Publishers & Dist. pp. 19–. ISBN 978-81-7156-362-3. Archived from the original on 16 January 2023. Retrieved 4 September 2018.
- ^ Farooqui, Salma Ahmed (2011). A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century. Pearson Education India. pp. 91–. ISBN 978-81-317-3202-1. Archived from the original on 16 January 2023. Retrieved 4 September 2018.
- ^ a b Khan, Muazzam Hussain (2012). "Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah". In Islam, Sirajul; Jamal, Ahmed A. (eds.). Banglapedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Second ed.). Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. Archived from the original on 2 July 2015. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- ^ "About Chittagong:History". Local Government Engineering Department, Government of Bangladesh. Archived from the original on 3 November 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- ^ "Historic archaeological sites need to be preserved". The Daily Star. UNB. 5 September 2009. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- ^ Ahmed, ABM Shamsuddin (2012). "Ilyas Shah". In Islam, Sirajul; Jamal, Ahmed A. (eds.). Banglapedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Second ed.). Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. Archived from the original on 2 November 2016. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- ^ Khan, Muazzam Hussain (2012). "Ibn Battuta". In Islam, Sirajul; Jamal, Ahmed A. (eds.). Banglapedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Second ed.). Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. Archived from the original on 9 July 2015. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- ^ Hanif, N. (2000). Biographical encyclopedia of Sufis. New Delhi: Sarup & Sons. p. 320. OCLC 786166571.
- ^ a b c Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 52. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Economy of the Mughal Empire
- ^ a b c d e f g Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 39. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 41. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 42. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Ray, Indrajit (2011). Bengal Industries and the British Industrial Revolution (1757-1857). Routledge. pp. 57, 90, 174. ISBN 978-1-136-82552-1. Archived from the original on 16 January 2023. Retrieved 20 January 2019.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. pp. 21–22. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b c d Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 51. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. pp. 51–52. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b c Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 30. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ "How did Bengalis become Muslims?". Times of India Blog. 8 August 2012. Archived from the original on 1 December 2019. Retrieved 17 November 2019.
- ^ a b c Karim, Abdul (2012). "Islam Khan Chisti". In Islam, Sirajul; Jamal, Ahmed A. (eds.). Banglapedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Second ed.). Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. Archived from the original on 2 February 2015. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- ^ a b c Karim, Abdul (2012). "Shaista Khan". In Islam, Sirajul; Jamal, Ahmed A. (eds.). Banglapedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Second ed.). Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. Archived from the original on 1 October 2014. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- ^ a b c d Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 56. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. pp. 22–23. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Gupta, Brijen Kishore (1962). Sirajuddaullah and the East India Company, 1756–1757. E. J. Brill. p. 23. OCLC 310573738. Archived from the original on 16 January 2023. Retrieved 10 February 2019.
- ^ a b Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 24. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. pp. 24–25. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b c Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 49. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 66. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. pp. 25–26. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. pp. 49–50. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 57. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b c van Schendel, Willem [in Dutch] (February 2002). "Stateless in South Asia: The Making of the India-Bangladesh Enclaves" (PDF). The Journal of Asian Studies. 61 (1): 115–130. doi:10.2307/2700191. JSTOR 2700191. S2CID 56506815. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- ^ a b c Hunter, William Wilson (1876). A Statistical Account of Bengal (10 ed.). pp. 414–. Archived from the original on 16 January 2023. Retrieved 13 February 2019.
- ^ a b c Majumdar, Ramesh Chandra (1977). Ancient India (1 ed.). Bungalow Road, Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass. p. 518. ISBN 9788120804364. Retrieved 13 February 2019.
- ^ a b Tong, Junie T. (2016). Finance and Society in 21st Century China: Chinese Culture Versus Western Markets. CRC Press. p. 151. ISBN 978-1-317-13522-7.
- ^ Esposito, John L., ed. (2004). "Great Britain". The Islamic World: Past and Present. Vol. 1. Oxford University Press. p. 174. ISBN 978-0-19-516520-3. Archived from the original on 20 December 2017.
- ^ a b Ray, Indrajit (2011). Bengal Industries and the British Industrial Revolution (1757-1857). Routledge. pp. 7–10. ISBN 978-1-136-82552-1. Archived from the original on 16 January 2023. Retrieved 20 January 2019.
- ^ Sengupta, Shombit (8 February 2010). "Bengals plunder gifted the British Industrial Revolution". The Financial Express. Noida, India. Archived from the original on 1 August 2017. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 58. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 59. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 60. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. pp. 60–63. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 63. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b c Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 64. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 65. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 77. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b c Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 78. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 31. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Nitish Sengupta (2001). History of the Bengali-speaking People. UBS Publishers' Distributors. p. 211. ISBN 978-81-7476-355-6.
The Bengal Renaissance can be said to have started with Raja Ram Mohan Roy (1775-1833) and ended with Rabindranath Tagore (1861-1941).
- ^ Kopf, David (December 1994). "Amiya P. Sen. Hindu Revivalism in Bengal 1872". American Historical Review (Book review). 99 (5): 1741–1742. doi:10.2307/2168519. JSTOR 2168519.
- ^ Gilmour, David (1994). Curzon: Imperial Statesman. John Murray. pp. 271–3. ISBN 978-0-7195-4834-5.
- ^ "Partition of Bengal". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 6 November 2013. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- ^ Chandra, Bipan (2009). History of Modern India. New Delhi: Orient Blackswan. pp. 248–249. ISBN 978-81-250-3684-5.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 80. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 81. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. pp. 81–82. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 82. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. pp. 82–83. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 83. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. pp. 83–85. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 85. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 86. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 49. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 50. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 51. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. pp. 51–52. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b c Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 74. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. pp. 86–87. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 87. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 93. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 55. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 94. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 57. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 109. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Van Schendel, Willem (2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 288. ISBN 9780521861748. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- ^ Van Schendel, Willem (2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 289. ISBN 9780521861748.
- ^ Glassie, Henry; Mahmud, Feroz (2008). Living Traditions. Cultural Survey of Bangladesh Series. Vol. 11. Dhaka: Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. p. 578. OCLC 299379800.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 115. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. pp. 115–116. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 116. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Van Schendel, Willem (2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 292. ISBN 9780521861748.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 121. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Van Schendel, Willem (2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 293. ISBN 9780521861748.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 123. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 78. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. pp. 78–79. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 79. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 125. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 126. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 129. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. pp. 129–130. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Van Schendel, Willem (2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 302. ISBN 9780521861748.
- ^ "Major Ziaur Rahman's revolt with 8 East Bengal Regiment at Chittagong". Newsbd71.blogspot.com. 20 March 2011. Archived from the original on 3 October 2013. Retrieved 18 February 2013.
- ^ "Zia clarifies his timing of declaration of independence". YouTube. 10 December 2007. Archived from the original on 3 June 2015. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ সংযোজনস্বাধীনতার ঘোষণা: বেলাল মোহাম্মদের সাক্ষাৎকার. bdnews24.com (in Bengali). Archived from the original on 29 March 2010. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ Gupta, Jyota Sen (1974). History of Freedom Movement in Bangladesh, 1943–1973: Some Involvement (First ed.). Calcutta: Naya Prokash. pp. 325–326. Archived from the original on 3 June 2016. Retrieved 15 November 2015.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 167. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b Baxter, Craig (1997). Bangladesh: From A Nation to a State. Westview Press. p. 88. ISBN 978-0-813-33632-9.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 169. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 170. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ a b "54 Indian PoWs of 1971 war still in Pakistan". DailyTimes. 19 January 2005. Archived from the original on 21 December 2012. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ "The 1971 war". BBC News. Archived from the original on 18 November 2011. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ Section 9. Situation in the Indian Subcontinent, 2. Bangladesh's international position Archived 20 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine – Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan
- ^ "Bangladesh: Unfinished Justice for the crimes of 1971 – South Asia Citizens Web". Sacw.net. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 23 June 2011.
- ^ "Bangladesh's genocide debate; A conscientious research". EFSAS. Archived from the original on 26 September 2020. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- ^ "The Simla Agreement". Story of Pakistan. 1 June 2003. Archived from the original on 3 June 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2011.
- ^ a b c Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 173. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 172. ISBN 9780511997419.
- ^ "Genesis of Bangladesh's Constitution". The Daily Star (Op-ed). Archived from the original on 26 December 2016. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ "Mujibnagar Government". Banglapedia. Archived from the original on 8 December 2016. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^
Husain, Syed Anwar (1990). "Bangladesh and Islamic Countries, 1972-1983". In Tepper, Elliot L.; Hayes, Glen A. (eds.). Bengal and Bangladesh: Politics and Culture on the Golden Delta. Asian Studies Center, Michigan State University. p. 103.
In April 1972, Israel also extended recognition to Bangladesh.
- ^ Pike, John. "Bangladesh Army – Modernization". globalsecurity.org. Archived from the original on 28 December 2016. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ Pike, John. "Bangladesh – Air Force Modernization". globalsecurity.org. Archived from the original on 26 December 2016. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ Mascarenhas, Anthony (1986). Bangladesh: A Legacy of Blood. Hodder and Stoughton. p. 52. ISBN 0-340-39420-X.
- ^ Mascarenhas, Anthony (1986). Bangladesh: A Legacy of Blood. Hodder and Stoughton. pp. 44–45. ISBN 0-340-39420-X.
- ^ Mascarenhas, Anthony (1986). Bangladesh: A Legacy of Blood. Hodder and Stoughton. p. 37. ISBN 0-340-39420-X.
- ^ Mascarenhas, Anthony (1986). Bangladesh: A Legacy of Blood. Hodder and Stoughton. p. 46. ISBN 0-340-39420-X.
- ^ a b c Lewis, David (2011). Bangladesh: Politics, Economy and Civil Society. Cambridge University Press. pp. 78–81. ISBN 978-1-139-50257-3. Archived from the original on 6 January 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f Mascarenhas, Anthony (1986). Bangladesh: A Legacy of Blood. Hodder and Stoughton. ISBN 0-340-39420-X.
- ^ "Why Bangladesh feared Indian invasion after 1975 coup". Indian Defence Review. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ Preston, Ian, ed. (2005) [First published 2001]. A Political Chronology of Central, South and East Asia. Europa Publications. p. 18. ISBN 978-1-135-35680-4.
- ^ Preston, Ian, ed. (2005) [First published 2001]. A Political Chronology of Central, South and East Asia. Europa Publications. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-1-135-35680-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Bureau of South and Central Asian Affairs (March 2008). "Background Note: Bangladesh". U.S. Department of State. Archived from the original on 27 October 2019. Retrieved 11 June 2008. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b Liton, Shakhawat (28 August 2010). "Ershad's desperate bids go in vain". The Daily Star. Archived from the original on 19 June 2018. Retrieved 3 January 2019.
- ^ Bangladesh Chief Claims Vote Victory Archived 27 December 2018 at the Wayback Machine The New York Times, 17 October 1986
- ^ "Martial Law Ends in Bangladesh". Washington Post. 11 November 1986. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on 29 December 2018. Retrieved 29 December 2018.
- ^ "Bangladeshis bring down Ershad regime, 1987-1990". Global Nonviolent Action Database. 17 November 2012. Archived from the original on 7 January 2019. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- ^ Protest Banned, Curfew Imposed in Bangladesh L.A. Times, 28 November 1987
- ^ "Tenure of All Parliaments". Parliament of Bangladesh. 30 December 2012. Archived from the original on 12 August 2018. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- ^ "After 28 years, Bangladesh revives case to drop Islam as state..." Reuters. 7 March 2016. Archived from the original on 22 June 2018. Retrieved 29 December 2018.
- ^ Van Schendel, Willem (2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 344. ISBN 9780521861748.
- ^ Van Schendel, Willem (2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 345. ISBN 9780521861748.
- ^ Rashiduzzaman, M. (1998). "Bangladesh's Chittagong Hill Tracts Peace Accord: Institutional Features and Strategic Concerns". Asian Survey. 38 (7): 653–670. doi:10.2307/2645754. ISSN 0004-4687. JSTOR 2645754. Archived from the original on 5 November 2022. Retrieved 17 February 2023.
- ^ Hossain, Kazi Liakat (6 September 2016). "Remembering the budget wizard". Dhaka Tribune (Op-ed). Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ Islam, Syed Serajul (2001). "Elections and politics in post-Ershad era in Bangladesh" (PDF). Asian and African Studies. 10 (1): 160–173. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 December 2018. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- ^ "Tenure of All Parliaments". 12 August 2018. Archived from the original on 12 August 2018. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- ^ Refugees, United Nations High Commissioner for. "Refworld | Political Developments December 1996 - April 1998". Refworld. Archived from the original on 15 September 2023. Retrieved 17 February 2023.
- ^ Conca, Ken; Dabelko, Geoffrey D. (2002). Environmental Peacemaking. Woodrow Wilson Center Press. p. 69. ISBN 978-0-8018-7193-1.
- ^ Roy, Rajkumari Chandra Kalindi (2000). Land Rights of the Indigenous Peoples of the Chittagong Hill Tracts, Bangladesh. IWGIA. p. 164. ISBN 978-87-90730-29-1.
- ^ Bangladesh Development Initiative (2007). Political culture in Bangladesh: perspectives and analysis : selections from the journal of Bangladesh studies. Bangladesh Development Initiative. p. 323. ISBN 978-984-05-1782-4.
- ^ Chen, Edwin (21 March 2000). "Clinton Touts Ties With Bangladesh". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 17 November 2016. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ Bhargava, Kant Kishore; Khatri, Sridhar K.; Coalition for Actions for South Asian Cooperation (Kathmandu, Nepal) (1999). Working paper for Conference on South Asia 2010: Opportunities and Challenges, Kathmandu, December 1–3, 1999. Coalition for Action on South Asian Cooperation. p. 16.
- ^ "Background Note: Bangladesh". U.S. Department of State. 6 September 2017. Retrieved 8 March 2025.
- ^ "Powell praises Bangladesh". BBC News. Archived from the original on 26 May 2017. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ "Bangladesh-China Defence Co-Operation Agreement's Strategic Implications: An Analysis". South Asia Analysis Group. Archived from the original on 12 December 2012. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ "The coup that dare not speak its name". The Economist. 18 January 2007. Archived from the original on 29 July 2017. Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- ^ Van Schendel, Willem (2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 356. ISBN 9780521861748.
- ^ "Bangladesh: restoring secular Constitution". The Hindu. 24 June 2011. ISSN 0971-751X. Archived from the original on 17 February 2023. Retrieved 17 February 2023.
- ^ a b Van Schendel, Willem (2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 358. ISBN 9780521861748.
- ^ Maîtrot, Mathilde; Jackman, David (3 July 2023). "Discipline, Development, and Duress: The Art of Winning an Election in Bangladesh". Critical Asian Studies. 55 (3): 424–439. doi:10.1080/14672715.2023.2229363. ISSN 1467-2715.
- ^ "Bangladesh court declares Jamaat illegal | News". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 6 January 2019. Retrieved 28 December 2018.
- ^ "EC scraps Jamaat's registration". The Daily Star. 30 October 2018. Archived from the original on 28 December 2018. Retrieved 28 December 2018.
- ^ Chowdhury, Syed Tashfin. "Violent Bangladesh poll 'not credible'". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 12 May 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- ^ "20 hostages killed in 'Isil' attack on Dhaka restaurant popular with foreigners". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 2 July 2016.
- ^ Sing, S.B. (21 January 2020). "Bangladesh: Exemplary Record – Analysis". EurasiaReview News&Analysis. Archived from the original on 9 August 2020. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ^ "Myanmar, Bangladesh 'sign Rohingya deal'". News.com.au. Archived from the original on 24 November 2017. Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- ^ "Rohingya crisis: Bangladesh will no longer take in Myanmar refugees - BBC News". BBC News. March 2019. Archived from the original on 10 September 2019. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ^ Bangladesh election: Opposition demands new vote Archived 31 December 2018 at the Wayback Machine BBC News, 30 December 2018
- ^ "Bangladesh Unveils Padma River Bridge". VOA. 25 June 2022. Archived from the original on 1 September 2022. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- ^ M, Patrick (6 November 2021). "Bangladesh: Dhaka Metro Rail Project Updates". Construction Review Online. Archived from the original on 2 September 2022. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- ^ "What's behind antigovernment protests in Bangladesh?". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 25 April 2023. Retrieved 11 December 2022.
- ^ Sud, Vedika; Xiong, Yong (11 December 2022). "Tens of thousands protest in Bangladesh to demand resignation of Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina". CNN. Archived from the original on 11 December 2022. Retrieved 11 December 2022.
- ^ "Bangladesh election: PM Sheikh Hasina wins fourth term in controversial vote". 7 January 2024.
- ^ Lu, Christina (7 August 2024). "What's Behind Bangladesh's Student Protests?". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 4 August 2024. Retrieved 3 August 2024.
- ^ "Is the system rigged against meritocracy?". The Daily Star. 10 July 2024. Archived from the original on 16 July 2024. Retrieved 3 August 2024.
- ^ Ahmed, Redwan; Ellis-Petersen, Hannah (26 July 2024). "Bangladesh student protests turn into 'mass movement against a dictator'". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 4 August 2024. Retrieved 3 August 2024.
- ^ Charlie Campbell (2 November 2023). "Sheikh Hasina and the Future of Democracy in Bangladesh". TIME. Archived from the original on 4 January 2024. Retrieved 3 August 2024.
- ^ "It's now one point". Manab Zamin. Archived from the original on 3 August 2024. Retrieved 3 August 2024.
- ^ "One Point Demand' announced from Central Shaheed Minar". Bonik Barta. Archived from the original on 3 August 2024. Retrieved 3 August 2024.
- ^ "PM resigned, interim govt to be formed: Army chief". The Daily Star. 5 August 2024. Archived from the original on 5 August 2024. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
- ^ "Bangladesh PM Sheikh Hasina resigns and flees country as protesters storm palace". BBC News. Archived from the original on 5 August 2024. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
- ^ "Meet Army Chief Waker-uz-Zaman who just took over after Sheikh Hasina's flight". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 5 August 2024. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
- ^ "Who will run Bangladesh's interim govt? I'm taking full responsibility, says army chief". Firstpost. 5 August 2024. Archived from the original on 5 August 2024. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
- ^ "Meet Muhammad Yunus, Nobel prize winner, who can become new leader of Bangladesh after..." DNA. Archived from the original on 5 August 2024. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
- ^ "Bangladesh protesters want Nobel laureate Muhammad Yunus to lead government". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 6 August 2024. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "Bangladeshi PM Sheikh Hasina resigns as widening unrest sees protesters storm her official residence". Associated Press. 5 August 2024. Archived from the original on 5 August 2024. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
Sources
[edit]- CIA World Factbook (July 2005). Bangladesh
- US Department of State (August 2005). "Background Note: Bangladesh"
- Ahmed, Helal Uddin (2012). "History". In Islam, Sirajul; Jamal, Ahmed A. (eds.). Banglapedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Second ed.). Asiatic Society of Bangladesh.
- Library of Congress (1988). A Country Study: Bangladesh
- "Declaration of Independence of Bangladesh Original Speech by Ziaur Rahman". scribd.com. Retrieved 25 May 2014.
Further reading
[edit]- Ali, S. Mahmud. Understanding Bangladesh. London: C. Hurst, 2010.
- Chatterji, Joya. Bengal Divided: Hindu Communalism and Partition, 1932—1947. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press 2002
- Guhaṭhākuratā, Meghanā., and Willem van Schendel. The Bangladesh Reader : History, Culture, Politics. Durham ;: Duke University Press, 2013.
- Hussain, Aklam. History of Bangladesh, 1704–1971 (Vol. 1. Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, 1997).
- Ikram, S. M. "Makers of Pakistan and Modern Muslim India", Lahore, 1970
- Islam, Sirajul. "History of Bangladesh 1701-1971", Dhaka 1992
- Khan, Muhammad Mojlum. Muslim Heritage of Bengal : the Lives, Thoughts and Achievements of Great Muslim Scholars, Writers and Reformers of Bangladesh and West Bengal. Leicestershire: Kube Publishing, 2013.
- Khan, Muin-ud-din Ahmad. Muslim Struggle for Freedom Bengal from Plassey to Pakistan, A.D. 1757-1947, Dacca 1960
- Muhith, A. M. A. Bangladesh : Emergence of a Nation. 2nd rev. ed. Dhaka, Bangladesh: University Press, 1992.
- Raghavan, Srinath. 1971: A Global History of the Creation of Bangladesh (Harvard University Press; 2014) 258 pages; scholarly history with worldwide perspective.
- Rahman, Mahmudur. The Political History of Muslim Bengal : An Unfinished Battle of Faith. Newcastle-upon-Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publisher, 2018.
- Rahman, Syedur, and Craig. Baxter. Historical Dictionary of Bangladesh. 4th ed. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press, 2010.
- Rashid, Harun-or-. "The Foreshadowing of Bangladesh: Bengal Muslim League and Muslim Politics, 1906–1947", Dhaka 1987
- Rashid, Harun-or-. "Inside Bengal Politics 1936–1947: Unpublished Correspondence of Partition Leaders", Dhaka 2003
- Sisson, Richard, and Leo E. Rose. War and Secession : Pakistan, India, and the Creation of Bangladesh. Berkeley, Calif. ;: University of California Press, 1990.
- D. K. Chakrabarti, 1992 Ancient Bangladesh: A Study of the Archaeological Sources (1992) Delhi: Oxford University Press
External links
[edit]- Banglapedia
- Rulers.org — Bangladesh List of rulers for Bangladesh



