Portal:Suriname
The Suriname portal
Suriname (/ˈsʊərɪnæm, -nɑːm/ ⓘ SOOR-in-A(H)M, Dutch: [syːriˈnaːmə] ⓘ, Sranan Tongo: [sraˈnãŋ]), officially the Republic of Suriname (Dutch: Republiek Suriname [reːpyˈblik syːriˈnaːmə]), is a country in northern South America, sometimes considered part of the Caribbean and the West Indies. It is a developing country with a medium level of human development; its economy is heavily dependent on its abundant natural resources, namely bauxite, gold, petroleum, and agricultural products. Suriname is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM), the United Nations, and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. Situated slightly north of the equator, over 90% of its territory is covered by rainforests, the highest proportion of forest cover in the world. Suriname is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, and Brazil to the south. It is the smallest country in South America by both population and territory, with around 612,985 inhabitants in an area of approximately 163,820 square kilometers (63,251 square miles).0 The capital and largest city is Paramaribo, which is home to roughly half the population. Suriname was inhabited as early as the fourth millennium BC by various indigenous peoples, including the Arawaks, Caribs, and Wayana. Europeans arrived and contested the area in the 16th century, with the Dutch controlling much of the country's current territory by the late 17th century. Under Dutch rule, Suriname was a lucrative plantation colony focused mostly on sugar; its economy was driven by African slave labour until the abolition of slavery in 1863, after which indentured servants were recruited mostly from British India and the Dutch East Indies. In 1954, Suriname became a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. On 25 November 1975, it became independent following negotiations with the Dutch government. Suriname continues to maintain close diplomatic, economic, and cultural ties with the Netherlands. Suriname's culture and society strongly reflect the legacy of Dutch colonial rule. It is the only sovereign nation outside Europe where Dutch is the official and prevailing language of government, business, media, and education; an estimated 60% of the population speaks Dutch as a native language. Sranan Tongo, an English-based creole language, is a widely used lingua franca. Most Surinamese are descendants of slaves and indentured labourers brought from Africa and Asia by the Dutch. Suriname is highly diverse, with no ethnic group forming a majority; proportionally, its Muslim and Hindu populations are some of the largest in the Americas. Most people live along the northern coast, centered around Paramaribo, making Suriname one of the least densely populated countries on Earth. (Full article...) Selected article -Suriname sent a delegation of four people to compete at the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing, China: two athletes (Jurgen Themen and Kirsten Nieuwendam and two swimmers (Gordon Touw Ngie Tjouw and Chinyere Pigot) who participated in four distinct events. The appearance of Suriname at Beijing marked its tenth Olympic appearance, which included every Olympic games since the 1968 Summer Olympics in Mexico City and excluded the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow. Its four athletes did not advance past the first round in each of their events. The Surinamese flag bearer in Beijing was not an athlete, but Anthony Nesty, the only medalist in Surinamese history (as of the Beijing Olympics) and the nation's Olympic swimming coach. (Full article...) General imagesThe following are images from various Suriname-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected biography -Elisabeth Samson (c. 1715 – 21 April 1771) was an Afro-Surinamese coffee plantation owner. She was born in about 1715 in Paramaribo to a freed slave, known as Mariana. All of her other siblings had been born as slaves and were emancipated by her half-brother Charlo Jansz. Raised in the home of her half-sister Maria Jansz, Samson was taught to read and write by her brothers-in law who also trained her in business. She began acquiring property at the age of 19, but was banished from the colony in 1736 after being convicted of slander. Her appeal, heard by the Dutch Parliament, was successful and she returned to Suriname in 1739. After acquiring slaves and two small coffee plantations, Samson entered a relationship with Carl Otto Creutz. Creutz was a soldier who was deeded property in 1749 by the governor for his service in making peace with local maroons. Focused on his military career and colonial politics, he turned his plantation, Clevia, over to Samson's management. She brought her own slaves to work on his plantation and within two years, the couple drew up a document confirming their joint ownership of Clevia, as well as of a cattle ranch and two townhomes in the city of Paramaribo. When he died in 1762, his half-ownership and other properties passed jointly to Samson and his brothers but she bought out their interests within two years. Samson continued to acquire properties with various family members, including her sister Nanette, with whom she established a successful export business, which traded using her own ship. (Full article...) Selected picture Sea Captains Carousing in Surinam
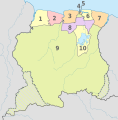
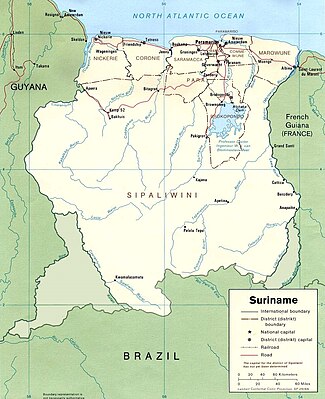
by John Greenwood MapTopics
CategoriesRelated portalsThings to do
WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
SourcesDiscover Wikipedia using portals
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||