Portal:North America
The North America Portal
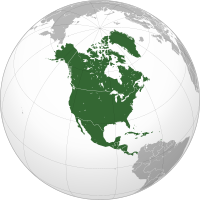
North America is a continent in the Northern and Western Hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes the Bahamas, Bermuda, Canada, the Caribbean, Central America, Clipperton Island, Greenland, Mexico, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the Turks and Caicos Islands, and the United States.
North America covers an area of about 24,709,000 square kilometres (9,540,000 square miles), representing approximately 16.5% of the Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. As of 2021[update], North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In human geography, the terms "North America" and "North American" can refer to Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Greenland or, alternatively, Canada, Greenland and the US (Mexico being classified as part of Latin America) or simply Canada and the US (Greenland being classified as either Arctic or European (due to its political status as a part of Denmark) and Mexico classified as Latin American).
It is unknown with certainty how and when first human populations first reached North America. People were known to live in the Americas at least 20,000 years ago, but various evidence points to possibly earlier dates. The Paleo-Indian period in North America followed the Last Glacial Period, and lasted until about 10,000 years ago when the Archaic period began. The classic stage followed the Archaic period, and lasted from approximately the 6th to 13th centuries. Beginning in 1000 AD, the Norse were the first Europeans to begin exploring and ultimately colonizing areas of North America.
In 1492, the exploratory voyages of Christopher Columbus led to a transatlantic exchange, including migrations of European settlers during the Age of Discovery and the early modern period. Present-day cultural and ethnic patterns reflect interactions between European colonists, indigenous peoples, enslaved Africans, immigrants from Europe, Asia, and descendants of these respective groups. (Full article...)
The Canada jay (Perisoreus canadensis), also known as the grey jay, gray jay, camp robber, or whisky jack, is a passerine bird of the family Corvidae. It is found in boreal forests of North America north to the tree line, and in the Rocky Mountains subalpine zone south to New Mexico and Arizona. A fairly large songbird, the Canada jay has pale grey underparts, darker grey upperparts, and a grey-white head with a darker grey nape. It is one of three members of the genus Perisoreus, a genus more closely related to the magpie genus Cyanopica than to other birds known as jays. The Canada jay itself has nine recognized subspecies.
Canada jays live year-round on permanent territories in coniferous forests, surviving in winter months on food cached throughout their territory in warmer periods. The birds form monogamous mating pairs, with pairs accompanied on their territories by a third juvenile from the previous season. Canada jays adapt to human activity in their territories and are known to approach humans for food, inspiring a list of colloquial names including "lumberjack", "camp robber", and "venison-hawk". The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) considers the Canada jay a least-concern species, but populations in southern ranges may be affected adversely by global warming. (Full article...)

Ursula Martius Franklin CC OOnt FRSC (16 September 1921 – 22 July 2016) was a Canadian metallurgist, activist, research physicist, author, and educator who taught at the University of Toronto for more than 40 years. Franklin is best known for her writings on the political and social effects of technology. She was the author of The Real World of Technology, which is based on her 1989 Massey Lectures; The Ursula Franklin Reader: Pacifism as a Map, a collection of her papers, interviews, and talks; and Ursula Franklin Speaks: Thoughts and Afterthoughts, containing 22 of her speeches and five interviews between 1986 and 2012. Franklin was a practising Quaker and actively worked on behalf of pacifist and feminist causes. She wrote and spoke extensively about the futility of war and the connection between peace and social justice. Franklin received numerous honours and awards, including the Governor General's Award in Commemoration of the Persons Case for promoting the equality of girls and women in Canada and the Pearson Medal of Peace for her work in advancing human rights. In 2012, she was inducted into the Canadian Science and Engineering Hall of Fame. A Toronto high school, Ursula Franklin Academy, as well as Ursula Franklin Street on the University of Toronto campus, have been named in her honor.
For Franklin, technology was much more than machines, gadgets or electronic transmitters. It was a comprehensive system that includes methods, procedures, organization, "and most of all, a mindset". She distinguished between holistic technologies used by craft workers or artisans and prescriptive ones associated with a division of labour in large-scale production. Holistic technologies allow artisans to control their own work from start to finish. Prescriptive technologies organize work as a sequence of steps requiring supervision by bosses or managers. Franklin argued that the dominance of prescriptive technologies in modern society discourages critical thinking and promotes "a culture of compliance". (Full article...)
Hurricane Greta, later Hurricane Olivia, was one of fourteen named Atlantic hurricanes to cross over Central America into the eastern Pacific while remaining a tropical cyclone. The seventh named storm of the 1978 Atlantic hurricane season, Greta formed from a tropical wave just northwest of Trinidad on September 13, and despite being in a climatologically unfavorable area, gradually intensified while moving west-northwestward. On September 16, it became a hurricane south of Jamaica. Two days later, the well-defined eye approached northeastern Honduras but veered to the northwest. After reaching peak winds of 130 mph (210 km/h) that day, Greta weakened while paralleling the northern Honduras coast just offshore. On September 19, it made landfall on Belize near Dangriga and quickly weakened into a tropical depression while crossing Guatemala and southeastern Mexico. After entering the eastern Pacific, the system re-intensified into a hurricane and was renamed Olivia, the eighteenth named storm of the 1978 Pacific hurricane season which weakened before landfall and dissipated over Chiapas on September 23.
Taking a similar path to Hurricane Fifi four years prior, Greta threatened to reproduce the devastating effects of the catastrophic storm; however, damage and loss of life was significantly less than feared. In Honduras, about 1,200 homes were damaged, about half of which in towns along the coastline. The storm damaged about 75% of the houses on Roatán along the offshore Bay Islands, and there was one death in the country. In the Belize Barrier Reef, Greta downed trees and produced high waves, while on the mainland, there was minimal flooding despite a high storm surge. In Dangriga where it made landfall, the hurricane damaged or destroyed 125 houses and the primary hospital. In Belize City, a tornado flipped over a truck and damaged four houses. Damage in Belize was estimated at $25 million (1978 USD), and there were four deaths. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ...that in 1869 the Spanish colonial authorities banned Baseball in Cuba because Cubans began to prefer baseball to viewing bullfights, the Spaniards' national sport?
- ... that tequila was first produced in the 16th century?
- ...that Navassa Island off the west coast of Haiti is claimed by the United States as an unorganized unincorporated territory?
- ... that the Valley of Mexico has been one of the most heavily populated places on the planet for almost two millennia?
- ... that the book The Complex: How the Military Invades Our Everyday Lives explores U.S. military expenditures on items including Southern catfish restaurants and Dunkin' Donuts?
Selected panorama

Topics
Categories
List articles
Related portals
Northern America
Central America
Caribbean
WikiProjects
 North America
North America-
 Canada
Canada -
 Greenland
Greenland -
 Mexico
Mexico -
 Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon -
 United States
United States  Central America
Central America-
 Belize
Belize -
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica -
 El Salvador
El Salvador -
 Guatemala
Guatemala -
 Honduras
Honduras -
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua -
 Panama
Panama  Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica Caribbean
Caribbean-
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda -
 Bahamas
Bahamas -
 Barbados
Barbados -
 Bermuda
Bermuda -
 Cuba
Cuba -
 Dominica
Dominica -
 Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic -
 Grenada
Grenada -
 Haiti
Haiti -
 Jamaica
Jamaica -
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico -
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis -
 Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia -
 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines -
 Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



























