Portal:Physics
The Physics Portal

Physics is the scientific study of matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. A scientist who specializes in the field of physics is called a physicist.
Physics is one of the oldest academic disciplines. Over much of the past two millennia, physics, chemistry, biology, and certain branches of mathematics were a part of natural philosophy, but during the Scientific Revolution in the 17th century, these natural sciences branched into separate research endeavors. Physics intersects with many interdisciplinary areas of research, such as biophysics and quantum chemistry, and the boundaries of physics are not rigidly defined. New ideas in physics often explain the fundamental mechanisms studied by other sciences and suggest new avenues of research in these and other academic disciplines such as mathematics and philosophy.
Advances in physics often enable new technologies. For example, advances in the understanding of electromagnetism, solid-state physics, and nuclear physics led directly to the development of technologies that have transformed modern society, such as television, computers, domestic appliances, and nuclear weapons; advances in thermodynamics led to the development of industrialization; and advances in mechanics inspired the development of calculus. (Full article...)

Jürgen Ehlers (German: [ˈjʏʁɡn̩ ˈʔeːlɐs]; 29 December 1929 – 20 May 2008) was a German physicist who contributed to the understanding of Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity. From graduate and postgraduate work in Pascual Jordan's relativity research group at Hamburg University, he held various posts as a lecturer and, later, as a professor before joining the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics in Munich as a director. In 1995, he became the founding director of the newly created Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics in Potsdam, Germany.
Ehlers' research focused on the foundations of general relativity as well as on the theory's applications to astrophysics. He formulated a suitable classification of exact solutions to Einstein's field equations and proved the Ehlers–Geren–Sachs theorem that justifies the application of simple, general-relativistic model universes to modern cosmology. He created a spacetime-oriented description of gravitational lensing and clarified the relationship between models formulated within the framework of general relativity and those of Newtonian gravity. In addition, Ehlers had a keen interest in both the history and philosophy of physics and was an ardent populariser of science. (Full article...)
Did you know -

- ...that on November 2009, CERN's Large Hadron Collider became the world's highest energy particle accelerator?
- ...that 2005 was endorsed by the United Nations as the World Year of Physics?
Selected image -
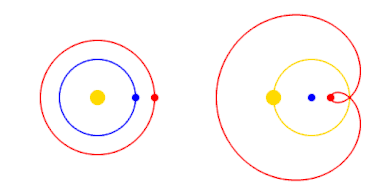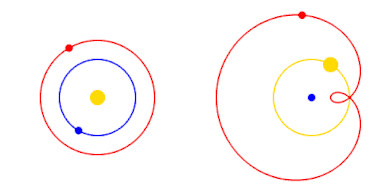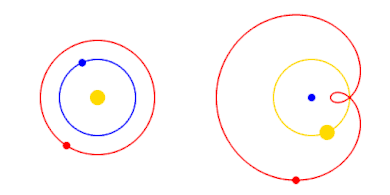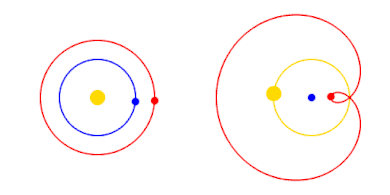
For simplicity, Mars' period of revolution is depicted as 2 years instead of 1.88, and orbits are depicted as perfectly circular or epitrochoid.
The Copernican Revolution was the paradigm shift from the Ptolemaic model of the heavens, which described the cosmos as having Earth stationary at the center of the universe, to the heliocentric model with the Sun at the center of the Solar System. This revolution consisted of two phases; the first being extremely mathematical in nature and the second phase starting in 1610 with the publication of a pamphlet by Galileo. Beginning with the 1543 publication of Nicolaus Copernicus’s De revolutionibus orbium coelestium, contributions to the “revolution” continued until finally ending with Isaac Newton’s work over a century later. (Full article...)
Related portals
January anniversaries
1 January
- 1894 - Satyendra Nath Bose's birthday.
- 1801 - Giuseppe Piazzi is the first to notice the dwarf planet Ceres. However, very soon astronomers lose sight of its orbital path. After some months, Giuseppe Piazzi finally calculates its correct position on December 31.
- 1985 - Ernie Wise, a comedian, places the first mobile phone call in the UK.
2 January
- 2 January 1822 - Rudolf Clausius was born.
8 January
- 8 January 1942 - Stephen Hawking was born, on the same day that Galileo Galilei died in 1642.
15 January
- 15 January 1908 - Edward Teller was born.
General images
Categories

Fundamentals: Concepts in physics | Constants | Physical quantities | Units of measure | Mass | Length | Time | Space | Energy | Matter | Force | Gravity | Electricity | Magnetism | Waves
Basic physics: Mechanics | Electromagnetism | Statistical mechanics | Thermodynamics | Quantum mechanics | Theory of relativity | Optics | Acoustics
Specific fields: Acoustics | Astrophysics | Atomic physics | Molecular physics | Optical physics | Computational physics | Condensed matter physics | Nuclear physics | Particle physics | Plasma physics
Tools: Detectors | Interferometry | Measurement | Radiometry | Spectroscopy | Transducers
Background: Physicists | History of physics | Philosophy of physics | Physics education | Physics journals | Physics organizations
Other: Physics in fiction | Physics lists | Physics software | Physics stubs
Physics topics
Classical physics traditionally includes the fields of mechanics, optics, electricity, magnetism, acoustics and thermodynamics. The term Modern physics is normally used for fields which rely heavily on quantum theory, including quantum mechanics, atomic physics, nuclear physics, particle physics and condensed matter physics. General and special relativity are usually considered to be part of modern physics as well.
More recognized content
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Sources
Portals on Wikipedia