Portal:Spain
Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
The Spain Portal (Bienvenido al portal español)

Spain, officially the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southwestern Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and largest city is Madrid, and other major urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, Zaragoza, Málaga, Murcia and Palma de Mallorca.
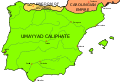
In early antiquity, the Iberian Peninsula was inhabited by Celts, Iberians, and other pre-Roman peoples. With the Roman conquest of the Iberian peninsula, the province of Hispania was established. Following the Christianization of Hispania, the fall of the Western Roman Empire ushered in the inward migration of tribes from Central Europe, including the Visigoths, who formed the Visigothic Kingdom centred on Toledo. In the early eighth century, most of the peninsula was conquered by the Umayyad Caliphate, and during early Islamic rule, Al-Andalus became a dominant peninsular power centred on Córdoba. Several Christian kingdoms emerged in Northern Iberia, chief among them Asturias, León, Castile, Aragon, Navarre, and Portugal; made an intermittent southward military expansion and repopulation, known as the Reconquista, repelling Islamic rule in Iberia, which culminated with the Christian seizure of the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada in 1492. The dynastic union of the Crown of Castile and the Crown of Aragon in 1479 under the Catholic Monarchs is often considered the de facto unification of Spain as a nation-state. (Full article...)
 Featured article – show another
Featured article – show another
-
Image 1

A carillonneur plays the 56-bell carillon of the Plummer Building, Rochester, Minnesota, US
A carillon is a pitched percussion instrument that is played with a keyboard and consists of at least 23 bells. The bells are cast in bronze, hung in fixed suspension, and tuned in chromatic order so that they can be sounded harmoniously together. They are struck with clappers connected to a keyboard of wooden batons played with the hands and pedals played with the feet. Often housed in bell towers, carillons are usually owned by churches, universities, or municipalities. They can include an automatic system through which the time is announced and simple tunes are played throughout the day. (Full article...) -
Image 2Nasr (1 November 1287 – 16 November 1322), full name Abu al-Juyush Nasr ibn Muhammad (Arabic: أبو الجيوش نصر بن محمد), was the fourth Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada from 14 March 1309 until his abdication on 8 February 1314. He was the son of Muhammad II al-Faqih and Shams al-Duha. He ascended the throne after his brother Muhammad III was dethroned in a palace revolution. At the time of his accession, Granada faced a three-front war against Castile, Aragon and the Marinid Sultanate, triggered by his predecessor's foreign policy. He made peace with the Marinids in September 1309, ceding to them the African port of Ceuta, which had already been captured, as well as Algeciras and Ronda in Europe. Granada lost Gibraltar to a Castilian siege in September, but successfully defended Algeciras until it was given to the Marinids, who continued its defense until the siege was abandoned in January 1310. James II of Aragon sued for peace after Granadan defenders defeated the Aragonese siege of Almería in December 1309, withdrawing his forces and leaving the Emirate's territories by January. In the ensuing treaty, Nasr agreed to pay tributes and indemnities to Ferdinand IV of Castile and yield some border towns in exchange for seven years of peace. (Full article...)
-
Image 3The siege of Nice by a Franco-Ottoman fleet in 1543 (drawing by Toselli, after an engraving by Aeneas Vico)
The Italian War of 1542–1546 was a conflict late in the Italian Wars, pitting Francis I of France and Suleiman I of the Ottoman Empire against the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and Henry VIII of England. The course of the war saw extensive fighting in Italy, France, and the Low Countries, as well as attempted invasions of Spain and England. The conflict was inconclusive and ruinously expensive for the major participants. (Full article...) -
Image 4The battle of New Carthage took place in early 209 BC when a Roman army under Publius Cornelius Scipio successfully assaulted New Carthage, the capital of Carthaginian Iberia, which was defended by a garrison under Mago. The battle was part of the Second Punic War. (Full article...)
-
Image 5

The Third of May 1808 in Madrid (also known as El tres de mayo de 1808 en Madrid or Los fusilamientos de la montaña del Príncipe Pío, or Los fusilamientos del tres de mayo. Commonly known as The Third of May 1808.) is a painting completed in 1814 by the Spanish painter Francisco Goya, now in the Museo del Prado, Madrid. In the work, Goya sought to commemorate Spanish resistance to Napoleon's armies during the occupation of 1808 in the Peninsular War. Along with its companion piece of the same size, The Second of May 1808 (or The Charge of the Mamelukes), it was commissioned by the provisional government of Spain at Goya's own suggestion shortly after the ousting of the French occupation and the restoration of King Ferdinand VII. (Full article...) -
Image 6

Rokeby Venus, c. 1647–1651. 122 cm × 177 cm (48 in × 70 in). National Gallery, London.
The Rokeby Venus (/ˈroʊkbi/ ROHK-bee; also known as The Toilet of Venus, Venus at her Mirror, Venus and Cupid; Whose original title was "The Mirror's Venus" Spanish: La Venus del espejo) is a painting by Diego Velázquez, the leading artist of the Spanish Golden Age. Completed between 1647 and 1651, and probably painted during the artist's visit to Italy, the work depicts the goddess Venus in a sensual pose, lying on a bed with her back facing the viewer, and looking into a mirror held by the Roman god of physical love, her son Cupid. The painting is in the National Gallery, London. (Full article...) -
Image 7Abu'l-Walid Ismail I ibn Faraj (Arabic: أبو الوليد إسماعيل الأول بن فرج, 3 March 1279 – 8 July 1325) was the fifth Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada on the Iberian Peninsula from 1314 to 1325. A grandson of Muhammad II on the side of his mother Fatima, he was the first of the lineage of sultans now known as the al-dawla al-isma'iliyya al-nasriyya (the Nasrid dynasty of Ismail). Historians characterise him as an effective ruler who improved the emirate's position with military victories during his reign. (Full article...)
-
Image 8
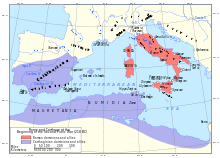
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war. (Full article...) -
Image 9

North View of Gibraltar from Spanish Lines by John Mace (1782)
The history of Gibraltar, a small peninsula on the southern Iberian coast near the entrance of the Mediterranean Sea, spans over 2,900 years. The peninsula has evolved from a place of reverence in ancient times into "one of the most densely fortified and fought-over places in Europe", as one historian has put it. Gibraltar's location has given it an outsized significance in the history of Europe and its fortified town, established in the Middle Ages, has hosted garrisons that sustained numerous sieges and battles over the centuries. (Full article...) -
Image 10Spanish Leopard 2E in Zaragoza, June 2008
The Leopardo 2E or Leopard 2A6E (E stands for España (Spanish for 'Spain')) is a variant of the German Leopard 2 main battle tank (specifically the Leopard 2A6 variant), tailored to the requirements of the Spanish army, which acquired it as part of an armament modernization program named Programa Coraza, or Program Cuirass. The acquisition program for the Leopard 2E began in 1994, five years after the cancellation of the Lince tank program that culminated in an agreement to transfer 108 Leopard 2A4s to the Spanish army in 1998 and started the local production of the Leopard 2E in December 2002. Despite postponement of production owing to the 2003 merger between Santa Bárbara Sistemas and General Dynamics, and continued manufacturing issues between 2006 and 2007, 219 Leopard 2Es have been delivered to the Spanish army. (Full article...) -
Image 11Conquistador Pedro de Alvarado led the initial efforts to conquer Guatemala.
In a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonisers gradually incorporated the territory that became the modern country of Guatemala into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. Before the conquest, this territory contained a number of competing Mesoamerican kingdoms, the majority of which were Maya. Many conquistadors viewed the Maya as "infidels" who needed to be forcefully converted and pacified, disregarding the achievements of their civilization. The first contact between the Maya and European explorers came in the early 16th century when a Spanish ship sailing from Panama to Santo Domingo was wrecked on the east coast of the Yucatán Peninsula in 1511. Several Spanish expeditions followed in 1517 and 1519, making landfall on various parts of the Yucatán coast. The Spanish conquest of the Maya was a prolonged affair; the Maya kingdoms resisted integration into the Spanish Empire with such tenacity that their defeat took almost two centuries. (Full article...) -
Image 12
The AMX-30E (E stands for España, Spanish for Spain) is a Spanish main battle tank based on France's AMX-30. Although originally the Spanish government sought to procure the German Leopard 1, the AMX-30 was ultimately awarded the contract due to its lower price and the ability to manufacture it in Spain. 280 units were manufactured by Santa Bárbara Sistemas for the Spanish Army, between 1974 and 1983. (Full article...) -
Image 13

Witches' Sabbath, 1821–1823. Oil on plaster wall, transferred to canvas; 140.5 × 435.7 cm (56 × 172 in). Museo del Prado, Madrid
Witches' Sabbath or The Great He-Goat (Spanish: Aquelarre or El gran cabrón) are names given to an oil mural by the Spanish artist Francisco Goya, completed sometime between 1821 and 1823. It depicts a Witches' Sabbath. It evokes themes of violence, intimidation, ageing and death; Satan hulks in the form of a goat in moonlit silhouette over a coven of terrified old witches. Goya was then around 75 years old, living alone and suffering from acute mental and physical distress. (Full article...) -
Image 14View of Badajoz, across the Guadiana river from the foothills of the San Cristóbal heights, by Eugène-Ferdinand Buttura
The Battle of the Gebora took place during the Peninsular War between Spanish and French armies on 19 February 1811, northwest of Badajoz, Spain. An outnumbered French force routed and nearly destroyed the Spanish Army of Extremadura. (Full article...) -
Image 15Muhammad III (Arabic: محمد الثالث; 15 August 1257 – 21 January 1314) was the ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula from 8 April 1302 until 14 March 1309, and a member of the Nasrid dynasty. He ascended the Granadan throne after the death of his father Muhammad II, which according to rumours, was caused by Muhammad III poisoning him. He had the reputation of being both cultured and cruel. Later in his life, he became visually impaired—which caused him to be absent from many government activities and to rely on high officials, especially the powerful Vizier Ibn al-Hakim al-Rundi. (Full article...)
-
Image 16

Joseph Anton Lopez SJ (born José Antonio López; October 4, 1779 – October 5, 1841) was a Mexican Catholic priest and Jesuit. Born in Michoacán, he studied canon law at the Colegio de San Nicolás and the Royal and Pontifical University of Mexico. He became acquainted with the future Empress consort Ana María Huarte and was made chaplain to the future imperial family. He was later put in charge of the education of all the princes in Mexico. Lopez was a close ally of Emperor Agustín de Iturbide, residing in Madrid for four years as his attorney and political informant, and accompanying him during his exile to Italy and England. (Full article...) -
Image 17
The Battle of Halmyros, known by earlier scholars as the Battle of the Cephissus or Battle of Orchomenos, was fought on 15 March 1311, between the forces of the Frankish Duchy of Athens and its vassals under Walter of Brienne against the mercenaries of the Catalan Company, resulting in a decisive victory for the mercenaries. (Full article...) -
Image 18
Verdeja was the name of a series of light tanks developed in Spain between 1938 and 1954 in an attempt to replace German Panzer I and Soviet T-26 tanks in Spanish service. (Full article...) -
Image 19

Hieronymus Bosch, The Garden of Earthly Delights, oil on oak panels, 205.5 cm × 384.9 cm (81 in × 152 in), Museo del Prado, Madrid
The Garden of Earthly Delights (Dutch: De tuin der lusten, lit. 'The garden of lusts') is the modern title given to a triptych oil painting on oak panel painted by the Early Netherlandish master Hieronymus Bosch, between 1490 and 1510, when Bosch was between 40 and 60 years old. Bosch's religious beliefs are unknown, but interpretations of the work typically assume it is a warning against the perils of temptation. The outer panels place the work on the Third Day of Creation. The intricacy of its symbolism, particularly that of the central panel, has led to a wide range of scholarly interpretations over the centuries. (Full article...) -
Image 20

Plate 34: Por una navaja (For a clasp knife). A garroted priest grasps a crucifix in his hands. Pinned to his chest is a description of the crime for which he was killed—possession of a knife.
The Disasters of War (Spanish: Los desastres de la guerra) is a series of 82 prints created between 1810 and 1820 by the Spanish painter and printmaker Francisco Goya (1746–1828). Although Goya did not make known his intention when creating the plates, art historians view them as a visual protest against the violence of the 1808 Dos de Mayo Uprising, the subsequent cruel war that ended in Spanish victory in the Peninsular War of 1808–1814 and the setbacks to the liberal cause following the restoration of the Bourbon monarchy in 1814. During the conflicts between Napoleon's French Empire and Spain, Goya retained his position as first court painter to the Spanish crown and continued to produce portraits of the Spanish and French rulers. Although deeply affected by the war, he kept private his thoughts on the art he produced in response to the conflict and its aftermath. (Full article...) -
Image 21

Boletus aereus, commonly known as the dark cep, bronze bolete, or queen bolete, is a highly prized and much sought-after edible mushroom in the family Boletaceae. The bolete is widely consumed in Spain (Basque Country and Navarre), France, Italy, Greece, and generally throughout the Mediterranean. Described in 1789 by French mycologist Pierre Bulliard, it is closely related to several other European boletes, including B. reticulatus, B. pinophilus, and the popular B. edulis. Some populations in North Africa have in the past been classified as a separate species, B. mamorensis, but have been shown to be phylogenetically conspecific to B. aereus and this taxon is now regarded as a synonym. (Full article...) -
Image 22
The Andalusian, also known as the Pure Spanish Horse or PRE (pura raza española), is a horse breed from the Iberian Peninsula, where its ancestors have lived for thousands of years. The Andalusian has been recognized as a distinct breed since the 15th century, and its conformation has changed very little over the centuries. Throughout its history, it has been known for its prowess as a war horse, and was prized by the nobility. The breed was used as a tool of diplomacy by the Spanish government, and kings across Europe rode and owned Spanish horses. During the 19th century, warfare, disease and crossbreeding reduced herd numbers dramatically, and despite some recovery in the late 19th century, the trend continued into the early 20th century. Exports of Andalusians from Spain were restricted until the 1960s, but the breed has since spread throughout the world, despite their low population. In 2010, there were more than 185,000 registered Andalusians worldwide. (Full article...) -
Image 23The Oran fatwa was a responsum fatwa, or an Islamic legal opinion, issued in 1502 to address the crisis that occurred when Muslims in the Crown of Castile, in present-day Spain, were forced to convert to Christianity in 1500–1502. It was authored by a maliki mufti Ahmad ibn Abi Jum'ah, an Algerian scholar of Islamic law of the Maliki school; the term "Oran fatwa" was applied by modern scholars, due to the word "Al-Wahrani" ("of Oran") that appears in the text as part of the author's name. (Full article...)
-
Image 24
The 2015 Vuelta a España was a three-week Grand Tour cycling race. The race was the 70th edition of the Vuelta a España and took place principally in Spain, although two stages took place partly or wholly in Andorra, and was the 22nd race in the 2015 UCI World Tour. The 3,358.1-kilometre (2,086.6 mi) race included 21 stages, beginning in Marbella on 22 August 2015 and finishing in Madrid on 13 September. It was won by Fabio Aru (Astana Pro Team), with Joaquim Rodríguez (Team Katusha) second and Rafał Majka (Tinkoff–Saxo) third. (Full article...) -
Image 25
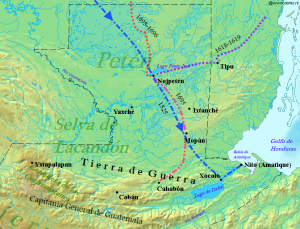
The Spanish conquest of Petén was the last stage of the conquest of Guatemala, a prolonged conflict during the Spanish colonisation of the Americas. A wide lowland plain covered with dense rainforest, Petén contains a central drainage basin with a series of lakes and areas of savannah. It is crossed by several ranges of low karstic hills and rises to the south as it nears the Guatemalan Highlands. The conquest of Petén, a region now incorporated into the modern republic of Guatemala, climaxed in 1697 with the capture of Nojpetén, the island capital of the Itza kingdom, by Martín de Ursúa y Arizmendi. With the defeat of the Itza, the last independent and unconquered native kingdom in the Americas fell to European colonisers. (Full article...)
Selected biography

Queen Sofía of Spain (Spanish: Su Majestad la Reina Sofía de España, Greek: Βασίλισσα Σοφία της Ισπανίας;) born Princess Sophia of Greece and Denmark on November 2, 1938; full name Sophía Margaríta Viktoría Frederíki), is the Queen Consort of King Juan Carlos I of Spain. Princess Sophia of Greece and Denmark was born in Athens, Greece on November 2, 1938, the eldest child of the King Paul I of the Hellenes (1901-1964) and his wife, Queen Frederika (1917-1981), a former princess of Hanover. Queen Sofia is a member of the Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg dynasty. Her brother is Constantine II of Greece and her sister Princess Irene of Greece and Denmark. However, since the restoration of democracy, the royal titles are not recognized in Greece, where the former royal family is held in low regard by most Greeks.
Princess Sophia spent her childhood in Egypt and South Africa during her family's exile from Greece during World War II. They returned to Greece in 1946. She finished her education at the prestigious Schloss Salem boarding school in Southern Germany, and then studied pediatrics, music, and archeology in Athens. On May 14, 1962 Princess Sophia of Greece and Denmark married Prince Juan Carlos of Spain, the future king, whom she met on a cruise of the Greek Islands in 1954. In doing so, she relinquished her rights to the throne of Greece and converted to Roman Catholicism from Greek Orthodoxy. Further, the Latin transliteration of her Greek name Σοφία was changed from Sophia to the Spanish variant Sofía, which nonetheless is pronounced
Selected picture
-
Image 2Photo credit: David IliffThe Queen Sofia Palace of the Arts (Valencian: Palau de les Arts Reina Sofía) is an opera house located in Valencia, Spain. The last to be completed of the City of Arts and Sciences complex, it was designed by architect Santiago Calatrava. The 14-story structure opened on 8 October 2005.
-
Image 3Photograph: Diego DelsoThe Assut de l'Or Bridge is a white single-pylon cable-stayed bridge in the City of Arts and Sciences, Valencia, Spain. Completed in 2008, it was designed by Valencian architect and civil engineer Santiago Calatrava as a variant of his cantilever spar cable-stayed bridge in Seville.
-
Image 4Photograph: Diego DelsoMoros is a municipality in the province of Zaragoza, Spain. Located in the Sistema Ibérico mountain range, the village lies on a hill, with the church and former town hall at the top, the residences in the middle, and the sheep pens at the bottom. The population of Moros has been steadily decreasing in recent decades, and was 478 in 2006.
-
Image 5

Windmills Credit: Lourdes Cardenal
Active windmills shown turning in La Mancha. The area is now famous for its windmills and scenic views. -
Image 6Painting credit: Federico de Madrazo y KuntzAmalia de Llano (April 29, 1822 – July 6, 1874) was a Spanish countess and writer. This 1853 oil-on-canvas portrait by Federico de Madrazo y Kuntz shows her seated in a fine armchair wearing sumptuous clothes, with her youth and beauty accentuated by the dark background, and is quite unlike a traditional Spanish portrait of the period.
-
Image 7
Cala Figuera Credit: BuzzWoof
The harbor entrance to Cala Figuera, a district of Mallorca in the Balearic Islands. The town is located approximately 60 kilometers north of Palma de Mallorca. The earliest records of the town date back to 1306, although houses were not built on the land until the early 19th century. -
Image 8Image: Royal Household of Spain; Restoration: Lise BroerA Grant of Arms by Philip II of Spain to Alonso de Mesa and Hernando de Mesa, signed 25 November 1566. In Spanish heraldry, coats of arms were granted based almost entirely on military service, which made it possible for commoners to join the ranks of the Spanish nobility. Also unique to Spain was that titles could be inherited through females and via illegitimacy.
-
Image 9
Aneto Peak Credit: BrugesFR
Aneto is a mountain located in Benasque municipality, Aragon, area of the Pyreenes. The mountain is the highest mountain in the Pyrenees, and Spain's third-highest mountain. -
Image 11

A light metro train Credit: FDV
A metro light train currently in operation with Madrid Metro. This train is pictured on line ML2 at Aravaca metro station. -
Image 12Photo credit: DiliffThe Torre Agbar is a landmark skyscraper and the third tallest building in Barcelona, Spain. It was designed by French architect Jean Nouvel, who stated that the shape of the Torre Agbar was inspired by the mountains of Montserrat that surround Barcelona, and by the shape of a geyser of water rising into the air. Its design combines a number of different architectural concepts, resulting in a striking structure built with reinforced concrete, covered with a facade of glass, and over 4,500 window openings cut out of the structural concrete.
-
Image 13Architecture credit: José Grases Riera; photographed by Carlos DelgadoThe Monument to Alfonso XII is located in Buen Retiro Park (El Retiro) in Madrid, Spain. Measuring 30 m (98 ft) high, 86 m (282 ft) long, and 58 m (190 ft) wide, it has at its center an equestrian statue of King Alfonso XII, cast in bronze by the Spanish sculptor Mariano Benlliure in 1904. The monument is situated on the eastern edge of an artificial lake near the center of the park and was inaugurated on 6 June 1922.
-
Image 14Coin design credit: Duchy of ParmaThe doubloon was a Spanish gold coin worth two escudos or 32 reales weighing 6.867 grams (0.221 troy ounces), introduced in 1537. It became the model for several other gold coins issued in Europe, including this 1626 two-doppie gold coin issued in Piacenza in northern Italy by the Duchy of Parma, depicting Odoardo Farnese, Duke of Parma, on the obverse. The coin is part of the National Numismatic Collection at the National Museum of American History.
-
Image 15Painting: Marià FortunyThe Spanish Wedding is an oil on panel painting by Marià Fortuny completed over a two-year period ending in 1870. It depicts the signing of a wedding contract in 18th century Spain and was influenced heavily by the works of Francisco Goya, whom the artist admired. It is currently exhibited at the National Art Museum of Catalonia.
-
Image 16Photograph: J.Ligero & I.BarriosA three-month old Spanish ibex (Capra pyrenaica) in Sierra de Gredos, Spain. These ibexes are strong mountain animals characterized by their large and flexible hooves and short legs.
The two sexes of adults form separate social groups; juveniles stay with the female groups from birth until the following birth season, when they leave. Yearling males then join male groups, while females eventually return to their mothers' groups and stay several years. -
Image 17

Seville Cathedral. Credit: Seville Tourism Bureau
The Cathedral of Seville, formally Catedral de Santa María de la Sede (Cathedral of Saint Mary of the See) was begun in 1402, with construction continuing into the 16th century. It is the largest of all Roman Catholic cathedrals (Saint Peter's Basilica not being a cathedral) and also the largest Medieval Gothic religious building, in terms of both area and volume. -
Image 18The Madrid Metro is a rapid transit system serving the Spanish capital, Madrid. It was inaugurated in 1919 by King Alfonso, with a single line which ran for 3.48 km (2.16 mi) between Puerta del Sol and Cuatro Caminos, with eight stops. The present system has 301 stations on 13 lines plus one branch line, totalling 294 km (183 mi).
-
Image 19An overturned tourer caravan which was damaged by the effects of Tropical Storm Delta (2005). Considerable other damage was caused to other areas of the Canary Islands during the storm.
-
Image 20Banknote: Bank of SpainThe Spanish peseta is a former currency of Spain and, alongside the French franc, a former de facto currency in Andorra. It was introduced in 1868, replacing the peso, at a time when Spain was considering joining the Latin Monetary Union. Spain joined the euro in 1999, and the peseta was replaced by euro notes and coins in 2002.
This picture shows a 1000 peseta banknote from 1957. The obverse depicts the Catholic Monarchs while the reverse shows the coat of arms of Spain. -
Image 21Photograph credit: Biblioteca Nacional de EspañaAna Santos Aramburo (born 1957) has been the director of the National Library of Spain since February 2013. Having received a degree in geography and history from the University of Zaragoza in Spain, she has spent much of her career working at the Complutense University of Madrid, first at the library of the Faculty of Economics and Business Sciences, and later serving as deputy director of the university library. Later she served as Director of the Historical Library Marquis of Valdecilla, General Director of Libraries and Archives of the City of Madrid, and Director of Cultural Action at the National Library. This photograph of Santos shows her at the headquarters of the National Library of Spain in Madrid.
-
Image 22Photo credit: David IliffThe Casa Milà, a 1912 work by Catalán architect Antoni Gaudi, in the Eixample district of Barcelona, Spain. Gaudí's fascination with trencadís-influenced decoration and curves (predating biomorphism by almost 20 years) can be seen here.
Did you know...
- ... that after fleeing the Spanish Civil War to Venezuela, Spanish anarchist Concha Liaño became a supporter of Hugo Chávez?
- ... that Spanish bishop Josep-Lluís Serrano Pentinat is expected to be a future head of state of Andorra?
- ... that Mariano R. Vázquez oversaw the integration of anarchists into the government during the Spanish Civil War?
- ... that the Kitāb al-ṭabīẖ, a medieval Andalusian cookbook, contains an early version of Jewish challah bread, which traveled with Jews expelled from Spain and likely influenced Ashkenazi cuisine?
- ... that after fleeing to Argentina as a Spanish Civil War refugee, Maria Muntañola Cvetković became one of Yugoslavia's first experts on microfungi?
- ... that the flag of La Guaira is based on the design of a banner from a 1797 conspiracy against Spanish rule in Venezuela?
 Good article – show another
Good article – show another
-
Image 1
Léon Joseph Marie Ignace Degrelle (French: [dəgʁɛl]; 15 June 1906 – 31 March 1994) was a Belgian Walloon politician and Nazi collaborator. He rose to prominence in Belgium in the 1930s as the leader of the Rexist Party (Rex). During the German occupation of Belgium during World War II, he enlisted in the German army and fought in the Walloon Legion on the Eastern Front. After the collapse of the Nazi regime, Degrelle escaped and went into exile in Francoist Spain, where he remained a prominent figure in neo-Nazi politics. (Full article...) -
Image 2Lempira stabbing a conquistador during the Spanish conquest, painting by Armando Lara
The Spanish conquest of Honduras was a 16th-century conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas in which the territory that now comprises the Republic of Honduras, one of the seven states of Central America, was incorporated into the Spanish Empire. In 1502, the territory was claimed for the king of Spain by Christopher Columbus on his fourth and final trip to the New World. The territory that now comprises Honduras was inhabited by a mix of indigenous peoples straddling a transitional cultural zone between Mesoamerica to the northwest, and the Intermediate Area to the southeast. Indigenous groups included Maya, Lenca, Pech, Miskitu, Mayangna (Sumu), Jicaque, Pipil and Chorotega. Two indigenous leaders are particularly notable for their resistance against the Spanish; the Maya leader Sicumba, and the Lenca ruler referred to as Lempira (a title meaning "Lord of the Mountain"). (Full article...) -
Image 3Prime Minister Felipe González (left) and Deputy Prime Minister Alfonso Guerra (right) in their seats during the debate on the motion of no confidence on 26 March 1987.
A motion of no confidence in the Spanish government of Felipe González was debated and voted in the Congress of Deputies between 26 and 30 March 1987. It was proposed by People's Alliance (AP) leader Antonio Hernández Mancha, motivated on the "deteriorating situation of the country" as a result of the social conflict sparked throughout the 1986–87 winter between the governing Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) and its erstwhile allied Workers' General Union (UGT), which had grown increasingly critical of González's economic policies. However, the motion's true motives were attributed to Mancha's need for public promotion as both AP and opposition leader after his recent election to the post, as well as to his party's perceived urge to vindicate its primacy within the centre-right political spectrum in Spain amid the internal crisis that had been beleaguering it in the previous months. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Luis Buñuel Portolés (Spanish: [ˈlwis βuˈɲwel poɾtoˈles]; 22 February 1900 – 29 July 1983) was a Spanish filmmaker who worked in Spain, Mexico and France. Buñuel is noted for his distinctive use of mise-en scene, distinctive sound editing, and original use of music in his films. Often Buñuel applies the techniques of mise-en-scène to combine multiple single scenes within a film directed by him to represent more encompassing aspects of the film when viewed as a whole. (Full article...) -
Image 5

José María Gil Tamayo (born 5 June 1957) is a Spanish prelate of the Roman Catholic Church. He has been serving as archbishop of Granada since his installation on 1 February 2023. He previously served as coadjutor archbishop of that archdiocese and as bishop of Ávila. (Full article...) -
Image 6Pikes Hotel, now known as Pikes Ibiza, is a luxury hotel in Ibiza, in the Balearic Islands of Spain. It is located in the countryside, 1.6 miles (2.6 km) to the northeast of the town of Sant Antoni de Portmany, and 10.2 miles (16.4 km) to the northwest of Ibiza Town. A 15th-century stone mansion which was a finca (farm estate), it was converted into a hotel in 1978 by British-born Australian Anthony Pike. (Full article...)
-
Image 7'Defeat of the Dutch States Army near Wesel, 1595'. By Simon Frisius and Frans Hogenberg.
The Battle of the Lippe was a cavalry action fought on 2 September 1595 on the banks of the Lippe river, in Germany, between a corps of Spanish cavalry led by Juan de Córdoba and a corps of Dutch cavalry, supported by English troops, led by Philip of Nassau. The Dutch stadtholder Maurice of Nassau, taking advantage of the fact that the bulk of the Spanish army was busied in operations in France, besieged the town of Groenlo in Gelderland, but the elderly governor of the citadel of Antwerp, Cristóbal de Mondragón, organized a relief army and forced Maurice to lift the siege. Mondragón next moved to Wesel, positioning his troops on the southern bank of the Lippe river to cover Rheinberg from a Dutch attack. Maurice aimed then, relying on his superior army, to entice Mondragón into a pitched battle, planning to use an ambush to draw the Spanish army into a trap. However, the plan was discovered by the Spanish commander, who organized a counter-ambush. (Full article...) -
Image 8Villa with Spain at the 2013 FIFA Confederations Cup
David Villa Sánchez (Spanish pronunciation: [daˈβið ˈbiʎa santʃeθ]; born 3 December 1981) is a Spanish former professional footballer who played as a striker. Regarded as one of the best strikers of his generation, Villa is the all-time top goalscorer of the Spain national team. He is currently the vice-president of Spanish Tercera Federación club CF Benidorm. (Full article...) -
Image 9
The Revolt of the Comuneros (Spanish: Guerra de las Comunidades de Castilla, "War of the Communities of Castile") was an uprising by citizens of Castile against the rule of Charles I and his administration between 1520 and 1521. At its height, the rebels controlled the heart of Castile, ruling the cities of Valladolid, Tordesillas, and Toledo. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Illustration of the dreadnought España in 1912
In the latter half of the 19th century, the Spanish Navy had built a series of ironclad warships that culminated in the barbette ship Pelayo in the 1880s. Following the destruction of much of the Spanish fleet in the Spanish–American War in 1898, Spain slowly began to rebuild its navy. In the early 20th century, the Spanish Navy built three battleships and planned several more; the three ships that were completed were the vessels of the España class. These ships were the smallest dreadnought-type battleships ever built. A further three ships of the Reina Victoria Eugenia class were authorized by the Navy Law of 1913, but the outbreak of World War I prevented these ships from being built, as Spain was heavily dependent on Great Britain for material and technical expertise. The three completed battleships all served in the Rif War in North Africa, where the lead ship, España, ran aground and was wrecked. (Full article...) -
Image 11The second season of The House of Flowers, a Mexican black comedy-drama television series about the privileged de la Mora family and their titular floristry shop, was released to Netflix in its entirety on October 18, 2019. The character Paulina de la Mora, played by Cecilia Suárez, becomes the main character. The season picks up a year after the end of the first season, and starts with Paulina learning of a challenge to her now-deceased mother Virginia's will and moving back to Mexico from Madrid. Paulina becomes overwhelmed trying to helm her family with different adversities along the way, while being mainly driven by revenge and unhappiness. The season had four directors, with the majority of episodes directed by show creator Manolo Caro, and written by Caro, Mara Vargas, Gabriel Nuncio, Hipatia Argüero Mendoza, and Alexandro Aldrete. (Full article...)
-
Image 12

The 1997 European Grand Prix (formally the XLII European Grand Prix) was a Formula One motor race held on 26 October 1997 at the Circuito Permanente de Jerez, Spain. Originally scheduled as the Portuguese Grand Prix at the Estoril circuit, it was moved when Estoril's management had financial difficulties. It was the 17th and final race of the 1997 FIA Formula One World Championship. The 69-lap race was won by Mika Häkkinen in a McLaren, his first Formula One race victory. His teammate David Coulthard finished second and Williams driver Jacques Villeneuve took third, which was sufficient for him to win the World Championship. (Full article...) -
Image 13"Miente" (English: "Lie") is a song by Spanish singer Enrique Iglesias from his second studio album, Vivir (1997). The song was written and produced by Rafael Pérez-Botija. It was released as the third single from the album in 1997. An uptempo pop power ballad backed by a piano and percussion, the song deals with the singer being in denial about a relationship ending. (Full article...)
-
Image 14Near the Saaler Bodden, Germany
The grey heron (Ardea cinerea) is a long-legged wading bird of the heron family, Ardeidae, native throughout temperate Europe and Asia, and also parts of Africa. It is resident in much of its range, but some populations from the more northern parts migrate southwards in autumn. A bird of wetland areas, it can be seen around lakes, rivers, ponds, marshes and on the sea coast. It feeds mostly on aquatic creatures which it catches after standing stationary beside or in the water, or stalking its prey through the shallows. (Full article...) -
Image 15
The siege of Castelnuovo was an engagement during the Ottoman-Habsburg struggle for control of the Mediterranean, which took place in July 1539 at the walled town of Castelnuovo, present-day Herceg Novi, Montenegro. Castelnuovo had been conquered by elements of various Spanish tercios the year before during the failed campaign of the Holy League against the Ottoman Empire in Eastern Mediterranean waters. The walled town was besieged by land and sea by a powerful Ottoman army under Hayreddin Barbarossa, who offered an honourable surrender to the defenders. These terms were rejected by the Spanish commanding officer Francisco de Sarmiento and his captains even though they knew that the Holy League's fleet, defeated at the Battle of Preveza, could not relieve them. During the siege, Barbarossa's army suffered heavy losses due to the stubborn resistance of Sarmiento's men. Even the Venetian refused the promised naval link to Castelnuovo with the supplies and reinforcements; after a general troop parliament, the commanding officer Francisco de Sarmiento asked his captains what his answer should be to Barbarossa's offer to surrender. The captains responded: "Que vengan cuando quieran" (Let them come whenever they want). However, Castelnuovo eventually fell into Ottoman hands and almost all the Spanish defenders, including Sarmiento, were killed. The loss of the town ended the Christian attempt to regain control of the Eastern Mediterranean. The courage displayed by the Old Tercio of Naples during this last stand, however, was praised and admired throughout Europe and was the subject of numerous poems and songs. (Full article...) -
Image 16"Ay mamá" (pronounced [aj maˈma]; American English: "Oh, mom", British English: "Oh, mum") is a song by Spanish music act Rigoberta Bandini. The song was independently released on 23 December 2021 and was a candidate to represent Spain in the 66th edition of the Eurovision Song Contest, taking part in its preselection, Benidorm Fest. Among the favourites to win, "Ay mamá" placed as the runner-up behind "SloMo" by Chanel. The song was included on Bandini's first studio album, La Emperatriz, released later in 2022. (Full article...)
-
Image 17Gómez de Alvarado y Contreras (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈɡomeθ ðe alβaˈɾaðoj konˈtɾeɾas]; 1482 – September 1542) was a Spanish conquistador and explorer. He was a member of the Alvarado family and the older brother of the famous conquistador Pedro de Alvarado. (Full article...)
-
Image 18Outgoing prime minister Mariano Rajoy (right) congratulating incoming prime minister Pedro Sánchez (left) upon losing the no confidence vote on 1 June 2018
A motion of no confidence in the Spanish government of Mariano Rajoy was debated and voted in the Congress of Deputies between 31 May and 1 June 2018. It was brought by Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) leader Pedro Sánchez after the governing People's Party (PP) was found to have profited from the illegal kickbacks-for-contracts scheme of the Gürtel case in a court ruling made public the previous day. This was the fourth motion of no confidence since the Spanish transition to democracy and the first one to be successful, as well the second to be submitted against Mariano Rajoy after Unidos Podemos's motion the previous year. Coincidentally, it was held 38 years after the first such vote of no confidence in Spain on 30 May 1980. (Full article...) -
Image 19

Barcelona supporters during a match at Camp Nou.
FC Barcelona is a professional multi-sports club based in Barcelona, formed in 1899 by a group of Swiss, Catalan, German and English footballers led by Joan Gamper. It has been part of the Spanish top-flight, La Liga, since the league's inception in 1928, winning it 27 times, along with a record 31 Copa del Rey and five UEFA Champions League victories. (Full article...) -
Image 20

The route of the 2015 Vuelta a España
The 2015 Vuelta a España was a three-week Grand Tour cycling race that took place principally in Spain between 22 August and 13 September 2015; two stages also took place partly or wholly in Andorra. The final ten stages took the race from the mountains of Andorra to the conclusion of the Vuelta in Madrid. After the first eleven stages, Fabio Aru (Astana) held the race lead, around half a minute ahead of Joaquim Rodríguez (Team Katusha) and Tom Dumoulin (Team Giant–Alpecin). (Full article...) -
Image 21

2011 memorial to two of those executed
The last use of capital punishment in Spain took place on 27 September 1975 when two members of the armed Basque nationalist and separatist group ETA political-military and three members of the Spanish anti-Francoist Marxist–Leninist group Revolutionary Antifascist Patriotic Front (FRAP) were executed by firing squads after having been convicted and sentenced to death by military tribunals for the murder of police officers and civil guards. Spain was Western Europe's only dictatorship at the time and had been unpopular and internationally isolated in the post-war period due to its relations with Nazi Germany in the 1930s and 1940s and the fact that its autocratic leader, Francisco Franco, had come to power by overthrowing a democratically elected government. As a result, the executions resulted in substantial criticism of the Spanish government, both domestically and abroad. Reactions included street protests, attacks on Spanish embassies, international criticism of the Spanish government and diplomatic measures, such as the withdrawal of the ambassadors of fifteen European countries. (Full article...) -
Image 221868 lithograph of Pacheco
María López de Mendoza y Pacheco (c. 1496–1531) was a Castilian revolutionary who led the Revolt of the Comuneros in the Kingdom of Toledo. (Full article...) -
Image 23The blockade of Orbetello, engraving by Matthäus Merian.
The Battle of Orbetello, also known as the Battle of Isola del Giglio, was a major naval engagement of the Franco-Spanish War of 1635. It was fought on 14 June 1646 off the Spanish-ruled town of Orbetello, on the coast of Tuscany, Italy, between a French fleet led by Admiral Armand de Maillé, Marquis of Brézé, and a Spanish fleet commanded by Miguel de Noronha, 4th Count of Linhares sent to break the blockade of Orbetello and relieve the town, besieged since 12 May by a French army under the command of Prince Thomas of Savoy. The Battle of Orbetello was tactically very unusual, since it was fought by sailing ships towed by galleys in a light breeze. (Full article...) -
Image 24Eugenio Lascorz y Labastida (26 March 1886 – 1 June 1962) was a Spanish lawyer who claimed to be a descendant of the medieval Laskaris family, which had ruled the Byzantine Empire in Nicaea from 1204 to 1261. In 1917 he legally changed his paternal surname from Lascorz to Láscaris, alleging that the former was a Hispanicization of the latter. Later he began styling himself as Príncipe Eugenio Láscaris Comneno (Prince Eugene Laskaris Komnenos). As the supposed titular Emperor of Constantinople,' Eugenio used the regnal name Eugene II Lascaris Comnenus. In addition to his royal and imperial claims, which he supported with fabricated and contradictory genealogies, Lascorz also claimed the titles "Prince Porphyrogenitus", Duke of Athens and Grand Master of the self-proclaimed "Sovereign and Imperial Order of Constantine the Great" (not to be confused with the Constantinian Order of Saint George) and the "Order of Saint Eugene of Trebizond".' (Full article...)
-
Image 25The Legazpi-Sikatuna Blood Compact or Sandugo (Spanish: Pacto de Sangre) was a blood compact, performed in the island of Bohol in the Philippines, between the Spanish explorer Miguel López de Legazpi and Datu Sikatuna, chieftain of Bohol, on March 16, 1565, to seal their friendship following tribal tradition. This is considered the first treaty of friendship between the Spaniards and Filipinos. "Sandugo" is a Visayan word which means "one blood". (Full article...)
General images
-
Image 2People's militias attacking on a Rebel position in Somosierra in the early stages of the war. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 3Cabeza de Luis Buñuel, sculptor's work by Iñaki, in the center Buñuel Calanda. (from Culture of Spain)
-
Image 5Two women and a man during the siege of the Alcázar (from History of Spain)
-
Image 8Proclamation of the Spanish Republic in Madrid (from History of Spain)
-
Image 9Execution of Torrijos and his men in 1831. Ferdinand VII took repressive measures against the liberal forces in his country. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 10In ictu oculi ("In the blink of an eye"), a vanitas by Juan de Valdés Leal (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 11Las Meninas (1656, English: The Maids of Honour) by Diego Velázquez (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 14Panoramic view of the lower level patio of the Palace (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 15Louis XIV of France and Philip IV of Spain at the Meeting on the Isle of Pheasants in June 1660, part of the process to put an end to the Franco-Spanish War (1635–59). (from History of Spain)
-
Image 16The Iberian Peninsula in the 3rd century BC (from History of Spain)
-
Image 18Felipe González signing the treaty of accession to the European Economic Community on 12 June 1985. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 22Map of territories that were once part of the Spanish Empire (from History of Spain)
-
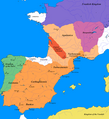
Image 24The realms of Philip II of SpainTerritories administered by the Council of CastileTerritories administered by the Council of AragonTerritories administered by the Council of PortugalTerritories administered by the Council of ItalyTerritories administered by the Council of the IndiesTerritories appointed to the Council of Flanders(from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 26The successful 1925 Alhucemas landing turned the luck in the Rif War towards Spain's favour. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 27Francisco Franco and his appointed successor Prince Juan Carlos de Borbón. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 28Members of the provisional government after the 1868 Glorious Revolution, by Jean Laurent. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 30Detail of the votive crown of Recceswinth from the Treasure of Guarrazar, (Toledo-Spain) hanging in Madrid. The hanging letters spell [R]ECCESVINTHVS REX OFFERET [King R. offers this]. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 32The Conquest of Tenochtitlán (from History of Spain)
-
Image 33Visigothic Hispania and its regional divisions in 700, prior to the Muslim conquest (from History of Spain)
-
Image 35Episode of the 1854 Spanish Revolution in the Puerta del Sol, by Eugenio Lucas Velázquez. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 38The title page of the Gramática de la lengua castellana (1492), the first grammar of a modern European language to be published. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 40The explosion of the USS Maine launched the Spanish–American War in April 1898 (from History of Spain)
-
Image 42Wedding portrait of the Catholic Monarchs (from History of Spain)
-
Image 43Illustration depicting the (now lost) Luzaga's Bronze, an example of the Celtiberian script. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 44The pro-independence forces delivered a crushing defeat to the royalists and secured the independence of Peru in the 1824 battle of Ayacucho. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 45The Second of May 1808 was the beginning of the popular Spanish resistance against Napoleon. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 46The promulgation of the Constitution of 1812, oil painting by Salvador Viniegra. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 49Plaza Mayor with the Casa de la Panadería to the left (from Spanish Golden Age)
-
Image 50Christopher Columbus leads expedition to the New World, 1492, sponsored by Spanish crown (from History of Spain)
-
Image 511894 satirical cartoon depicting the tacit accord for seamless government change (turnismo) between the leaders of two dynastic parties (Sagasta and Cánovas del Castillo), with the country being lied in an allegorical fashion. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 53Charles I of Spain (better known in the English-speaking world as the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V) was the most powerful European monarch of his day. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 54Celebrations of the proclamation of the 2nd Republic in Barcelona. (from History of Spain)
-
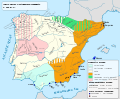
Image 56The Christian kingdoms of Hispania and the Islamic Almohad empire c. 1210
-
Image 57Ethnology of the Iberian Peninsula c. 200 BC (from History of Spain)
-
Image 58El paseo de las Delicias, a 1784–1785 painting by Ramón Bayeu depicting a meeting of members of the aristocracy in the aforementioned location. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 60Visigothic church, San Pedro de la Nave. Zamora. Spain (from History of Spain)
-
Image 62The Port of Seville in the late 16th century. Seville became one of the most populous and cosmopolitan European cities after the expeditions to the New World. (from History of Spain)
-
Image 64The greatest extent of the Visigothic Kingdom of Toulouse, c. 500, showing Territory lost after Vouillé in light orange (from History of Spain)
-
Image 66Recognition of the Duke of Anjou as King of Spain, under the name of Philip V, November 16, 1700 (from History of Spain)
-
Image 69Visigothic King Roderic haranguing his troops before the Battle of Guadalete (from History of Spain)
In the news
- 22 December 2024 –
- Residents of Logroño, La Rioja, Spain, win the world's biggest lottery, the Spanish Christmas Lottery's El Gordo €2.7 billion prize. (DW)
- 18 December 2024 – 2024 FIFA Intercontinental Cup
- In association football, Real Madrid wins the inaugural FIFA Intercontinental Cup after defeating Pachuca 3–0 in the final in Lusail, Qatar. Vinícius Júnior is awarded the Golden Ball. (The Guardian)
Spain topics
Categories
WikiProjects
- Main project
- Related projects
WikiProject Basque • WikiProject Catalan-speaking Countries • WikiProject Galicia • Spanish Translation of the Week
Things you can do

- Add {{WikiProject Spain}} to article talk pages which have some relation to Spain
- Help write new Spain-related articles and improve and expand existent ones
- Assess: unassessed Spain-related articles
- Suggest: selected articles, biographies, pictures, did you knows? and quotes for this Portal
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
- Pages using Template:Post-nominals with customized linking
- Pages with French IPA
- Pages with Spanish IPA
- Portals with triaged subpages from June 2018
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with no named maintainer
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 41–50 articles in article list
- Random portal component with 6–10 available subpages
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list




















































































![Image 30Detail of the votive crown of Recceswinth from the Treasure of Guarrazar, (Toledo-Spain) hanging in Madrid. The hanging letters spell [R]ECCESVINTHVS REX OFFERET [King R. offers this]. (from History of Spain)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f2/Corona_de_%2829049230050%29.jpg/57px-Corona_de_%2829049230050%29.jpg)