List of gendarmeries
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

A gendarmerie or gendarmery is a military force with law enforcement duties among the civilian population. The term maréchaussée (lit. 'marshalcy') may also be used (e.g., Royal Marechaussee) but is now uncommon.
Although pioneered in France, the concept of a gendarmerie was adopted by several other European nations during the Napoleonic Wars.[1] It remains an integral part of the military establishment in most Francophone states and territories.[1] A somewhat related phenomenon has been the formation of paramilitary units which fall under the authority of civilian police agencies. Since these are not strictly military forces, however, they are not considered gendarmeries.[2] 20 gendarmeries and 1 observer are part of the International Association of Gendarmeries and Police Forces with Military Status (FIEP) as of 2024.[3] 7 EU states are part of the European Gendarmerie Force, with 1 partner and 1 observer.[4]
List of active gendarmeries
[edit]| Country or territory | Image | English name | Native-language name | Notes | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algeria | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale (الدرك الوطني) |
Formed in 1962 following Algerian independence and attached to the Ministry of Defence | [5] |
| Argentina | Argentine National Gendarmerie | Gendarmería Nacional Argentina | Formed in 1938, and a member of FIEP | [6][3] | |
| Azerbaijan | 
|
Internal Troops of Azerbaijan | Azərbaycan Respublikası Daxili Qoşunları | ||
| Bangladesh | Bangladesh Ansar | বাংলাদেশ আনসার | |||
| Belarus | 
|
Internal Troops | Унутраныя войскі (Unutranyja vojski) Внутренние войска (Vnutrennie voyska) |
||
| Bosnia and Herzegovina (Republika Srpska) |

|
Gendarmerie of Republika Srpska | Жандармерија Републике Српске (Žandarmerija Republike Srpske) |
Bosnia and Herzegovina has two major entity-level ministries of interior, so only Republika Srpska has gendarmerie type unit formed in September 2019. | |
| Brazil | 
|
Military Police | Polícia Militar | Brazilian states have their own gendarmeries. Member of FIEP | [3] |
| Bulgaria | 
|
Gendarmerie (Bulgaria) | Жандармерия (Zhandarmeriya) |
||
| Burkina Faso | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | Established in 1960 following independence as part of the army, and operates within the Defence Ministry | [7][8] |
| Burundi | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | ||
| Bhutan | 
|
Royal Bhutan Police | རྒྱལ་གཞུང་འབྲུག་གི་འགག་སྡེ (gyal-zhung druk-ki gaag-de) |
||
| Cambodia | 
|
Royal Gendarmerie of Cambodia | កងរាជអាវុធហត្ថ (kangreachaavouthohat) |
First formed in 1954 and operated until the Khmer Rouge dictatorship in 1975. Reformed in 1993 with assistance from France. | [9][10] |
| Cameroon | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | Formed in 1960, and operates under the Defence Ministry as one of the two primary law enforcement organisations, alongside the Cameroonian National Police | [11][12] |
| Central African Republic | 
|
Gendarmerie | |||
| Chad | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | Created following independence from France in 1960 | [13] |
| Chile | 
|
Carabineros of Chile | Carabineros de Chile | Formed in 1903 as part of the army. In 1927 it was merged with the civilian Fiscal Police and Rural Police to create the Carabineros de Chile. Member of FIEP | [14][3] |
| China | 
|
People's Armed Police | 中国人民武装警察部队 (Zhōngguó Rénmín Wǔzhuāng Jǐngchá Bùduì) |
Formed in 1982, the PAP perform military-civilian police duties. The PAP is a component of the Paramilitary forces of China. | [15][16] |
| Comoros | 
|
Gendarmerie | Formed in 1978 | [17] | |
| Republic of the Congo | 
|
Congolese National Gendarmerie | Initially formed in 1960 following independence before being dissolved and split between the Army and Police in 1970. Restored in 1991 and shares policing duties with the National Police. Controlled by the Defense Ministry | [18][19] | |
| Côte d'Ivoire | 
|
Gendarmerie | In 1958 the French Gendarmerie began to supervise the first elements of the Ivorian Republican Guard, before becoming the National Gendarmerie following independence in 1960 | [20] | |
| Djibouti | 
|
Djiboutian National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale Djiboutienne | The first French Gendarmes arrived in 1919, following independence in 1977 the Djiboutian Gendarmerie was created and is primarily under the Ministry of Defense. Member of FIEP | [21][22] [3] |
| Dominican Republic | Dominican Republic National Police | Policía Nacional Dominicana | |||
| France | National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | Established in 1791 and member of FIEP and the European Gendarmerie Force | [23][3] [4] | |
| Gabon | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | Formed in 1960 following independence with Gabonization occurring in 1964. A branch of the Defense Ministry | [24][25] |
| Guinea | 
|
Gendarmerie | Formed following independence in 1958 and shares policing duties with the National Police | [26][27] | |
| Guinea-Bissau | 
|
National Guard | Guarda Nacional | Created in 2010 through the merger of several former security agencies. Modeled on the Portuguese National Republican Guard and other similar organizations. | |
| Hungary | 
|
Law Enforcement and Public Safety Service | Rendészeti Biztonsági Szolgálat | ||
| Iraqi Kurdistan | 
|
Zeravani | Zêrevanî (زێرەڤانی) |
Established in 1997 and has been described as a gendarmerie. Under the operational control of the Kurdistan Regional Government's Ministry of Interior, but are part of the Peshmerga armed forces of Iraqi Kurdistan. | [28][29] [30] |
| Italy | 
|
Corps of Carabineers | Arma dei Carabinieri | The Carabinieri is a component of the Italian Armed Forces. Formed in 1814 and a part of the Defence Ministry but coordinated by the Interior Ministry. Member of FIEP and the European Gendarmerie Force | [31][32] [33][3] [4] |
| Jordan | 
|
General Directorate of Gendarmerie | قوات الدرك الأردني | Established in 2008 and member of FIEP | [34][3] |
| Kazakhstan | National Guard of Kazakhstan | Ұлттық ұланы, Ūlttyq ūlany | Established in 2014 on the basis of Kazakhstan Interior Troops | ||
| Kuwait | 
|
Kuwait National Guard | الحرس الوطني الكويتي | Member of FIEP | [3] |
| Lithuania | 
|
Public Safety Service | Viešojo saugumo tarnyba | Created following independence in 1991 as the Internal Service Unit and reorganised in 2002. | [35][34] |
| Madagascar | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | Formed following independence in 1960 and reports to the National Defence Ministry | [36][37] |
| Mali | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | Established in 1960 and shares policing duties with the National Police. Administratively controlled by the Ministry of Defence, with operational control shared between the Ministry of Defense and the Ministry of Security and Civil Protection. | [38][39] |
| Mauritania | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | Established in 1960 and part of the Defence Ministry | [40][41] |
| Mexico | 
|
National Guard | Guardia Nacional | The National Guard was created in 2019 by merging the Federal Police (including the National Gendarmerie). | [42][43] |
| Moldova | 
|
Carabinier Troops | Trupele de Carabinieri | Created in 1991 under the control of the Ministry of Internal Affairs. FIEP observer | [44][45] [3] |
| Monaco | 
|
Prince's Company of Carabiniers | Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince | The Corps des Sapeurs-Pompiers provide an armed support service. | |
| Mongolia | 
|
National Police Agency | Цагдаагийн Ерөнхий Газар (Tsagdaagiin Erönkhii Gazar) |
||

|
Internal Troops of Mongolia | Монгол Улсын Дотоод цэргүүд | Disestablished in 2013, reestablished in 2017[46] | ||
| Morocco | 
|
Royal Moroccan Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Royale (الدرك الملكي) | Formed in 1957 and with law enforcement primarily in rural areas. Member of FIEP | [47][48] [3] |
| Netherlands | 
|
Royal Marechaussee | Koninklijke Marechaussee | Established in 1814, and part of the Ministry of Defence although non-military operations are performed under the Ministry of Justice and Security and Ministry of the Interior and Kingdom Relations. Member of FIEP and the European Gendarmerie Force | [49][50] [3][4] |
| Niger | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale Nigérienne | Established in 1960 and part of the Defence Ministry | [51][52] |
| Palestine | 
|
Palestinian National Security Forces | قوات الأمن الوطني الفلسطيني (Quwwat al-Amn al-Watani al-Filastini) |
Member of FIEP | [3] |
| Pakistan | 
|
Balochistan Levies | |||

|
Frontier Constabulary | جمیعتِ سپاہیانِ سرحدی | |||
| Poland | 
|
Military Gendarmerie | Żandarmeria Wojskowa | Created in 1812 and directed by the Ministry of Defence. Member of the European Gendarmerie Force | [53][4] |
| Portugal | 
|
National Republican Guard | Guarda Nacional Republicana | Precursor units date back to 1801, with the National Republican Guard created in 1911. In peacetime it responds to the Ministry of Internal Administration, and in wartime the Ministry of National Defence. Member of FIEP and the European Gendarmerie Force | [54][55] [56][3] [4] |
| Romania | 
|
Romanian Gendarmerie | Jandarmeria Română | Formed in 1850 and under the control of the Ministry of Internal Affairs. Member of FIEP and the European Gendarmerie Force | [57][58] [3][4] |
| Qatar | 
|
Internal Security Force | لخويا | Established in 2003 as part of the Interior Ministry. Member of FIEP | [59][60] [3] |
| Russia | National Guard of Russia (Rosgvardiya) | Федеральная служба войск национальной гвардии РФ (Росгвардия) | The first Russian gendarmerie units were created in 1817 with the current National Guard established in 2016 containing SOBR, OMON, and the Internal Troops and reporting directly to the President. | [61][62] | |
| San Marino | 
|
Corps of Gendarmerie of San Marino | Gendarmeria | Established in 1824 and member of FIEP | [63][3] |
| Saudi Arabia | Saudi Arabian National Guard | الحَرَس الوَطنيّ (al-Ḥaras al-Waṭanī) |
|||
| Senegal | 
|
Senegalese Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | Established in 1962 The Gendarmerie and civilian National Police are the two main law enforcement bodies. It is under the responsibility of the Ministry of Armed Forces. Member of FIEP | [64][65] [3] |
| Serbia | 
|
Gendarmery | Жандармерија (Žandarmerija) |
Originally formed in 1860, it was disbanded in 1945 and re-established in 2001. | [66] |
| Spain | 
|
Civil Guard | Guardia Civil | Formed in 1844 with control for functions shared between the Ministry of Defence and Ministry of the Interior and one of the two national Policing bodies. Member of FIEP and the European Gendarmerie Force | [67][68] [3][4] |
| Taiwan | Military Police | 中華民國憲兵 | may be mobilized by prosecutors to investigate civilian crimes | ||
| Tajikistan | 
|
Internal Troops | Қӯшунҳои дохилӣ | ||
| Togo | 
|
National Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Nationale | Created in 1962 and is part of the Ministry of Defense, although may report to the Ministry of Security and Civil Protection for law enforcement. | [69][70] |
| Tunisia | 
|
National Guard | Garde Nationale | Member of FIEP | [3] |
| Turkey | 
|
Gendarmerie General Command | Jandarma Genel Komutanlığı | Subordinate to the Turkish Ministry of Interior since 2016. Member of FIEP and observer of the European Gendarmerie Force | [3][71] |
| Turkmenistan | 
|
Internal Troops | Türkmenistanyň içeri işler edaralarynyň işgärlerine | ||

|
Turkmen National Guard | Türkmenistanyň Milli Garawul | |||
| Ukraine | 
|
National Guard | Національна гвардія України (Natsionalna hvardiia Ukrainy) |
Created 1991 from the Internal Troops of Ukrainian SSR, reverted to old name between 2000 and 2014. Member of FIEP | [3] |
| United States | United States Coast Guard | The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, law enforcement, and military service branch of the United States Armed Forces[72] and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The Coast Guard is a maritime, military, multi-mission service unique among the U.S. military branches for having a maritime law enforcement mission with jurisdiction in both domestic and international waters and a federal regulatory agency mission as part of its duties. | |||
| Uzbekistan | 
|
Uzbekistan National Guard | Oʻzbekiston Respublikasi Milliy gvardiyasi | ||
| Vatican City | 
|
Corps of Gendarmerie of Vatican City | Corpo della Gendarmeria dello Stato della Città del Vaticano | General responsibility for security and public order which encompasses all regular police duties, including border control, crime prevention and investigation, and enforcement of financial and commercial regulations. | |
| Venezuela | 
|
Venezuelan National Guard | Guardia Nacional Bolivariana de Venezuela | ||
| Europe | 
|
European Gendarmerie Force | French: Force de gendarmerie européenne Italian: Forza di Gendarmeria Europea Portuguese: Força de Gendarmaria Europeia Spanish: Fuerza de Gendarmería Europea |
Formed by seven members of the European Union: France, Italy, The Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, and Spain. The European Gendarmerie Force was created as an intervention force at the service of the EU, the NATO, the UN, the OSCE, or other "ad hoc" alliances. It is characterized by its robustness, and quick deployability, and it specializes in the management of crisis areas. Lithuania is currently a Partner Member, and Turkey has Observer status.[73] |
Ranks
[edit]| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
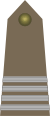
| Suboficial Mayor | Suboficial Principal | Sargento Ayudante | Sargento Primero | Sargento | Cabo Primero | Cabo | Gendarme
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ayudante mayor | Ayudante principal | Ayudante de primero | Ayudante de segundo | Ayudante de tercera | Cabo primero | Cabo segundo | Marinero
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subtenente | Primeiro-sargento | Segundo-sargento | Terceiro-sargento | Aluno sargento | Cabo | Soldado primeira classe | Soldado segunda classe | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjudant major | Adjudant-chef | Adjudant | Maréchal-des-logis-chef | Maréchal-des-logis | Gendarme | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ព្រឹន្ទបាលឯក Prœ̆ntôbal êk |
ព្រឹន្ទបាលទោ Prœ̆ntôbal toŭ |
ពលបាលឯក Pôlôbal êk |
ពលបាលទោ Pôlôbal toŭ |
ពលបាលត្រី Pôlôbal trei |
នាយឯក Néay êk |
នាយទោ Néay toŭ |
ពលឯក Pôl êk |
ពលទោ Pôl toŭ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-commissioned officers | Constables | Depot | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|
No insignia | 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corps sergeant major | Sergeant major | Staff sergeant major | Staff sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Constable | Cadet | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sergent-major du corps | Sergent-major | Sergent-major d'état major | Sergent d'état-major | Sergent | Caporal | Gendarme | Cadet | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sergent major | Sergent-chef | Sergent | Caporal | Soldat première | Soldat | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Suboficial mayor | Suboficial | Sargento primero | Sargento segundo | Cabo primero | Cabo segundo | Carabinero | Carabinero alumno | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Suboficial mayor | Suboficial | Sargento primero | Sargento segundo | Cabo primero | Cabo segundo | Cabo | Gendarme primero | Gendarme segundo | Gendarme | Gendarme alumno | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 一级军士长 Yījí jūnshìzhǎng |
二级军士长 Èrjí jūnshìzhǎng |
三级军士长 Sānjí jūnshìzhǎng |
四级军士长 Sìjí jūnshìzhǎng |
上士 Shàngshì |
中士 Zhōngshì |
下士 Xiàshì |
上等兵 Shàngděngbīng |
列兵 Lièbīng
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjudant-chef | Adjudant | Maréchal des logis-chef | Maréchal des logis | Èleve gendarme | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major | Adjudant-chef | Adjudant | Maréchal-des-logis-chef | Gendarme | Gendarme sous contrat | Gendarme Adjoint Maréchal-des-logis | Gendarme Adjoint Brigadier Chef | Gendarme Adjoint Brigadier | Gendarme Adjoint première classe | Gendarme Adjoint
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subedar major सूबेदार मेजर |
Subedar सूबेदार |
Naib subedar नायब सूबेदार |
Warrant officer - |
Havildar[note 10] हवलदार |
Rifleman[note 11] -
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| استوار یکم Ostovar yekom |
استوار دوم Ostovar dovom |
گروهبان یکم Goruhban yekom |
گروهبان دوم Goruhban dovom |
گروهبان سوم Goruhban sevom |
سرجوخه Sarjukheh |
سرباز یکم Sarbaz yekom |
سرباز دوم Sarbaz dovom |
سرباز Sarbaz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| רב נגד Rav nagad |
רב סמל בכיר Rav samal bakhir |
רב סמל מתקדם Rav samal mitkadem |
רב סמל ראשון Rav samal rishon |
רב סמל Rav samal |
סמל ראשון Samal rishon |
סמל שני Samal sheni |
רב שוטר Rav shoter |
שוטר Shoter
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primo luogotenente c.s. s.u.p.s | Luogotenente s.u.p.s. | Primo Maresciallo | Maresciallo Capo | Maresciallo Ordinario | Maresciallo | Sergente Maggiore Capo | Sergente Maggiore | Sergente
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
No equivalent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luogotenente s.u.p.s. | Maresciallo Aiutante s.u.p.s | Maresciallo Capo | Maresciallo Ordinario | Maresciallo | Brigadiere Capo | Brigadiere | Vice Brigadiere | Appuntato scelto | Appuntato | Finanziere scelto | Finanziere
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sergeant | Corporal | Constable
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agente Mayor | Agente | Subagente | Guardia Nacional | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjudant-chef | Adjudant | Maréchal-des-logis-major | Maréchal-des-logis-chef | Maréchal-des-logis | Brigadier | Carabinier de première classe | Carabinier de deuxième classe | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjudant-chef | Adjudant | Sergent-major | Sergent-chef | Sergent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjudant-onderofficier | Opperwachtmeester | Wachtmeester der 1e klasse | Wachtmeester | Marechaussee der 1e klasse | Marechaussee der 2e klasse | Marechaussee der 3e klasse | Marechaussee der 4e klasse | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major | Adjudant-chef | Adjudant | Maréchal des logis chef | Maréchal des logis | Gendarme de 1re classe | Gendarme de 2e classe | Gendarme de 3e classe | Gendarme de 4e classe | Gendarme auxiliaire | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pakistan Frontier Constabulary |
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inspector انسپکٹر |
Sub inspector سب انسپکٹر۔ |
Assistant sub inspector اسسٹنٹ سب انسپکٹر۔ |
Head Constable ہیڈ کانسٹیبل۔ |
Constable کانسٹیبل
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pakistan Rangers |

|

|

|
No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior inspector سینئر انسپکٹر۔ |
Inspector انسپکٹر |
Sub inspector سب انسپکٹر۔ |
Havildar حوالدار۔ |
Naik نائیک۔ |
Lance Naik لانس نائیک۔ |
Sepoy سپاہی۔
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Starszy chorąży sztabowy | Starszy chorąży | Chorąży | Młodszy chorąży | Starszy sierżant | Sierżant | Plutonowy | Starszy kapral | Kapral | Starszy szeregowy | Szeregowy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sargento-mor | Sargento-chefe | Sargento-ajudante | Primeiro-sargento | Segundo-sargento | Furriel | Cabo-mor | Cabo-chefe | Cabo-de-curso | Cabo | Guarda principal | Guarda | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plutonier adjutant șef | Plutonier adjutant | Plutonier-major | Plutonier | Sergent-major | Sergent | Caporal | Fruntaș | Jandarm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maresciallo | Brigadiere | Vice-brigadiere | Appuntato | Gendarme | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjutant-major | Adjutant-chef | Adjutant | Maréchal des logis-chef | Maréchal des logis | Gendarme | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Suboficial mayor | Subteniente | Brigada | Sargento primero | Sargento | Cabo mayor | Cabo primero | Cabo | Guardia Civil de Primera (Rank honorary, currently extinct) |
Guardia Civil*
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Astsubay kıdemli başçavuş | Astsubay başçavuş | Astsubay kıdemli üstçavuş | Astsubay üstçavuş | Astsubay kıdemli çavuş | Astsubay çavuş | Uzman onbaşı | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 一等士官長 Yīděng shìguānzhǎng |
二等士官長 Èrděng shìguānzhǎng |
三等士官長 Sānděng shìguānzhǎng |
上士 Shàngshì |
中士 Zhōngshì |
下士 Xiàshì |
上等兵 Shàngděngbīng |
一等兵 Yīděngbīng |
二等兵 Èrděngbīng | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Command master chief petty officer | Master chief petty officer | Senior chief petty officer | Chief petty officer | Petty officer first class | Petty officer second class | Petty officer third class | Seaman | Seaman apprentice | Seaman recruit | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
 |

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant Officer Class 1 |
Warrant Officer Class 2 |
Staff Sergeant Staf Sajen |
Sergeant Sajen |
Corporal Kofol |
Lance Corporal | Constable Polis |
Recruit Rikrut | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ispettore | Vice ispettore | Brigadiere | Vice brigadiere | Gendarme
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Public Security |
|

|
|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
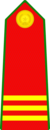
| Master sergeant (Thượng sĩ) |
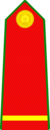
Sergeant (Trung sĩ) |
Corporal (Hạ sĩ) |
Constable 1st class (Chiến sĩ bậc 1) |
Constable 2nd class (Chiến sĩ bậc 2)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
List of former gendarmeries
[edit]| Country or territory | English name | Native-language name | Formed | Disbanded | Notes | Refs. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defenders of the Revolution | Sarandoy | 1978 | 1992 | Formed after the Saur Revolution, Sarandoy was dominated by the Khalq faction of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan and would often clash with the Parchamite Dominated Khad. | |||
| Afghan National Civil Order Force | 2006 | 2020 | Originally part of Afghan National Police, most personnel transferred to Afghan National Army in 2018 | [91][92] [93] | |||
| International Gendarmerie | 1913 | 1914 | [94] | ||||
| Royal Albanian Gendarmerie | Xhandarmëria Mbretërore e Shqipëris | 1919 | 1939 | Formed as a counterweight to the Royal Albanian Army, it employed British advisors on its staff and with the units | [94] | ||
| Imperial and Royal Gendarmerie | k.k. Gendarmerie | 1849 | 1918 | Gendarmerie of Cisleithanian part of Austria-Hungary | [95] | ||
| Federal Gendarmerie | Bundesgendarmerie | 1918 | 2005 | Renamed k.k. Gendarmerie, dissolved under occupation from 1938 to 1945. Merged with other agencies to form new Bundespolizei in 2005 | |||
| B-Gendarmerie | 1949 | 1955 | The precursor of the Austrian Armed Forces | ||||
| Special Purpose Police Unit | Xüsusi Təyinatlı Polis Dəstəsi | 1990 | 1995 | Fought in the First Nagorno-Karabakh war, disbanded after mutiny | |||
| Grand Duchy of Baden Gendarmerie Corps | 1829 | 1918 | Part of the Baden Army until 1870 when the Army became part of the Prussian Army. Subordinated to the Ministry of the Interior. Strength 248 – 560 gendarmes in six, later four, districts. | ||||
| Belgian Gendarmerie | French: Gendarmerie Dutch: Rijkswacht |
1796 | 2001 | Was formed under French rule in what now is Belgian territory, even before the establishment of Belgium itself (1830). Merged with federal and local police to form a new policing system | |||
| Garde Civique | Dutch: Burgerwacht | 1830 | 1920 | ||||
| National Gendarmerie | French: Gendarmerie Nationale | 1960 | 2018 | Merged with the civilian National Police in 2018 to become the Republican Police of Benin | [96] | ||
| Bulgarian Gendarmerie | Zhandarmeriya | The Bulgarian Gendarmerie was disbanded by the country's General Directorate of Police, and its personnel were absorbed into various specialized police units. | |||||
| North-West Mounted Police | 1873 | 1920 | Merged with the Dominion Police to create Royal Canadian Mounted Police | ||||
| National Gendarmerie Corps | Cuerpo de Gendarmeria Nacional | 1906 | 1909 | Created to function decentralized from the National Police command and more militarized regime, managed by the Ministry of War. In 1909 General Jorge Holguín suppressed the National Gendarmerie Corps and gave the provincial governors the authority to organize police services at their own will | |||
| Cretan Gendarmerie | Κρητική Χωροφυλακή, Kritiki Chorofylaki | 1899 | 1916 | ||||
| Cyprus Military Police | Κυπριακή Στρατιωτική Αστυνομία Kıbrıs Jandarması |
1880 | 1935 | ||||
| Czechoslovakian Gendarmerie | Československé četnictvo | 1918 | 1942 | Managed by the Ministry of Interior. In 1942 merged with police and fire brigades. After the liberation in 1945 created a unified police force—the Corps of National Security (SNB)—that amalgamated gendarmerie, police and intelligence. | |||
| Border Gendarmerie | Grænsegendarmeriet | 1838 | 1958 | ||||
| The Blue Gendarms | De Blå Gendarmer | 1885 | 1897 | ||||
| The Royal Danish West Indies Gendarmerie Corps | Det Kongelige Dansk Vestindiske Gendarmerikorps | 1907 | 1917 | ||||
| Marshal Corps On Foot | Korps Marechaussee te voet | 1890 | 1942 | ||||
| Ethiopian Gendarmery | Zabagna | 1916 | 1936 | Included the Kebur Zabagna Imperial Guard | |||
| Internal Troops of Georgia | საქართველოს შინაგანი ჯარები sak'art'velos shinagani jarebi |
1991 | 2004 | [97] | |||
| Field Gendarmerie | Feldgendarmerie | 1866 | 1918 | Military police units of the army of the German Empire. | |||
| Field Gendarmerie | Feldgendarmerie | 1933 | 1945 | Military police units of the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany. | |||
| Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie, Landjägerei (rural ranger), Landpolizei (rural police), Dragoner, Husaren and other denominations | 19th century | mid-20th century | Due to the distinctive autonomy of the German states, every state has its own history of establishing and denomination. In Prussia for example it was called Royal Prussian State Gendarmerie | |||
| Hellenic Gendarmerie | Ελληνική Χωροφυλακή, Elliniki Chorofylaki | 1833 | 1984 | Merged with the City Police and formed the current Hellenic Police | |||
| Gendarmerie of Haiti | 1915 | 1928 | Established following a US intervention, later reorganized into Garde d'Haïti | [98] | |||
| Gendarmerie of Honduras | Gendarmería de Honduras | 1866 | 1882 | ||||
| Hungarian Royal Gendarmerie | Magyar Királyi Csendőrség | 1881 | 1945 | Until 1918 Gendarmerie of Transleithanian part of Austria-Hungary; disbanded by the Interim National Government after WWII because Hungarian Royal Gendarmerie took part in the Holocaust by gathering the Hungarian Jews and giving them to the Nazi German forces. | |||
| Law Enforcement and Public Safety Service | Rendészeti Biztonsági Szolgálat | 2004 | 2008 | Couple years after the fall of the communist regime, a new gendarmerie-type police force within the frameworks of the Hungarian National Police:, Rendészeti Biztonsági Szolgálat was formed and existed between 2004 and 2008. | |||
| Islamic Republic of Iran Gendarmerie | ژاندارمری (Zhāndārmerī) | 1979 | 1990 | Persian Central Government Gendarmerie 1911–1921, Amniyeh Kol-e Mamlekati 1921–1943; GENMISH 1943–1957; State Gendarmerie 1957–1979; gendarmerie dissolved in 1990 | |||
| Royal Irish Constabulary[99] | 1822 | 1922 | Royal added to the name in 1867.[100] | ||||
| Italian African Police | Polizia dell'Africa Italiana | 1936 | 1941 | Operated throughout Italian East Africa | |||
| Zaptié | 1889 | 1942 | |||||
| Corps of Law Soldiers (lit) | Kempeitai, 憲兵隊 | 1881 | 1945 | Part of the Imperial Japanese Army | |||
| Naval Secret Police | Tokkeitai, 特警隊 | 1945 | The Imperial Japanese Navy's military police, they were equivalent to the Imperial Japanese Army's Kempeitai. They were also the smallest military police service. | ||||
| National Police Reserve | 警察予備隊, Keisatsu Yobitai | 1950 | 1952 | National force in Japan until formation of JSDF and NPA. According to Article 3, National Police Reserve Order (警察予備隊令第三條), the NPR took action upon appointment by the Prime Minister when it was particularly necessary to maintain public security. | [101]
Original text in Japanese: 警察予備隊は、治安維持のため特別の必要がある場合において、内閣総理大臣の命を受け行動するものとする。[102] | ||
| Katangese Gendarmerie | 1960 | 1963 | |||||
| Internal Troops of Kazakhstan | Қазақстан IIМ iшкi әскері, Qazaqstan IIM ishki áskeri | 1992 | 2014 | Reformed into National Guard of Kazakhstan | |||
| Grand Ducal Gendarmerie | Gendarmerie Grand-Ducale | 1733 | 2000 | Dissolved under Nazi occupation from 1940 to 1944. Merged on 1 January 2000 with local Police to form the new Grand Ducal Police | [103] | ||
| Rural Guard | Guardia Rural | 1861 | 1914 | In modern Mexico, the name is applied to the part-time Rural Defence Corps. | |||
| National Gendarmerie | Gendarmeria Nacional | 1877 | 1970 | It was a body that has militarized police functions whose jurisdiction in large urban areas. | |||
| Federal Police (Mexico) | Policía Federal | 2009 | 2019 | Reformed into the National Guard of Mexico | |||
| Republican Guard of Lourenço Marques | Guarda Republicana de Lourenço Marques | 1913 | 1924 | Replaced both the former military Guarda Cívica (Civic Guard) and the Civil Police of Lourenço Marques. | |||
| Police Guard of the Mozambique Company | Guarda Policial da Companhia de Moçambique | 1914 | 1925 | Military and police force of the territory under administration of the Mozambique Company (Territory of Manica and Sofala). Replaced by the Police Forces of the Mozambique Company (Forças Policiais da Companhia de Moçambique). | |||
| National Guard (Nicaragua) | Guardia Nacional | 1925 | 1979 | ||||
| Royal Ulster Constabulary | 1922 | 2001 | Reformed into the civilian Police Service of Northern Ireland following the Good Friday Agreements | ||||
| Ottoman Gendarmerie | 1869 | 1918 | Briefly split into forces serving the declining Ottoman regime and those working with the Ankara Government in the Turkish War of Independence. Reformed into the Gendarmerie General Command after the Abolition of the Ottoman Sultanate in 1923 without being disbanded. | ||||
| Palestine (British Mandate) | British Gendarmerie | 1920 | 1926 | Replaced by the Transjordan Frontier Force on 1 April | |||
| Peruvian Gendarmerie | Gendarmería Nacional del Perú | 1852 | 1924 | Became the basis of the Civil Guard. | |||
| Republican Guard | 1919 | 1991 | [104] | ||||
| Guardia Civil en las Filipinas | 1868 | 1898 | The Guardia Civil en las Filipinas (Spanish) translated to the "Civil Guard in the Philippines" was the branch of the Civil Guard organised under the Spanish colonial government in the Philippines and a component of the Spanish Army. | ||||
| Philippine Constabulary | Hukbóng Pamayapà ng Pilipinas | 1901 | 1991 | Replaced the former Civil Guard as a gendarmerie law enforcement force. | [105] | ||
| Territorial Defense Forces | Obrona Terytorium Kraju | 1965 | 2008 | ||||
| Fiscal Guard | Guarda Fiscal | 1885 | 1993 | It was military force controlled by the Portuguese Ministry of Finance, responsible for the tax and customs law enforcement and border surveillance. In 1993, it became part of the National Republican Guard, as the Fiscal Brigade. | |||
| Police and Supervion Corps of India | Corpo de Polícia e Fiscalização da Índia | 1924 | 1946 | Transformed in the entirely civilian Polícia do Estado da Índia (State of India Police) in 1946. | |||
| Royal Prussian State Gendarmerie | 1812 | 1918 | |||||
| Internal Troops of Russia | Внутренние войска МВД России | 1992 | 2016 | ||||
| Special Corps of Gendarmes | Отдельный корпус жандармов | 1836 | 1917 | Part of the Russian Imperial Army under the 3rd Section until 1880, under the Police Department of Russia afterwards | |||
| United States Occupation Zone of West Germany and Austria | United States Constabulary | 1946 | 1952 | [106] | |||
| Feldgendarmerie | 1810 | 1812 | Military police units of the army of the kingdom of Saxony. | ||||
| South African Constabulary | 1900 | 1908 | Used for policing the former territories of Transvaal and Orange Free State | ||||
| Natal Mounted Police | 1874 | 1913 | |||||
| Internal Troops | Внутренние войска МВД СССР | 1919 | 1991 | ||||
| Carabineros | 1829 | 1940 | Border patrol and customs service of Spain until the end of the Spanish Civil War | ||||
| National Republican Guard | Guardia Nacional Republicana | 1936 | 1937 | Created from the faction of Civil Guard loyal to the Republicans in the Spanish Civil War | |||
| Colonial Guard of Spanish Guinea | 1908 | 1968 | |||||
| Syrian Gendarmerie | 1921 | 1958 | Formed by the French to combat local insurgencies,[107] and maintained as late as 1958.[108] | ||||
| Royal Siamese Provincial Gendarmerie | 1897 | 1915 | Formed in 1897 by Danish mercenaries, integrated with the Royal Thai Police in 1915.[109] | ||||
| Free Cossacks | 1917 | 1918 | |||||
| Internal Troops of Ukraine | Внутрішні війська МВС України | 1991 | 2014 | National Guard in 1992–2000, name reverted to 'Internal Troops' afterwards until the Euromaidan | |||
| Lighthorse | ? | The name given by the Five Civilized Tribes of the United States to their mounted police force. The US Army's cavalry performed gendarme duties until the advent of law and order. | |||||
| Corps of Gendarmerie of Vatican City | Corpo della Gendarmeria dello Stato della Città del Vaticano | 1816 | 1974 | Formed 1816. Replaced by a civilian Central Security Office, in 1970, which itself became the Corpo di Vigilanza dello Stato della Città del Vaticano in 1991. Was restored as the Gendarmerie in 2002. | |||
See also
[edit]- List of law enforcement agencies
- List of border guards
- Gendarmerie (disambiguation)
- Military aid to the civil power
- Militarization of police
- Paramilitary
- Military police
- Police
- Carabinier
- Field Force
- National Guard (disambiguation)
- United States National Guard
- State Police (United States)
- Constabulary
- People's Armed Police
- International Association of Gendarmeries and Police Forces with Military Status
Notes
[edit]- ^ Equivalent to the rank lieutenant general (लेफ्टिनेंट - जनरल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank lieutenant general (लेफ्टिनेंट - जनरल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank lieutenant general (लेफ्टिनेंट - जनरल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank major general (मेजर - जनरल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank brigadier (ब्रिगेडियर)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank colonel (कर्नल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank lieutenant colonel (लेफ्टिनेंट - कर्नल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank major (मेजर)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank captain (कप्तान)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank head constable (-)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank constable (-)
References
[edit]- ^ a b Lioe, Kim Eduard (3 December 2010). Armed Forces in Law Enforcement Operations? - The German and European Perspective (1989 ed.). Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. pp. 52–57. ISBN 978-3-642-15433-1.
- ^ Kumar, Kuldeep (14 April 2016). Police and Counterinsurgency: The Untold Story of Tripura's COIN Campaign (2016 ed.). SAGE Publications India. pp. 90–94. ISBN 978-9351507475.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v "The Association - FIEP". fiep.org. International Association of Gendarmeries and Police Forces with Military Status. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Members". eurogendfor.org. European Gendarmerie Force. Archived from the original on 1 January 2014.
- ^ "Algérie". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French and English). 2023. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Argentine". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French and English). 2022. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Burkina Faso". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French and English). 2023. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Burkina Faso Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 21 May 2022. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "History of the Royal Gendarmerie of Cambodia". www.globalsecurity.org. 2012. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Cambodge". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2017. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Cameroun". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2019. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Cameroon Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 3 March 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Tchad". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2022. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Chili". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2022. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ Plapinger, David; Knoll, Kevin; Pollpeter, Sam (27 April 2021). "China's Irregular Approach to War: The Myth of a Purely Conventional Future Fight". Modern War Institute. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Chine". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2022. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Comores". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French and English). 2023. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Congo". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French and English). 2017. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Republic of the Congo Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 18 November 2021. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Côte d'Ivoire". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2023. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Djibouti". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Djibouti Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 25 January 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "La gendarmerie, héritière des maréchaussées". www.gendarmerie.interieur.gouv.fr (in French). Archived from the original on 8 December 2021. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Gabon". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2017. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Gabon Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 27 March 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Guinée Conakry". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2019. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Guinea Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 22 February 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Commander of the Zêrevanî Pêşmerge Forces, Maj. Gen. Aziz Waisi, sheds light on the role and future of Zeravani forces". Kurdish Globe. Free Online Library. 25 June 2011. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ Khidhir, Qassim (27 February 2007). "Zeravani Army is the Guardian of Kurdistan Regional Capital". The Kurdish Globe. p. 7. Archived from the original on 12 June 2010.
- ^ "A hint of harmony, at last". The Economist. 3 December 2009. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Arma dei Carabinieri Historical References". carabinieri.it. Archived from the original on 11 October 2009.
- ^ "Italie". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2017. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Italy Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 29 November 2021. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ a b "Jordanie". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2022. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ Vaitkus, Evaldas (23 January 2019). "History | Public Security Service under the Ministry of Interior". vstarnyba.lrv.lt. Archived from the original on 11 August 2021.
- ^ "Madagascar". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Madagascar Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 7 March 2022. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Mali". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Mali Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 5 May 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Mauritanie". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2021. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Mauritania Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 23 February 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Mexique". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Mexico Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 5 February 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Moldavie". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2022. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Moldova Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 2 November 2021. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Internal troops reinstated by Parliament". MONTSAME News Agency. Retrieved 2022-01-11.
- ^ "Maroc". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2018. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Morocco Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 17 July 2021. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Pays-Bas". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2017. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ Blok, Chan (January 2004). "Policing in the Netherlands" (PDF). pp. 31–32. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 October 2012.
- ^ "Niger". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2019. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Niger Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 29 April 2022. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Pologne". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2017. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Portugal". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2018. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Portugal Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 6 March 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Portugese National Republican Guard - FIEP". fiep.org. International Association of Gendarmeries and Police Forces with Military Status. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Roumanie". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2018. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Romania Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 30 January 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Qatar". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Qatar Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 21 August 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Russie". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2018. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ McDermott, Roger (12 April 2016). "Countering Color Revolution Drives Russia's Creation of National Guard". Eurasia Daily Monitor. 13 (71) – via The Jamestown Foundation.
- ^ "San Marino - Gendarmeria - Presentazione". www.gendarmeria.sm (in Italian). Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Sénégal". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2022. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Senegal Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 16 May 2022. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Serbie". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2017. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "Espagne". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2019. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "Spain Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 22 February 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "Togo". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French). 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "Togo Country Security Report". www.osac.gov. Overseas Security Advisory Council. 26 June 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "Observers". eurogendfor.org. European Gendarmerie Force. Archived from the original on 1 January 2014.
- ^ 14 U.S.C. § 1
- ^ Arcudi, Giovanni; Smith, Michael E. (2013). "The European Gendarmerie Force: A solution in search of problems?". European Security. 22: 1–20. doi:10.1080/09662839.2012.747511.
- ^ a b "Insígnias". Polícia Militar do Estado de São Paulo (in Portuguese). Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- ^ a b "Ranks of the Force". rcmp-grc.gc.ca. Royal Canadian Mounted Police. 21 May 2015. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ a b "Grades appellations distinctions". defense.gouv.cg (in French). Ministry of National Defense (Republic of the Congo). Retrieved 7 June 2021.
- ^ "असम राइफल्स विनियमन 2016 - Assam Rifles Regulation 2016" (PDF). 18 November 2016. Retrieved 20 August 2022.
- ^ "Two Hundred Thirteenth Report - Security Situation in the North Eastern States of India" (PDF). Department-Related Parliamentary Standing Committee on Home Affairs. 19 July 2018. pp. 6–8. Retrieved 21 August 2022.
- ^ "Distintivi di grado: Ufficiali." Carabinieri. Retrieved 2020-03-11.
- ^ a b "De rangonderscheidingstekens van de krijgsmacht" (PDF) (in Dutch). Ministry of Defence (Netherlands). 19 December 2016. Retrieved 18 March 2021.
- ^ a b Bureau international des droits des enfants (December 2012). "État des Lieux: Formation des forces de défense et de sécurité sur les droit de l'enfant au Niger" (PDF) (in French). p. 34. Retrieved 28 September 2020.
- ^ a b "Distintivos". gnr.pt (in Portuguese). Republican National Guard. Retrieved 11 May 2021.
- ^ a b "Lùhǎikōng jūnfú zhì tiáolì fù tú" 陸海空軍服制條例附圖 [Drawings of the Uniform Regulations of the Army, Navy and Air Force] (PDF). Gazette of the Presidential Palace (6769): 65–67. 7 November 1996. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 March 2017. Retrieved 15 August 2022.
- ^ a b "U.S. Military Rank Insignia". defense.gov. Department of Defense. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ "Two Hundred Thirteenth Report - Security Situation in the North Eastern States of India" (PDF). Department-Related Parliamentary Standing Committee on Home Affairs. 19 July 2018. pp. 6–8. Retrieved 21 August 2022.
- ^ "Distintivi di grado: Marescialli." Carabinieri. Retrieved 2020-03-11.
- ^ "Distintivi di grado: Brigadiere." Carabinieri. Retrieved 2020-03-11.
- ^ "Distintivi di grado: Appuntati e Carabinieri." Carabinieri. Retrieved 2020-03-11.
- ^ "Uzman Jandarma Kanunu" (PDF) (in Turkish). mevzuat.gov.tr. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 January 2018. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
- ^ "Uzman Erbaş Kanunu" (PDF) (in Turkish). mevzuat.gov.tr. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 March 2020. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
- ^ Perito, Robert (14 May 2012). "Afghanistan's Civil Order Police". United States Institute of Peace. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ United States. Department of Defense (December 2018). Enhancing Security and Stability In Afghanistan (PDF). pp. 42, 71. A-20E89FB. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ United States. Department of Defense (December 2020). Enhancing Security and Stability In Afghanistan (PDF). pp. 38, 40. 7-653B15D. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ a b "Historik i shkurtër i Policisë së shtetit shqiptar". asp.gov.al (in Albanian). 14 October 2016. Archived from the original on 14 October 2016.
- ^ Gebhardt, Helmut (July 2015). "The Military Organisation of the Habsburg Gendarmerie from 1849 to 1918" (PDF). SIAK-Journal − Journal for Police Science and Practice. (International Edition Vol. 5) (5): 85–95. doi:10.7396/IE_2015_H – via bmi.gv.at.
- ^ "Bénin". MUSÉE DE LA GENDARMERIE NATIONALE (in French and English). 2023. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Interior Troops Abolished, Units Merged with the Defense Ministry". civil.ge. 15 September 2004. Archived from the original on 16 August 2016.
- ^ "Military In Haitian History". globalsecurity.org. Archived from the original on 26 February 2016.
- ^ Emsley, Clive (1999), Gendarmes and the State in Nineteenth-Century Europe, Oxford University Press, pp. 246–247, 267, ISBN 978-0-19-820798-6,
Henry Goulburn...drafted a bill for a centralized, permanent armed constabulary linked to salaried police magistrates ... Even Grant condemned what he considered as an attempt 'to place the whole of Ireland under an armed police, to subject it to a species of gendarmerie'.
- ^ Replaced by the Royal Ulster Constabulary and the Garda Síochána on the partition of Ireland in 1922
- ^ 佐道明廣 (2017). 自衛隊史:日本防衛政策七十年. Translated by 趙翊達. 八旗文化、遠足文化. p. 37. ISBN 978-986-93844-1-4.
- ^ 松本昌悦; 尾崎利生; 箭川哲 (1988). 原典 日本憲法資料集. 創成社. p. 475. ISBN 978-4794440082.
- ^ "Mémorial A, 1999, No. 87" (PDF) (in French). Service central de législation. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 January 2006.
- ^ "Un día como hoy: se creó la Guardia Republicana del Perú". Federación de Periodistas del Perú (in Spanish). 7 August 2017.
- ^ https://www.armyupress.army.mil/Journals/Military-Review/English-Edition-Archives/September-October-2021/Cross-Philippine-Constabulary/
- ^ "History of the U. S. Constabulary 10 Jan 46 - 31 Dec 46". www.history.army.mil. 1947. Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- ^ Deep, Daniel (2012). Occupying Syria Under the French Mandate: Insurgency, Space and State Formation. Cambridge University Press. p. 204. ISBN 978-1-107-00006-3.
- ^ Podeh, Elie (1999), The Decline of Arab Unity: The Rise And Fall of the United Arab Republic, Sussex Academic Press, p. 54, ISBN 1-84519-146-3 – via Google Books
- ^ "Phraya Vasuthep: The Good Danish Soldier of Fortune". Scandasia. 17 August 2011.