Chilean jack mackerel
| Chilean jack mackerel | |
|---|---|

| |
| A school of about 400 tons of Chilean jack mackerel encircled by a purse seine | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Carangiformes |
| Suborder: | Carangoidei |
| Family: | Carangidae |
| Genus: | Trachurus |
| Species: | T. murphyi
|
| Binomial name | |
| Trachurus murphyi Nichols, 1920
| |
| |
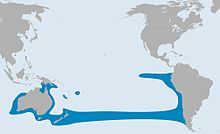
Estimated distribution
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
The Chilean jack mackerel (Trachurus murphyi), sometimes called the Jurel, Inca scad or Peruvian jack mackerel, is a species of jack mackerel in the genus Trachurus of the family Carangidae.[3] Since the 1970s, it has become one of the world's more important commercial fish species.[4] High volumes have been harvested, but the fishery may now be in danger of collapsing.[5][6]
Description
[edit]Chilean jack mackerels are commonly 45 cm (18 in) long, though they can grow to 70 cm (28 in). They have elongated and laterally compressed bodies. The head is large with well-developed transparent protective membranes (the adipose eyelid) covering the eyes. The mouth is also large, with the rear edge of the lower jaw aligning with the front edge of the eyes. It possesses small teeth. Each opercle of the gill covers has a distinct notch on its rear edge. The second dorsal fin is much longer than the first. The pectoral fins are long and pointed. The origin of the pelvic fins is below the bottom point of attachment of the pectorals. The anal fin is also long, but shorter than the second dorsal fin. At its front are two strong spines. The upper parts of the body are metallic blue in color, while the bottom surfaces are a silvery white.[4][2]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]The Chilean jack mackerel is an epipelagic fish that swims in schools around coasts and in the open ocean. Normally it swims at depths between 10 and 70 m, but it can swim as deep as 300 m.[4] They are found in the south Pacific off the coasts of Chile and Peru, around New Zealand and south Australia, and in a band across the open ocean in between.[4][2] In 1993, Elizarov et al. referred to this band on the high seas as the "jack mackerel belt".[7] The jack mackerel belt ranges from 35 to 45° S, which means it has a north–south breadth of 10° (about 1100 km). "Spawning groups concentrate mainly in the north of 40° S in spring and summer and south of 40° S in autumn and winter to feed".[7][8] Chilean jack mackerel normally spawn in summer. Their eggs are pelagic, that is, they float free in the open sea.[4]
Not enough data are available to know for sure the Chilean jack mackerel stock structure.[1] However, four separate stocks have been proposed: "a Chilean stock which is a straddling stock with respect to the high seas; a Peruvian stock which is also a straddling stock with the high seas; a central Pacific stock which exists solely in the high seas; and, a southwest Pacific stock which straddles the high seas and both the New Zealand and Australian EEZs."[8]
Ecology
[edit]Chilean jack mackerels mainly eat fish larvae, shrimp, and other small crustaceans such as copepods, although they also eat squid and small fishes. They can live up to 16 years.[4] Not a lot is known about their predators, though they have been found in the stomachs of albacore tuna and swordfish. Tunas, billfish, and sharks are known to prey on other carangid mackerels, and will presumably also prey on Chilean jack mackerels.[8]
Taxonomy and naming
[edit]The Chilean jack mackerel was original described in 1920 by the American ichthyologist John Treadwell Nichols (1883-1958), in 1996 Konchina et al treated it as a synonym of the Pacific jack mackerel (Trachurus symmetricus) but as a valid subspecies. It is treated as a valid species by most authorities.[9] The specific name honours the American ornithologist Robert Cushman Murphy (1887-1973), the Curator of Birds at the American Museum of Natural History, who collected the type.[10] Murphy collected the type off Central Island, Chincha Islands, Peru.[9]
The Chilean jack mackerel has been recognised as a sister species of the Pacific jack mackerel, Trachurus symmetricus, since 2004.[3][2][1][11]
Fisheries
[edit]This section needs to be updated. (March 2015) |
Chilean jack mackerels are the most commonly fished species which is not a true mackerel. They are caught commercially with surround nets designed for small pelagic purse seining, or with midwater trawls, or by trolling or longlining.[4][8][13]
In the early 1970s, Chilean jack mackerels started flourishing along the west coast of South America, and became important as a commercial species. The mackerel then expanded in a westward movement out into and across the open ocean, eventually reaching the coastal waters around New Zealand and Australia.[8] During 1997 and 1998, a precipitous decline occurred in the catch (see the graph on the right), which can be attributed to changes in the sea surface temperature that accompanied the 1997–98 El Niño.[14]
On the eastern side of the south Pacific, the Chilean fishery operating mainly within its own EEZ has taken 75% of the global catch over the years. The Peruvian fishery captured 800,000 tonnes in 2001, but overall is an order of magnitude smaller.[8] On the western side of the south Pacific, New Zealand fishes jack mackerel mainly inside their own EEZ, peaking modestly at 25,000 tonnes in 1995–96. From 1978 to 1991, the USSR fishing fleet intensively fished the jack mackerel belt on the high seas, taking 13 million tonnes. In subsequent years, other distant fishing nations, such as Belize, China, the Netherlands, and the Republic of Korea, have joined Russia fishing the jack mackerel belt, and by 2007, these nations were taking 18% of the global catch.[8]
There are fears the fishery may collapse due to overfishing.[15] From 2006 to 2011, the biomass of the stocks declined another 63%.[6] Fisheries scientists provisionally estimated in 2011 that to achieve the maximum sustainable yield a spawning biomass of about 7.4 million tons was required with a fishing mortality rate of 0.15.[16] If the spawning stock is to rebuild, current catches should probably be less than 390,000 tons.[16]
New data and indicators on the status of the jack mackerel stock suggest that conditions evaluated in detail from the last benchmark assessment (2022) are relatively unchanged. The population trend is estimated to be increasing. The indications of stock improvement (higher abundance observed in the acoustic survey in the northern part of Chile, better catch rates apparent in all fisheries for which data are available, and increase in average age in the Chilean fisheries) drive the increase. Near term spawning biomass is expected to increase from the 2018 estimate of 4.8 million t to 5.6 million t in 2019 (with approximate 90% confidence bounds of 4.5 – 7.0 million t) [17]
In Chile, a small number of wealthy families own 87% of the jack mackerel harvest. With government agreement, they have been allocated quotas which scientists say are not sustainable.[18] In 2012, a heated dispute developed between Peru and Chile over the fishing of the mackerel.[5][19] Attempts have been made since 2006 to empower the South Pacific Regional Management Organisation so it can effectively regulate the jack mackerel industry on the high seas and across national boundaries. Geopolitical rivalries and lack of international cooperation is preventing this.[6] In an interview with the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, the French marine biologist Daniel Pauly compared jack mackerels to American bison, whose populations also collapsed in the 19th century from overhunting: "This is the last of the buffaloes. When they’re gone, everything will be gone ... This is the closing of the frontier."[6]
As a way to protect the migrating mackerel, in 2013 the countries Chile, Peru, New Zealand and Australia, as well as six more agreed to form the "South Pacific Regional Fishing Management Organisation (RFMO)". The act has led to significant improvements; in 2019 the species had already recovered to a degree similar to the population in the 1990s.[20]
As food
[edit]Chilean jack mackerels are canned or marketed fresh for human consumption;[4] they are a staple food in Africa. They are also processed into fishmeal, which is fed to swine and salmon; five kilograms of jack mackerel are needed to raise one kilogram of farmed salmon.[6]
Similar species
[edit]The Chilean jack mackerel looks very much like the greenback horse mackerel (Trachurus declivis) found around Australia and New Zealand. The two species can be distinguished by the number of gill rakers (T. declivis 50–57, T. murphyi 51–65) and the number of scales and scutes in the lateral line (T. declivis 81–82, T. murphyi 89–113).[4]
All three species are found schooling around the coast of New Zealand. They are mainly captured using purse seine nets, and are managed as though they were one species or stock.[21]
In its statistical returns, the FAO still treats the Pacific jack mackerel as though it were a subspecies.[4] The capture graph in the fisheries section above is based on the figures supplied by the FAO for the capture of Chilean jack mackerel, and presumably includes also the capture amounts for Pacific jack mackerel.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Smith-Vaniz, B.; Robertson, R.; Dominici-Arosemena, A. (2010). "Trachurus murphyi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2010: e.T183965A8207652. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-3.RLTS.T183965A8207652.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ a b c d Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Trachurus murphyi". FishBase. August 2019 version.
- ^ a b "Trachurus murphyi". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 8 March 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Trachurus murphyi (Nichols, 1920) FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved 2 March 2012.
- ^ a b In mackerel's plunder, hints of epic fish collapse The New York Times, 25 January 2012.
- ^ a b c d e Jack mackerel, down 90 percent in 20 years in once-rich southern seas, foretells wider global calamity; world’s largest trawlers compete for what is left Archived 2012-03-18 at the Wayback Machine iWatch News, 25 January 2012.
- ^ a b Elizarov AA, Grechina AS, Kotenev BN and Kuzetsov AN (1993)" "Peruvian jack mackerel, Trachurus symmetricus murphyi, in the open waters of the South Pacific" Journal of Ichthyology, 33: 86–104.
- ^ a b c d e f g SPRFMO (2009) Information describing Chilean jack mackerel (Trachurus murphyi) fisheries relating to the South Pacific Regional Fishery Management Organisation Archived 2013-02-27 at the Wayback Machine Working draft.
- ^ a b Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Trachurus murphyi". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ Christopher Scharpf; Kenneth J. Lazara (10 August 2019). "Order CARANGIFORMES (Jacks)". The ETYFish Project Fish Name Etymology Database. Christopher Scharpf and Kenneth J. Lazara. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ a b Poulin E, Cárdenas L, Hernández CE, Kornfield I and Ojeda FP (2004) "Resolution of the taxonomic status of Chilean and Californian jack mackerels using mitochondrial DNA sequence Journal of Fish Biology, 65 (4): 1160–1164. doi:10.1111/j.0022-1112.2004.00514.x
- ^ "Fisheries and Aquaculture - Global Production". Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Retrieved 2024-05-06.
- ^ Surrounding nets Fishing Gear Types, FAO, Rome. Retrieved 13 March 2012.
- ^ Arcos DF, Cubillos LA and Núñez SP (2001) "The jack mackerel fishery and El Niño 1997–98 effects off Chile" Progress In Oceanography, 49 (1–4): 597–617.
- ^ Preventing the collapse of one of the world’s largest fisheries Digital Journal, 14 February 2012.
- ^ a b Report of the Jack Mackerel Subgroup Archived 2013-02-27 at the Wayback Machine South Pacific Regional Management Organisation, Annex SWG-10-03, Report of the Science Working Group, 19–23 September 2011.
- ^ "FIRMS - Marine Resource fact sheets - Jack mackerel - Southeast Pacific".
- ^ Lords of the fish Archived 2012-03-20 at the Wayback Machine iWatch News, 25 January 2012.
- ^ Peru and Chile in heated dispute over Jack Mackerel overfishing Digital Journal, 8 February 2012.
- ^ "Chilean Jack Mackerel: Bust To Boom". MSC International - English. Retrieved 2024-08-03.
- ^ Jack Mackerel Archived 2012-03-05 at the Wayback Machine NZ Forest and Bird. Retrieved 13 March 2012.
- Sources
- Angel A and Ojeda FP (2001) "Structure and trophic organization of subtidal fish assemblages on the northern Chilean coast: the effect of habitat complexity" Marine Ecology Progress Series, 217: 81–91. doi:10.1016/S0079-6611(01)00043-X
- Arnaud Bertranda A, Barbierib MA, Hernández C, Gómezc F and Leiva F (2004) "Diel vertical behaviour, predator–prey relationships, and occupation of space by jack mackerel (Trachurus murphyi) off Chile" Journal of Marine Science, 61 (7): 1105–1112. doi:10.1016/j.icesjms.2004.06.010
- Bailey K (1989) "Description and surface distribution of juvenile Peruvian jack mackerel, Trachurus murphyi, Nichols from the subtropical convergence zone of the central South Pacific" Fishery Bulletin, 87: 273–278.
- Bertrand A, MA Barbieri, F Gerlotto, F Leiva and J Cordova (2006) "Determinism and plasticity of fish schooling behaviour as exemplified by the South Pacific jack mackerel Trachurus murphyi"[permanent dead link] Marine Ecology Progress Series, 311: 145–156.
- Canales C and R Serra (2008) "Updated Status of the Chilean Jack Mackerel Stock" FAO: South Pacific Regional Management Organisation, Chilean Jack Workshop, CHJMWS:6..
- Cárdenas L, Silva AX, Magoulas A, Cabezas J, Poulinc E and Ojeda FP (2009) "Genetic population structure in the Chilean jack mackerel, Trachurus murphyi (Nichols) across the South-eastern Pacific Ocean"[permanent dead link] Fisheries Research, 100: 109–115.
- Cubillos LA, Paramo J, Ruiz P, Nunez S, Sepulveda A (2008) "The spatial structure of the oceanic spawning of jack mackerel (Trachurus murphyi) off central Chile (1998–2001)" Fisheries Research, 90: 261–270.
- Durand NS and Seminario MG (2009) "Status of and trends in the use of small pelagic fish species for reduction fisheries and for human consumption in Peru" Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper, 518: 325–369. FAO, Rome.
- Kawahara S, Uozumi Y and Yamada H (1988) "First record of a carangid fish, Trachurus murphyi from New Zealand" Japanese Journal of Ichthyology, 35 (2): 212–214. doi:10.1007/BF02905408
- Ñiquen M and Bouchon M (2004) "Impact of El Niño events on pelagic fisheries in Peruvian waters" Oceanography of the Eastern Pacific: Volume III, 51 (6–9): 563–574.
- FAO workshop
- Meeting documents FAO: South Pacific Regional Management Organisation, Chilean Jack Workshop, 30 June to 4 July 2008.
- Canales C (2008) "Catch per Unit Effort of Chilean Jack Mackerel (Trachurus murphyi) of the purse seine fishery off south-central Chile (32° 10′ – 40° 10′ S) 1981–2005 FAO: South Pacific Regional Management Organisation, Chilean Jack Workshop, CHJMWS:10.
- Núñez S, S Vásquez, P Ruiz and A Sepúlveda (2008) "Distribution of early developmental stages of jack mackerel in the Southeastern Pacific Ocean" FAO: South Pacific Regional Management Organisation, Chilean Jack Workshop, CHJMWS:2.
- Peña, Hector (2008) "In situ target-strength measurements of Chilean jack mackerel (Trachurus symmetricus murphyi) collected with a scientific echosounder installed on a fishing vessel" ICES J. Mar. Sci. 65 (4): 594–604. {doi|10.1093/icesjms/fsn043}
- Penney A and P Taylor (2008) "An Overview of the New Zealand Jack Mackerel Fishery: Catch Composition, Catch Trends, Seasonality and Length-Frequency Composition" FAO: South Pacific Regional Management Organisation, Chilean Jack Workshop, CHJMWS:19.
- Vasilyev D and A Glubokov (2008) "Preliminary estimation of current state of Chilean Jack Mackerel (Trachurus murhyi) stock in the high seas of the South East Pacific" FAO: South Pacific Regional Management Organisation, Chilean Jack Workshop, CHJMWS:22.
External links
[edit]- Crisis management and jack mackerel fishing in the south Pacific Greenpeace briefing, 25 January 2012.
- Nesterov AA and Chu VN "El-Nino and distribution of Jack mackerel (Trachurus murphyi) in the open part (outside 200-mile zone) of the South-Eastern Pacific Ocean"[permanent dead link] Atlantic Research Institute of Marine Fisheries and Oceanography.
- Outcome of the Third Preparatory Conference of The South Pacific Regional Fisheries Management Organization WWF draft statement, 3 February 2012.







