1943 in paleontology
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| +... | |||
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils.[1] This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1943.
Dinosaurs
[edit]Newly named dinosaurs
[edit]Data are courtesy of George Olshevky's dinosaur genera list.[2]
| Name | Status | Authors | Location | Notes | Images | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pachycephalosaurus[3] | Valid taxon |
|
|
A large pachycephalosaurid |  | |
Plesiosaurs
[edit]New taxa
[edit]
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Synapsids
[edit]Non-mammalian
[edit]| Name | Status | Authors | Age | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Valid |
Romer | 237 millions of years ago | The Dicinodont with terrible teeth. | 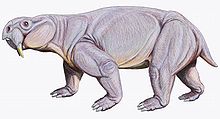  | ||
|
Valid |
Cabrera | 226 millions of years ago | This was a plant-eating Cynodont. | |||
|
Valid |
References
[edit]- ^ Gini-Newman, Garfield; Graham, Elizabeth (2001). Echoes from the past: world history to the 16th century. Toronto: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. ISBN 9780070887398. OCLC 46769716.
- ^ Olshevsky, George. "Dinogeorge's Dinosaur Genera List". Archived from the original on 2011-07-15. Retrieved 2008-08-07.
- ^ Brown, B. and E.M. Schlaikjer. 1943. A study of the troodont dinosaurs with the description of a new genus and four new species. Bull. Am. Museum. Nat. Hist. 82: pp. 121-149.

