Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017
| Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017 | |
|---|---|
 Totality from Madras, Oregon | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.4367 |
| Magnitude | 1.0306 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 160 s (2 min 40 s) |
| Coordinates | 37°00′N 87°42′W / 37°N 87.7°W |
| Max. width of band | 115 km (71 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 15:46:48 |
| (U1) Total begin | 16:48:32 |
| Greatest eclipse | 18:26:40 |
| (U4) Total end | 20:01:35 |
| (P4) Partial end | 21:04:19 |
| References | |
| Saros | 145 (22 of 77) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9546 |
On Monday, August 21, 2017, a total solar eclipse will be visible within a band across the entire contiguous United States. This eclipse will only be visible in other countries as a partial eclipse.[1][2]
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon's apparent diameter is larger than the sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometers wide.
The last time a total solar eclipse was visible across the entire contiguous United States was during the June 8, 1918 eclipse, and not since the February 1979 eclipse has a total eclipse been visible from anywhere in the mainland United States.[3] The path of totality will touch 14 states, although a partial eclipse will be visible in all fifty states.[3] The total area of the path of totality will be about 16% of the area of the United States,[4] although most of this area is over the ocean and not actually over the United States. The event will touch land on the Oregon coast as a partial eclipse at 9:06 a.m. PDT on August 21, and will end later that day as a partial eclipse along the South Carolina coast at about 4:06 p.m. EDT.[3]
There are expected to be logistical problems with the influx of visitors, especially for smaller communities.[5][6] There have also been problems with counterfeit eclipse glasses being sold.[7][8]
Future total solar eclipses will cross the United States in April 2024 (12 states) and August 2045 (10 states), and annular solar eclipses—meaning the apparent size of the Moon is smaller than that of the Sun—will occur in October 2023 (9 states) and June 2048 (9 states).
Visibility

The total eclipse will have a magnitude of 1.0306 and will be visible within a narrow corridor 70 miles (110 km) wide crossing fourteen states of the contiguous United States: Oregon, Idaho, Wyoming, Montana, Iowa, Kansas, Nebraska, Missouri, Illinois, Kentucky, Tennessee, Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina.[9][10] It will be first seen from land in the US shortly after 10:15 a.m. PDT (17:15 UTC) at Oregon's Pacific coast, and then it will progress eastward through Salem, Oregon; Casper, Wyoming; Lincoln, Nebraska; Kansas City, Missouri; St. Louis, Missouri; Hopkinsville, Kentucky; Nashville, Tennessee; Columbia, South Carolina; and finally Charleston, South Carolina. (A partial eclipse will be seen for a greater time period, beginning shortly after 9:00 a.m. PDT along the Pacific Coast of Oregon.)
The longest duration of totality will be 2 minutes 41.6 seconds at about 37°35′0″N 89°7′0″W / 37.58333°N 89.11667°W in Giant City State Park, just south of Carbondale, Illinois, and the greatest extent (width) will be at 36°58′0″N 87°40′18″W / 36.96667°N 87.67167°W near the village of Cerulean, Kentucky, located in between Hopkinsville and Princeton.[11] This will be the first total solar eclipse visible from the Southeastern United States since the solar eclipse of March 7, 1970, which was only visible from Florida.
A partial solar eclipse will be seen from the much broader path of the Moon's penumbra, including all of North America, northern South America, Western Europe, and some of Africa and north-east of Asia.
Related eclipses over the United States

This eclipse will be the first total solar eclipse visible from the United States since the solar eclipse of July 11, 1991[12] (which was seen only from part of Hawaii),[13] and the first visible from the contiguous United States since 1979.[14]
The path of totality of the solar eclipse of February 26, 1979 passed only through the states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Montana, and North Dakota. Many visitors traveled to the Pacific Northwest to view the eclipse, since it was the last chance to view a total solar eclipse in the contiguous United States for almost four decades.[15][16]
Some American scientists and interested amateurs seeking to experience a total eclipse participated in a four-day Atlantic Ocean cruise to view the solar eclipse of July 10, 1972 as it passed near Nova Scotia. Organizers of the cruise advertised in astronomical journals and in planetarium announcements emphasizing the lack of future total eclipses observable in U.S. until this 2017 event.[17]
The August 2017 eclipse will be the first with a path of totality crossing the Pacific and Atlantic coasts of the U.S. since 1918. Also, its path of totality makes landfall exclusively within the United States, making it the first such eclipse since the country's independence in 1776. (The path of totality of the eclipse of June 13, 1257, was the last to make landfall exclusively on lands currently part of the United States.[18])
The path of this eclipse crosses the path of the upcoming total solar eclipse of April 8, 2024, with the intersection of the two paths being in southern Illinois in Makanda Township at Cedar Lake just south of Carbondale. A small land area, including the cities of Makanda, Carbondale, Cape Girardeau, Missouri, and Paducah, Kentucky, will thus experience two total solar eclipses within a span of less than seven years.
The solar eclipse of August 12, 2045 will have a very similar path of totality over the U.S., about 400 km (250 mi) to the southwest, also crossing the Pacific and Atlantic coasts of the country; however, duration of totality will last over twice as long.[19]
An eclipse of comparable length (up to 3 minutes, 8 seconds, with the longest eclipse being 6 minutes and 54 seconds) occurred over the contiguous United States on March 7, 1970 along the southern portions of the Eastern Seaboard, from Florida to Virginia.[20]
Total eclipse viewing events

Oregon
- Corvallis – The Corvallis campus of Oregon State University will host OSU150 Space Grant Festival: A Total Eclipse Experience a weekend-long celebration of the eclipse. A watch party will also be hosted on campus the day of the eclipse.
- Keizer – The Salem-Keizer Volcanoes a Class A baseball team will play a morning game that will feature the first ever "eclipse delay" in baseball history.[21]
- Madras – The city will sponsor a four-day Solarfest at two locations.[22][23]
- Prineville – Symbiosis Gathering will be hosting a global eclipse gathering.[24] Dubbed Oregon Eclipse.[25]
- Salem – The Oregon Museum of Science and Industry will host an event at the Oregon State Fairgrounds.[26]
Idaho

- Craters of the Moon – The National Monument and Preserve will host NASA presentations, evening star parties hosted by the Idaho Falls Astronomical Society, high altitude balloon launches by the USC Astronautical Engineering department and NASA, and presentations by the New Mexico Chapter of the Charlie Bates Solar Astronomy Project.[27]
- Idaho Falls – Free entertainment and educational seminars and an eclipse-watching event at the Museum of Idaho (an official NASA viewing site) and elsewhere, and a free eclipse-watching event at Melaleuca Field.[28][29]
- Rexburg – Brigham Young University Idaho will offer a series of eclipse related educational events.[30]
- Weiser – The city will sponsor a five-day festival prior to the eclipse.[31]
Wyoming
- Casper – The Astronomical League, an alliance of amateur astronomy clubs, will hold its annual Astrocon conference,[32] and there will be other public events, called Wyoming Eclipse Festival 2017.[33]
Nebraska
- Alliance – Entertainment and educational seminars will be offered.[34]
- Auburn – Nemaha County Hospital will host an eclipse viewing event, including sharing safety tips from Lifetime Vision Center. The event is sponsored by Auburn State Theater.[35]
- Grand Island – Stuhr Museum will host an eclipse viewing event, including the launch of a NASA eclipse observing balloon.[36]
- Beatrice – Homestead National Monument of America – Events with NASA Saturday, Sunday and the day of the eclipse homestead events page[37]
Missouri
- Arnold, Missouri – The Parks & Recreation Department of the City of Arnold (which fell in the path of the totality) organized a free three-day event in Arnold City Park in anticipation of (and culminating in) the eclipse, complete with educational activities for children and a bluegrass festival. Viewing glasses were made available for the eclipse itself.[38]
- Kansas City – A 5-mile bicycle ride from downtown KCMO (where totality will only last about 30 seconds) to Macken Park in North Kansas City (where totality will last 1 minute 13 seconds) has been organized by KC Pedal Party Club, a local Meetup group.[39]
- Columbia – The COSMO Park and the GANS CREEK Park are open for the eclipse.[40] For the Students of the University of Missouri-Columbia there is a watch party on the campus.[41] and the MU Health care has also released eye safety info.[42]
- Lathrop – The city will celebrate its 150th anniversary with an eclipse festival.[43]
- Parkville – TotalEclipseofthePark – August 20 educational program featuring NASA Glenn Research Center Hall of Famer Lynn Bondurant, '61, and August 21 watch party organized by Park University.[44]
- St. Clair – An event organized by the St. Clair City Chamber of Commerce.[45]
- St. Joseph – An event organized by Front Page Science will be held at Rosecrans Memorial Airport.[46]
Illinois
- Carbondale – The area is calling itself the Eclipse Crossroads of America since it will also be in totality during the solar eclipse of April 8, 2024, and since Giant City State Park, just south of the city, will experience the longest period of totality during the eclipse (approximately 2 minutes and 40 seconds). Southern Illinois University will sponsor many eclipse related educational events, including the two day Crossroads Astronomy, Science and Technology Expo, and viewing at Saluki Stadium.[47] Amtrak will run a special train, the Eclipse Express, from Chicago to Carbondale.[48]
- Carterville – A three-day rock festival called Moonstock will be headlined by Ozzy Osbourne, who will perform during the eclipse.[49]
- Goreville – View the eclipse with the University of Illinois Astronomy Department.[50]
Kansas
- Atchison — Benedictine College will host thousands in its football stadium. There will be students from schools from Kansas, Missouri, Nebraska and Oklahoma attending, plus numerous other guests who will hear from, amongst others, astronomers from the Vatican Observatory.[51]
Kentucky
- Bowling Green — Western Kentucky University will host thousands of K-12 students in its football stadium.[52]
- Hopkinsville – A four-day eclipse festival will be held at Jefferson Davis State Historic Site.[53]
Tennessee
- Clarksville – Austin Peay State University will present several educational events, including an appearance by astronaut Rhea Seddon.[54]
- Cookeville – Tennessee Technological University will be hosting a solar eclipse viewing party at Tucker Stadium, which is open to the public. Cookeville will be hosting special events Saturday-Monday.[55]
- McMinnville - celebrating the eclipse by hosting BLACKOUT 2017, an eclipse viewing event to be held in the city square. In addition to the viewing, a selection of food trucks and musical acts which features The Pink Floyd Appreciation Society band who will be performing Pink Floyd's The Dark Side of the Moon in its entirety prior to the totality event. [56]
- Nashville – offering many special events, including the Music City Eclipse Science & Technology Festival at the Adventure Science Center.[57] The Italian Lights Festival is hosting the largest Eclipse Viewing Party in Nashville, a free NASA-Certified Eclipse Event held at the Bicentennial Mall.[58] Two astrophysicists from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory will emcee the countdown.[59]
North Carolina
- Bryson City – Planetarium shows will be offered, as well as rides on the Great Smoky Mountains Railroad to an eclipse location.[60]
- Rosman – Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute (PARI) will be hosting a viewing event. The event at PARI has garnered international attention and the visitors will include amateur astronomers.
Georgia
- Blairsville, Get off the Grid Festival[61]
South Carolina
- Columbia – The South Carolina State Museum will host four days of educational events, including an appearance by Apollo 16 astronaut Charles Duke.[62]
- Greenville – Viewing at Furman University.[63] Events include streaming coverage from NASA, educational activities, and live music.[64]
Viewing from outside the United States

Canada
A partial eclipse will be visible across the width of Canada, ranging from 89% in Victoria, British Columbia to 11% in Resolute, Nunavut.[65]
Central America, Mexico, Caribbean islands
A partial eclipse will be visible from Central America, Mexico, and the Caribbean islands.
Europe
In northwestern Europe, the eclipse will only be visible partially, in the evening or at sunset. Only those in Iceland, Ireland, Northern Ireland, Scotland and the Portuguese Azores archipelago will see the eclipse from beginning to end; in the rest of the UK, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Spain and Portugal, sunset will occur before the end of the eclipse. In Germany, the beginning of the eclipse will be potentially visible just at sunset only in the extreme northwest of the country. In all regions east of the orange line in the map, the eclipse will not be visible.[66]
Russia
A partial eclipse will be visible only in the Chukchi Peninsula (with about ~40%).
Media coverage
A large number of media outlets also announced plans to broadcast coverage of the eclipse, including television and internet outlets. NASA announced plans to offer streaming coverage through its NASA TV and NASA Edge outlets, using cameras stationed on the ground along the path of totality, along with cameras on high-altitude balloons, jets, and coverage from the International Space Station; NASA stated that "never before will a celestial event be viewed by so many and explored from so many vantage points—from space, from the air, and from the ground."[67] ABC, CBS, and NBC announced that they would respectively broadcast live television specials to cover the eclipse with correspondents stationed across the path of totality, along with CNN, Fox News Channel, Science, and The Weather Channel. The PBS series Nova will present streaming coverage on Facebook hosted by Miles O'Brien, and air a special episode chronicling the event—"Eclipse Over America"—later in the day (which will mark the fastest production turnaround time in Nova history).[68][69]
Other institutions and services also announced plans to stream their perspectives of the eclipse, including the Exploratorium in San Francisco, the Elephant Sanctuary of Hohenwald, Slooh, and The Virtual Telescope Project. The Eclipse Ballooning Project, a consortium of schools and colleges that will send 50 high-altitude balloons into the sky during the eclipse to conduct experiments, will provide streams of footage and GPS tracking of its launches [67][70]
Problem of counterfeit eclipse glasses
| External image | |
|---|---|
Many counterfeit glasses tested have actually been found to have been good enough, but the only way to tell for sure is with a spectrophotomer.[7] The issue is whether the glasses will block the full spectrum of light, including ultraviolet and infrared light. The eye's retina does not contain pain receptors, so with inadequate protection, infrared radiation could potentially be damaging and "cooking" this retina without the person being aware of it.[72]
Counterfeit eclipse glasses often have the same ISO number and company name as genuine classes. The American Astronomical Society has issued guidance and a list of reputable vendors of solar filtering products. The user should be able to see very little through adequate filter except for the Sun itself, or something comparably bright, such as the Sun reflected in a mirror, a sunglint off shiny metal, the hot filament of an unfrosted incandescent bulb, a bright halogen light bulb, a bright-white LED bulb (including the flashlight on a smartphone), or an arc-welding torch. All such sources, except perhaps the welding torch, should appear quite dim.[7][8][72]
A large number of untested filtering glasses began to proliferate on websites such as Amazon.com during the lead-up to the eclipse, including those that claimed to have ISO certification but did not undergo actual testing or had incomplete certification information, and those that were counterfeits of those from vendors the AAS considered reputable such as, in particular, American Paper Optics, which published information detailing the differences between its glasses and counterfeits.[71] On July 27, 2017, Amazon began to require that all eclipse viewing products sold on its website have a submission of origin and safety information, and proof of an accredited ISO certification. In mid-August 2017, Amazon recalled and pulled listings for eclipse viewing glasses that "may not comply with industry standards", and issued refunds to those that had purchased them.[7][8][73]
Further images
-
August 21, 2017 total solar eclipse
-
Animation
-
Umbra (black oval), penumbra (concentric shaded ovals), and path of totality (red).
-
High-resolution map of the path in the United States.
-
This video features several visualizations of the event.
Planning
Logistically, the demand for portable toilets will be "astronomical,"[74] with municipalities inside and alongside the path of totality planning (in some cases for three years, with the participation of several levels of governance, as with southern Illinois) for the sudden influx of people.[75] Volunteers in smaller towns (as with Lathrop, Missouri, which will be coincidentally celebrating the 150th anniversary of its founding) struggled to arrange viewing sites and logistics for what could be either a tourism boom or a disaster.[5]
In the American West, illegal camping is a major concern, including near cities like Jackson Hole, Wyoming.[6] Idaho's Office of Emergency Management noted that Idaho was a prime viewing state, and advised jurisdictions to prepare for increased loads on their services; nearly every hotel and motel room, campground, and in some cases backyards for nearly 100 miles (160 km) miles north and south of the path of totality had been reserved several months if not years in advance.[76] The state's population may temporarily increase by a third, with 370,000 to 500,000 visitors projected in state of 1.6 million people.[77]
Oregon Governor Kate Brown authorized the deployment of the National Guard (six aircraft and approximately 150 soldiers), given that the sudden influx of tourists will occur during the peak of that state's fire season; the soldiers will perforce also be available for fire-fighting duties if needed.[78] Furthermore, given that the expected increase in population of one million will closely mimic the increased demand in emergency services, hospital staffing will be augmented (overnight tents will be provided), as well as blood supplies and anti-snake bite antidote (which has a short shelf-life) along the totality line. The emergency room of the hospital of Madras, Oregon (population 6,700), for example, is anticipating a six-fold increase in patients; as the hospital only has 25 beds, medical evacuation is anticipated.[79] The closest precedent for statewide planners is the annual Sturgis motorcycle rally in South Dakota, when approximately half a million people descend on the town.[79]
Traffic problems
In Oregon at one point on August 17, four days before the eclipse itself, traffic was backed up for fifteen miles on U.S. Highway 26 near Prineville, the turnoff to an eclipse festival, as thousands arrived; some gas stations there and in Bend had briefly run out of product the day before.[80]
Impact on solar power
The eclipse will cause a reduction of solar power where the shadow reaches solar panels. The North American Electric Reliability Corporation measures impacts of this event,[81] and predicts minor impacts.[82] In California, solar power may decrease by 4–6,000 megawatts[83] at 70 MW/minute, and then ramp up by 90 MW/minute as the shadow passes. CAISO's typical ramp rate is 29 megawatts per minute.[84] Around 4 GW mainly in North Carolina and Georgia are expected to be 90% obscured.[83] The Solar eclipse of March 20, 2015 caused manageable solar power decreases in Europe;[85] in Germany, solar power dropped from 14 GW to 7 GW, of a 38 GW solar power capacity.[86]
Commemorative stamp
On June 20, 2017,[87] the United States Postal Service released the first application of thermochromic ink to postage stamps in its Total Eclipse of the Sun Forever stamp[88] to commemorate the solar eclipse of August 21, 2017. When pressed with a finger, body heat turns the black circle in the center of the stamp into an image of the full moon. The stamp image is a photo of the solar eclipse of March 29, 2006 seen in Jalu, Libya. The photo was taken by retired NASA astrophysicist Fred Espenak.[88]
Related eclipses
A partial lunar eclipse took place on August 7, 2017, in the same eclipse season. It was visible over eastern Europe, Africa, Asia, and Australia.
Solar eclipses 2015–2018
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[89]
The partial solar eclipse on July 13, 2018 occurs in the next lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2015 to 2018 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
120 Totality in Longyearbyen, Svalbard |
March 20, 2015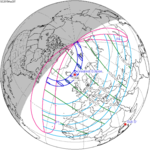 Total |
0.94536 | 125 Solar Dynamics Observatory |
September 13, 2015  Partial |
−1.10039 | |
130 Balikpapan, Indonesia |
March 9, 2016 Total |
0.26092 | 135 Annularity in L'Étang-Salé, Réunion |
September 1, 2016 Annular |
−0.33301 | |
140 Partial from Buenos Aires, Argentina |
February 26, 2017 Annular |
−0.45780 | 145 Totality in Madras, OR, USA |
August 21, 2017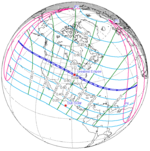 Total |
0.43671 | |
150 Partial in Olivos, Buenos Aires, Argentina |
February 15, 2018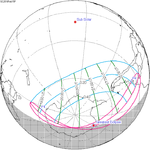 Partial |
−1.21163 | 155 Partial in Huittinen, Finland |
August 11, 2018 Partial |
1.14758 | |
Saros series 145
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 145, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 77 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on January 4, 1639. It contains an annular eclipse on June 6, 1891; a hybrid eclipse on June 17, 1909; and total eclipses from June 29, 1927 through September 9, 2648. The series ends at member 77 as a partial eclipse on April 17, 3009. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of annularity was produced by member 15 at 6 seconds (by default) on June 6, 1891, and the longest duration of totality will be produced by member 50 at 7 minutes, 12 seconds on June 25, 2522. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit.[90]
| Series members 10–32 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 11 | 12 |
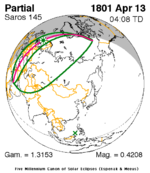 April 13, 1801 |
 April 24, 1819 |
 May 4, 1837 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 |
 May 16, 1855 |
 May 26, 1873 |
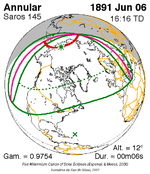 June 6, 1891 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 |
 June 17, 1909 |
 June 29, 1927 |
 July 9, 1945 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 |
 July 20, 1963 |
 July 31, 1981 |
 August 11, 1999 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 |
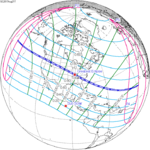 August 21, 2017 |
 September 2, 2035 |
 September 12, 2053 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 |
 September 23, 2071 |
 October 4, 2089 |
 October 16, 2107 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 |
 October 26, 2125 |
 November 7, 2143 |
 November 17, 2161 |
| 31 | 32 | |
 November 28, 2179 |
 December 9, 2197 | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 20 eclipse events between June 10, 1964 and August 21, 2036 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 10–11 | March 28–29 | January 14–16 | November 3 | August 21–22 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 June 10, 1964 |
 March 28, 1968 |
 January 16, 1972 |
 November 3, 1975 |
 August 22, 1979 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 June 11, 1983 |
 March 29, 1987 |
 January 15, 1991 |
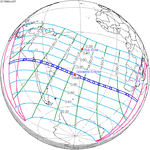 November 3, 1994 |
 August 22, 1998 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
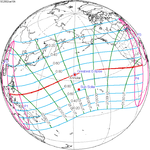 June 10, 2002 |
 March 29, 2006 |
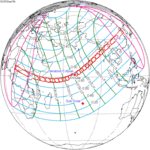 January 15, 2010 |
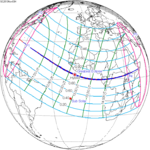 November 3, 2013 |
 August 21, 2017 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 10, 2021 |
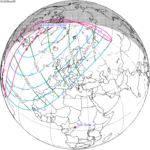 March 29, 2025 |
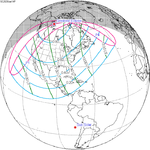 January 14, 2029 |
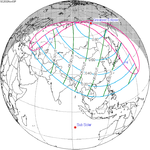 November 3, 2032 |
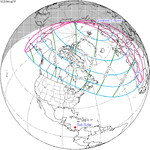 August 21, 2036 |
See also
Notable total solar eclipses crossing the United States from 1900 to 2050:
- Solar eclipse of June 8, 1918
- Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017
- Solar eclipse of April 8, 2024
- Solar eclipse of August 12, 2045
Notable annular solar eclipses crossing the United States from 1900 to 2050:
References
- ^ Fraknoi, A.; Schatz, D.; Shore, L. (2015). "The Great American Eclipse of 2017: An Outreach Opportunity and Challenge" (PDF). Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series. 500, Celebrating Science: Putting Education Best Practices to Work: 55. Retrieved July 3, 2017.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Tracing The Path Of The Solar Eclipse Across The U.S. On August 21, 2017 | Solar Eclipse 2017 on YouTube published on Aug 2, 2017 TIME
- ^ a b c Chan, Melissa. "The 2017 Total Solar Eclipse: Everything You Need to Know", Time (July 25, 2017).
- ^ Wolfram, Stephen (2017-08-15). "When Exactly Will the Eclipse Happen? A Multimillenium Tale of Computation". Wolfram Blog. Retrieved 2017-08-17.
- ^ a b Serven, Ruth (2017-07-13). "Total solar eclipse offers small towns a tourism boom—if they can get ready". The Kansas City Star. Retrieved 2017-07-29.
- ^ a b "Wyoming prepares for total solar eclipse in 2017". CTV News. 2017-07-29.
- ^ a b c d e Wolfson, Elijah. "Solar-eclipse fever means counterfeit glasses are flooding Amazon's market". Quartz. Retrieved 2017-08-19.
- ^ a b c "Amazon offers refunds to customers who bought fake eclipse glasses". CBC News. Retrieved 2017-08-19.
- ^ "Eclipse: Who? What? Where? When? and How?", NASA.
- ^ "Voyages of Discovery: 2017 Total Solar Eclipse". Voyages of Discovery. Retrieved 2017-07-30.
- ^ "2017 August 21 Total Solar Eclipse". USNO. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ^ "The Great Baja Eclipse", Discover January 1991. p. 90.
- ^ "Total and Annular Solar Eclipse Paths 1981–2000".
- ^ "Total and Annular Solar Eclipse Paths 1961–1980".
- ^ "Thousands Go West for a Total Solar Eclipse Tomorrow; Data May Aid Energy Research Partial Eclipse for New York Best Types of Film Image of Sun on Screen", The New York Times February 25, 1979. p. 26.
- ^ Browne, Malcolm W. (February 27, 1979). "Total Eclipse of the Sun Darkens Skies in Northwest; Total Eclipse Casts Two Minutes of Darkness in West Temperature Falls Sharply Learned of Weather Peculiarities Data on Plasma Sought". The New York Times. p. C4. Retrieved February 19, 2017.
- ^ Schrag, Philip (July 30, 1972). "Let There Be Darkness, Please; When Mercury Is at Quadrature, the Social Director Is a Lonely Man For Two Extremely Short Minutes Everyone Gaped Into the Sky". The New York Times. p. 15. Retrieved February 19, 2017.
- ^ Jubier, F. Espenak and Xavier. "NASA – Total Solar Eclipse of 1257 June 13". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
- ^ Google Earth Gallery for Solar and Lunar Eclipses, Xavier M. Jubier, 2011
- ^ Total Solar Eclipse of 1970 Mar 07, Fred Espenak
- ^ "EclipseFest". Retrieved August 8, 2017.
- ^ Quintana, Pedro (November 4, 2016). "Thousands will flock to Madras to view solar eclipse: City gearing up for space, shuttles next August". KTVZ. Retrieved April 2, 2017.
- ^ "Eclipse chasers blaze trail to Oregon for view of a lifetime". The Seattle Times. 2017-06-23. Retrieved 2017-06-30.
- ^ "Oregon Scores International Collaborative Festival With 'Oregon Eclipse'". Dance Music NW. 2016-11-11. Retrieved 2016-11-13.
- ^ "Oregon Eclipse — A Total Solar Eclipse Gathering 17–23 August, 2017 – Oregon Eclipse 2017Oregon Eclipse 2017". oregoneclipse2017.com. Retrieved 2016-11-13.
- ^ "OMSI Total Solar Eclipse Viewing in Salem, Oregon — August 21, 2017". NASA. Retrieved April 2, 2017.
- ^ "Event Details – Craters Of The Moon National Monument & Preserve (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. Retrieved 2017-08-08.
- ^ "Events Around Eastern Idaho". Eastern Idaho Eclipse. 2016-10-24. Retrieved 2017-08-08.
- ^ "Idaho Falls Eclipse | Big Kid Science". www.bigkidscience.com. Retrieved 2017-08-08.
- ^ "Total Solar Eclipse 2017". Brigham Young University Idaho. Retrieved April 2, 2017.
- ^ "Eclipse Festival and Map". Weiser Eclipse 2017. Retrieved 2017-08-08.
- ^ "2017Astrocon, Casper, Wyoming". Astronomical League. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
a unique opportunity for professional astronomers to intermingle with knowledgeable amateurs; gathering together to learn from each other and exchange ideas.
- ^ "Wyoming Eclipse Festival 2017". Retrieved April 2, 2017.
- ^ "Eclipse Events: We are planning a party – and YOU are invited!". 2017 Solar Eclipse in Alliance. Retrieved April 2, 2017.
- ^ "Eclipse Lunch on the Lawn". Nemaha County Hospital.
- ^ "Gem of the Prairie Eclipse Event". Stuhr Museum.
- ^ "Total Solar Eclipse Weekend of Events at Homestead National Monument of America – Homestead National Monument of America (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. Retrieved 2017-08-06.
- ^ "Solar Eclipse Arnold MO". www.facebook.com. Retrieved 2017-08-20.
- ^ "Total solar eclipse ride". KC-PPC. Retrieved May 1, 2017.
- ^ "Show me totality COMO". Lathrop Eclipse.
August 20, 2017
- ^ "MU hosts weekend full of events leading to Mondays solar eclipse". Lathrop Eclipse.
August 20, 2017
- ^ "Eclipse 2017". Lathrop Eclipse.
August 20, 2017
- ^ "Total Solar Eclipse/150 Years Festival". Lathrop Eclipse.
April 2, 2017
- ^ "Eclipsing Park University". Park University. Retrieved July 13, 2017.
- ^ "Darkening of the Sun – Eclipse 2017 – St. Clair MO".
- ^ "St. Joseph Eclipse". Front Page Science. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "Southern Illinois: eclipse crossroads of America". Southern Illinois University Carbondale. May 5, 2016.
- ^ Johnston, Bob (August 7, 2017). "Amtrak announces 'Eclipse Express' special to southern Illinois". (subscription required)
- ^ Carley, Sean (March 28, 2017). "Remainder of "Moonstock" eclipse festival lineup announced". Daily Egyptian. Retrieved April 2, 2017.
- ^ "View the Eclipse with University of Illinois Astronomers in Goreville, IL". University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ "The Great American Eclipse Viewing at Benedictine College". www.benedictine.edu.
- ^ "WKU Eclipse Events". www.wku.edu.
- ^ "A Monumental Solar Eclipse Festival: August 18 – August 21". Solar Eclipse Hopkinsville, KY. Retrieved April 2, 2017.
- ^ "Eclipse: Events". Austin Peay State University. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "Eclipse 2017". Oakley STEM Center. Retrieved April 26, 2017.
- ^ "BLACKOUT 2017". Main Street McMinnville. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- ^ "Eclipse-Themed Programs & Events". Music City Solar Eclipse. Retrieved April 2, 2017.
- ^ "Nashville's Italian Lights festival is official NASA location for solar eclipse". Music City Eclipse at Italian Lights Festival. WKRN News2. Retrieved July 22, 2017.
- ^ "Solar Eclipse 2017 Viewing Event, Free Music City Eclipse Party". Music City Eclipse at Italian Lights Festival. Retrieved July 20, 2017.
- ^ "The 2017 Total Solar Eclipse Will Pass Through the Great Smoky Mountains of North Carolina". Bryson City North Carolina. Retrieved April 2, 2017.
- ^ Get Off the Grid Fest
- ^ "Solar Eclipse 2017 at the South Carolina State Museum". South Carolina State Museum.
- ^ "Furman".
- ^ "Eclipse at Furman". Eclipse at Furman. Furman University. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ Mortillaro, Nicole (July 2, 2017). "When day turns into night: Canadians, Americans prepare for total solar eclipse". CBC News. Retrieved July 2, 2017.
- ^ Littmann, Espenak, Willcox: Totality: Eclipses of the Sun. pp 253ff
- ^ a b Rubin, Molly. "How to watch the Great American Eclipse, no matter where you are in the world". Quartz. Retrieved 2017-08-18.
- ^ "Here Are The TV Network Plans For Covering the Total Solar Eclipse". TVNewser. Adweek. Retrieved 2017-08-18.
- ^ Nyren, Erin (2017-08-18). "Solar Eclipse Coverage: TV Goes Totally Looney for Lunar Moment". Variety. Retrieved 2017-08-18.
- ^ Potenza, Alessandra (2017-08-15). "Why NASA is sending bacteria into the sky on balloons during the eclipse". The Verge. Retrieved 2017-08-18.
- ^ a b "ECLIPSE GLASSES SAFETY". Eclipse Glasses.com. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
- ^ a b How to Tell If Your Eclipse Glasses or Handheld Solar Viewers Are Safe, American Astronomical Society, 2017.
- ^ "How to tell if your solar eclipse glasses are safe or fake". CNET. Retrieved 2017-08-19.
- ^ Canzano, Anna (2017-07-22). "Demand for eclipse toilets is 'astronomical': Officials recommend travelers bring a personal toilet". KOIN. Retrieved 2017-07-29.
- ^ Mariano, Nick (2016-06-17). "Local tourism, businesses make plans for solar eclipse in 2017". The Southern Illinosian. Retrieved 2017-07-29.
- ^ Richy, Brad (2017-07-29). "IOEM-Letter-to-Eclipse-Communities" (PDF).
- ^ MOELLER, KATY (2017-08-17). "Oregon eclipse traffic is already backing up. Idaho has an app for that". The Idaho Statesman. Retrieved 2017-08-17.
- ^ "Oregon governor authorizes National Guard for solar eclipse". KBTX-TV. 2017-07-27. Retrieved 2017-07-29.
- ^ a b Lynne, Terry (2017-08-10). "Eclipse 2017: Hospitals stock up on blood, rattlesnake bite antidote". The Oregonian. Retrieved 2017-08-10.
- ^ FLACCUS, GILLIAN FLACCUS (2017-08-17). "Eclipse traffic already heavy in central Oregon". The Idaho Statesman. Retrieved 2017-08-17.
- ^ "2016 Long-Term Reliability Assessment" (PDF). North American Electric Reliability Corporation. December 2016. p. 70. Retrieved April 18, 2017.
causes substantial effects to wide-scale solar generation within a very short amount of time. The output generated by PV/solar systems will be either diminished or drastically reduced within the window of this event. Sudden widespread diminishing of solar irradiance may heavily affect areas with large amounts of utility scale PV energy installations or behind-the-meter DERs.
- ^ "A Wide-Area Perspective on the August 21, 2017 Total Solar Eclipse" (PDF). North American Electric Reliability Corporation. April 2017. p. 20. Retrieved May 1, 2017.
The analysis performed in this study showed no reliability impacts to bulk power system (BPS) operations.
- ^ a b "Solar eclipse on August 21 will affect photovoltaic generators across the country - Today in Energy". www.eia.gov. U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 13, 2017.
- ^ Pyper, Julia (11 May 2017). "This Summer's Eclipse Will Put California's Solar-Powered Grid to the Test". Retrieved 14 May 2017.
- ^ "European power grids keep lights on through solar eclipse". 20 March 2015 – via Reuters.
- ^ "German power net survives solar eclipse". DW.COM. 2015-03-20. Retrieved 14 May 2017.
- ^ "Total Eclipse of the Sun to be commemorated on a Forever Stamp". United States Postal Service. 2017-04-27. Retrieved 2017-07-10.
- ^ a b "Total Eclipse of the Sun". United States Postal Service (store). Retrieved 2017-06-27.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 145". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
Further reading
- Bakich, Michael E. (2016). Your Guide to the 2017 Total Solar Eclipse. The Patrick Moore Practical Astronomy Series. New York, NY: Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-27630-4.
External links
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
Frequently Asked Questions / Misconceptions / Information
- Eclipse FAQ – NASA
- Eclipse misconceptions – NASA
- Location-based eclipse calculations
- Determine eclipse viewing details for any city in USA – U.S. Navy
- An Observer's Guide to Viewing the Eclipse – National Science Teachers Association
Maps
- Interactive map – Google
- Color map – NASA
Solar filters / glasses / viewers
- Reputable vendors of solar filters & viewers – American Astronomical Society
- How to determine if your paper glasses are safe? – NASA
- How to view the 2017 solar eclipse safely – NASA
- 2D/3D printable pinhole projectors – NASA
Other
- Eclipse Site – NASA
- Eclipse resource guide – Astronomical Society of the Pacific
- Map, animations, and state-by-state guide to the eclipse of 2017
- 2017 eclipse site with eclipse overview, maps, cities, events, animations, safety, gear, history, and calendar.
- Solar power impact, diagram from EIA
- When Exactly Will the Eclipse Happen? A Multimillenium Tale of Computation





