User:Oberberg/sandbox
| Sweet chestnut | |
|---|---|

| |
| Sweet chestnut fruit | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | C. sativa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Castanea sativa | |
| |
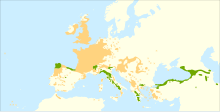
| Distribution map | |

| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 891 kJ (213 kcal) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
45.54 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dietary fiber | 8.1 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2.26 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saturated | 0.425 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monounsaturated | 0.780 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Polyunsaturated | 0.894 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2.42 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tryptophan | 0.027 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Threonine | 0.086 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isoleucine | 0.095 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Leucine | 0.143 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lysine | 0.143 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methionine | 0.057 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cystine | 0.077 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenylalanine | 0.102 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tyrosine | 0.067 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Valine | 0.135 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arginine | 0.173 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Histidine | 0.067 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alanine | 0.161 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aspartic acid | 0.417 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glutamic acid | 0.312 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glycine | 0.124 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proline | 0.127 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serine | 0.121 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other constituents | Quantity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Water | 48.65 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| †Percentages estimated using US recommendations for adults,[2] except for potassium, which is estimated based on expert recommendation from the National Academies.[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Castanea sativa, or sweet chestnut, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fagaceae, native to Southern Europe and Asia Minor, and widely cultivated throughout the temperate world. A substantial, long-lived deciduous tree, it produces an edible seed, the chestnut, which has been used in cooking since ancient times.
Names
[edit]The tree is commonly called the "chestnut", or "sweet chestnut" to distinguish it from the horse chestnut Aesculus hippocastanum, to which it is only distantly related. Other common names include "Spanish chestnut",[4] "Portuguese chestnut" and "marron" (French for "chestnut"). The Latin sativa means "cultivated by humans".[5] Some selected varieties are smaller and more compact in growth yielding earlier in life with different ripening time: the Marigoule, the Marisol and the Maraval.
Description
[edit]C. sativa attains a height of 20–35 m (66–115 ft) with a trunk often 2 m (7 ft) in diameter. The bark often has a net-shaped (retiform) pattern with deep furrows or fissures running spirally in both directions up the trunk. The trunk is mostly straight with branching starting at low heights. Sweet chestnut trees live to an age of 500 to 600 years.[6] If cultivated, sweet chestnut trees might even grow as old as 1000 years or more.[7] Their large genetic diversity and different cultivars are being nursed for uses like flour, boiling, roasting, drying, candying or wood.[8] The oblong-lanceolate, boldly toothed leaves are 16–28 cm (6–11 in) long and 5–9 cm (2–4 in) broad.
Reproduction
[edit]The flowers of both sexes are borne in 10–20 cm (4–8 in) long, upright catkins, the male flowers in the upper part and female flowers in the lower part. In the northern hemisphere, they appear in late June to July, and by autumn, the female flowers develop into spiny cupules containing 3-7 brownish nuts that are shed during October. The female flowers eventually form a spiky sheath that deters predators from the seed.[9] The sweet chestnut is self incompatible, meaning that the plant can’t pollinate itself, making cross-pollination necessary.[10] Some cultivars only produce one large nut per cupule, while others produce up to three nuts.[10] The nut itself is composed of two skins: an external, shiny brown part, and an internal skin adhering to the fruit. Inside, there is an edible, creamy-white part developed from the cotyledon.[10]
The tree requires a mild climate and adequate moisture for good growth and a good nut harvest. Its year-growth (but not the rest of the tree)[11] is sensitive to late spring and early autumn frosts, and is intolerant of lime. Under forest conditions, it will tolerate moderate shade well. It can live to more than 2,000 years of age in natural conditions, see the poetically-named "hundred-horse chestnut" in eastern Sicily for example.
Pests and Diseases
[edit]The leaves provide food for some animals, including Lepidoptera such as the case-bearer moth Coleophora anatipennella and rose chafer Macrodactylus subspinosus.
The two major fungal pathogens of the sweet chestnut are the chestnut blight (Cryphonectria parasitica) and the ink disease caused by Phytophthora cambivora and Phytophthora cinnamomi.[12][13] In North America as well as in Southern Europe Cryphonectria parasitica destroyed most of the chestnut population in the 20th century. With biological control, the population of the sweet chestnut is not threatened anymore by the chestnut blight and is regenerating.[14][15] Ink disease is infesting trees mostly in humid soils, with the mycelium invading the root and resulting in wilting of the leaf. Absence of fruit formation leads to die back of the petal. The ink disease is named after the black exudates at the base of the trunk.[13] Nowadays there are cultivars that are resistant to the ink disease. Phytophthora cambivora caused serious damage in Asia and the USA, and it still continues to destroy new plantations in Europe.[13]
Another serious pest which is difficult to control is the gall wasp (Dryocosmus kuriphylus) which was recently introduced in Southern Europe, originating from Asia.[16]

Distribution
[edit]
Historic Development
[edit]C. sativa is found across the Mediterranean region, from the Caspian Sea to the Atlantic Ocean. It is thought to have survived the last ice age in several refuges in southern Europe, on the southern coast of the Black sea with a main centre on the southern slope of the Caucasus and in the region of north-western Syria, possibly extending into Lebanon.[17] Pollen data indicates that the first spreading of C. sativa due to human activity started around 2100-2050 B.C. in Anatolia, northeastern Greece and southeastern Bulgaria.[18] Compared to other crops, the sweet chestnut was probably of relatively minor importance and distributed very heterogeneously throughout these regions.[18] The first charcoal remains of sweet chestnut only date from around 850-950 B.C., making it very difficult to infer a precise origin history. A newer but more reliable source are the literary works of Ancient Greece, with the richest being Theophrastus’ Inquiry into plants written in the third century B.C.[17] Theophrastus focuses mainly on the use of sweet chestnut wood as timber and charcoal, only mentioning the use of the fruit once when commenting on the digestive difficulties it causes, but praising its nourishing quality.[17] Several Greek authors wrote about medicinal properties of the sweet chestnut, specifically as a remedy against lacerations of the lips and of the oesophagus.[17]
Similar to the introduction of grape vine and olive cultivation to the Latin world, C. sativa is thought to have been introduced during the colonisation of the Italian peninsula by the Greeks.[19] Further clues pointing to this theory can be found in the work of Pliny the Elder, who mentions only Greek colonies in connection with sweet chestnut cultivation.[17] Today’s phylogenetic map of the sweet chestnut, while not fully understood, shows greater genetic similarity between Italian and western Anatolian C. sativa trees compared to eastern Anatolian specimen, reinforcing these findings.[20] Nonetheless, until the end of the pre-Christian era, the spread and use of the chestnut in Italy remained limited.[17] Carbonised sweet chestnuts were found in the Roman Villa Torre Annunziata, destroyed by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in A.D. 79.[21]
Clues in art and literature indicate a dislike of the sweet chestnut by the Roman aristocracy.[17] Like Theophrastus, Latin authors are sceptical of the sweet chestnut as a fruit, and Pliny the Elder even goes as far as admiring how well nature has hidden this fruit of apparently so little value.[17] In the beginning of the Christian era, people probably started to realize the value and versatility of sweet chestnut wood, leading to a slow spread of the cultivation of C. sativa trees, a theory that is supported by pollen data and literary sources, as well as the increased use of sweet chestnut wood as poles and in supporting structures, wood works and pier building between A.D. 100 and 600.[17]
Increasing sweet chestnut pollen appearances in Switzerland, France, Germany and the Iberian peninsula in the first century A.D. suggests the spreading of cultivated sweet chestnut trees by the Romans.[22] [23] Contrary to that notion, other scientists found no indication of the Romans spreading C. Sativa before the fifth century.[24] In fact, so far no center of sweet chestnut cultivation outside the Italian peninsula in Roman times has been detected.[17] Widespread use of chestnut in western Europe started in the early Middle Ages and flourished in the late Middle Ages.[25] Since the beginning of the 20th century, due to depopulation of the countryside and the abandonment of the sweet chestnut as a staple food as well as the spread of chestnut blight and ink disease, C. sativa cultivation has dramatically decreased.[25] Nowadays, sweet chestnut production is sometimes seen at a turning point again, because the development of high-value sweet chestnut products combined with changing needs of an urban society is leading to a revival in C. sativa cultivation.[26]
Distribution
[edit]The species is widely distributed throughout Europe, where in 2004 C. sativa was grown on 2.25 million hectares of forest, of which 1.78 million hectares were mainly cultivated for wood and 0.43 million hectares for fruit production.[26] Italy, France, southern Switzerland, Spain, Portugal and Greece are countries with a strong sweet chestnut tradition, with trees cultivated intensively in coppices and orchards. Countries like England, Croatia, Turkey and Georgia only have a partially developed sweet chestnut tradition due to geography or history. Nevertheless, centuries-old specimens may be found in Great Britain today. Examples can be seen particularly in the London Boroughs of Islington and Camden. In other European ountries, C. sativa has only been introduced recently, for example in Slovakia or the Netherlands.[26]

Uses
[edit]The species is widely cultivated for its edible seeds (also called nuts) and for its wood.
A tree grown from seed may take 20 years or more before it bears fruits, but a grafted cultivar such as 'Marron de Lyon' or 'Paragon' may start production within five years of being planted. Both cultivars bear fruits with a single large kernel, rather than the usual two to four smaller kernels.[11]
The ornamental cultivar C. sativa 'Albomarginata'[27] has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit
Sweet chestnut has been listed as one of the 38 substances used to prepare Bach flower remedies,[28] a kind of alternative medicine promoted for its effect on health. However, according to Cancer Research UK, "there is no scientific evidence to prove that flower remedies can control, cure or prevent any type of disease, including cancer".[29]
Cultivation
[edit]Cultivation Forms
[edit]Three different cultivation systems for the sweet chestnut can be distinguished:[30]
- Coppicing: Mainly for wood extraction. Standard conditions yield 15 m3 wood per ha and year.
- Selve: Fruit production from grafted trees. The trees have a short tribe and a big crown. Trees have a high density and the ground between the trees is often used as pasture.
- High forest: Wood and fruit production. This cultivation form is less intensive with a yield of 4-12 dt/ha and replacement of trees every 50-80 years. The trees grow from seeds and build a dense canopy.
The field management is dependent on the cultivation system. While cleaning the soil from the leaves and pruning is the norm, the use of fertilizer, irrigation and pesticides is less common and reserved for more intensive cultivation.[31]
Requirements
[edit]The sweet chestnut tree grows well on limestone-free, deeply weathered soil.[32] The optimal pH value of the soil is between 4.5 and 6, and the tree cannot tolerate soil compaction.[30] The tolerance to wet ground and to clay-rich soils is very low.[33] It is a heat-loving tree which needs a long vegetation period. The optimal average temperature is between 8°C and 15° C[30] and in January the temperature must not be below -1°C[32] but it may tolerate temperatures as low as -15°C.[30] Low temperature in autumn can damage the fruit.[32] The maximal altitude is strongly dependent on the climate. In general, the climate should be similar to viticulture[30]. Optimal precipitation is between 400 and 1600 mm.[33] Before planting, seeds must be stratified at 2-3°C so germination can start 30-40 days later. After a year, the young trees are being transplanted.[30]
Harvest
[edit]The fruit yield per tree is usually between 30-100 kg, but can get as high as 300 kg.[30] Harvest time is between middle of September and middle of November. There are three harvesting techniques:
- By hand: The sweet chestnuts are harvested by rake or broom, with a harvest speed of 5 to 30 kg every hour depending on the soil relief. Also, the capsule makes the harvest more complicated and even painful for the worker.[33]
- By hand with nets: This technique is less time-consuming and protects the fruits from injuries. However, setting up the nets is work intensive.
- Mechanical: The fruits are collected with a machine that works similarly to a vacuum cleaner. Doing so is time-saving and economical, but it’s possible that some fruits get injured, and a big initial investment is needed. Furthermore, a visual sorting is not possible.
The total world chestnut harvest was 1,17 Mio Tons in 2006, but only 151 000 Tons were C. sativa.[34]
Post-harvest Treatment
[edit]The most widespread treatment before storage is water curing, a process in which the sweet chestnuts are immersed in water for nine days.[35] The aim of this practice is to limit the main storage problems threatening the sweet chestnut: fungi development and the presence of insect worms.[35] As an alternative to water curing, hot water treatment is also commercially used.
After water treatment, the sweet chestnuts are stored in a controlled environment with high carbon dioxide concentrations. In contrast to a cold storage system, where the fruits are stored at low temperatures in untreated air, the controlled environment method avoids flesh hardening which negatively impacts the processability of the product.[35]
Food
[edit]The raw nuts, though edible, have a skin which is astringent and unpleasant to eat when still moist; after drying for a time the thin skin loses its astringency but is still better removed to reach the white fruit underneath. Cooking dry in an oven or fire normally helps remove this skin. Chestnuts are traditionally roasted in their tough brown husks after removing the spiny cupules in which they grow on the tree, the husks being peeled off and discarded and the hot chestnuts dipped in salt before eating them. Roast chestnuts are traditionally sold in streets, markets and fairs by street vendors with mobile or static braziers.
The skin of raw peeled chestnuts can be relatively easily removed by quickly blanching the nuts after scoring them by a cross slit at the tufted end.[36] Once cooked, chestnuts acquire a sweet flavour and a floury texture similar to the sweet potato. The cooked nuts can be used for stuffing poultry, as a vegetable or in nut roasts. They can also be used in confections, puddings, desserts and cakes. They are used for flour, bread making, a cereal substitute, coffee substitute, a thickener in soups and other cookery uses, as well as for fattening stock. A sugar can be extracted from them.[11] The Corsican variety of polenta (called pulenta) is made with sweet chestnut flour. A local variety of Corsican beer also uses chestnuts. The product is sold as a sweetened paste mixed with vanilla, crème de marrons, sweetened or unsweetened as chestnut purée or purée de marron, and candied chestnuts as marrons glacés.[37] In Switzerland, it is often served as Vermicelles.
Roman soldiers were given chestnut porridge before going into battle.[9]
Leaf infusions are used in respiratory diseases and are a popular remedy for whooping cough.[11] A hair shampoo can be made from infusing leaves and fruit husks.[11]
Food Constituents
[edit]Castanea sativa is considered as having very interesting nutritional characteristics. The fruit contains significant amounts of a wide range of valuable nutrients. In the past, its characteristic and nutritional components gave sweet chestnut an important role in human nutrition due to its beneficial health effects.[38][39][40] Sweet Chestnut is also appreciated in a gluten-free diet. Furthermore, this characteristic is valuable in cases of celiac diseases[41] as well as reducing coronary heart diseases and cancer rates.[42] Various composition and health studies have shown its big potential as a food ingredient and functional food.[40][43] The fat content is very low and is dominated for the most part by unsaturated fatty acids.[44][45] Sweet chestnut is a good source for starch,[46] although it is generally true that chestnuts of all varieties contain about the same amount of starch.[47] The energy value per 100 g (3.5 oz) of C. sativa amounts to 891 kJ (213 kcal)[48]. C. sativa is characterized by high moisture content which ranges from 41 % to 59 %[49] and a considerable level of starch (~40 g 100 g-1 dry matter). Regarding mineral content, the chestnut provides a good source for Cu, Fe, Mg, Mn and K.[44] Its sugar content ranges from 14 % to 20 % dry weight depending on the cultivar;[50] which is very important, since the sensory appeal of sweet chestnut is correlated with its sugar content. However, high sugar amounts seem to have a negative impact on the fiber content.[51] Generally, glucose content in European chestnuts is very low and ranges from zero to traces. Instead, fructose is mostly responsible for the sweet taste.[50]
Effect of Processing
[edit]Sweet chestnut is suited for human nutrition. Most sweet chestnut is consumed in processed form, which has an impact on the nutrient composition. Its naturally high concentration of organic acids is a key factor influencing the organoleptic characteristics of fruits and vegetables, namely flavor.[46] Organic acids are thought to play an important role against diseases as an antioxidant.[52][53] Heat appears to be the most influencing factor when it comes to decreasing the organic acid content. However, even after heating sweet chestnuts, antioxidant activity remains relatively high.[54] On the other hand, the consumer must consider that roasting, boiling or frying has a big impact on the nutritional profile of chestnut.[52][55] Vitamin C significantly decreases between 25-54 % when boiled and 2-77 % when roasted. Nevertheless, roasted or boiled chestnuts may still be a solid vitamin C source, since 100 gram still represent about 20 % of the recommended daily dietary intake. The sugar content is also affected by the high temperatures. Four processes are decisive for the degrading process of sugar while cooking: hydrolysis of starch to oligosaccharide and monosaccharide, decomposition of sucrose to glucose and fructose, caramelization of sugars and degradation of sugars.[56] Organic acids are also affected by high temperatures: their content decreases about 50 % after frying, and 15 % after boiling.[54] Responsible for the aromatic characteristics of cooked chestnuts is the effect of degradation of saccharides, proteins and lipids, the caramelization of saccharides and the maillard reaction that is reducing sugar and amino acids.[57][58]
-
Roasted chestnuts
-
Street vendors in Istanbul
Wood
[edit]
This tree responds very well to coppicing, which is still practised in Britain, and produces a good crop of tannin-rich wood every 12 to 30 years, depending on intended use and local growth rate. The tannin renders the young growing wood durable and resistant to outdoor use, thus suitable for posts, fencing or stakes.[59] The wood is of light colour, hard and strong. It is used to make furniture, barrels (sometimes used to age balsamic vinegar), and roof beams notably in southern Europe (for example in houses of the Alpujarra, Spain, in southern France and elsewhere). The timber has a density of 560 kg per cubic meter,[60] and due to its durability in ground contact is often used for external purposes such as fencing.[60] It is also a good fuel, though not favoured for open fires as it tends to spit.[11]
Tannin is found in the following proportions on a 10% moisture basis: bark (6.8%), wood (13.4%), seed husks (10 - 13%). The leaves also contain tannin.[11]
Cultivars
[edit]French origin
[edit]American origin
[edit]- Colossal
- Labor Day
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Miller. Gardeners Dictionary ed. 8 no. 1 (1768). Flora Europaea: Castanea sativa
- ^ United States Food and Drug Administration (2024). "Daily Value on the Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels". FDA. Archived from the original on 2024-03-27. Retrieved 2024-03-28.
- ^ National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Food and Nutrition Board; Committee to Review the Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium (2019). Oria, Maria; Harrison, Meghan; Stallings, Virginia A. (eds.). Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium. The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health. Washington, DC: National Academies Press (US). ISBN 978-0-309-48834-1. PMID 30844154. Archived from the original on 2024-05-09. Retrieved 2024-06-21.
- ^ Royal Botanic Garden, Sydney blooming calendar
- ^ Harrison, Lorraine (2012). RHS Latin for gardeners. United Kingdom: Mitchell Beazley. p. 224. ISBN 9781845337315.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:15was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:6was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Bounous, G. (October 2005). "The Chestnut: A Multipurpose Resource for the New Millennium". Acta Horticulturae (693): 33–40. doi:10.17660/actahortic.2005.693.1. ISSN 0567-7572.
- ^ a b Kew Gardens - Rhizotron & Xstrata Treetop Walkway - Castanea sativa[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
:62was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g “Plants For A Future” (PFAF)
- ^ Anagnostakis, Sandra L. (1987). "Chestnut Blight: The Classical Problem of an Introduced Pathogen". Mycologia. 79 (1): 23–37. doi:10.2307/3807741. JSTOR 3807741.
- ^ a b c Vannini, Andrea (2001). "Ink disease in chestnuts: impact on the European chestnut". Forest Snow and Landscape Research. 76: 345–350 – via researchgate.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:162was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Anagnostakis, Sandra L. (1982-01-29). "Biological Control of Chestnut Blight". Science. 215 (4532): 466–471. doi:10.1126/science.215.4532.466. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17771259. S2CID 36933270.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:164was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h i j Conedera, Marco (July 2004). "The Cultivation of Castanea sativa (Mill.) in Europe, from its origin to its diffusion on a continental scale". Vegetation History and Archaeobotany. 13 (3): 161–179. doi:10.1007/s00334-004-0038-7. S2CID 55465239 – via Springer.
- ^ a b van Zeist, Willem (1991). Late Quaternary Vegetation of the Near East. Wiesbaden: L. Reichert. ISBN 3882265302.
- ^ Forni, Gaetano (1990). Gli albori dell'agricoltura: origine ed evoluzion fino agli etruschi ed italici. Rome: REDA.
- ^ Villani, Fiorella (1990). "Genetic structure of Castanea sativa in Turkey: evidence of a hybrid zone". Journal of Evolutionary Biology. 12: 233–244. doi:10.1046/j.1420-9101.1999.00033.x. S2CID 84817286.
- ^ Meyer, Frederick (1980). "Carbonized food plants of Pompeii, Herculaneum, and the Villa at Torre Annunziata". Economic Botany. 34 (4): 401–437. doi:10.1007/BF02858317. S2CID 22625450 – via Springer.
- ^ van Mourik, J. M. (1986). Pollen profiles of slope deposits in the Galician area (N.W. Spain). Amsterdam. ISBN 9068090186.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Santos, Luisa (September 2000). "History of vegetation during the Holocene in the Courel and Queixa Sierras, Galicia, northwest Iberian Peninsula". Journal of Quaternary Science. 15 (6): 621–632. doi:10.1002/1099-1417(200009)15:6<621::AID-JQS524>3.0.CO;2-L – via Wiley Online Library.
- ^ Di Pasquale, Gaetano (December 2010). "Reworking the idea of chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) cultivation in Roman times: New data from ancient Campania". Plant Biosystems. 144 (4): 865–873. doi:10.1080/11263504.2010.491974. S2CID 86527704 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ a b Pitte, J. R. (1987). "Terres de Castanide: hommes et paysages du châtaignier de l'Antiquité à nos jours". Méditerranée. 60: 52.
- ^ a b c Conedera, Marco (2004). "Distribution and economic potential of the sweet chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) in Europe". Ecologia Mediterranea. 30 (2): 179–193. doi:10.3406/ecmed.2004.1458 – via researchgate.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Castanea sativa 'Albomarginata'". Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ^ D. S. Vohra (1 June 2004). Bach Flower Remedies: A Comprehensive Study. B. Jain Publishers. p. 3. ISBN 978-81-7021-271-3. Retrieved 2 September 2013.
- ^ "Flower remedies". Cancer Research UK. 2017-08-30. Retrieved September 2, 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g Lüdders, P. (February 2004). "Esskastanie". Erwerbs-Obstbau. 46 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ Mariotti, Barbara (January 2009). "Tradizione, innovazione e sostenibilità: una selvicoltura per il castagno da frutto". Conference Paper: III Congresso Nazionale Selvicoltura – via ResearchGate.
- ^ a b c Koch, Henrike (2012). "Projektstudie: Die Edelkastanie auf Obstwiesen - Eine Alternative zum Kirschanbau?" (PDF). wald-rlp.de.
- ^ a b c Conedera, Marco (2016). European Atlas of Forest Tree Species - Chapter: Castanea sativa in Europe: distribution, habitat, usage and threats. Publication Office of the European Union. ISBN 9789279367403.
- ^ "FAOStat". FAOStat. 2018.
- ^ a b c Botondi (2009). "Technological Parameters of Water Curing Affect Postharvest Physiology and Storage of Marrons (Castanea Sativa Mill., Marrone Fiorentino)". Postharvest Biology and Technology. 51: 97–103. doi:10.1016/j.postharvbio.2008.06.010 – via academia.edu.
- ^ An easy way of peeling the pellicle, or pithy skin
- ^ Lori Alden. 2006 The Cook's Thesaurus. nut pastes
- ^ Goncalves, Berta (September 2010). "Metabolite composition of chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) upon cooking: Proximate analysis, fibre, organic acids and phenolics". Food Chemistry. 122: 154–160. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.02.032. hdl:10348/6417 – via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ^ Liu, Chang; Wang, Shujun; Chang, Xuedong; Wang, Shuo (January 2015). "Structural and functional properties of starches from Chinese chestnuts". Food Hydrocolloids. 43: 568–576. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.07.014. ISSN 0268-005X.
- ^ a b De Vasconcelos, Maria CBM; Bennett, Richard N; Rosa, Eduardo AS; Ferreira-Cardoso, Jorge V (2010-06-03). "Composition of European chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) and association with health effects: fresh and processed products". Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 90 (10): 1578–1589. doi:10.1002/jsfa.4016. ISSN 0022-5142. PMID 20564434.
- ^ Pazianas, M.; Butcher, G. P.; Subhani, J. M.; Finch, P. J.; Ang, L.; Collins, C.; Heaney, R. P.; Zaidi, M.; Maxwell, J. D. (2004-06-17). "Calcium absorption and bone mineral density in celiacs after long term treatment with gluten-free diet and adequate calcium intake". Osteoporosis International. 16 (1): 56–63. doi:10.1007/s00198-004-1641-2. ISSN 0937-941X. PMID 15221205. S2CID 513378.
- ^ Handbook of nutraceuticals and functional foods. Wildman, Robert E. C., 1964-. Boca Raton, Fla.: CRC Press. 2001. ISBN 1420036696. OCLC 85602811.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Desmaison, A.M. (1986). "La place de la châtaigne en alimentation". Médicine et nutrition. 22: 174–180.
- ^ a b Borges, Olga; Gonçalves, Berta; de Carvalho, José L. Soeiro; Correia, Paula; Silva, Ana Paula (February 2008). "Nutritional quality of chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) cultivars from Portugal". Food Chemistry. 106 (3): 976–984. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.07.011. hdl:10348/6419. ISSN 0308-8146.
- ^ De Vasconcelos, Maria Do Carmo Barbosa Mendes; Bennett, Richard N.; Rosa, Eduardo A. S.; Cardoso, Jorge Ventura Ferreira (May 2007). "Primary and Secondary Metabolite Composition of Kernels from Three Cultivars of Portuguese Chestnut (Castanea sativaMill.) at Different Stages of Industrial Transformation". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 55 (9): 3508–3516. doi:10.1021/jf0629080. ISSN 0021-8561. PMID 17407304.
- ^ a b Griffith), Vaughan, J. G. (John (2009). The new Oxford book of food plants. Geissler, Catherine., Nicholson, Barbara., Dowle, Elisabeth., Rice, Elizabeth. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780191567742. OCLC 500808884.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Künsch, U.; Schärer, H.; Patrian, B.; Hurter, J.; Conedera, M.; Sassella, A.; Jermini, M.; Jelmini, G. (July 1999). "Quality Assessment of Chestnut Fruits". Acta Horticulturae (494): 119–128. doi:10.17660/actahortic.1999.494.17. ISSN 0567-7572.
- ^ Fernandes, Ângela; Barreira, João C.M.; Antonio, Amilcar L.; Bento, Albino; Luisa Botelho, M.; Ferreira, Isabel C.F.R. (September 2011). "Assessing the effects of gamma irradiation and storage time in energetic value and in major individual nutrients of chestnuts". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 49 (9): 2429–2432. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.06.062. ISSN 0278-6915. PMID 21740949.
- ^ De La Montaña Mı́guelez, J.; Mı́guez Bernárdez, M.; Garcı́a Queijeiro, J.M. (February 2004). "Composition of varieties of chestnuts from Galicia (Spain)". Food Chemistry. 84 (3): 401–404. doi:10.1016/s0308-8146(03)00249-8. ISSN 0308-8146.
- ^ a b Neri, L.; Dimitri, G.; Sacchetti, G. (February 2010). "Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of cured chestnuts from three sweet chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) ecotypes from Italy". Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. 23 (1): 23–29. doi:10.1016/j.jfca.2009.03.002. ISSN 0889-1575.
- ^ Pereira-Lorenzo, S.; Ramos-Cabrer, A.M.; Díaz-Hernández, M.B.; Ciordia-Ara, M.; Ríos-Mesa, D. (February 2006). "Chemical composition of chestnut cultivars from Spain". Scientia Horticulturae. 107 (3): 306–314. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2005.08.008. ISSN 0304-4238.
- ^ a b Silva, Branca M.; Andrade, Paula B.; Valentão, Patrícia; Ferreres, Federico; Seabra, Rosa M.; Ferreira, Margarida A. (July 2004). "Quince (Cydonia oblongaMiller) Fruit (Pulp, Peel, and Seed) and Jam: Antioxidant Activity". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 52 (15): 4705–4712. doi:10.1021/jf040057v. ISSN 0021-8561. PMID 15264903.
- ^ Blomhoff, Rune; Carlsen, Monica H.; Andersen, Lene Frost; Jacobs, David R. (2006/11). "Health benefits of nuts: potential role of antioxidants". British Journal of Nutrition. 96 (S2): S52–S60. doi:10.1017/BJN20061864. ISSN 1475-2662. PMID 17125534. S2CID 4649715.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b Barros, Ana I.R.N.A.; Nunes, Fernando M.; Gonçalves, Berta; Bennett, Richard N.; Silva, Ana Paula (September 2011). "Effect of cooking on total vitamin C contents and antioxidant activity of sweet chestnuts (Castanea sativa Mill.)". Food Chemistry. 128 (1): 165–172. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.013. hdl:10348/6571. ISSN 0308-8146. PMID 25214344.
- ^ Ribeiro, Bárbara; Rangel, Joana; Valentão, Patrı́cia; Andrade, Paula B.; Pereira, José Alberto; Bölke, Hanna; Seabra, Rosa M. (January 2007). "Organic acids in two Portuguese chestnut (Castanea sativa Miller) varieties". Food Chemistry. 100 (2): 504–508. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.09.073. hdl:10198/735. ISSN 0308-8146.
- ^ Attanasio, Gerardina; Cinquanta, Luciano; Albanese, Donatella; Matteo, Marisa Di (December 2004). "Effects of drying temperatures on physico-chemical properties of dried and rehydrated chestnuts (Castanea sativa)". Food Chemistry. 88 (4): 583–590. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.01.071. ISSN 0308-8146.
- ^ Morini, G.; Maga, J.A. (July 1995). "Volatile compounds in roasted and boiled Chinese chestnuts (Castanea molissima)". LWT - Food Science and Technology. 28 (6): 638–640. doi:10.1016/0023-6438(95)90014-4. ISSN 0023-6438.
- ^ Li, Qian; Shi, Xianhe; Zhao, Qiaojiao; Cui, Yahui; Ouyang, Jie; Xu, Fang (June 2016). "Effect of cooking methods on nutritional quality and volatile compounds of Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume)". Food Chemistry. 201: 80–86. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.068. ISSN 0308-8146. PMID 26868551.
- ^ Oleg Polunin. Trees and Bushes of Britain and Europe. Ed Paladin, 1973, pp. 51, 188 and 195).
- ^ a b Chestnut. Niche Timbers. Accessed 19-08-2009.
- Rushforth, K. (1999). Trees of Britain and Europe. HarperCollins ISBN 0-00-220013-9.
- Fao.org Castanea sativa
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Castanea sativa at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Castanea sativa at Wikimedia Commons
- U.C. Davis, California: Castanea sativa in horticulture
- Plants for a Future database: Castanea sativa
- Castanea sativa - distribution map, genetic conservation units and related resources. European Forest Genetic Resources Programme (EUFORGEN)
sativa
Category:Edible nuts and seeds
Category:Flora of Western Asia
Category:Flora of Europe
Category:Flora of Greece
Category:Flora of Italy
Category:Flora of Turkey
Category:Medicinal plants of Asia
Category:Medicinal plants of Europe
Category:Trees of Mediterranean climate
Category:Garden plants of Asia
Category:Garden plants of Europe
Category:Ornamental trees
Category:Flora of Montenegro





![Crème de marrons [fr]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/77/Crema_di_castagne_o_confettura_di_marroni.jpg/90px-Crema_di_castagne_o_confettura_di_marroni.jpg)
![Chestnut flour [fr] (AOC)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f5/Farine_de_ch%C3%A2taigne_corse.jpg/81px-Farine_de_ch%C3%A2taigne_corse.jpg)