User:Dbsseven/sandbox/Battle of San Carlos (1982)
Engagements[edit]
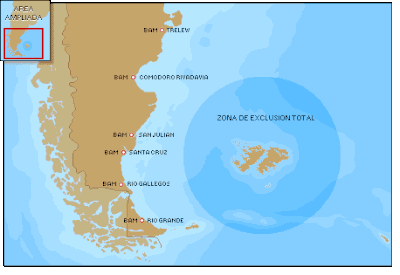
Due to the distance required to fly to the islands, two minutes was the average time Argentine attack aircraft had available in the target area.
This is a list of the main sorties carried out by Argentine air units showing approximate local time, Aircraft and Call signal.
21 May[edit]



The Argentine Army force on site was a section from the 25th Infantry Regiment named Combat team Güemes (Spanish: Equipo de Combate Güemes) located at Fanning Head. The British fleet entered San Carlos during the night and at 02:50 was spotted by EC Güemes which opened fire with 81mm mortars and two recoilless 105mm rifles. They were soon engaged by British naval gunfire and a 25-man SBS team and forced to retreat, losing their communications equipment but shooting down two Gazelle helicopters with small-arms fire, killing three members of the two aircrews.
1st Lt Carlos Daniel Esteban from EC Güemes informed Goose Green garrison about the landings at 08:22 (he was finally evacuated by helicopter on 26 May). The Argentine high command at Stanley initially suggested that a landing operation was not feasible at San Carlos and the operation was just a diversion. Finally, at 10:00, a COAN Aermacchi MB-339 jet based on the islands was dispatched to San Carlos on a reconnaissance flight. In the meantime, the FAA had already started launching their mainland-based aircraft at 09:00.
Between 10:15 and 17:12 seventeen sorties were carred out by FAA and COAN. Dagger and A-4C of the FAA made attacks on HMS Antrim, HMS Argonaut, HMS Broadsword, HMS Brilliant, HMS Ardent, HMS Brilliant. Sorties of MIIIEA aircraft were used as diversions as-well. While many of the bombs did not explode, HMS Ardent and HMS Argonaut were hit, sustaining damage and casualties. Sea Harriers intercepted some of the attackers, destroying 8 FAA aircraft.
22 May[edit]
Bad weather over the Patagonia airfields prevented the Argentines from carrying out most of their air missions; only a few Skyhawks managed to reach the islands. The British completed their surface-to-air Rapier battery launcher deployments.
23 May[edit]
On 23 May Argentine aircraft resumed attacking, striking HMS Antelope, HMS Broadsword, HMS Yarmouth, and HMS Antelope. Only HMS Antelope was damaged, sinking after an unexploded bomb detonated while being defused. Of the attacking aircraft, two were shot down. An additional COAN pilot was killed after ejecting from his' A-4Q's tyre burst upon landing.
24 May[edit]

On 24 May the Argentine pilots on the continent openly expressed their concern about the lack of collaboration between the three branches of the armed forces, and protested with passive resistance. General Galtieri, acting president of Argentina, decided to visit Comodoro Rivadavia the next day, 25 May (Argentina's National Day), to try to convince them to keep fighting, but when he arrived in the morning the pilots had changed their minds and were already flying to the islands.[2]
Six sorties were launched by the FAA against the British forces. RFA Sir Lancelot and probably Sir Galahad and Sir Bedivere and ground targets were attacked. Four attack aircraft were shot down, with one pilot killed.
25 May[edit]
Attacks by the FAA on 25 May proved more successful than the previous day. HMS Coventry after hitting the ship with 500 lb (230 kg) bombs. Attacks on HMS Broadsword damaging the frigate's communication systems and hydraulics and and shattering the nose of her Sea Lynx helicopter. RFA Sir Lancelot was also attacked. One sorte accidentally attacked Goose Green, mistaking it for Ajax bay, and were hit by small arms friendly fire. Three attackers were shot down; one by a Rapier Missile from 'T' Battery of 12 Regiment Royal Artillery, and two by Sea Dart fired by HMS Coventry.
| List of Sorties | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Branch | Aircraft | Callsign | Pilot(s) | Summary |
| 21 May | |||||
| 10:15 | COAN | MB339 | 4-A-115 | Lt Guillermo Owen Crippa | A reconnaissance flight flew over the landing force twice to determine the exact composition of the fleet, earning the highest national military decoration, the Argentine Nation to the Heroic Valour in Combat Cross. He attacked HMS Argonaut and an unidentified RFA ship with guns and rockets, then withdrew. |
| 10:15 | FAA | Pucara | Tigre | Cpt Benítez Mj Tomba 1st Lt Micheloud |
Three (of four) planes scrambled from Goose Green and were engaged by gunfire from HMS Ardent. Cpt Benítez was shot down by a Stinger missile fired by the Special Air Service; he ejected and walked back to his base, arriving at 19:00. The other two pilots, Mj Tomba and 1st Lt Micheloud, fired 2.75-inch rockets at a shed apparently used by British forces as an observation post, but were intercepted by two Sea Harriers during their escape. Mj Tomba was shot down (ejecting safely) by pilot Nigel Ward,[3] while Lt Micheloud's aircraft escaped and landed at Port Stanley's airfield. |
| 10:20 | FAA | MIIIEA | Four aircraft made a diversion north of the islands. | ||
| 10:25 | FAA | Dagger | Leon | Cpt Dimeglio Lt Castillo |
From San Julian, Cpt Dimeglio and Lt Castillo attacked HMS Antrim with their 30mm cannon. Their 1,000 lb (450 kg) bombs failed to explode. |
| 10:30 | FAA | Dagger | Ñandú | Cpt Rodhe Lt Bean |
From Rio Grande, Tierra del Fuego, Cpt Rodhe and Lt Bean attacked HMS Argonaut, Lt Bean was shot down by a Sea Wolf SAM from HMS Broadsword; Broadsword was attacked by pilot Cpt Janet. |
| 10:35 | FAA | Dagger | Zorro | Cpt Dellepine Cpt Diaz Cpt Aguirre-Faget |
Cpt Dellepine, Cpt Diaz and Cpt Aguirre-Faget bombed and strafed HMS Brilliant but the bombs hang-up. |
| 10:50 | FAA | Dagger | Perro | Mj Martinez Cpt Moreno Lt Volponi |
Mj Martinez, Cpt Moreno and Lt Volponi attacked HMS Antrim. Their 1,000 lb (450 kg) bombs did not explode, but one of them hit the stern of the destroyer, which also received damage from 30 mm strafing. During their escape, Sea Harriers launched Sidewinders against the Daggers but they fell short. |
| 12:45 | FAA | A-4C | Pato | Cpt Almoño Cpt Garcia 1st Lt Daniel Manzotti Lt Nestor Lopez |
Intercepted by Sea Harriers; Manzotti and López were shot down and killed by Sidewinders. |
| 12:45 | FAA | A-4B | Mula | Cpt Carballo Ensign Carmona |
Mula 2 attacked an unknown ship, most probably the abandoned Argentine cargo vessel Rio Carcaraña, and withdrew,[4] Carballo continued alone and attacked HMS Ardent straddling her with two bombs, both of which failed to explode.[5] |
| 13:37 | FAA | A-4B | Leo | 1st Lt Filippini Lt Autiero Lt Osses Lt Robledo Ensign Vottero |
Hit HMS Argonaut with 1,000 lb (450 kg) bombs which did not explode, with one crashing through her Sea Cat magazine, detonating two missiles and causing damage and two fatalities among Argonaut's crew. |
| 14:30 | FAA | MIIIEA | Two aircraft took off as a diversion. | ||
| 14:35 | FAA | Dagger | Cueca | Cpt Mir Gonzales Cpt Robles 1st Lt Luna Lt Bernhard. |
Intercepted by Sea Harriers, and Lt Luna was hit by a Sidewinder but ejected safely. The other three pilots attacked HMS Ardent and return to base. |
| 14:53 | FAA | Dagger | Laucha | Mj Puga 1st Lt Román |
Attacked HMS Brilliant. The third pilot attacked an unknown ship, probably HMS Antrim. |
| 14:58 | FAA | Dagger | Raton | Mj Piuma Cpt Donadille 1st lt Senn. |
Intercepted by Sea Harriers of Nigel Ward and Lt Thomas. The Daggers dropped their ordnance −2 fuel tanks and one 1,000 lb (450 kg)- and tried to escape, but the three were shot down by Sidewinders, with all pilots ejecting safely. After recovering the pilots, the FAA realised that the San Julian-based Daggers' approach corridor had been discovered and made efforts to correct the situation. |
| 15:15 | COAN | A-4Q | Tabanos | Cpt Philipi Lt Arca Lt Marquez |
Hit HMS Ardent with several 500 lb (230 kg) retarding tail bombs and cannon fire. Two aircraft were shot down by Sea Harriers during their escape, killing Lt Marcelo Márquez. Lt. Philippi ejected safely and, after being sheltered by local farmer Tony Blake during the night,[6] he rejoined the Argentine forces. The third A-4Q, Lt Arca, was damaged and the pilot bailed out into the sea approximately 800 to 1,000 meters off Cape Pembroke, Port Stanley. Arca was rescued from the water by Capt. Jorge “Picho” Svendsen's Huey UH-1H from the Army's 601 Helicopter Battalion. HMS Ardent sank. Both crew were decorated with the Valour in Combat Medal. |
| 17:02 | FAA | A-4C | No ships found. | ||
| 17:12 | FAA | A-4B | No ships found. | ||
| 23 May | |||||
| 13:30 | FAA | A-4B | Nene | Carballo 1st Lt Guadagnini Lt Rinke Ensign Gomez |
Attacked HMS Broadsword and HMS Antelope. Carballo's plane was damaged by a Sea Cat missile, fired from Antelope, during his bombing run, so he broke off the attack and returned to Rio Gallegos. A second Argentine plane dropped a 1,000 lb (450 kg) bomb on Antelopes starboard side, killing Crewman Mark R. Stephens. Lieutenant Guadagnini was hit and killed by HMS Antelope's 20mm cannon and crashed through her main mast while carrying out his bombing run; his bombs pierced the frigate's hull without exploding.[7] After the attack, one of these detonated while being defused, sinking the ship. |
| 13:45 | COAN | A-4Q | Tabanos | Cpt Castro Fox Cpt Zubizarreta Lt Benitez |
Attacked HMS Broadsword, HMS Yarmouth and HMS Antelope without visible success. Cpt Carlos María Zubizarreta was killed in Rio Grande, Tierra del Fuego when his parachute did not fully open after he ejected from his A-4Q due to a tyre bursting on landing with his bombs still loaded. The plane stopped by itself and did not suffer any damage.[8][9] |
| 15:10 | FAA | Dagger | Puñal | Mj Martinez Lt Volponi |
Intercepted by Sea Harriers, which shot down the second aircraft, whilst Martinez returned to base. |
| 15:10 | FAA | Dagger | Daga | Struck targets inside Ajax Bay | |
| 15:10 | FAA | Dagger | Coral | Struck targets inside Ajax Bay | |
| 24 May | |||||
| 10:15 | FAA | A-4B | Chispa Nene |
Com Mariel 1st Lt Sanchez Lt Roca Lt Cervera Ensign Moroni |
Attacked ships inside the bay. RFA Sir Lancelot was hit by a 1,000 lb (450 kg) bomb, which did not explode. Two LCUs are also attacked. |
| 11:02 | FAA | Dagger | Azul | Cpt Mir Gonzalez Cpt Maffeis Cpt Robles Lt Bernhardt |
Attacked unidentified ships, probably RFA Sir Bedivere, inside the bay. |
| 11:07 | FAA | Dagger | Plata | Cpt Dellepiane 1st Lt Musso Lt Callejo |
Struck ground targets with 500 lb (230 kg) retarding tail bombs. |
| 11:08 | FAA | Dagger | Oro | Mj Puga Cpt Diaz 1st Lt Castillo |
Intercepted and shot down by Sea Harriers. Castillo was killed and the other two ejected safely. |
| 11:20 | FAA | A-4C | Halcon | Cpt Pierini 1st Lt Ureta Lt Mendez |
Intercepted by Sea Harriers but managed to return to base. |
| 11:30 | FAA | A-4C | Jaguar | 1st Lt Vazquez Lt Bono Ensign Martinez |
Attacked unidentified ships, possibly RFA Sir Galahad, inside the bay. The three aircraft all received battle damage with Bono's aircraft crashing during the return flight. The other two Skyhawks were rescued by a KC-130 tanker, which approached the islands and delivered 30,000 litres of fuel while accompanying them to the airfield at San Julian. |
| 25 May | |||||
| 09:00 | FAA | A-4B | Marte | Cpt Hugo Palaver Lt Daniel Gálvez |
Cpt Hugo Palaver's aircraft was damaged in a friendly fire incident when he and Lt Daniel Gálvez accidentally flew over Goose Green and strafed the pier there, in the belief that they were over Ajax Bay.[10] The main anti-aircraft artillery identified the fighters as friendly and did not fire, but soldiers on the ground engaged with small arms fire.[11] When they returned to the strait, Palaver was shot down by a Sea Dart missile fired by HMS Coventry |
| 12:25 | FAA | A-4C | Toro | Cpt Garcia Lt Lucero Lt Paredi Ensign Issac |
Attacked ships inside the bay, probably RFA Sir Lancelot. After the attack Lucero was shot down by a Rapier Missile, from 'T' Battery of 12 Regiment Royal Artillery. He successfully ejected over the landing force,[12] was rescued and then transferred to the hospital ship SS Uganda. A Sea Dart, fired by HMS Coventry, shot down Garcia, whose aircraft had been damaged by small arms fire during the attack, to the North of San Carlos. Cpt Garcia ejected, but was not recovered and died. Ensign Isaac was losing fuel but was rescued by the KC-130, which accompanied him to his base while refuelling him in flight. |
| 15:20 | FAA | A-4B | Vulcano | Cpt Carballo Lt Carlos Rinke |
Attacked HMS Broadsword,picture from shipdamaging the frigate's communication systems and hydraulics and electrics[13] and shattering the nose of her Sea Lynx helicopter Pictures of the Damage |
| 15:20 | FAA | A-4B | Zeus | 1st Lt Velasco Ensign Barrionuevo |
Attacked and sank destroyer HMS Coventry after hitting the ship with three 500 lb (230 kg) bombs.British video Argentine video |
- ^ "Argentine Airpower in the Falklands War: An Operational View". Airpower.maxwell.af.mil. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- ^ Costa, Eduardo José (1988). Guerra Bajo la Cruz del Sur. Hyspamérica, p. 334. ISBN 950-614-749-3 (in Spanish)
- ^ "Major Carlos Tomba's Pucara". BBC News. Retrieved 24 June 2009.
- ^ Some sources identify this ship as the Rio Carcaraña but other sources place the cargo vessel in Bahía Rey ( King George Bay? ) at the time
- ^ "Board of Inquiry – Report into the Loss of HMS Ardent, page 2" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 September 2012. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- ^ La balada del piloto bahiense y el estanciero kelper (in Spanish)
- ^ "Primer Teniente Guadagnini". Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- ^ "3ra. Escuadrilla Aeronaval de Caza y Ataque". Institutoaeronaval.org. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- ^ "Carlos Zubizarreta". Archived from the original on 17 December 2009. Retrieved 2009-12-06.
- ^ Official site of the Argentine Air Force: Fuerza Aérez Argentina – Martes 25 de Mayo Archived 4 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine (in Spanish)
- ^ Piaggi, Italo A. (1986). Ganso Verde. Ed. Planeta, p. 83. ISBN 950-37-0186-4. (in Spanish)
- ^ "Cpt Tomas Lucero interview". Youtube. 10 December 2009. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- ^ "HMS Broadsword damage control". Retrieved 18 May 2012.
