Thiomalic acid
Appearance
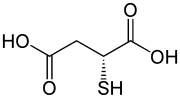 D-Thiomalic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Sulfanylbutanedioic acid | |
| Other names
2-Mercaptosuccinic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.670 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O4S | |
| Molar mass | 150.15 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 151 to 154 °C (304 to 309 °F; 424 to 427 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Thiomalate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Thiomalic acid or mercaptosuccinic acid is a dicarboxylic acid containing a thiol functional group. As suggested by its name, it contains a thiol group (SH) in place of the hydroxy group (OH) in malic acid. Salts and esters are known as thiomalates.
Thiomalic acid is an intermediate in the synthesis of corrosion inhibitors, soil fumigants, active pharmaceutical ingredients, and electroplating agents.[1]
The sodium and gold salt of thiomalic acid, sodium aurothiomalate, is used as a pharmaceutical drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.[2]
Thiomalic acid forms the backbone of the pesticide malathion.
References
[edit]- ^ "Thiomalic acid". Inxight Drugs. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
- ^ Kean WF, Kean IR (June 2008). "Clinical pharmacology of gold". Inflammopharmacology. 16 (3): 112–25. doi:10.1007/s10787-007-0021-x. PMID 18523733. S2CID 808858.
