Symphyotrichum retroflexum
| Symphyotrichum retroflexum | |
|---|---|

| |
| S. retroflexum, Macon County, North Carolina | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Tribe: | Astereae |
| Subtribe: | Symphyotrichinae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Subgenus: | Symphyotrichum subg. Symphyotrichum |
| Section: | Symphyotrichum sect. Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. retroflexum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum retroflexum | |
| |
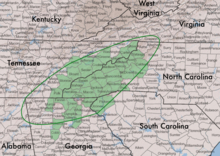
| Native distribution[3][4] | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
Symphyotrichum retroflexum (formerly Aster retroflexus) is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae native to the southeastern United States. Commonly known as rigid whitetop aster, it is a perennial, herbaceous plant that may reach 40 to 100 centimeters (16 to 39 inches) tall. Its flowers have blue to purple ray florets and cream to pale yellow then pinkish disk florets. It is known only from the Blue Ridge Mountains in Alabama, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia, where it grows in wooded areas at elevations of 400–1,500 meters (1,300–4,900 feet).[5] As of September 2021[update], NatureServe classified it as Apparently Secure (G4); it had been reviewed last in 1994 and is marked as "needs review".[1] There is an introduced presence of S. retroflexum in southeast China.[2]

Notes
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ a b c NatureServe 2021.
- ^ a b c POWO 2019.
- ^ USDA 2014.
- ^ Semple 2021.
- ^ Brouillet et al. 2006.
References
[edit]- Brouillet, L.; Semple, J.C.; Allen, G.A.; Chambers, K.L.; Sundberg, S.D. (2006). "Symphyotrichum retroflexum". In Flora of North America Editorial Committee (ed.). Flora of North America North of Mexico (FNA). Vol. 20. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press. Retrieved 8 July 2021 – via eFloras.org, Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA.
- NatureServe (3 September 2021). "Symphyotrichum retroflexum Rigid Whitetop American-aster". NatureServe Explorer (explorer.natureserve.org). Arlington, Virginia: NatureServe. Retrieved 8 September 2021.
- POWO (2019). "Symphyotrichum retroflexum (Lindl.) G.L.Nesom". Plants of the World Online (www.plantsoftheworldonline.org). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- Semple, J.C. (6 May 2021). "Symphyotrichum retroflexum — Rigid Whitetop Aster". www.uwaterloo.ca. Ontario. Archived from the original on 8 September 2021. Retrieved 8 September 2021.
- NRCS (2014). "Symphyotrichum retroflexum". USDA PLANTS Database (plants.usda.gov). United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 8 September 2021.

