Strategy and tactics of guerrilla warfare
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (September 2010) |
The main strategy and tactics of guerrilla warfare tend to involve the use of a small attacking, mobile force against a large, unwieldy force. The guerrilla force is largely or entirely organized in small units that are dependent on the support of the local population. Tactically, the guerrilla army makes the repetitive attacks far from the opponent's center of gravity with a view to keeping its own casualties to a minimum and imposing a constant debilitating strain on the enemy. This may provoke the enemy into a brutal, excessively destructive response which will both anger their own supporters and increase support for the guerrillas, ultimately compelling the enemy to withdraw. One of the most famous examples of this was during the Irish War of Independence. Michael Collins, a leader of the Irish Republican Army, often used this tactic to take out squads of British soldiers, mainly in Munster, especially Cork.
Guerrilla warfare as a continuum
[edit]
An insurgency, or what Mao Zedong referred to as a war of revolutionary nature, guerrilla warfare can be conceived of as part of a continuum.[1] On the low end are small-scale raids, ambushes and attacks. In ancient times these actions were often associated with smaller tribal policies fighting a larger empire, as in the struggle of Rome against the Spanish tribes for over a century. In the modern era they continue with the operations of insurgent, revolutionary and terrorist groups. The upper end is composed of a fully integrated political-military strategy, comprising both large and small units, engaging in constantly shifting mobile warfare, both on the low-end "guerrilla" scale, and that of large, mobile formations with modern arms.
The latter phase came to fullest expression in the operations of Mao Zedong in China and Võ Nguyên Giáp in Vietnam. In between are a large variety of situations – from the wars waged against Israel by Palestinian irregulars in the contemporary era, to Spanish and Portuguese irregulars operating with the conventional units of British General Wellington, during the Peninsular War against Napoleon.[2]
Modern insurgencies and other types of warfare may include guerrilla warfare as part of an integrated process, complete with sophisticated doctrine, organization, specialist skills and propaganda capabilities. Guerrillas can operate as small, scattered bands of raiders, but they can also work side by side with regular forces, or combine for far ranging mobile operations in squad, platoon or battalion sizes, or even form conventional units. Based on their level of sophistication and organization, they can shift between all these modes as the situation demands. Successful guerrilla warfare is flexible, not static.
Strategic models of guerrilla warfare
[edit]The 'classic' three-phase Maoist model
[edit]
In China, the Maoist Theory of People's War divides warfare into three phases. In Phase One, the guerrillas earn population's support by distributing propaganda and attacking the organs of government. In Phase Two, escalating attacks are launched against the government's military forces and vital institutions. In Phase Three, conventional warfare and fighting are used to seize cities, overthrow the government, and assume control of the country. Mao's doctrine anticipated that circumstances may require shifting between phases in either directions and that the phases may not be uniform and evenly paced throughout the countryside. Mao Zedong's seminal work, On Guerrilla Warfare,[4] has been widely distributed and applied most successfully in Vietnam, by military leader and theorist Võ Nguyên Giáp, whose "Peoples War, Peoples Army"[5] closely follows the Maoist three-phase approach, but emphasizing flexibility in shifting between guerrilla warfare and a spontaneous "General Uprising" of the population in conjunction with guerrilla forces. Some authors have stressed this interchangeability of phases inherent in this model and guerrilla warfare more generally, especially as applied by the North Vietnamese guerrilla.[6]
The more fragmented contemporary pattern
[edit]The classical Maoist model requires a strong, unified guerrilla group and a clear objective. However, some contemporary guerrilla warfare may not follow this template at all, and might encompass vicious ethnic strife, religious fervor, and numerous small, 'freelance' groups operating independently with little overarching structure. These patterns do not fit easily into neat phase-driven categories, or formal three-echelon structures (Main Force regulars, Regional fighters, part-time Guerrillas) as in the People's Wars of Asia.
Some jihadist guerrilla attacks for example, may be driven by a generalized desire to restore a reputed golden age of earlier times, with little attempt to establish a specific alternative political regime in a specific place. Ethnic attacks likewise may remain at the level of bombings, assassinations, or genocidal raids as a matter of avenging some perceived slight or insult, rather than a final shift to conventional warfare as in the Maoist formulation.[7]
Environmental conditions such as increasing urbanization, and the easy access to information and media attention also complicate the contemporary scene. Guerrillas need not conform to the classic rural fighter helped by cross-border sanctuaries in a confined nation or region, (as in Vietnam) but now include vast networks of peoples bound by religion and ethnicity stretched across the globe.[8]
Tactics
[edit]Guerrilla warfare is distinguished from the small unit tactics used in screening or reconnaissance operations typical of conventional forces. It is also different from the activities of pirates or robbers. Such criminal groups may use guerrilla-like tactics, but their primary purpose is immediate material gain, and not a political objective.
Guerrilla tactics are on intelligence, ambush, deception, sabotage, and espionage, undermining an authority through long, low-intensity confrontation. It can be quite successful against an unpopular foreign or local regime, as demonstrated by the Cuban Revolution, Afghanistan War and Vietnam War. A guerrilla army may increase the cost of maintaining an occupation or a colonial presence above what the foreign power may wish to bear. Against a local regime, the guerrilla fighters may make governance impossible with terror strikes and sabotage, and even combination of forces to depose their local enemies in conventional battle. These tactics are useful in demoralizing an enemy, while raising the morale of the guerrillas. In many cases, guerrilla tactics allow a small force to hold off a much larger and better equipped enemy for a long time, as in Russia's Second Chechen War and the Second Seminole War fought in the swamps of Florida (United States of America). Guerrilla tactics and strategy are summarized below and are discussed extensively in standard reference works such as Mao's "On Guerrilla Warfare."[4]
Types of tactical operations
[edit]Ambushes
[edit]Ambushes have been used for as long as guerrilla warfare has been a tactic, and many guerrilla and insurgent groups have used ambushes as a way of defeating superior enemy forces with minimal risk to the insurgents. The ability of an insurgent force to launch an ambush against unsuspecting enemy forces and then withdraw in order to avoid engaging superior enemy reinforcements, or as a tactic of attrition to gradually wear down enemy forces by inflicting casualties and damaging morale, with minimal risk to the insurgents, makes ambushes a very useful tactic for guerrilla and insurgent forces.
Ambushes were frequently used by the Viet Cong and North Vietnamese army against the United States and South Vietnam during the Vietnam War, as the forested and rural farmland provided ideal cover for such activities. The terrain for the ambush had to meet strict criteria, allowing for the provision of concealment from both ground or air, to allow the ambush force to deploy, encircle and divide the enemy, the positioning of heavy weapons emplacements in kill zones to provide sustained fire, to enable the ambush force to set up observation posts for detection of the enemy, and to permit the concealed movement of troops to the ambush position and the dispersal of troops during withdrawal. One important feature of the ambush was that the target units should 'pile up' after being attacked, thus preventing them any easy means of withdrawal from the kill zone and hindering their use of heavy weapons and supporting airstrikes and artillery fire. Terrain was usually selected which would facilitate this and slow down the enemy. The terrain around the ambush site which was not favorable to the ambushing force, or which offered some protection to the target, was heavily mined and booby trapped or pre-registered for mortars.
Iraqi insurgents frequently launched ambushes of Coalition and Iraqi military convoys and patrols during the Iraq War, using numerous types of weapons such as small arms, rocket-propelled grenades, snipers, improvised explosive devices and car bombs. Soft-skinned vehicles such as Humvees were the most commonly targeted. The congested and constricted terrain of the urban areas, and in the rural areas, palm groves and other crops, offered idea cover and concealment for insurgents launching ambushes. The Shia Islamic insurgent group known as the Mahdi Army was one of the primary users of ambush tactics, but ambushes were also used by the Jihadist groups Al-Qaeda in Iraq and Jamaat Ansar al-Sunna. Attacks were usually broken off before support could be called in, in traditional guerrilla fashion. Direct ambushes of U.S. forces declined in the later stages of the war, however, to avoid insurgent casualties as U.S. defences and tactics improved. Ambushes against the poorly equipped and experienced Iraqi security forces, however, proved very lethal. Most Mahdi Army ambushes prior to April 5, 2004 involved no more than seven ambushers with kill zones no larger than 100 meters, however after that night, kill zones became much larger (some several hundred meters long) with many more attackers. There were occasional isolated cases of larger ambushes, such as an attack on a coalition convoy in Samarra on November 30, 2003 that involved 100 fighters and a massive ambush of a coalition convoy in Sadr City on April 4, 2004 by over 1,000 Mahdi Army militiamen.
Assassinations
[edit]Insurgent groups have often employed assassination as a tool to further their causes. Assassinations provide several functions for such groups, namely the removal of specific enemies and as propaganda tools to focus the attention of media and politics on their cause.
The Irish Republican Army guerrillas of 1919–21 killed many RIC Police Intelligence officers during the Irish War of Independence. Michael Collins set up a special unit – the Squad – for this purpose, which had the effect of intimidating many policemen into resigning from the force. The Squad's activities peaked with the killing of 14 British agents in Dublin on Bloody Sunday in 1920.
This tactic was used again by the Provisional IRA during the Troubles in Northern Ireland (1969–1998). Killing of RUC officers and assassination of RUC politicians was one of a number of methods used in the Provisional IRA campaign 1969–1997. The IRA also attempted to assassinate British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher by bombing the Conservative Party Conference in a Brighton hotel. Loyalist paramilitaries retaliated by killing Catholics at random and assassinating Irish nationalist politicians.
Basque terrorists ETA in Spain have assassinated many security and political figures since the late 1960s, notably Luis Carrero Blanco, 1st Duke of Carrero-Blanco Grandee of Spain, in 1973. Since the early 1990s, they have also targeted academics, journalists and local politicians who publicly disagreed with them.
The Red Brigades in Italy carried out assassinations of political figures, as to a lesser extent, did the Red Army Faction in Germany in the 1970s and 1980s.
In the Vietnam War, Communist insurgents routinely assassinated government officials and individual civilians deemed to offend or rival the revolutionary movement. Such attacks, along with widespread military activity by insurgent bands, almost brought the Diem regime to collapse before the U.S. intervention.[9]
Guerrilla operations typically include a variety of strong surprise attacks on transportation routes, individual groups of police or military, installations and structures, economic enterprises, and targeted civilians. Attacking in small groups, using camouflage and often captured weapons of that enemy, the guerrilla force can constantly keep pressure on its foes and diminish its numbers, while still allowing escape with relatively few casualties. The intention of such attacks is not only military but political, aiming to demoralize target populations or governments, or goading an overreaction that forces the population to take sides for or against the guerrillas. Examples range from the chopping off of limbs in various internal African rebellions, to the suicide attacks in Israel and Sri Lanka, to sophisticated manoeuvres by Viet Cong and NVA forces against military bases and formations.
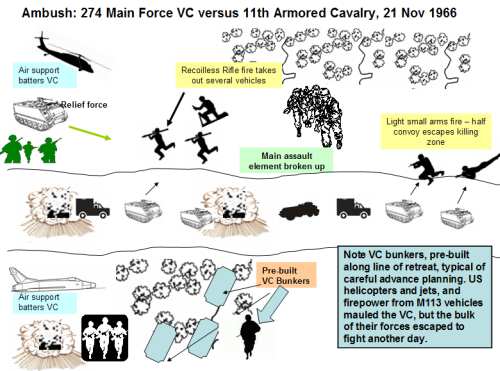
Whatever the particular tactic used, the guerrilla primarily lives to fight another day, and to expand or preserve his forces and political support, not capture or holding specific blocks of territory as a conventional force would. Above is a simplified version of a typical ambush attack by one of the most effective of post-World War II guerrilla forces, the Viet Cong (VC).
Ambushes on key transportation routes are a hallmark of guerrilla operations, causing both economic and political disruption. Careful planning is required for operations, indicated here by VC preparation of the withdrawal route. In this case the Viet Cong assault was broken up by American aircraft and firepower. However, the VC did destroy several vehicles and the bulk of the main VC force escaped. As in most of the Vietnam War, American forces would eventually leave the area, but the insurgents would regroup and return afterwards. This time dimension is also integral to guerrilla tactics.[10]
Organization
[edit]
Guerrilla warfare resembles rebellion, yet it is a different concept. Guerrilla organization ranges from small, local rebel groups of a few dozen guerrillas, to thousands of fighters, deploying from cells to regiments. In most cases, the leaders have clear political aims for the warfare they wage. Typically, the organization has political and military wings, to allow the political leaders "plausible denial" for military attacks.[11] The most fully elaborated guerrilla warfare structure is by the Chinese and Vietnamese communists during the revolutionary wars of East and Southeast Asia.[12] A simplified example of this more sophisticated organizational type – used by revolutionary forces during the Vietnam War, is shown above.
Law and order
[edit]Insurgents may attempt to create a parallel system of "justice" with punishment beatings and killings of criminals in order to ingratiate themselves with the populace. Especially in corrupt and failed regimes where there is a deficit of true justice people's and revolutionary courts aim to legitimize the insurgents as a government in waiting. This is doubly so if insurgents are seen as bringing order in failed regimes, ones with weak central control, and ones in which the security forces are as bad as the criminals. An example of guerrilla law-and-order is found in the Myanmar Civil War where groups such as the National Unity Government and Karen National Union established their own systems of education, law enforcement, and civil service.[13] [14] [15]
Propaganda
[edit]Propaganda is used to sell to the populace the legitimacy, morality and ability of the insurgents, whilst simultaneously portraying the government and its security forces in a negative light. This propaganda can be of the deed, spectacular acts of assassination, sabotage and violence, relying on the mass media to spread the insurgents message. If the state seeks to starve the insurgents of the "oxygen of publicity" the older means of disseminating the insurgents message is by pamphletting (e.g. Thomas Paine's Common Sense) and through use of the oral tradition of stories, rebel and revolutionary songs. Modern insurgents use the internet.[16]
Agents and sympathizers in place
[edit]Insurgent organizations may recruit members of the government's civil and security forces to their cause or to have their own members join them. In addition to being able to provide intelligence and possibly provide direct and indirect aid, doing so allows insurgent members to gain military training and skills which they would not otherwise be able to access, these members may then serve as a cadre to train other insurgents, those who rise high enough may become agents of influence.
Surprise and intelligence
[edit]For successful operations, surprise must be achieved by the guerrillas. If the operation has been betrayed or compromised it is usually called off immediately. Intelligence is also extremely important, and detailed knowledge of the target's dispositions, weaponry and morale is gathered before any attack. Intelligence can be harvested in several ways. Collaborators and sympathizers will usually provide a steady flow of useful information. If working clandestinely, the guerrilla operative may disguise his membership in the insurgent operation, and use deception to ferret out needed data. Employment or enrollment as a student may be undertaken near the target zone, community organizations may be infiltrated, and even romantic relationships struck up as part of intelligence gathering.[17] Public sources of information are also invaluable to the guerrilla, from the flight schedules of targeted airlines, to public announcements of visiting foreign dignitaries, to Army Field Manuals. Modern computer access via the World Wide Web makes harvesting and collation of such data relatively easy.[18] The use of on the spot reconnaissance is integral to operational planning. Operatives will "case" or analyze a location or potential target in depth- cataloguing routes of entry and exit, building structures, the location of phones and communication lines, presence of security personnel and a myriad of other factors. Finally intelligence is concerned with political factors- such as the occurrence of an election or the impact of the potential operation on civilian and enemy morale.
Relationships with the civil population
[edit]
"Why does the guerrilla fighter fight? We must come to the inevitable conclusion that the guerrilla fighter is a social reformer, that he takes up arms responding to the angry protest of the people against their oppressors, and that he fights in order to change the social system that keeps all his unarmed brothers in ignominy and misery."
Relationships with civilian populations are influenced by whether the guerrillas operate among a hostile or friendly population. A friendly population is of immense importance to guerrilla fighters, providing shelter, supplies, financing, intelligence and recruits. The "base of the people" is thus the key lifeline of the guerrilla movement. In the early stages of the Vietnam War, American officials "discovered that several thousand supposedly government-controlled 'fortified hamlets' were in fact controlled by Viet Cong guerrillas, who 'often used them for supply and rest havens'."[20] Popular mass support in a confined local area or country however is not always strictly necessary. Guerrillas and revolutionary groups can still operate using the protection of a friendly regime, drawing supplies, weapons, intelligence, local security and diplomatic cover.
An apathetic or hostile population makes life difficult for guerrilleros and strenuous attempts are usually made to gain their support. These may involve not only persuasion, but a calculated policy of intimidation. Guerrilla forces may characterize a variety of operations as a liberation struggle, but this may or may not result in sufficient support from affected civilians. Other factors, including ethnic and religious hatreds, can make a simple national liberation claim untenable. Whatever the exact mix of persuasion or coercion used by guerrillas, relationships with civil populations are one of the most important factors in their success or failure.[21]
Use of terror
[edit]In some cases, the use of terrorism can be an aspect of guerrilla warfare. Terrorism is used to focus international attention on the guerrilla cause, kill opposition leaders, extort money from targets, intimidate the general population, create economic losses, and keep followers and potential defectors in line. As well, the use of terrorism can provoke the greater power to launch a disproportionate response, thus alienating a civilian population which might be sympathetic to the terrorist's cause. Such tactics may backfire and cause the civil population to withdraw its support, or to back countervailing forces against the guerrillas.[11]
Such situations occurred in Israel, where suicide bombings encouraged most Israeli opinion to take a harsh stand against Palestinian attackers, including general approval of "targeted killings" to kill enemy cells and leaders.[22] In the Philippines and Malaysia, communist terror strikes helped turn civilian opinion against the insurgents. In Peru and some other countries, civilian opinion at times backed the harsh countermeasures used by governments against revolutionary or insurgent movements.
Bank robberies
[edit]Bank robberies have been used by insurgents and revolutionaries in order to fund their activities, for example the 1907 Tiflis bank robbery, using violence in excess of that needed to achieve the aims of the robberies helps contributes to a climate of fear.
Group participation in atrocities
[edit]As an initiation new recruits, especially forced ones, will be encouraged or forced to participate in atrocities, such as torture, rape and murder, unwilling recruits will be forced to do this against their own communities and families or be killed themselves. The goal of these atrocities is to divorce the new recruit from his or her previous life and bind them to the insurgency; criminals in their own eyes and in the eyes of society, such recruits will be led to believe that they cannot go back to their previous lives and have no other family other than the insurgency. In order to break the hold the insurgency may hold over such members, the authorities may offer amnesties and pardons for crimes committed.
Kidnapping
[edit]Insurgents kidnap and take hostage members of the general public or military for purposes such as the provision of funding or the release of prisoners. The kidnapping of family members may be used to coerce co-operation, the provision of information, use of a property as a safe house, a copy of a key etc. High value hostages may be taken in order to force the release of captured comrades and as media spectaculars. At all levels creating a fear of kidnapping reinforces a message that the state and its security forces cannot provide protection. Members of the military have also been kidnapped for propaganda purposes, or to hold them hostage in order to receive supplies and funding, or the release of insurgent prisoners[citation needed].
Kidnappings emerged as another tactic of the Iraqi insurgency in April 2004, as a way of intimidating foreign civilians, acquiring the payment of a ransom or the release of captured insurgents, and as a propaganda technique of attracting media attention and inspiring recruits. Foreign civilians bore the brunt of the kidnappings, although U.S. military personnel were also targeted, as was the case with Ahmed Kousay al-Taie. After kidnapping the victim, the insurgents typically made some sort of demand of the government of the hostage's nation and give a time limit for the demand to be carried out, often 72 hours. Execution is often threatened if the government fails to heed the wishes of the hostage takers. Several individuals, including American radio tower repairman Nick Berg and South Korean Christian missionary Kim Sun-il, among others, have been beheaded. In many cases, tapes of the beheadings are distributed for propaganda purposes. However, 80% of hostages taken by insurgents have been peacefully released[citation needed]. Jill Carroll, a journalist for the Christian Science Monitor, was kidnapped in early 2006, and although later let go, her Iraqi interpreter was killed. Almost all of the kidnappings were conducted by radical Sunni groups on the fringe of the insurgency.
During the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, kidnapping of Israeli soldiers and civilians has been employed by Palestinian nationalists for years, who have integrated kidnapping into their guerrilla warfare-style tactics. Numerous members of the Israel Defense Forces have been kidnapped by militants such as Hamas or Hezbollah, who demand the release of Palestinian militants from Israeli jails and the funding and supply of the insurgents as part of a ransom. Several of these Israeli soldiers who have been kidnapped have died in captivity from poor conditions or other causes. One of the most notable examples of Palestinian kidnapping is that of the 2006 Gaza cross-border raid, where IDF Sergeant first class Gilad Shalit was wounded and captured by members of the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades (the military wing of Hamas), Popular Resistance Committees and the Army of Islam, who abducted him through tunnels dug under the Gaza Strip. A cross-border raid in 2006 by Hezbollah also succeeded in kidnapping IDF soldiers Ehud Goldwasser and Eldad Regev, but these two later died of injuries sustained during the battle. In 1982, IDF tank commander Hezi Shai was also kidnapped by members of the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine-General Command, and held captive until the Jibril Agreement in 1985[citation needed].
Sabotage
[edit]Sabotage against infrastructure, for example power stations, airports and reservoirs at the upper end, and for example electricity pylons, substations, telephone exchanges and railway tracks at the lower end make real to the populace that an insurgency is underway; and if sustained can affect the quality of life of the populace. In order to protect all the possible targets that the insurgents may attack, government forces may be stretched to the point where they become vulnerable to a defeat in detail[citation needed].
Sabotage was used extensively by resistance movements during the Second World War as a way of aiding the Allies by attacking Axis supply lines in occupied territories in Nazi-occupied Europe and the Japanese-occupied Pacific. An example of this was the sabotage of infrastructure by the Polish Armia Krajowa, which commanded the majority of resistance organizations in Poland and coordinated and aided the Jewish Military Union as well as more reluctantly helping the Jewish Combat Organization, which was responsible for the greatest number of acts of sabotage in German-occupied Europe. The Home Army's sabotage operations Operation Garland and Operation Ribbon are just two examples. In all, the Home Army damaged 6,930 locomotives, set 443 rail transports on fire, damaged over 19,000 rail cars "wagony", and blew up 38 rail bridges, not to mention the attacks against the railroads. The Home Army was also responsible for 4,710 built-in flaws in parts for aircraft engines and 92,000 built-in flaws in artillery projectiles, among other examples of significant sabotage. In addition, over 25,000 acts of more minor sabotage were committed. Communist groups, such as the Armia Ludowa and Gwardia Ludowa, often caused casualties among German soldiers and civilians and their Polish collaborators, resulting in a great number of Polish and Jewish hostages, mostly civilians, being murdered in reprisal by the Germans. The Gwardia Ludowa destroyed around 200 German trains during the war, and indiscriminately threw hand grenades into places frequented by Germans. The French Resistance also ran an extremely effective sabotage campaign against the Germans. Receiving their sabotage orders through messages over the BBC radio or by aircraft, the French used both passive and active forms of sabotage. Passive forms included losing German shipments and allowing poor quality material to pass factory inspections. Many active sabotage attempts were against critical rail lines of transportation. German records count 1,429 instances of sabotage from French Resistance forces between January 1942 and February 1943. From January through March 1944, sabotage accounted for three times the number of locomotives damaged by Allied air power[citation needed].
From 1948 to 1960 during the Malayan Emergency, the armed branch of the Malayan Communist Party, the Malayan National Liberation Army committed numerous effective acts of sabotage against the British colonial authorities. Most of their efforts were centered around crippling Malaya's colonial economy and involved sabotage against trains, railway bridges, rubber trees, water pipes, electric lines and military camps. Although highly successful, they caused backlash among the Malayan population, who gradually withdrew support for the Communist movement as their livelihoods became threatened[citation needed].
During the Vietnam War, the Liberation Army of South Vietnam used "swimmer saboteurs", specially trained frogmen, to destroy or damage naval assets of the U.S and its allies. Between 1969 and 1970, swimmer saboteurs sunk, destroyed, or damaged 77 allied assets. Although poorly equipped, they were well-trained and resourceful. The swimmers provided a low-cost/low-risk option with high payoff; possible loss to the country for failure compared to the possible gains from a successful mission led to the conclusion that the swimmer saboteurs were a good idea.[23]
During the Soviet–Afghan War, the Afghan mujahideen favoured sabotage operations. They concentrated on both civilian and military targets, such as cutting power lines, knocking out pipelines and radio stations, blowing bridges, closing major roads, attacking convoys, disrupting the electric power system and industrial production, bombing government office buildings, air terminals, hotels and cinemas, and attacking police stations and Soviet military installations and air bases. They assassinated government officials and People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan members, and laid siege to small rural outposts. In the border region with Pakistan, the Mujahideen would often launch 800 rockets per day. They also used land mines heavily. Often, they would enlist the services of local inhabitants, even children. In March 1982, a bomb exploded at the Ministry of Education, damaging several buildings. In the same month, a widespread power failure darkened Kabul when a pylon on the transmission line from the Naghlu power station was blown up. In June 1982 a column of about 1,000 young PDPA members sent out to work in the Panjshir valley were ambushed within 30 km of Kabul, with heavy loss of life. On 4 September 1985, insurgents shot down a domestic Bakhtar Airlines plane as it took off from Kandahar airport, killing all 52 people aboard[citation needed].
During the Contras insurgency following the Nicaraguan Revolution, the Central Intelligence Agency developed The Freedom Fighter's Manual, a fifteen-page propaganda booklet that was airdropped over Nicaragua in 1983, which explained numerous sabotage methods by which the average citizen could cause civil disorder and disruption.[24] Methods mentioned include destroying utility poles, blocking and destroying highways and being unproductive at work. The Contras also contributed to the sabotage campaign by attacking civilian targets such as healthcare clinics, schools and cooperatives, and industrial targets such as mining ports, pipelines and refineries. Civil servants such as doctors, nurses, judges and Sandinista National Liberation Front officials were also killed as part of the campaign[citation needed].
Sniper attacks
[edit]Snipers have historically been used by insurgents as a method of psychological warfare and attrition in Iraq, Syria, Yemen, Vietnam and Northern Ireland, including mobile units transported in vehicles. The highly urban areas of the Yemeni and Syrian civil wars and the Iraqi insurgencies and the rural areas of the Vietnam War and The Troubles provide ideal cover and positions for insurgent snipers, who kill or injure soldiers whenever possible and melt away to avoid enemy reinforcements and counterattacks.
Insurgents in Iraq have used snipers, including vehicle-borne units, to isolate enemy combatants from larger forces and strike at officers and commander—a demonstration of their technological capabilities and tactical patience. They generally engage targets from 100 to 1000 meters and primarily use the SVD sniper rifle, however they have also been known to use .50 Cal and captured coalition M24 sniper rifles. Although an insurgent sniper unit usually operates from a dominant terrain feature, they have also been shown to use cars and vans resourcefully to quickly move from position to position. The sniper or snipers usually films the shot, extracts, and then posts the very graphic and shocking event to the internet for propaganda purposes, focusing on lucrative targets that will earn them a lot of media attention.[25]
Suicide attacks
[edit]Over the past several decades, suicide bombings have emerged as one of the prominent tactics of many insurgent groups across the world. Although crude and reliant on the expenditure of personnel, they have proven remarkably effective at causing significant damage and spreading terror in conflict zones such as Afghanistan, Pakistan and Iraq in which they are deployed, becoming a primary tactic of many insurgent groups in these regions.
Suicide bombing as a military tactic was pioneered by Hezbollah, a Shia Jihadist militant group and political party that originated during the Lebanese Civil War as a resistance movement against Israel and its allies during the Israeli occupation of southern Lebanon.[26] Beginning with the Beirut barracks bombing that year, in which a base of the Multinational Force in Lebanon was destroyed by two suicide truck bombs that killed nearly 300 U.S. and French soldiers, Hezbollah (often with the assistance of Iranian military intelligence)[27] carried out a number of devastating suicide bombings against U.S. and Israeli targets, including the U.S. embassy in Beirut in 1983 and 1984; the Israeli embassy in Buenos Aire in 1992; and the Buenos Aires AMIA in 1994, with each attack claiming the lives of multiple U.S. and Israeli civilians and military personnel.
During the Sri Lankan Civil War, the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (better known as the Tamil Tigers) also made heavy use of suicide bombers against the Sri Lankan government and military targets. Beginning in July 1987, LTTE suicide bombers (known as "Black Tigers") were used to devastating effect in either terrorist attacks against specific targets or to support conventional attacks during battle with Sri Lankan forces. Made up of both male and female suicide bombers, the Black Tigers killed 981 people in 83 attacks over the course of the civil war, with particularly notable attacks including the first attack carried out by "Captain Miller" during the Battle of Nelliady, the assassination of former Indian prime minister Rajiv Gandhi;[28][29] the killing of Sri Lankan president Ranasinghe Premadasa;[30][31][32][33] and the assassination of Admiral Clancy Fernando, the highest Sri Lankan military official killed during the conflict.
During the Second Intifada in Palestine, suicide bombing emerged as the deadliest tactic of Palestinian militant groups such as Hamas, Palestinian Islamic Jihad, Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP) and the al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades. Conducted as a single or double bombing, suicide bombings were generally conducted against "soft" targets, or "lightly hardened" targets (such as Israel Defense Forces checkpoints) to try to raise the cost of the war to Israelis and demoralize the Israeli society. Most suicide bombing attacks (although not all) targeted civilians, and were conducted in crowded places in Israeli cities, such as public transport, restaurants, shopping malls and markets. One major development was the use of suicide bombs carried by children. Unlike most suicide bombings, the use of these not only earned condemnation from the United States and from human rights groups such as Amnesty International, but also from many Palestinians and much of the Middle East press. The youngest Palestinian suicide bomber was 16-year-old Issa Bdeir, a high school student from the village of Al Doha, who shocked his friends and family when he blew himself up in a park in Rishon LeZion, killing a teenage boy and an elderly man. The youngest attempted suicide bombing was by a 14-year-old captured by soldiers at the Huwwara checkpoint before managing to do any harm.
Withdrawal
[edit]Guerrillas must plan carefully for withdrawal once an operation has been completed, or if it is going badly. The withdrawal phase is sometimes regarded as the most important part of a planned action, and to get entangled in a lengthy struggle with superior forces is usually fatal to insurgent, terrorist or revolutionary operatives. Withdrawal is usually accomplished using a variety of different routes and methods and may include quickly scouring the area for loose weapons, evidence cleanup, and disguise as peaceful civilians.[4]
Logistics
[edit]Guerrillas typically operate with a smaller logistical footprint compared to conventional formations; nevertheless, their logistical activities can be elaborately organized. A primary consideration is to avoid dependence on fixed bases and depots which are comparatively easy for conventional units to locate and destroy. Mobility and speed are the keys and wherever possible, the guerrilla must live off the land, or draw support from the civil population in which it is embedded. In this sense, "the people" become the guerrilla's supply base.[4] Financing of both terrorist and guerrilla activities ranges from direct individual contributions (voluntary or non-voluntary), and actual operation of business enterprises by insurgent operatives, to bank robberies, kidnappings and complex financial networks based on kin, ethnic and religious affiliation (such as that used by modern Jihadist/Jihad organizations).
Permanent and semi-permanent bases form part of the guerrilla logistical structure, usually located in remote areas or in cross-border sanctuaries sheltered by friendly regimes.[34] These can be quite elaborate, as in the tough VC/NVA fortified base camps and tunnel complexes encountered by US forces during the Vietnam War. Their importance can be seen by the hard fighting sometimes engaged in by communist forces to protect these sites. However, when it became clear that defence was untenable, communist units typically withdrew without sentiment.
Terrain
[edit]
Guerrilla warfare is often associated with a rural setting, and this is indeed the case with the definitive operations of Mao and Giap, the mujahadeen of Afghanistan, the Ejército Guerrillero de los Pobres (EGP) of Guatemala, the Contras of Nicaragua, and the FMLN of El Salvador. Guerrillas however have successfully operated in urban settings as demonstrated in places like Argentina and Northern Ireland. In those cases, guerrillas rely on a friendly population to provide supplies and intelligence. Rural guerrillas prefer to operate in regions providing plenty of cover and concealment, especially heavily forested and mountainous areas. Urban guerrillas, rather than melting into the mountains and forests, blend into the population and are also dependent on a support base among the people. Removing and destroying guerrillas out of both types of areas can be difficult.
Foreign support and sanctuaries
[edit]Foreign support in the form of soldiers, weapons, sanctuary, or statements of sympathy for the guerrillas is not strictly necessary, but it can greatly increase the chances of an insurgent victory.[17] Foreign diplomatic support may bring the guerrilla cause to international attention, putting pressure on local opponents to make concessions, or garnering sympathetic support and material assistance. Foreign sanctuaries can add heavily to guerrilla chances, furnishing weapons, supplies, materials and training bases. Such shelter can benefit from international law, particularly if the sponsoring government is successful in concealing its support and in claiming "plausible denial" for attacks by operatives based in its territory.
The VC and NVA made extensive use of such international sanctuaries during their conflict, and the complex of trails, way-stations and bases snaking through Laos and Cambodia, the famous Ho Chi Minh Trail, was the logistical lifeline that sustained their forces in the South. Also, the United States funded a revolution in Colombia in order to take the territory they needed to build the Panama Canal. Another case in point is the Mukti Bahini guerrilleros who fought alongside the Indian Army in the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971 against Pakistan that resulted in the creation of the state of Bangladesh. In the post-Vietnam era, the Al Qaeda organization also made effective use of remote territories, such as Afghanistan under the Taliban regime, to plan and execute its operations.
Guerrilla initiative and combat intensity
[edit]
Able to choose the time and place to strike, guerrilla fighters will usually possess the tactical initiative and the element of surprise. Planning for an operation may take weeks, months or even years, with a constant series of cancellations and restarts as the situation changes.[35] Careful rehearsals and "dry runs" are usually conducted to work out problems and details. Many guerrilla strikes are not undertaken unless clear numerical superiority can be achieved in the target area, a pattern typical of VC/NVA and other "Peoples War" operations. Individual suicide bomb attacks offer another pattern, typically involving only the individual bomber and his support team, but these too are spread or metered out based on prevailing capabilities and political winds.
Whatever approach is used, the guerrilla holds the initiative and can prolong his survival though varying the intensity of combat. This means that attacks are spread out over quite a range of time, from weeks to years. During the interim periods, the guerrilla can rebuild, resupply and plan. In the Vietnam War, most communist units (including mobile NVA regulars using guerrilla tactics) spent only a limited number of days a year fighting. While they might be forced into an unwanted battle by an enemy sweep, most of the time was spent in training, intelligence gathering, political and civic infiltration, propaganda indoctrination, construction of fortifications, or stocking supply caches.[12] The large numbers of such groups striking at different times however, gave the war its "around the clock" quality.
Other aspects
[edit]Agitation
[edit]Often grouped together with propaganda as agitprop, agitation is the use of agitators to stir up discontent both real and imagined with the regime and to propose a course of action to right these perceived wrongs. The traditional targets of agitators have been the shop floor, students' unions and the junior officer's mess halls of the military.
Foreign and native regimes
[edit]Examples of successful guerrilla warfare against a native regime include the Cuban Revolution and the Chinese Civil War, as well as the Sandinista Revolution which overthrew a military dictatorship in Nicaragua. The many coups and rebellions of Africa often reflect guerrilla warfare, with various groups having clear political objectives and using guerrilla tactics. Examples include the overthrow of regimes in Uganda, Liberia and other places. In Asia, native or local regimes have been overthrown by guerrilla warfare, most notably in Vietnam, China and Cambodia.
Foreign forces intervened in all these countries, but the power struggles were eventually resolved locally.
There are many unsuccessful examples of guerrilla warfare against local or native regimes. These include Portuguese Africa (Angola, Mozambique and Guinea-Bissau), Malaysia (then Malaya) during the Malayan Emergency, Bolivia, Argentina, and the Philippines. It was even able to use these tactics effectively against the Indian Peace Keeping Force sent by India in the mid-1980s, which were later withdrawn for varied reasons, primarily political. The Tigers are fighting to create a separate homeland for Sri Lankan Tamils, many of whom complain of marginalisation by successive governments led by the Sinhalese majority since independence from Britain in 1948.
Ethical dimensions
[edit]Civilians may be attacked or killed as punishment for alleged collaboration, or as a policy of intimidation and coercion. Such attacks are usually sanctioned by the guerrilla leadership with an eye toward the political objectives to be achieved. Attacks may be aimed to weaken civilian morale so that support for the guerrilla's opponents decreases. Civil wars may also involve deliberate attacks against civilians, with both guerrilla groups and organized armies committing atrocities. Ethnic and religious feuds may involve widespread massacres and genocide as competing factions inflict massive violence on targeted civilian population.
Guerrillas in wars against foreign powers may direct their attacks at civilians, particularly if foreign forces are too strong to be confronted directly on a long-term basis. In Vietnam, bombings and terror attacks against civilians were fairly common, and were often effective in demoralizing local opinion that supported the ruling regime and its American backers. [citation needed]While attacking an American base might involve lengthy planning and casualties, smaller scale terror strikes in the civilian sphere were easier to execute. Such attacks also had an effect on the international scale, demoralizing American opinion, and hastening a withdrawal[citation needed].
In Iraq, most of the deaths since the 2003 US invasion have not been suffered by US troops but by civilians, as warring factions plunged the country into civil war based on ethnic and religious hostilities.[citation needed] [36] Arguments vary on whether such turmoil will succeed in turning American opinion against the US troop deployment. However, the use of attacks against civilians to create an atmosphere of chaos (and thus political advantage where the atmosphere causes foreign occupiers to withdraw or offer concessions), is well established in guerrilla and national liberation struggles. Claims and counterclaims of the morality of such attacks, or whether guerrillas should be classified as "terrorists" or "freedom fighters" are beyond the scope of this article. See Terrorism and Genocide for a more in-depth discussion of the moral and ethical implications of targeting civilians.
Laws of war
[edit]Guerrilleros are in danger of not being recognized as lawful combatants because they may not wear a uniform, (to mingle with the local population), or their uniform and distinctive emblems may not be recognized as such by their opponents. This occurred in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71; see Franc-Tireurs.
Article 44, sections 3 and 4 of the 1977 First Additional Protocol to the Geneva Conventions, "relating to the Protection of Victims of International Armed Conflicts", does recognize combatants who, because of the nature of the conflict, do not wear uniforms as long as they carry their weapons openly during military operations. This gives non-uniformed guerrilleros lawful combatant status against countries that have ratified this convention. However, the same protocol states in Article 37.1.c that "the feigning of civilian, non-combatant status" shall constitute perfidy and is prohibited by the Geneva Conventions. So is the wearing of enemy uniform, as happened in the Boer War.
Counter-guerrilla warfare
[edit]Classic guidelines
[edit]The guerrilla can be difficult to beat, but certain principles of counter-insurgency warfare are well known since the 1950s and 1960s and have been successfully applied. The widely distributed and influential work of Sir Robert Thompson, counter-insurgency expert of the Malayan Emergency, offers several such guidelines. Thompson's underlying assumption is that of a country minimally committed to the rule of law and better governance. Some governments, however, give such considerations short shrift, and their counter-insurgency operations have involved mass murder, genocide, starvation and the massive spread of terror, torture and execution. In the Soviet–Afghan War for example, the Soviets countered the Mujahideen with a policy of wastage and depopulation,[citation needed] driving over one third of the Afghan population into exile (over 5 million people), and carrying out widespread destruction of villages, granaries, crops, herds and irrigation systems, including the deadly and widespread mining of fields and pastures.
Elements of Thompson's moderate approach are adapted here:[37]
- The people are the key base to be secured and defended rather than territory won or enemy bodies counted. Contrary to the focus of conventional warfare, territory gained, or casualty counts are not of overriding importance in counter-guerrilla warfare. The support of the population is the key variable. Since many insurgents rely on the population for recruits, food, shelter, financing, and other materials, the counter-insurgent force must focus its efforts on providing physical and economic security for that population and defending it against insurgent attacks and propaganda.
- There must be a clear political counter-vision that can overshadow, match, or neutralize the guerrilla vision. This can range from granting political autonomy, to economic development measures in the affected region. The vision must be an integrated approach, involving political, social and economic and media influence measures. A nationalist narrative for example, might be used in one situation, an ethnic autonomy approach in another. An aggressive media campaign must also be mounted in support of the competing vision or the counter-insurgent regime will appear weak or incompetent.
- Practical action must be taken at the lower levels to match the competitive political vision. It may be tempting for the counter-insurgent side to simply declare guerrillas "terrorists" and pursue a harsh liquidation strategy. Brute force however, may not be successful in the long run. Action does not mean capitulation, but sincere steps such as removing corrupt or arbitrary officials, cleaning up fraud, building more infrastructure, collecting taxes honestly, or addressing other legitimate grievances can do much to undermine the guerrillas' appeal.
- Economy of force. The counter-insurgent regime must not overreact to guerrilla provocations, since this may indeed be what they seek to create a crisis in civilian morale. Indiscriminate use of firepower may only serve to alienate the key focus of counterinsurgency- the base of the people. Police level actions should guide the effort and take place in a clear framework of legality, even if under a State of Emergency. Civil liberties and other customs of peacetime may have to be suspended, but again, the counter-insurgent regime must exercise restraint, and cleave to orderly procedures. In the counter-insurgency context, "boots on the ground" are even more important than technological prowess and massive firepower, although anti-guerrilla forces should take full advantage of modern air, artillery and electronic warfare assets.[38]
- Big unit action may sometimes be necessary. If police action is not sufficient to stop the guerrilla fighters, military sweeps may be necessary. Such "big battalion" operations may be needed to break up significant guerrilla concentrations and split them into small groups where combined civic-police action can control them.
- Aggressive mobility. Mobility and aggressive small unit action is extremely important for the counter-insurgent regime. Heavy formations must be lightened to aggressively locate, pursue and fix insurgent units. Huddling in static strong-points simply concedes the field to the insurgents. They must be kept on the run constantly with aggressive patrols, raids, ambushes, sweeps, cordons, roadblocks, prisoner snatches, etc.
- Ground level embedding and integration. In tandem with mobility is the embedding of hardcore counter-insurgent units or troops with local security forces and civilian elements. The US Marines in Vietnam also saw some success with this method, under its CAP (Combined Action Program) where Marines were teamed as both trainers and "stiffeners" of local elements on the ground. US Special Forces in Vietnam like the Green Berets, also caused significant local problems for their opponents by their leadership and integration with mobile tribal and irregular forces.[39] The CIA's Special Activities Division created successful guerrilla forces from the Hmong tribe during the war in Vietnam in the 1960s,[40] from the Northern Alliance against the Taliban during the war in Afghanistan in 2001,[41] and from the Kurdish Peshmerga against Ansar al-Islam and the forces of Saddam Hussein during the war in Iraq in 2003.[42][43] In Iraq, the 2007 US "surge" strategy saw the embedding of regular and special forces troops among Iraqi army units. These hardcore groups were also incorporated into local neighborhood outposts in a bid to facilitate intelligence gathering, and to strengthen ground level support among the masses.[38]
- Cultural sensitivity. Counter-insurgent forces require familiarity with the local culture, mores and language or they will experience numerous difficulties. Americans experienced this in Vietnam and during the US Iraqi Freedom invasion and occupation, where shortages of Arabic speaking interpreters and translators hindered both civil and military operations.[44]
- Systematic intelligence effort. Every effort must be made to gather and organize useful intelligence. A systematic process must be set up to do so, from casual questioning of civilians to structured interrogations of prisoners. Creative measures must also be used, including the use of double agents, or even bogus "liberation" or sympathizer groups that help reveal insurgent personnel or operations.
- Methodical clear and hold. An "ink spot" clear and hold strategy must be used by the counter-insurgent regime, dividing the conflict area into sectors, and assigning priorities between them. Control must expand outward like an ink spot on paper, systematically neutralizing and eliminating the insurgents in one sector of the grid, before proceeding to the next. It may be necessary to pursue holding or defensive actions elsewhere, while priority areas are cleared and held.
- Careful deployment of mass popular forces and special units. Mass forces include village self-defence groups and citizen militias organized for community defence and can be useful in providing civic mobilization and local security. Specialist units can be used profitably, including commando squads, long range reconnaissance and "hunter-killer" patrols, defectors who can track or persuade their former colleagues like the Kit Carson Scouts in Vietnam, and paramilitary style groups. Strict control must be kept over specialist units to prevent the emergence of violent vigilante style reprisal squads that undermine the government's program.
- The limits of foreign assistance must be clearly defined and carefully used. Such aid should be limited either by time, or as to material and technical, and personnel support, or both. While outside aid or even troops can be helpful, lack of clear limits, in terms of either a realistic plan for victory or exit strategy, may find the foreign helper "taking over" the local war, and being sucked into a lengthy commitment, thus providing the guerrillas with valuable propaganda opportunities as the toll of dead foreigners mounts. Such a scenario occurred with the US in Vietnam, with the American effort creating dependence in South Vietnam, and war-weariness and protests back home. Heavy-handed foreign interference may also fail to operate effectively within the local cultural context, setting up conditions for failure.
- Time. A key factor in guerrilla strategy is a drawn-out, protracted conflict that wears down the will of the opposing counter-insurgent forces. Democracies are especially vulnerable to the factor of time. The counter-insurgent force must allow enough time to get the job done. Impatient demands for victory centered around short-term electoral cycles play into the hands of the guerrillas, though it is equally important to recognize when a cause is lost and the guerrillas have won.
Variants
[edit]Some writers on counter-insurgency warfare emphasize the more turbulent nature of today's guerrilla warfare environment, where the clear political goals, parties and structures of such places as Vietnam, Malaysia, or El Salvador are not as prevalent. These writers point to numerous guerrilla conflicts that center around religious, ethnic or even criminal enterprise themes, and that do not lend themselves to the classic "national liberation" template.
The wide availability of the Internet has also cause changes in the tempo and mode of guerrilla operations in such areas as coordination of strikes, leveraging of financing, recruitment, and media manipulation. While the classic guidelines still apply, today's anti-guerrilla forces need to accept a more disruptive, disorderly and ambiguous mode of operation.
- "Insurgents may not be seeking to overthrow the state, may have no coherent strategy or may pursue a faith-based approach difficult to counter with traditional methods. There may be numerous competing insurgencies in one theater, meaning that the counterinsurgent must control the overall environment rather than defeat a specific enemy. The actions of individuals and the propaganda effect of a subjective 'single narrative' may far outweigh practical progress, rendering counterinsurgency even more non-linear and unpredictable than before. The counterinsurgent, not the insurgent, may initiate the conflict and represent the forces of revolutionary change. The economic relationship between insurgent and population may be diametrically opposed to classical theory. And insurgent tactics, based on exploiting the propaganda effects of urban bombing, may invalidate some classical tactics and render others, like patrolling, counterproductive under some circumstances. Thus, field evidence suggests, classical theory is necessary but not sufficient for success against contemporary insurgencies..."[45]
Writings
[edit]Theories of Mao Zedong
[edit]Mao Zedong, during the Chinese Civil War, summarized the People's Liberation Army's principles of Revolutionary Warfare in the following points for his troops: The enemy advances, we retreat. The enemy camps, we harass. The enemy tires, we attack. The enemy retreats, we pursue. A common slogan of the time went "Draw back your fist before you strike." This referred to the tactic of baiting the enemy, "drawing back the fist", before "striking" at the critical moment where they are overstretched and vulnerable. Mao made a distinction between Mobile Warfare (yundong zhan) and Guerrilla Warfare (youji zhan), but they were part of an integrated continuum aiming towards a final objective. Mao's seminal work, On Guerrilla Warfare,[46] has been widely distributed and applied, successfully in Vietnam, under military leader and theorist Võ Nguyên Giáp. Giap's "Peoples War, Peoples Army"[5] closely follows the Maoist three-stage approach.
Writings of T. E. Lawrence
[edit]T. E. Lawrence, best known as "Lawrence of Arabia", introduced a theory of guerrilla warfare tactics in an article he wrote for the Encyclopædia Britannica published in 1938. In that article, he compared guerrilla fighters to a gas. The fighters disperse in the area of operations more or less randomly. They or their cells occupy a very small intrinsic space in that area, just as gas molecules occupy a very small intrinsic space in a container. The fighters may coalesce into groups for tactical purposes, but their general state is dispersed. Such fighters cannot be "rounded up." They cannot be contained. They are extremely difficult to "defeat" because they cannot be brought to battle in significant numbers. The cost in soldiers and material to destroy a significant number of them becomes prohibitive, in all senses, that is physically, economically, and morally. Lawrence describes a non-native occupying force as the enemy (such as the Turks).
Lawrence wrote down some of his theories while ill and unable to fight the Turks in his book Seven Pillars of Wisdom. There, he reviews von Clausewitz and other theorists of war, and finds their writings inapplicable to his situation. The Arabs could not defeat the Turks in pitched battle since they were individualistic warriors not disciplined soldiers used to fight in large formations.
So instead Lawrence proposed if possible never meeting the enemy, thus giving their soldiers nothing to shoot at, unable to control anything except what ground their rifles could point to. Meanwhile, Lawrence and the Arabs could ride camels into and out of the desert, attacking railroad lines and isolated outposts with impunity, avoiding the heavily garrisoned positions and cities.
Writings of Che Guevara
[edit]One of the main guerrilla strategists was the Berber leader Abd el-Krim who fought both Spanish and French armies in the Rif Mountains in North Africa during the beginning of the 20th century. His guerrilla tactics are known to have inspired Ho Chi Minh, Mao Zedong, and Che Guevara.[47] Guevara, an Argentinian revolutionary, wrote extensively on Guerrilla Warfare and stressed the revolutionary potential of the guerrillas.
"The guerrilla band is an armed nucleus, the fighting vanguard of the people. It draws its great force from the mass of the people themselves. The guerrilla band is not to be considered inferior to the army against which it fights simply because it is inferior in fire power. Guerrilla warfare is used by the side which is supported by a majority but which possesses a much smaller number of arms for use in defense against oppression."
Writing of Abdul Haris Nasution
[edit]The fullest expression of the Indonesian army's founding doctrines is found in Abdul Haris Nasution's 1953 Fundamentals of Guerrilla Warfare.[49] The work is a mix of reproduced strategic directives from 1947 to 1948, Nasution's theories of guerrilla warfare, his reflections on the period just past (post-Japanese occupation) and the likely crises to come, and outlines of his legal frameworks for military justice and "guerrilla government". The work contains similar principles to those espoused or practiced by other theorists and practitioners from Michael Collins in Ireland, T. E. Lawrence in the Middle East and Mao in China in the early Twentieth Century, to contemporary insurgents in Afghanistan and Iraq. Nasution willingly shows his influences, frequently referring to some guerrilla activities as "Wingate" actions, quoting Lawrence and drawing lessons from the recent and further past to develop and illustrate his well-thought out arguments. Where the work substantially differs from other theorist/practitioners is that General Nasution was one of the few men to have led both a guerrilla and a counter-guerrilla war. This dual perspective on the realities of ‘people's war’ leaves the work refreshingly free of the perceived hyperbole and ideological leanings of similar revolutionary works from the period. It is direct when discussing the methods and the effect of revolutionary guerrilla war on all involved, especially civilians.[50]
Texts and treatises
[edit]Guerrilla tactics were summarized into the Minimanual of the Urban Guerrilla[51] in 1969 by Carlos Marighella. The text has been banned in many countries, but remains in print and on bookshelves in several others, including the United States.
According to Lenny Frank junior Marighella's booklet was considered the bible of the Baader-Meinhof Gang, among many other left-wing terror groups. Unfortunately for them, and as Lenny Frank points out, much of the book was fatally flawed. Basic assumptions about how the public would react to Marighella's tactics, and how some of these tactics would work in an urban environment, proved to be exactly wrong.
World War II American and British writings
[edit]
John Keats wrote about an American guerrilla leader in World War II: Colonel Wendell Fertig, who in 1942 organized a large guerrilla force which harassed the Japanese occupation forces on the Philippine Island of Mindanao all the way up to the liberation of the Philippines in 1945. His abilities were later utilized by the United States Army, when Fertig helped found the United States Army Special Warfare School at Fort Bragg, North Carolina. Others included Col. Aaron Bank, Col. Russell Volckmann, and Col. William R. Peers.[52] Volckmann commanded a guerrilla force which operated out of the Cordillera of Northern Luzon in the Philippines from the beginning of World War II to its conclusion. He remained in radio contact with US Forces,[53] prior to the invasion of Lingayen Gulf. Peers, who later became a general, commanded OSS Detachment 101 in Burma and authored a book on its operations following the war. Because the 101 was never larger than a few hundred Americans, it relied on support from various Burmese tribal groups. In particular, the vigorously anti-Japanese Kachin people were vital to the unit's success.[52][54]
Brigadier C. Aubrey Dixon, OBE, chief small arms ammunition designer for the British during World War II and a member of the tribunal responsible for the trial of Field Marshal von Manstein, wrote Communist Guerrilla Warfare with Otto Heilbrunn.[55]
See also
[edit]- Guerrilla warfare
- History of guerrilla warfare
- NLF and PAVN strategy, organization and structure
- NLF and PAVN logistics and equipment
- Viet Cong and PAVN battle tactics
Notes
[edit]- ^ On Guerrilla Warfare, by Mao Zedong, 1937, See the text of Mao's work online at www.marxists.org
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica, "Warfare Conduct Of, Guerrilla Warfare", 1984 ed, p. 584)
- ^ Võ Nguyên Giáp, Big Victory, Great Task, Pall Mall Press, London (1968)
- ^ a b c d Mao, op. cit.
- ^ a b Peoples War, Peoples Army, Võ Nguyên Giáp
- ^ Dan Jakopovich, "Time Factor in Insurrections", Strategic Analysis, Vol. 32, No. 3, May 2008.
- ^ Counterinsurgency Redux – David Kilcullen, 2006, retrieved June 1, 2007
- ^ FRANK G. HOFFMAN, "Neo-Classical counterinsurgency?", United States Army War College, Parameters Journal: Summer 2007, pp. 71-87.
- ^ Viet Cong – Pike, Douglas, The MIT Press; New Ed edition, Wednesday December 16, 1970
- ^ Cash, John A.; Albright, John; Sandstrum, Allan W. (1985) [1970]. "Chapter 2: CONVOY AMBUSH ON HIGHWAY 1, 21 NOVEMBER 1966". Seven Firefights in Vietnam. Vietnam Studies. WASHINGTON, D. C.: United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 70-4.
- ^ a b "Insurgency & Terrorism: Inside Modern Revolutionary Warfare", Bard E. O'Neill
- ^ a b Inside the VC and the NVA, Michael Lee Lanning and Dan Cragg
- ^ Normalizing Abnormalities: Life in Myanmar’s Resistance Zone Helen Li. The Diplomat. September 16, 2024
- ^ From war to governance in resistance-liberated areas of Myanmar Aung Thura Ko Ko. November 27, 2024. Asia Times
- ^ War, lack of resources complicate judicial plans in Myanmar rebel zones Kiana Duncan. July 26, 2024. Radio Free Asia
- ^ The mobile game funding a revolution in Myanmar BBC News. August 27, 2023. Oliver Slow.
- ^ a b Lanning/Cragg, op. cit.
- ^ Terrorist use of web spreads
- ^ Guerrilla Warfare, by Ernesto Guevara & Thomas M. Davies, Rowman & Littlefield, 1997, ISBN 0-8420-2678-9, pg 52
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica, 14ed, "Guerrilla Warfare" p. 460-464
- ^ "Defeating Communist Insurgency: The Lessons of Malaya and Vietnam", Robert Thompson
- ^ Steven R. David (September 2002). "Fatal Choices: Israel's Policy of Targeted Killing" (PDF). THE BEGIN-SADAT CENTER FOR STRATEGIC STUDIES; BAR-ILAN UNIVERSITY. Retrieved on 2006-08-01.
- ^ Babyak, E.E., Jr., LtJG, USNM (1971). Swimmer Sabotage or The Most Dangerous Mine. Charleston: Naval Mine Warfare School.
- ^ Blum, William (2014). Killing hope : US Military and CIA Interventions since World War II. London. ISBN 978-1-78360-177-6. OCLC 892861923.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Australia; Australian Army; Royal Australian Infantry Corps (1969). "Australian infantry". Australian Infantry. ISSN 1447-5545. OCLC 911257696.
- ^ Kurz, Robert W.; Charles K. Bartles (2007). "Chechen suicide bombers" (PDF). Journal of Slavic Military Studies. 20 (4): 529–547. doi:10.1080/13518040701703070. S2CID 96476266. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 6, 2014.
- ^ Threat Tactics Report: Iran January 2017. Retrieved 30/4/2023.
- ^ "Tamil Tiger 'regret' over Gandhi". BBC News. 27 June 2006. Retrieved 10 May 2007.
- ^ "We killed Rajiv, confesses LTTE". The Times of India. 28 June 2006. Archived from the original on 8 September 2011. Retrieved 10 May 2007.
- ^ Baker, Mark (16 September 2002). "Hopes high for end to Sri Lanka war". The Age. Melbourne. Retrieved 10 May 2007.
- ^ "Sri Lanka assassination plot". BBC News. 27 July 1998. Retrieved 10 May 2007.
- ^ Sambandan, V. S. (5 September 2005). "Inquiries into Premadasa, Dissanayake killings closed". The Hindu. Chennai, India. Archived from the original on 1 March 2007. Retrieved 10 May 2007.
- ^ "CHRONOLOGY-Assassinations of political figures in Sri Lanka". Reuters UK. 10 November 2006. Archived from the original on 24 April 2007. Retrieved 10 May 2007.
- ^ Mao, op. cit., Lanning/Cragg, op. cit.
- ^ Lanning/Cragg, op. cit
- ^ See also: Civil war in Iraq (2006–2007)
- ^ Robert Thompson (1966). Defeating Communist Insurgency: The Lessons of Malaya and Vietnam, Chatto & Windus, ISBN 0-7011-1133-X
- ^ a b Learning from Iraq: Counterinsurgency in American Strategy – Steven Metz. US Army Strategic Studies Institute monograph, December 2006, http://www.strategicstudiesinstitute.army.mil/pubs/display.cfm?pubID=752, retrieved June 1, 2007
- ^ Michael Lee Lanning and Daniel Craig, Inside the VC and NVA, and Inside the LRRP's
- ^ Shooting at the Moon: The Story of America's Clandestine War in Laos, Steerforth Press, 1996 ISBN 978-1-883642-36-5
- ^ Bush at War, Bob Woodward, Simon & Schuster, 2002
- ^ Operation Hotel California: The Clandestine War inside Iraq, Mike Tucker, Charles Faddis, 2008, The Lyons Press ISBN 978-1-59921-366-8
- ^ Plan of Attack, Bob Woodward, Simon and Schuster, 2004 ISBN 978-0-7432-5547-9
- ^ Learning from Iraq, op. cit.
- ^ Kilcullen, David (24 Oct 2006). "Counterinsurgency Redux" (PDF). Archived from the original on Jun 14, 2007. Retrieved 19 July 2023.
- ^ On Guerrilla Warfare, by Mao Tse-tung, 1937
- ^ Castro, Fidel; Ignacio Ramonet; Andrew Hurley (2008). Fidel Castro: My Life : a Spoken Autobiography (2008 ed.). Scribner. p. 680. ISBN 978-1-4165-5328-1.
- ^ "Che Guevara: Revolutionary & Icon", by Trisha Ziff, Abrams Image, 2006, pg 73
- ^ Abdul Haris Nasution,Fundamentals of Guerrilla Warfare, Informations Service of the Indonesian Armed Forces, Jakarta, 1953.https://archive.org/details/AbdulHarisNasutionFundamentalsOfGuerrillaWarfare
- ^ http://smallwarsjournal.com/mag/docs-temp/59-mcelhatton.pdf Guerrilla Warfare and the Indonesian Strategic Psyche, Small Wars Journal article by Emmet McElhatton
- ^ "Minimanual of the Urban Guerrilla". Archived from the original on November 25, 2005. Retrieved December 25, 2007.
- ^ a b Peers, William R. and Dean Brelis. Behind the Burma Road: The Story of America's Most Successful Guerrilla Force. Boston: Little, Brown & Co., 1963.
- ^ Russell W. Volckmann (1954), We Remained: Three Years Behind the Enemy Lines in the Philippines page 157. Online text here
- ^ Central Intelligence Agency. Behind Japanese Lines in Burma: The Stuff of Intelligence Legend (2001). Retrieved 2012-05-30.
- ^ Dixon, Brigadier C. Aubrey and Heilbrunn, Otto, Communist Guerrilla Warfare (Frederick A. Praeger, New York: 1954)
Books
[edit]Peter Polack, Guerrilla Warfare; Kings of Revolution, Casemate,ISBN 9781612006758.
