Propargite
Appearance
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
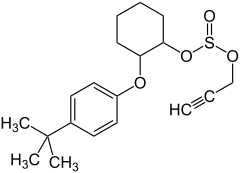
2-(4-tert-butylphenoxy)cyclohexyl prop-2-yne-1-sulfonate
| |
| Other names
Omite, Comite, Uniroyal D014
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.279 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H26O4S | |
| Molar mass | 350.47 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | dark amber viscous liquid |
| Density | 1.10 g/cm3 |
| 0.5 ppm | |
| Solubility | miscible in organic solvents |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Cornell University |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Propargite (IUPAC name 2-(4-tert-butylphenoxy)cyclohexyl prop-2-yne-1-sulfonate, trade names Mitex, Omite and Comite) is a pesticide used to kill mites (an acaricide).[2] It acts through inhibition of mitochondrial ATP synthase, and is in IRAC group 12C.[3] Symptoms of excessive exposure are eye and skin irritation, and possibly sensitization. It is highly toxic to amphibians, fish, and zooplankton, as well as having potential carcinogenity.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 3–482, ISBN 978-0-8493-0594-8
- ^ a b "propargite (Omite, Comite) Chemical Fact Sheet 9/86". Cornell University. 1986-09-30. Retrieved 2009-12-02.
- ^ Kadir, Habsah A.; Knowles, Charles O. (1 June 1991). ", Inhibition of ATP Dephosphorylation by Acaricides with Emphasis on the Anti-ATPase Activity of the Carbodiimide Metabolite of Diafenthiuron". Journal of Economic Entomology. 84 (3): 801–805. doi:10.1093/jee/84.3.801.
- ^ "Integrated Risk Information System". 2013-03-15.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2087/epdf
External links
[edit]- Propargite in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
