Pollination of orchids



The pollination of orchids represents a complex aspect of the biology of this plant family, characterized by intricate flower structures and diverse ecological interactions with pollinator. Notably, the topic has garnered significant scientific interest over time, including the attention of Charles Darwin, who is recognized for his contributions to the theory of evolution by natural selection. In 1862, Darwin published his observations on the essential role of insects in orchid pollination in his work The Fertilization of Orchids.[1][note 1] He noted that the various strategies employed by orchids to attract their pollinators are complex.
Adaptations of orchids to pollination by animals
[edit]Approximately 97% of orchid species rely on pollinator for the transfer of pollen from one plant to the pistils of another, which is essential for fertilization and seed formation.[3] The pollen of orchids is organized into compact masses known as pollinia (singular: "pollinium"), preventing dispersal by wind and necessitating the presence of pollinators for sexual reproduction.[3] These pollinators vary widely and may include flies, mosquitos, bees, wasps, butterflies, coleopterans, and birds, particularly hummingbirds.[4][5][3]
The phenomenon of zoophily in orchids requires that pollinating animals frequently visit the flowers and remain long enough to contact both the anthers and stigma. For successful pollen transfer, it is crucial that the pollen adheres effectively to the pollinators, enabling it to reach the stigmas of other flowers. The effectiveness of zoophily depends on the ability of these animals to recognize flowers from a distance and their attraction to flowers of the same species. Consequently, zoophilous flowers typically possess "attractive products" such as pollen and nectar, "means of attraction" like scents and colors, and pollen that is viscous or adhesive.[4]
Throughout the evolution of angiosperms, there has been significant differentiation in the means of attraction and flower morphology, allowing a broader range of animals to participate in pollination. This evolutionary process has led to the establishment of close relationships between pollinating animals and zoophilous flowers, benefiting both groups. For plants, this relationship has resulted in more precise attraction of specific pollinators, facilitating the transfer of pollen to the stigmas of other plants and reducing the overall production of pollen. In contrast to anemophilous plants, which may produce around one million pollen grains per ovule, orchids typically produce a one-to-one ratio. For specialized pollinators, this mutualism has reduced competition from other anthophilous animals, making targeted pollination advantageous.[3][4]
The evolutionary development of zoophilous angiosperms and their adapting animal partners is best understood as a process of coevolution characterized by reciprocal relationships. In some cases, orchids and their pollinators have become so interdependent that their existence is mutually exclusive.[4] Pollination mechanisms resulting from this coevolution generally benefit both parties: pollinators obtain nectar from the flowers, while orchids gain pollen transfer. However, in numerous instances, the attraction of pollinators to orchids may rely on deceptive strategies that do not offer any rewards.[3]
Orchid flowers
[edit]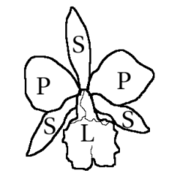


Orchid flowers are predominantly hermaphroditic, with unisexual forms being rare, and they typically exhibit zygomorphic (bilateral) symmetry. Most genera feature three outer elements known as sepals—two lateral and one dorsal—and three inner elements called petals, with the lower petal often modified into a lip or labellum. This labellum is usually larger and more vividly colored than the other petals, often exhibiting a trilobed or uniquely shaped structure, sometimes adorned with fleshy bumps or ridges, and may feature a basal spur with distinct color patterns.[6]
The androecium of orchids generally comprises one or two stamens, occasionally three, and is fused with the style and stigma to form a structure known as the column (or gynostema/gynostegium). The pollen is organized into masses called pollinia, which can vary in number from one to twelve, though two or four are most common. These pollinia, combined with a sticky stalk derived from the anther or stigma, form the transport unit during pollination. The gynoecium consists of three fused carpels and is situated below the calyx. It features a highly modified style that is solitary and terminal, forming a key component of the column. Near the apex, the stigma has an elongated lobe known as the rostellum, which is typically non-receptive and positioned above the stigmatic region. A part of the rostellum may develop into a sticky platform called the viscidium, which attaches to the pollinium stem.[6]
Orchids generally produce nectar as a reward for pollinators, with nectaries varying in their location and type. They may be situated on the lip spur, at the tips of the sepals, or on the septa of the gynoecium. Additionally, some orchid species are capable of self-pollinatings or are apomictics, meaning they can produce seeds without the need for pollinators.[7]
Attraction of pollinators by means of rewards
[edit]Many orchid species provide various rewards to pollinators, including nectar, food hairs, oils, and other compounds such as waxes, resins, and fragrances. These rewards serve to reinforce pollinator behavior, enhancing the likelihood of effective pollen transfer. Over time, this specialization on a single type of pollinator has led to increased morphological and structural adaptations in orchid flowers, aimed at attracting specific insect species.[3][8][9][10]
This evolutionary aspect of the interspecific relationships between orchids and their pollinators was notably examined by Charles Darwin in his studies of both British and exotic orchid species. A prominent example is the Madagascar species Angraecum sesquipedale, which features a spur exceeding 30 cm in length that contains nectar. Darwin's attempts to extract the pollinia from this flower using needles were unsuccessful; he was only able to do so by inserting a cylinder with a diameter of 2.5 mm into the spur and pulling it out, causing the viscidium to adhere to the cylinder. Darwin proposed that when a butterfly reached the bottom of the spur to access the nectar, the pollinia would attach to its head as it withdrew its proboscis. Upon visiting another flower, the butterfly would then transfer the pollinia to its stigma. Based on this reasoning, Darwin suggested that the pollinator of Angraecum sesquipedale would need to have a proboscis longer than 30 cm, an idea that seemed implausible to contemporary biologists. However, this prediction was confirmed in 1903 with the discovery of the moth Xanthopan morganii praedicta[11] in Madagascar, which possesses a proboscis of the predicted length. The subspecific epithet "praedicta" reflects the foretelling of its existence by Darwin.[3]
The moth is attracted to Angraecum sesquipedale by its fragrance, particularly during the night. Upon approaching the flower, the moth unrolls its proboscis and inserts it into a crevice of the rostellum that leads to the spur. After accessing the nectar at the base of the spur, the moth lifts its head while withdrawing its proboscis, causing the viscidium to adhere to its head or another part of its body. The viscidium contains a small pedicel, known as the caudicle, which carries the pollinia. When the moth finishes feeding and moves to another flower, the caudicle dehydrates, altering its angle relative to the insect’s body. This positioning ensures that when the moth inserts its proboscis into the next flower, the pollinia are properly aligned to attach to the stigma. After successful pollination, the flowers stop producing fragrance, and their tepals wither shortly thereafter. Nonetheless, the processes of pollen transfer, fertilization, and the formation of numerous new individuals have already been secured.[3]
Many orchids, including Angraecum sesquipedale, are pollinated by nocturnal butterflies and, as a result, tend to have light-colored or nearly white flowers that emit fragrance in the evening or night. Other examples of such orchids include Bonatea speciosa, Habenaria epipactidea, species in the genus Satyrium, Disa cooperi and D. ophrydea.[12] In contrast, some orchid genera have evolved to be pollinated by diurnal butterflies, exhibiting bright colors and providing nectar as a reward.[12]
Melitophilous orchids, which are pollinated by bees, typically produce a strong fragrance during the day and are robustly colored. Examples include Satyrium erectum and Disa versicolor. These bee-pollinated orchids often offer not only nectar but also oils—a relatively rare reward in the plant kingdom—used by various bee species to nourish their larvae. Notable genera that provide oil rewards include Disperis, Pterygodium, Corycium, Ceratandra, Evotella, Satyrium, and Pachites.[12]
Pollination by flies, known as myophily, is the second most prevalent method of pollination among orchids, involving pollinators from twenty different dipteran families.[13] These flowers typically emit scents reminiscent of decaying organic materials, excrement, or carrion, which attract flies seeking food or suitable sites for egg deposition.[8] Various floral parts produce putrescent or carrion-like odors and often incorporate traps to retain the pollinators, alongside appendages and colors that may mimic flesh or other aspects of rotting matter.[14][15][16][17] For example, species in the genus Bulbophyllum, which are daciniphilous, attract true fruit flies from the Dacini tribe (Tephritidae) using pleasant or spicy scents as floral synomones, establishing mutualistic relationships that confer reproductive benefits to both the orchids and the male flies. Notably, B. hortorum has coevolved with male fruit flies to develop a unique pollination mechanism that selects for optimal-sized individuals as potential pollinators.[18]
Stelis hymenantha produces a strong aroma of sweet menthol. It secretes a sticky substance at the base of the labellum that resembles nectar. Another species, S. immersa, also emits a fragrance, described as melon-like, with its sticky substance located on both the petals and the labellum’s base. The primary visitors to these species are dipterans from various families. Typically, flies remain outside the flowers, investigating the viscous liquid on the petal surfaces. In the case of Stelis immersa, female flies from the genus Megaselia (Phoridae) are specifically adapted for effective pollen transfer. After inspecting the nectar-like substance, these insects enter the flower laterally and land on the downward-facing labellum. When this occurs, the labellum rises, pressing the fly against the viscid pollinium and trapping it. To exit, the fly backs up, causing the viscidium to adhere to its thorax. The labellum then returns to its original position, releasing the fly, which has now facilitated pollination.[19]
Attraction and reward by means of perfumes
[edit]The flowers of the subtribes Stanhopeinae and Catasetinae exhibit specialized pollination mechanisms. These species are exclusively pollinated by male euglossine bees, which collect perfumes from the flowers. The reasons behind this behavior are not entirely understood, as the perfumes do not provide nutrition or protection but may play a role in the mating rituals of these bees.
The process of scent collection is quite similar across species. The male bee approaches the osmophore, the scent-producing part of the flower, and perches on the labellum. Using the long, dense hairs on its front legs, the bee gathers the aromatic substances, which are typically liquid but can also be found in crystalline form. If the scent compounds are solid, the bee dissolves them with secretions from its salivary glands. Once saturated with the aroma, the bee transfers the scents using its middle legs to storage cavities in its hind legs, where they can be preserved for extended periods. Different orchid genera attach pollinia to various parts of the bee’s body.[20]
Orchids, like many plants, attract specific groups of male euglossine bees by producing species-specific scent mixtures, which likely act as reproductive isolation mechanisms. Some orchids exhibit morphological adaptations that ensure pollinia are only released upon visitation by particular bee species, depending on their size and behavior. Consequently, not all euglossine bees that visit a given orchid species are effective pollinators.[21]
Additionally, certain species of Bulbophyllum attract specific male Dacini fruit flies through particular male attractants such as methyl eugenol (ME), raspberry ketone (RK), or zingerone (ZN). Methyl eugenol serves as a sex pheromone precursor for several quarantine pest species of Bactrocera, including the oriental fruit fly (B. dorsalis), B. carambolae, B. occipitalis, and B. umbrosa. Similarly, raspberry ketone and zingerone function as sex pheromone components for male fruit flies like Zeugodacus caudatus, Z. cucurbitae, and Z. tau.[22][23][24][25][26][27]
Attraction of pollinators by means of deception
[edit]
Many orchids employ various deceptive tactics to attract pollinators by mimicking scents, shapes, colors, or movements associated with resources of interest to the pollinators, without providing any actual rewards. The mechanisms of deception are diverse and can be categorized as follows:[28][29]
- Generalized Feeding Deception: Flowers mimic the shape and coloration of species that typically offer rewards to pollinators.
- Feeding Deception Mediated through Floral Mimicry:[note 2] In this case, flowers closely resemble a specific species that rewards pollinators, cohabiting in the same environment.[30]
- Mimicry of Nesting Sites: Flowers imitate the egg-laying sites of certain pollinators.
- Mimicking Shelter Sites: Flowers provide potential shelter for pollinators, a strategy that may not be deceptive but can be mutually beneficial for both the insect and the orchid.
- Pseudo-Antagonism: This mechanism attracts pollinators by invoking their innate defense responses. Flowers mimic the appearance of another insect species that the pollinator may perceive as a threat, prompting the pollinator to attack the flower. In doing so, the insect inadvertently transfers pollen to other flowers.[31]
- Rendezvous Attraction: Flowers imitate other flowers that are attractive to female pollinators.
- Sexual Deception: In this scenario, flowers mimic the visual and olfactory mating signals of female pollinators.
Among these mechanisms, generalized feeding deception is the most commonly observed in orchids, reported in 38 genera, followed by sexual deception, which has been identified in 18 genera.[28][29]
Attraction of pollinators by luring them for food
[edit]The ability to attract pollinators without offering rewards has evolved independently across several angiosperm lineages, although it typically occurs in only a few species within each family.[32] In contrast, it is estimated that approximately one-third of orchid species employ a food-deceptive mechanism.[33][34] This strategy involves signaling the presence of food, such as nectar or pollen, to attract pollinators without providing any actual reward. Orchids often achieve this by resembling species that do offer rewards and that cohabit in the same environment.[35] Feeding deception commonly manifests as a general resemblance to rewarding species, with orchids featuring large, brightly colored flowers that exploit pollinators' innate preferences for such floral characteristics.[29][34][36]
Imitation of other plants
[edit]Another method employed by orchids to attract pollinators involves mimicking the flowers of other plant species. A notable example is Epidendrum ibaguense, a terrestrial or lithophilous orchid found from Mexico to Bolivia and Brazil. This orchid features orange flowers with an intense yellow labellum, closely resembling the flowers of Asclepias curassavica, a member of the Asclepiadaceae family. The butterfly Agraulis vanillae, which typically visits Asclepias curassavica to collect nectar in exchange for pollen transport, is frequently drawn to the mimetic flowers of Epidendrum ibaguense. When the butterfly approaches the orchid, it inserts its proboscis into the narrow duct (gynostemium) of the flower. The small diameter of this duct can cause the butterfly's spiracles to become temporarily trapped. In its struggle to escape, the insect inadvertently picks up the orchid's pollinia. After being released, the butterfly may visit another Epidendrum flower, transferring the pollinia and facilitating pollination without receiving nectar for its efforts.[37]
Attraction of pollinators by sexual luring
[edit]Certain orchids have evolved deceptive flowers that mimic the shape, hairiness, and scent of female wasps or bees to attract male pollinators. A well-known example is Ophrys insectifera, found in southern Europe, which is exclusively visited by two species of wasps from the genus Argogorytes. Male wasps emerge in spring, weeks before females, and are attracted to the fragrance of Ophrys flowers, which resembles the pheromones secreted by female wasps. Additionally, the labellum of Ophrys insectifera closely resembles the shape, color, and texture of female wasps. This interaction is referred to as pseudocopulation, as male wasps attempt to mate with the flower, during which they come into contact with the anther and transfer pollinia between flowers.[38]
The phenomenon of pollination by pseudocopulation was first documented by A. Pouyanne and H. Correvon in 1916 and 1917 while studying the relationship between the orchid Ophrys speculum and the scoliidae wasp Campsoscolia ciliata in Algeria.[39][40] Their findings initially went unnoticed until Robert Godfrey validated their observations in 1925, prompting increased interest in this area of study.[note 3] Following this, Australian biologist Edith Coleman published numerous papers on the pollination of orchids from the genus Cryptostylis by males of the ichneumonoidea wasp Lissopimpla excelsa.[41][42][43]
Several genera of terrestrial orchids employ this pseudocopulation mechanism, including Ophrys, Cryptostylis, Drakaea, Caladenia,[44] Chiloglottis,[45] Geoblasta,[46] Arthrochilus, Calochilus,[47] Leporella,[48] and Spiculaea. Most terrestrial orchid genera utilizing pseudocopulation are found in Australia, with Ophrys being the largest and best-documented genus in Europe. This mechanism is not limited to a specific continent; it has also been observed in the South American species Geoblasta penicillata[49] and in two South African orchids of the genus Disa.[50]
A similar mechanism is found in Tolumnia henekenii, whose flowers mimic the female of the bee species Centris insularis. The resemblance is so convincing that male bees attempt to copulate with the flower, thereby facilitating its pollination.
In the genus Caleana, commonly known as the duck orchid due to its labellum resembling the head of a duck and the overall flower resembling a flying duck, a distinct mechanism of pseudocopulation has been observed. This species utilizes a spring mechanism to trap pollinating insects in a pouch, with their only means of escape being through the pollinium and stigma. When male insects land on the labellum, they activate a two-hinged relaxation mechanism involving the labellum-lamellum and the lamina-perianth, which flips the insect into the pouch containing the stigma and pollinia.[51][52]
Pseudocopulation is not limited to pollinators from the Hymenoptera order (such as bees and wasps); it has also been documented in certain Diptera. For instance, male mosquitoes of the genus Bradysia have been observed to pseudocopulate with species of Lepanthes, a large genus of orchids found in neotropical rainforests.[53]
In Ophrys orchids, the flowers not only mimic the shape, size, and color of female pollinators but also emit fragrances that include compounds found in female sex pheromones. This reinforces the sexual attraction of males to the flowers. Chemical and electrophysiological comparisons have been made between the volatile compounds emitted by Ophrys iricolor and the female pheromones of its pollinator, Andrena morio. More than 40 compounds have been identified, including alkanes and alkenes with 20 to 29 carbon atoms, aldehydes with 9 to 24 carbons, and two esters. Most of these compounds are present in similar proportions in both floral extracts of O. iricolor and extracts from the cuticular surface of A. morio females.[54]
The biologically active volatile compounds in Ophrys species are largely similar to those utilized by other Ophrys species that engage in pseudocopulation with males of the genera Andrena and Colletes.[55][56][57][58][59]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ The book was edited under the title On the various contrivances by which British and foreign orchids are fertilized by insects, and on the good effects of intercrossing. This book was the first detailed demonstration of the power of natural selection, which could explain how the complex interrelationships between orchids and their pollinators had arisen. Darwin described detailed observations of the pollination mechanism of various orchids, his experiments and dissections of flowers, and explained a number of previously ignored aspects of the pollination biology of this family, such as the Catasetum puzzle, which was thought to consist of flowers of three different species on the same plant, and also made predictions that were later confirmed in nature.[2]
- ^ There are two general types of mimicry relevant to pollination ecology: Müllerian and Batesian mimicry. In the first case (which many authors take as convergence rather than mimicry) several species with similar abundance in nature develop to their mutual advantage the same propaganda style as a warning to predators, for example. In contrast, an organism sparsely represented in nature, which mimics a more abundant one to deceive a third, develops a unidirectional advantage that is called Batesian mimicry. (Proctor & Yeo, p. 375)
- ^ Subject that came to be called "Pouyanian mimicry" in honor of its discoverer.
References
[edit]- ^ "Darwin Online: Fertilisation of Orchids".
- ^ Darwin, Charles (2006). "Journal". In van Wyhe, John (ed.). [Darwin's personal 'Journal' (1809-1881)]. Darwin Online. CUL-DAR158.1-76. Retrieved 7 February 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h van der Cingel, N. 2001. An atlas of orchid pollination: America, Africa, Asia and Australia. CRC Press. ISBN 9789054104865
- ^ a b c d Strassburger, E. (1994). Tratado de Botánica. 8th edition. (In Spanish). Omega, Barcelona, 1088 p.
- ^ Gola, G., Negri, G. and Cappeletti, C. 1965. Tratado de Botánica. 2nd edition. (In Spanish). Editorial Labor S.A., Barcelona, 1110 p.
- ^ a b Cribb, Phillip (2001). "Morphology of Orchidaceae." In: A. M. Pridgeon, P. J. Cribb, M. W. Chase, and F. N. Rasmussen eds, Genera Orchidacearum, vol. 1. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK ISBN 0-19-850513-2.
- ^ Neiland, M. R. M.; Wilcock, C. C. (1998). "Fruit set, nectar reward, and rarity in the Orchidaceae". American Journal of Botany. 85 (12): 1657–1671. doi:10.2307/2446499. JSTOR 2446499. PMID 21680327. (subscription required)
- ^ a b Pijl, L. van der and C. H. Dodson. (1969). Orchid flowers. Their pollination and evolution. University of Miami Press. Coral Gables. pp. 101-122.
- ^ Dressler, Robert L. (1993). Phylogeny and classification of the orchid family. Cambridge University Press ISBN 0-521-45058-6, 9780521450584
- ^ Proctor, Michael; Yeo, Peter and Lack, Andrew. (1996). The natural history of pollination. Portland, Oregon. Timber Press. 479 p.
- ^ [1]
- ^ a b c Kurzweil, H. (2000). South African orchids: reproduction and pollination. National Biodiversity Institute, South Africa.
- ^ Christensen, D. E. (1994). "Fly pollination in the Orchidaceae." In: Arditti, J. (ed.). Orchid biology: reviews and perspectives. VI. John Wiley & Sons. Ithaca. New York. pp. 415-454.
- ^ Chase, M. W. (1985). Pollination of "Pleurothallis endosthachys". Am. Orch. Soc. Bull. 54:431-434
- ^ Johnson, S. D. and T. J. Edwards. (2000). The structure and function of orchid pollinaria. Pl. Syst. Evol. 222: 243-269.
- ^ Borba, E. L., J. M. Felix, V. N. Solferini, and J. Semir. (2001b). "Fly-pollinated Pleurothallis (Orchidaceae) species have high phenetic variability: evidence from isozyme markers." Am. J. Bot. 88: 419-428.
- ^ Borba, E. L. and J. Semir. (2001). "Pollinator specificity and convergence in fly pollinated Pleurothallis (Orchidaceae) species: a multiple population approach." Ann. Bot. 88: 75-88.
- ^ Tan, K. H., P. T. Ong, and L.T. Tan. (2023)."Morphology and movement of Bulbophyllum hortorum (Orchidaceae) flowers enable selection of optimal-sized Dacini fruit fly males. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 17: 647–660.
- ^ Albores-Ortiz, Octavio and Victoria Sosa. (2006). Pollination of two sympatric species of Stelis (PLEUROTHALLIDINAE, ORCHIDACEAE). Acta Botanica Mexicana 74: 155-168
- ^ GÜNTER GERLACH. (2003). LANKESTERIANA 7: 104-106.
- ^ Ramírez, Santiago; Robert L. Dressler and Mónica Ospina. (2002). Abejas euglosinas (Hymenoptera: Apidae) de la Región Neotropical: Listado de especies con notas sobre su biología. (in Spanish) Biota Colombiana 3:7-118.
- ^ Tan, K.H. and Nishida, R. (2000) Mutual reproductive benefits between a wild orchid, Bulbophyllum patens, and Bactrocera fruit flies via a floral synomone. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 26: 533-546.
- ^ Tan, K.H., Nishida R. and Toong, Y.C. (2002) Floral synomone of a wild orchid, Bulbophyllum cheiri, lures Bactrocera fruit flies to perform pollination. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 28:1161-1172.
- ^ Tan, K.H. and Nishida, R. (2005) Synomone or Kairomone? - Bulbophyllum apertum (Orchidaceae) flower releases raspberry ketone to attract Bactrocera fruit flies. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 31(3): 497-507.
- ^ Tan, K. H., Tan, L. T. and Nishida, R. (2006) Floral phenylpropanoid cocktail and architecture of Bulbophyllum vinaceum orchid in attracting fruit flies for pollination. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 32: 2429-2441.
- ^ Tan, K.H. and Nishida, R. (2007) Zingerone in the floral synomone of Bulbophyllum baileyi (Orchidaceae) attracts Bactrocera fruit flies during pollination. Biochemical Systematics & Ecology, 31: 334-341.
- ^ Katte, T., Tan, K.H., Su, Z-H., Ono, H. and Nishida, R. (2020) Phenylbutanoids in two closely related fruit fly orchids, Bulbophyllum hortorum and B. macranthoides subspecies tollenoniferum: multiple attractive components for the raspberry ketone sensitive tephritid fruit fly species. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 55 (1): 55-64.
- ^ a b Jersáková, Jana; Steven D. Johnson & Pavel Kindlmann. (2006). Mechanisms and evolution of deceptive pollination in orchids. Biological Reviews, 81:2:219-235
- ^ a b c Waterman, Richard J. & Martin I. Bidartondo. (2008). Deception above, deception below: linking pollination and mycorrhizal biology of orchids. J. Exp. Bot. 59: 1085-1096.
- ^ Dafni, A. (1984). Mimicry and Deception in Pollination. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. Vol. 15: 259-278
- ^ Orlean, S. "A Plant With Smarts." NOVA.
- ^ Renner, S. S. (2006). "Rewardless flowers in the angiosperms and the role of insect cognition in their evolution." In: Waser, N. M., Ollerton. J., eds. Plant-pollinator interactions: from specialization to generalization. Chicago, IL, USA: University of Chicago Press. 123-144.
- ^ Ackerman, J. D. (1986). "Mechanisms and evolution of food-deceptive pollination systems in orchids." Lindleyana. 1:108-113
- ^ a b Nilsson, L. A. (1992) "Orchid pollination biology." Trends in Ecology and Evolution 7:255-259.
- ^ Johnson, S. D. (2000). "Batesian mimicry in the non-rewarding orchid Disa pulchra, and its consequences for pollinator behavior." Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 71:119-132.
- ^ Schiestl, F. P. (2005). "On the success of a swindle: pollination by deception in orchids." Naturwissenschaften 92:255-264.
- ^ Eduardo Taborda, Alejandro. "Polinización natural en Orquídeas". Club Peruano de Orquídeas (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 18 February 2009.
- ^ Wolff, T. (1950). "Pollination and fertilization of the fly ophrys, Ophrys insectifera L. in Allindelille Fredskov, Denmark." Oikos 2:20-59.
- ^ Correvon, H. & Pouyanne, A. (1916). "Un curieux cas de mimetisme chez les Ophrydées." (in French). J. Soc. Nat. Horticult. France. 17, 29, 41, 84.
- ^ Pouyanne, A. (1917). "La fécondation des Ophrys par les insectes." (in French). Bull Soc Hist Nat Afr Nord 1917;8:6-7
- ^ Coleman, E. (1927). "Pollination of the orchid Cryptostylis leptochila." Victorian Naturalist 44: 20-22.
- ^ Coleman, E. (1929). "Pollination of Cryptostylis subulata (Labill.) Reichb." Victorian Naturalist 46: 62-66.
- ^ Coleman, E. (1930). "Pollination of Cryptostylis erecta R.Br." Victorian Naturalist 46: 236-238
- ^ Peakall, R. and Beattie, A. J. (1996). "Ecological and genetic consequences of pollination by sexual deception in the orchid Caladenia tentaculata." Evolution 50, 2207-2220.
- ^ Mant, J., Peakall, R. and Weston, P. H. (2005) "Specific pollinator attraction and the diversification of sexually deceptive Chiloglottis (Orchidaceae)." Plant Systematics and Evolution, 253, 185-200.
- ^ Correa, M. N. (1968). Rehabilitación del género Geoblasta Barb Rodr." Rev. Museo La Plata n.s. 11, 69-74.
- ^ Fordham, F. (1946). "Pollination of Calochilus campestris." Vict. Naturalist. 62, 199-201.
- ^ Peakall, R. (1989a). "The unique pollination of Leporella fimbriata (Orchidaceae) by pseudocopulating winged male ants Myrmecia urens (Formicidae)." Plant Systematics and Evolution 167, 137-148.
- ^ Ciotek, L., P. Giorgis, S. Benitez-Vieyra & A. A. Cocucci. (2006). "First confirmed case of pseudocopulation in terrestrial orchids of South America: pollination of Geoblasta pennicillata (Orchidaceae) by Campsomeris bistrimacula (Hymenoptera, Scoliidae)." Flora 201:365-69.
- ^ Whitehead, V. B. & Steiner, K. E. (1991). "Males of Podalonia canescens (Sphecidae) pollinating the orchid Disa atricapilla." Proceedings 8th Congress, Entomological Society of southern Africa, Bloemfontein, 1–4 July.
- ^ Cady, L. (1965). "Notes on the pollination of Caleana major." Orchadian. 2:34.
- ^ Hopper, Stephen D.; Andrew P. Brown. (2006) "Australia's wasp-pollinated flying duck orchids revised (Paracaleana: Orchidaceae)." Australian Systematic Botany 19:3, 211.
- ^ BLANCO, Mario A. & Gabriel BARBOZA. (2005). "Pseudocopulatory Pollination in Lepanthes (Orchidaceae: Pleurothallidinae) by Fungus Gnats." Ann Bot 95: 763-772.
- ^ Stökl, Johannes; Robert Twele, Dirk H. Erdmann, Wittko Francke, Manfred Ayasse. (2007). "Comparison of the flower scent of the sexually deceptive orchid Ophrys iricolor and the female sex pheromone of its pollinator Andrena morio." Chemoecology Volume 17 (4): 231-233.
- ^ Mant, J. G., Brändli, C., Vereecken, N. J., Schulz, C., Francke, W. & Schiestl, F. P. (2005). "Cuticular hydrocarbons as source of the sex pheromone in Colletes cunicularius (Hymenoptera: Colletidae) and the key to its mimicry by the sexually deceptive orchid Ophrys exaltata."
- ^ Schiestl, F. P., M. Ayasse, H. F. Paulus, C. Löfstedt, B. S. Hansson, F. Ibarra, W. Francke. (2000). "Sex pheromone mimicry in the early spider orchid (Ophrys sphegodes): patterns of hydrocarbons as the key mechanism for pollination by sexual deception." Journal of Comparative Physiology A: Neuroethology, Sensory, Neural, and Behavioral Physiology 186:567-574.
- ^ Ayasse, M., F. P. Schiestl, H. F. Paulus, D. Erdmann, and W. Francke. (1997). "Chemical communication in the reproductive biology of Ophrys sphegodes." Mitteilungen der Deutschen Gesellschaft für allgemeine und angewandte Entomologie 11:473-476.1
- ^ Ayasse, M., F. P. Schiestl, H. F. Paulus, F. Ibarra and W. Francke. (2003). "Pollinator attraction in a sexually deceptive orchid by means of unconventional chemicals." Proceedings of the Royal Society B:Biological Sciences 270:517-522.
- ^ Schiestl, F. P., Peakall, R., and Mant, J. (2004) "Chemical communication in the sexually deceptive orchid genus Cryptostylis." Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 144, 199-205.
