Phrenicocolic ligament
| Phrenicocolic ligament | |
|---|---|
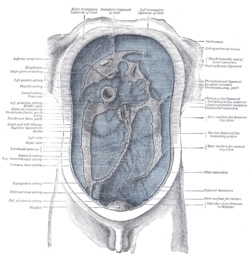 Diagram to show the lines along which the peritoneum leaves the wall of the abdomen to invest the viscera. (Phrenicocolic ligament labeled at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ligamentum phrenicocolicum |
| TA98 | A10.1.02.211 |
| TA2 | 3769 |
| FMA | 16551 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A fold of peritoneum, the phrenicocolic ligament is continued from the left colic flexure to the thoracic diaphragm opposite the tenth and eleventh ribs; it passes below and serves to support the spleen, and therefore has received the name of sustentaculum lienis.[1]

The phrenicocolic ligament is also called Hensing's ligament after Friedrich Wilhelm Hensing (1719–1745), a German professor for medicine in Giessen.[2][3]
Clinical significance
[edit]Knowledge of basic anatomic and the variations of suspensory ligament of the spleen is essential in the case of open surgery or laparoscopic splenectomy.[4] Moreover, during some surgical procedures, in many cases it is necessary to exert a certain degree of traction on the spleen and on its peritoneal insertions. This traction may result in a rupture of the fibrous capsule of the organ, resulting in severe bleeding which is difficult to control. Particularly hazardous is the downward traction of the phrenicocolic ligament (this maneuver may be necessary for the mobilization of splenic flexure).[citation needed] This ligament marks the site where the colon exits the peritoneal cavity: the phrenicocolic ligament is thus an important point of intersection of abdominal anatomy and, consequently, a crucial point for the spread of abdominal disease.[5]
References
[edit]- ^
 This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1158 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1158 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Hensing ligament in The Free Dictionary by Farlex, Medical Eponyms, Farlex, 2012.
- ^ Friedrich W. Hensing in The Free Dictionary by Farlex, Medical Eponyms, Farlex, 2012.
- ^ Poulin EC, Thibault C (October 1993). "The anatomical basis for laparoscopic splenectomy". Can J Surg. 36 (5): 484–8. PMID 8221408.
- ^ Meyers MA, Oliphant M, Berne AS, Feldberg MA (June 1987). "The peritoneal ligaments and mesenteries: Pathways of intraabdominal spread of disease". Radiology. 163 (3): 593–604. doi:10.1148/radiology.163.3.3575702. PMID 3575702.
External links
[edit]- spleen at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- "Phrenicocolic ligament". Medcyclopaedia. GE. Archived from the original on 2011-05-26.
