Mohegan-Pequot language
| Mohegan-Pequot | |
|---|---|
| Mohiks-Piqut Uyôtowáwôk | |
| Native to | United States |
| Region | Southern New England, Eastern Long Island |
| Ethnicity | Mohegan, Montauk, Niantic, Pequot, and Shinnecock |
| Extinct | 1908, with the death of Fidelia Fielding[1] |
| Revival | beginning 2010 |
Algic
| |
| Latin script | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | xpq |
| Glottolog | pequ1242 |
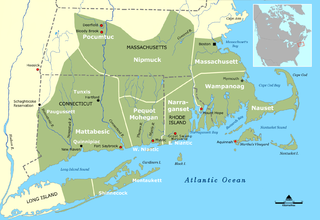 The location of the Mohegan, Pequot, Montaukett, Niantic, and Shinnecock, and their neighbors, c. 1600 | |
Mohegan-Pequot (also known as Mohegan-Pequot-Montauk, Secatogue, and Shinnecock-Poosepatuck; dialects in New England included Mohegan, Pequot, and Niantic; and on Long Island, Montaukett and Shinnecock) is an Algonquian language formerly spoken by indigenous peoples in southern present-day New England and eastern Long Island.[2]
Language endangerment and revitalization efforts
[edit]As of 2014, there are between 1,400 and 1,700 recorded tribal members (these figures vary by source). The Mohegan language has been dormant for approximately 100 years; the last native speaker, Fidelia Fielding, died in 1908. Fielding, a descendant of Chief Uncas, is deemed the preserver of the language. She left four diaries that are being used in the 21st-century process of restoring the language. She also took part in preserving the traditional culture. She practiced a traditional Mohegan way of life and was the last person to live in the traditional log dwelling.
Another important tribal member was Gladys Tantaquidgeon, who was the tribe's medicine woman from 1916 until her death in 2005. She too assisted greatly in maintaining the Mohegan culture, as she collected thousands of tribal documents and artifacts. These documents were of critical importance to supporting the tribe's documentation for its case for federal recognition, which was approved in 1994.[3]
As of 2010, the Shinnecock and Unkechaug nations of Long Island, New York, had begun work with the State University of New York at Stony Brook, Southampton Campus, to revive their languages, or dialects of the above.[4]
As of 2012, the Mohegan Language Project had created lessons, a dictionary, and other online learning materials to revive their language.[5] The project also has a complete grammar in the works, which has been put together by Stephanie Fielding. The primary goal of the project is for the next generation of Mohegan people to be fluent.
Many of the dictionaries circulating are based on John Dyneley Prince and Frank G. Speck's interpretation of testimony by Dji's Butnaca (Flying Bird), also known as Fidelia Fielding.[6]
The Mashantucket Pequot Museum and Research Center collection includes a 1992 menu "which attempts to translate such words as hamburger and hot dog into Mohegan-Pequot."[7]
The language was documented as early as the 17th century.
"In 1690, a Pequot vocabulary list was compiled by Rev. James Noyes in Groton. In 1717, Experience Mayhew, a Congregational Minister translated the Lord's Prayer into Mohegan-Pequot. Ezra Stiles, president of Yale University collected Pequot linguistic data in Groton in 1762."[7]
Prayers from the Baháʼí Faith have been translated into the Mohegan-Pequot language.[8]
"It is a sacred obligation," says the Golden Hill Paugussett Chief, Big Eagle. "Indian people must keep their languages alive. If the language is not spoken, it must be made to live again."[7]
Phonology
[edit]| Labial | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | lab. | |||||
| Nasal | m (m) | n (n) | ||||
| Stop | p (p) | t (t) | k (k) | kʷ (q) | ||
| Affricate | tʃ (c) | |||||
| Fricative | s (s) | ʃ (sh) | h (h) | |||
| Approximant | j (y) | w (w) | ||||
/n/ is realized as [ŋ] only before [k].
Vowel sounds
Simple vowels
[edit]| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | iː (i) | uː~oː (o) | |
| Mid | ə (u) | ɔ̃ː~ɔː (ô) | |
| Open | a aː (a á) |
The nasal /ɔ̃/ sound can range to being an oral /ɔ/ sound. ⟨a⟩ written with an acute accent (⟨á⟩) represents a long /aː/ sound.
Diphthongs
[edit]| Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|
| Close | au | |
| Mid | ɔ̃i | |
| Open | ai |
Orthography
[edit]Historically, Mohegan-Pequot has not had a writing system, and its speakers relied on oral transfer of knowledge, as opposed to writing. The only significant historic writings have been produced by European colonizers who interacted with the speakers of Mohegan-Pequot.
The dictionaries, grammar books, and other materials that are being developed in recent decades as part of the effort to revitalize Mohegan-Pequot Language, have adopted and used a standardized Latin orthography consisting of twelve consonants and six vowels.[11]
| Sound | Phonetic | Mohegan-Pequot examples | Gloss | English equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c | [dʒ] ~ [tʃ] | nutcôhtam | 'I want' | beach |
| h | [h] | mohiks | 'Mohegan, Mohegan Indian' | hi |
| k | [g] ~ [k] | ôkatuq | 'cloud' | geese, ski |
| m | [m] | pôcum | 'cranberry' | man |
| n | [n] | nupáw | 'five' | name |
| p | [b] ~ [p] | páyaq | 'ten' | spit |
| q | [kw] ~ [kw] | sôyôqat piyámáq |
'It is cold' 'fish' |
queen |
| s | [s] ~ [z] [z] beginning of a word [z] between two vowels [s] ~ [ʃ] in clusters sk, sp, sq |
nis pahsukôsq |
'two' 'board, floorboard' |
miss |
| sh | [ʃ] | nihsh ôtshohkôk |
'eel' 'legend, myth' |
shoreline |
| t | [d] ~ [t] | manto | 'God' | do, stop |
| w | [w] | wacuw | 'hill, mountain' | weasel |
| y | [j] | nut'huyô | 'I call him' | mayor |
| Sound | Phonetic | Mohegan-Pequot examples | Gloss | English equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | [ə] ~ [a] | ahki | 'land, Earth' | handle |
| á | [aː] | yáw | 'four' | father |
| i | [ɪ] ~ [i] | maci | 'bad, wicked' | pin |
| o | [uː] ~ [o] | nupotawá | 'I make a fire' | obey, book |
| ô | [ɔ̃:] ~ [ɔː] | kôq | 'porcupine' | bonbon |
| u | [ʌ] | shwut | 'third' | cut |
Morphology
[edit]Nouns[11]
Nouns in Mohegan have two forms: animate and inanimate. They are further distinguished by number. Animate nouns include people, animals, heavenly bodies (sun, moon, stars, but not clouds), and spirits. There are other items that fall into the category of animate such as certain cultural items and plants, but it is not known why these items are considered animate. It is something that is simply learned and memorized. One way to help identify if a noun is animate or inanimate is to look at its plural form. Plural animate nouns typically end in -k while plural inanimate nouns end in -sh.
Animate nouns have four forms: singular, plural, obviative and locative. The obviate form is used when there are two or more animate third person nouns in a sentence to mark the noun which is less salient (less relevant to the discourse). The unmarked noun is called the proximate, which is more salient/relevant to the discourse. The obviative is also used to mark a third-person possessed noun, with the possessor considered as the proximate, even if the possessed noun is more salient than its possessor. The locative is used to show where something is spatially. There is no obviative form for inanimate nouns, and neither the obviative nor the locative have plural forms (plurality is known through context).
| Animate Nouns (with regular stems) | Mohegan Form | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Singular | winay | old woman |
| Plural | winayak | old women |
| Obviative | winayah | old woman/women |
| Locative | winayuk | at the old woman/women |
| Inanimate Nouns (with regular stems) | Mohegan Form | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Singular | wacuw | hill |
| Plural | wacuwash | hills |
| Locative | wacuwuk | at the hill/on the hill |
Verbs[11]
Verbs in Mohegan come in several forms. Independent verbs exist in four forms: inanimate intransitive, animate intransitive, transitive inanimate and transitive animate. There is also the conjunct form which does not carry the affixes (used to clarify person) that the aforementioned hold.
Person, number and gender
[edit]Person[11]
Mohegan animate intransitive verbs show who the subject is by utilizing affixes. Singular forms have prefixes, but third person (singular and plural) only have suffixes. In the plural forms there are inclusive and exclusive suffixes; the inclusive we includes the person who is speaking as well as the person he/she is talking to whereas the exclusive we does not include the person the speaker is talking to. When an animate intransitive verb stem ends in a long vowel (á, i, o or ô) the third person singular does not take a final -w, and in the third person plural these same verbs take -k as an ending in lieu of - wak.
| Person | Mohegan | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | nukumotu | I steal |
| 2nd person singular | kukumotu | you steal |
| 3rd person singular | kumotuw | he/she steals |
| 3rd person obviative | kumotuh | he/she (obviative) steals |
| 1st person plural exclusive | nukumotumun | we (I and he/she) steal |
| 1st person plural inclusive | kukumotumun | we (I and you) steal |
| 2nd person plural | kukumotumô | you (more than one) steal |
| 3rd person plural | kumotuwak | they steal |
*affixes indicated in bold type
| Person | Mohegan | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | nuyáhshá | I breathe |
| 2nd person singular | kuyáhshá | you breathe |
| 3rd person singular | yáhshá | he/she breathes |
| 3rd person obviative | yásháh | he/she (obviative) breathes |
| 1st person plural exclusive | nuyáhshámun | we (I and he/she) breathe |
| 1st person plural inclusive | kuyáhshámun | we (I and you) breathe |
| 2nd person plural | kuyáhshámô | you (more than one) breathe |
| 3rd person plural | yáhshák | they breathe |
*affixes indicated in bold type
Numbers[11]
| Cardinal | Ordinal | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| nuqut | one | nikôni | first |
| nis | two | nahahtôwi | second |
| shwi | three | shwut | third |
| yáw | four | yáwut | fourth |
| nupáw | five | nupáwut | fifth |
| qutôsk | six | qutôskut | sixth |
| nisôsk | seven | nisôskut | seventh |
| shwôsk | eight | shwôskut | eighth |
| pásukokun | nine | pásukokunut | ninth |
| páyaq | ten | páyaqut | tenth |
Space
[edit]Locative case
The locative case is used to show where something is. Mohegan utilizes the suffix -uk to indicate spatial relationships, which can be compared to the English prepositions on, at, and in. In Mohegan there is no plural form to go with the obviative and the locative: the same form is used for singular and plural with the difference being distinguished by context.
Example of the Locative Case
| Mohegan | English Translation |
|---|---|
| cáhqin | house |
| cáhqinash | houses |
| cáhqinuk | in the house/houses |
Absentative case
The absentative case is used to when referencing a person who has died (this includes any property that they left behind). This is accomplished by adding a suffix to either his/her name, title or the property.
| Mohegan | English Translation | |
|---|---|---|
| singular | nokunsi | my late grandfather |
| plural | nokunsuk | my late grandfathers |
| obviative singular | wokunsah | his late grandfather |
| obviative plural | wokunsukah | his late grandfathers |
| departed's possession singular | mushoyi | my late father's boat |
| departed's possessions plural | mushoyuk | my late father's boats |
*suffix indicated by bold type
The following example shows the absentative case in use:
Niswi nusihsuk wikôtamak áposuhutut.
'Both of my late uncles enjoyed cooking.'
Syntax
[edit]Possession
In Mohegan, there are two types of possession, alienable possession and inalienable possession. Nouns receive different marking depending on the relationship between the possessor and the possessed noun. If the possessed noun is connected (physically or sometimes metaphorically) to the possessed noun it is considered inalienable possession. For example in the phrase "the man's hand", the hand is possessed inalienably because it is inseparable from the man. Inalienable possession can also be metaphorical; for example, in the phrase "the man's mother", the mother is possessed inalienably because of a cultural perception of kinship as a "strong" connection. Inalienable nouns must always receive marking. If the possessor owns the possessed noun, but is not physically attached to it, it is considered alienable possession. In the phrase "the man's house", the house is possessed alienably because the house is not attached to the man.
Nouns pertaining to kinship and body parts are always classified as inalienable, but there are some terms that do not fall under either of these umbrellas that must be classified as inalienable, such as the noun home. Various affixes are used to denote inalienability and different affixes are used to differentiate animate/inanimate and singular/plural. Additionally, when a term requires possession but the possessor is unclear or unknown it is marked with a prefix that indicates an indefinite possessor.
| Person | Mohegan | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | nutônihs | my daughter |
| 2nd person singular | kutônihs | your daughter |
| 3rd person singular | wutônihsah | his/her daughter |
| 1st person plural exclusive | nutônihsun | our (exclusive) daughter |
| 1st person plural inclusive | kutônihsun | our (inclusive) daughter |
| 2nd person plural | kutônihsuw | your (plural) daughter |
| 3rd person plural | wutônihsuwôwah | their daughter |
| indefinite possessor | mutônihs | an unknown person's daughter |
| Person | Mohegan | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | nusit | my foot |
| 2nd person singular | kusit | your foot |
| 3rd person singular | wusit | his/her foot |
| 1st person plural exclusive | nusitun | our (exclusive) foot |
| 1st person plural inclusive | kusitun | our (inclusive) foot |
| 2nd person plural | kusituw | your (plural) foot |
| 3rd person plural | wusituw | their foot |
| indefinite possessor | musit | an unknown person's foot |
The locative (-uk) and obviate (-ah) suffixes are added to the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd person singular forms. Whether the word is singular or plural should be suggested in the content of the sentence. The obviate affixes only go on animate nouns.
When a possessed noun is plural it must be shown. With an animate noun then suffix -ak is combined with the possessive ending (with the exception of third person singular and third person plural, where the plural is the same as the singular).
| Person | Mohegan | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | nutônihsak | my daughters |
| 2nd person singular | kutônihsak | your daughters |
| 3rd person singular | wutônihsah | his/her daughters |
| 1st person plural exclusive | nutônihsunônak | our (exclusive) daughters |
| 1st person plural inclusive | kutônihsunônak | our (inclusive) daughters |
| 2nd person plural | kutônihsuwôwak | your (plural) daughters |
| 3rd person plural | wetônihsuwôwah | their daughters |
| Person | Mohegan | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | nusitash | my feet |
| 2nd person singular | kusitash | your feet |
| 3rd person singular | wusitash | his/her feet |
| 1st person plural exclusive | nusitunônash | our (exclusive) feet |
| 1st person plural inclusive | kusitunônash | our (inclusive) feet |
| 2nd person plural | kusituwôwash | your (plural) feet |
| 3rd person plural | wusituwôwash | their feet |
| indefinite possessor | musitash | an unknown person's feet |
*affixes on all charts are marked by bold type
Clause combining
In Mohegan grammar verbs that are in a dependent clause are said to be in the conjunct order. Conjunct verbs have the same numbers of persons for each verb, but they do not have prefixes, only suffixes. In turn, all of the person information is at the end of the word.
| Person | Mohegan | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | yáhsháyôn | that I breathe |
| 2nd person singular | yáhsháyan | that you breathe |
| 3rd person singluar | yáhshát | that he/she breathes |
| 1st person plural (incl & excl) | yáhsháyak | that we breathe |
| 2nd person plural | yáhsháyáq | that you (more than one) breathe |
| 3rd person plural | yáhsháhutut | that they breathe |
| 3rd person plural participle | yáhshácik | those who breathe |
| indefinite subject | yáhshámuk | that someone breathes |
*suffixes on chart marked by bold type
Example: Mô yáyuw maci ákacuyǒn.
Translation: 'It was so bad that I am ashamed.'
When in the conjunct form if the first vowel of the word is a short vowel, that is /a/ or /u/, it changes to a long /á/.
Transitive verbs with inanimate objects take only a suffix as well. The suffix varies based on the ending of the stem.
For stems that end in -m- or -n- the suffixes are as follows:
1st person singular: -ôn
2nd person singular: -an
3rd person singular: -k
1st person plural: -ak
2nd person plural: -áq
3rd person plural: -hutut
3rd person plural participle: -kik
Indefinite subject (passive): -uk
For stems that end in -o- the suffixes are as follows:
1st person singular: -yôn
2nd person singular: -yan
3rd person singular: -ôk
1st person plural: -yak
2nd person plural: -yáq
3rd person plural: -w'hutut
3rd person plural participle: -ôkik
Indefinite subject (passive): -muk
For stems that end in -u- the suffixes are as follows:
1st person singular: -wôn
2nd person singular: -wan
3rd person singular: -k
1st person plural: -wak
2nd person plural: -wáq
3rd person plural: -'hutut
3rd person plural participle: -kik
Indefinite subject (passive): -muk
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ "Canku Ota - Aug. 11, 2001 - Mohegans Rebuilding Language". Archived from the original on 2014-05-02. Retrieved 2014-12-23.
- ^ Lewis, M. Paul (ed.), 2009. Ethnologue: Languages of the World. 16th edition. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics
- ^ "Medicine Woman Gladys Tantaquidgeon and Mohegan Cultural Renewal". Connecticut History. 2022-03-08. Retrieved 2024-09-11.
- ^ Cohen, Patricia (2010-04-05). "Indian Tribes Go in Search of Their Lost Languages". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2024-05-09.
- ^ "Mohegan Language Project". Archived from the original on 2010-04-24. Retrieved 2012-11-12.
- ^ J. Dyneley Prince and Frank G. Speck (March 1904). "Glossary of the Mohegan-Pequot Language" (PDF). American Anthropologist. New Series. 6 (1): 18–45. doi:10.1525/aa.1904.6.1.02a00030. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0015-3ED6-D.
- ^ a b c Libby, Sam (18 October 1998). "Tribes to Revive Language". The New York Times. p. 6.
- ^ "Ôkosuwôkak wuci Mohiks-Piqut Uyôtowáwôk - Bahá'í Prayers in the Mohegan-Pequot Language". Retrieved 2012-11-12.
- ^ Granberry, Julian (2003). A Lexicon of Modern Mohegan. Lincom Europa.
- ^ Fielding, Stephanie (2006). A Modern Mohegan Dictionary.
- ^ a b c d e Fielding, Stephanie (2006), A Modern Mohegan Dictionary 2006 Ed.
References
[edit]Articles
[edit]- Cowan, William. Pequot from Stiles to Speck. International Journal of American Linguistics. The University of Chicago Press. Vol. 39, No. 3 (Jul., 1973), pp. 164–172
- De Forest, John W. "The Lord's Prayer in the Pequot Tongue." In History of the Indians of Connecticut. 1852. Reprint, Brighton, MI: Native American Book Publishers, 1994.
- Michelson, Truman. "The Linguistic Classification of Pequot-Mohegan." American Anthropologist 26 (1924): 295. doi:10.1525/aa.1924.26.2.02a00240
- Pickering, John, ed. "Doctor Edwards' Observations on the Mohegan Languages." Collections of the Massachusetts Historical Society. Series 2 Volume 10 (1823): 81-160.
- Prince, J. Dyneley and Frank G. Speck. "Glossary of the Mohegan-Pequot Language." American Anthropologist 6 (1904): 18-45. doi:10.1525/aa.1904.6.1.02a00030
- Prince, J. Dyneley and Frank G. Speck. "The Modern Pequots and Their Language." American Anthropologist 5 (1903): 193-212. doi:10.1525/aa.1903.5.2.02a00010
- Speck, Frank. "A Modern Mohegan-Pequot Text." American Anthropologist 6 (1904): 469-76. doi:10.1525/aa.1904.6.4.02a00070
- Speck, Frank and Fidelia Fielding. "A Pequot Mohegan Witchcraft Tale." Journal of American Folklore 16 (1903): 104-6.
- Speck, Frank. "Native Tribes and Dialects of Connecticut: A Mohegan-Pequot Diary." Smithsonian Institution Bureau of American Ethnology Annual Report 43 (1903): 199-287.
- Speck, Frank. Speck Papers and Photograph Collection. (17 microfilm reels)
- Speck, Frank. "Text of the Pequot Sermon." American Anthropologist 5 (1903): 199-212.
External links
[edit]- Mohegan Language Project, website with assorted Mohegan Language resources
- A Modern Mohegan Dictionary (2006 Edition)—contains Guide to Using the Dictionary, Mohegan Grammar Paradigms, Mohegan to English Dictionary, and English to Mohegan Word Finder
- Mohegan-English Dictionary (December 2012 edition by S.Fielding ) — update of the Mohegan to English Dictionary section of above
- Mahican vs. Mohegan
- OLAC resources in and about the Mohegan-Pequot language
