Outline of China


The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to China:
The People's Republic of China is the most extensive country in East Asia and the third most extensive country in the world.[1][note 1] With a population of over 1,400,000,000, it is the second most populous country in the world.
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) has led the PRC under a one-party system since the state's establishment in 1949. The PRC is involved in a dispute over the political status of Taiwan. The CCP's rival during the Chinese Civil War, the Kuomintang (KMT), fled to Taiwan and surrounding islands after its defeat in 1949, claiming legitimacy over China, Mongolia, and Tuva while it was the ruling power of the Republic of China (ROC). The term "mainland China" is often used to denote the areas under PRC rule, but sometimes excludes its two special administrative regions: Hong Kong and Macau.
Because of its vast population, rapidly growing economy, and large research and development investments, China is considered an "emerging superpower".[2][3] It has the world's second largest economy (largest in terms of purchasing power parity.) China is also a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council and Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation.[4][5][6][7] Since 1978, China's market-based economic reforms have brought the poverty rate down from 53% in 1981 to 8% by 2001.[8] However, China is now faced with a number of other socioeconomic problems, including an aging population, an increasing rural-urban income gap, and rapid environmental degradation.[9][10]
China plays a major role in international trade. The country is the world's largest consumer of steel and concrete, using, respectively, a third and over a half of the world's supply of each.[11] Counting all products, China is the largest exporter and the second largest importer in the world.[12][13]
General reference
[edit]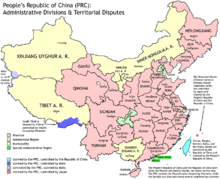
- Pronunciation: /ˈtʃaɪ.nə/ ⓘ
- Mandarin: [tʂʊŋ˥ kuɔ˧˥]
- Common English country name: China
- Official English country name: The People's Republic of China
- Common endonym: 中国 (Zhōngguó) (The Middle Kingdom or Central Realm)
- Official endonym: 中华人民共和国 (Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó)
- Adjectivals: China, Chinese
- Demonym: Chinese
- Etymology: Name of China
- International rankings of the People's Republic of China
- ISO country codes: CN, CHN, 156
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:CN
- Internet country code top-level domain: .cn
Geography of China
[edit]
- China is a megadiverse country
- Location:
- Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
- Eurasia
- Time zone: China Standard Time (UTC+08)
- Extreme points of China
- High: Mount Everest 8,848 m (29,029 ft) – highest point on Earth
- Low: Turpan Depression −154 m (−505 ft)
- Land boundaries: 22,117 km[note 2][note 3]
 Mongolia 4,677 km
Mongolia 4,677 km Russia 3,645 km
Russia 3,645 km India (excluding the territorial border disputes; McMahon Line) 3,380 km
India (excluding the territorial border disputes; McMahon Line) 3,380 km Myanmar 2,185 km
Myanmar 2,185 km Kazakhstan 1,533 km
Kazakhstan 1,533 km North Korea 1,416 km
North Korea 1,416 km Vietnam 1,281 km
Vietnam 1,281 km Nepal 1,236 km
Nepal 1,236 km Kyrgyzstan 858 km
Kyrgyzstan 858 km Pakistan 523 km
Pakistan 523 km Bhutan 470 km
Bhutan 470 km Laos 423 km
Laos 423 km Tajikistan 414 km
Tajikistan 414 km Afghanistan 76 km
Afghanistan 76 km
- Coastline: 14,500 km
- Population of China: 1,321,851,888(2007) - 1st most populous country
- Area of China: 9,640,821 square kilometres (3,722,342 sq mi) - 3rd largest country
- Atlas of China
Environment of China
[edit]
- Climate of China
- Environmental issues in China
- Ecoregions in China
- Renewable energy in China
- Geology of China
- Protected areas of China
- Wildlife of China
Natural geographic features of China
[edit]- Glaciers of China
- Islands of China
- Lakes of China
- Mountains of China
- Rivers of China
- Volcanoes in China
- Waterfalls of China
Regions of China
[edit]Administrative divisions of China
[edit]Provinces of China
[edit]Cities of China
[edit]- Direct-administered municipalities of China
- Districts of China
- Counties of China
- Villages of China (list)
Demography of China
[edit]Government and politics of China
[edit]- Form of government: one-party socialist republic.
- Capital of China: Beijing
- Elections in China
- Political parties in China
- Taxation in China
- Democracy in China
United front
[edit]Ruling party
[edit]Branches of government
[edit]Ultimate authority and Legislative branch
[edit]- National People's Congress (unicameral)
- Standing Committee
- Head of state (nominal): President, Xi Jinping
Administrative branch
[edit]Judicial branch
[edit]- Supreme People's Court
- President and Chief Justice: Zhang Jun
Procuratorial branch
[edit]- Supreme People's Procuratorate
- Prosecutor-General: Ying Yong
Supervisory branch
[edit]- Central Commission for Discipline Inspection (National Supervisory Commission)
- Secretary: Li Xi
- Director: Liu Jinguo
Military branch
[edit]Foreign relations of China
[edit]International organization membership
[edit]The People's Republic of China is a member of:[1]
Law and order in China
[edit]- Capital punishment in China
- Constitution of the People's Republic of China
- Crime in China
- Human rights in China
- Law enforcement in the People's Republic of China
Military of China
[edit]Local government in China
[edit]History of China
[edit]Culture of China
[edit]- Architecture of China
- Art in China
- Cinema of China
- Chinese clothing
- Cuisine of China
- Ethnic minorities in China
- Festivals in China
- Languages of China
- Media in China
- National symbols of China
- People of China
- Prostitution in China
- Public holidays in the People's Republic of China
- Religion in China
- List of World Heritage Sites in China
- Literature of China
- Music of China
- Television in the People's Republic of China
- Theatre in China
Sports in China
[edit]Economy and infrastructure of China
[edit]- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2011): 2nd (second)
- Agriculture in China
- Banking in China
- Communications in China
- Currency of China: Renminbi Yuan
- Economic history of China
- Energy in China
- Health care in China
- Chinese stock exchanges
- Tourism in China
- Transport in China
- Water supply and sanitation in China
Education in China
[edit]See also
[edit]- All pages with titles beginning with China
- All pages with titles containing China
- All pages with titles beginning with Chinese
- All pages with titles containing Chinese
- All pages with titles beginning with People's Republic of China
- All pages with titles containing People's Republic of China
- International rankings of China
- List of China-related topics
- Member state of the Group of Twenty Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Asia
- Outline of geography
- Outline of Hong Kong
- Outline of Macau
- Outline of Taiwan
- Outline of Tibet
Notes
[edit]- ^ Area rank is disputed with the United States and is either ranked third or fourth. See List of countries and dependencies by area for more information.
- ^ China has the longest total land boundaries of any country.
- ^ China and Russia each border 14 countries, more than any other countries.
- ^ Article 93 of the Constitution of the People's Republic of China places the authority to direct the armed forces of the PRC in the Central Military Commission. However, Article 80 gives the President of the People's Republic of China the power to proclaim martial law, proclaim a state of war, and issue mobilization orders. Since the mid-1990s, it has been standard practice to have the President, the CMC Chairman, and the General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party be the same person although the differences in the start of terms means that there is some overlap between an occupant and his predecessor.
References
[edit]- ^ a b "China". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. July 8, 2009. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ^ Gordon, Peter. "Review of "China: The Balance Sheet -- What the World Needs to Know Now About the Emerging Superpower"". The Asia Review of Books. Archived from the original on 2012-05-27. Retrieved 2007-12-24.
- ^ Miller, Lyman. "China an Emerging Superpower?". Stanford Journal of International Relations. Retrieved 2007-12-24.
- ^ China Passes U.S. In Trade With Japan
- ^ Trade Policy Outlook for Second-term Bush Administration
- ^ "China - Taiwan Economic Ties". Archived from the original on 2019-05-11. Retrieved 2008-07-02.
- ^ "Beijing's Growing Politico-Economic Leverage Over Ulaanbaatar". Archived from the original on 2008-10-19. Retrieved 2008-07-02.
- ^ Fighting Poverty: Findings and Lessons from China's Success Archived 2013-09-22 at the Wayback Machine (World Bank). Retrieved August 10, 2006.
- ^ Yardley, Jim (December 29, 2007). "Beijing's Olympic Quest: Turn Smoggy Sky Blue". The New York Times. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ "China fails environment targets". BBC News. January 10, 2007. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ Center for International Trade in Forest Products Archived 2008-06-24 at the Wayback Machine China's Building Boom. Retrieved December 2, 2006,
- ^ The World Factbook, Rank Order - Imports.
- ^ "WTO: China overtakes US as second biggest exporter". Geneva: China Daily. 2007-04-12. Retrieved 2016-09-16.
External links
[edit]- China.org.cn China news, weather, business, travel, language courses, archives
- U.S. Department of State, Background Note on China
- Interactive China map with province and city guides.
- China Digital Times Online China news portal, run by the Graduate School of Journalism of University of California at Berkeley.
- China Worker
- China Map
- China Flights
- NY Inquirer: China's 21st Century
- The Chinese Superpower-Historical Background, Dr Rivka Shpak-Lissak
- China Map Quest
- The 200 best books on China


