Monstrillidae
| Monstrillidae | |
|---|---|

| |
| Monstrilla longiremis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Copepoda |
| Infraclass: | Neocopepoda |
| Superorder: | Podoplea |
| Order: | Monstrilloida G. O. Sars, 1901 [2] |
| Family: | Monstrillidae Dana, 1849 [1] |
Monstrilloida is an order of copepods with a cosmopolitan distribution in the world's oceans. The order contains a single family, Monstrillidae.[2] The name of the first ever described genus Monstrilla is derived from Latin, meaning "tiny monster", because the lack of usual diagnostic features of copepods puzzled early taxonomists.[3]
Description
[edit]The family Monstrillidae is characterised by having a well-developed fourth pair of swimming legs, but a rudimentary or absent fifth pair. Adults have no oral appendages, and the mouth leads only to a short, blind pharynx. They also lack second antennae, but show large, multiramous and setaceous antennulae. These antennulae are rigid and anteriorly oriented. Females carry a long pair of spines to which the eggs are attached, while males have a "genital protuberance, which is provided with lappets"; in both sexes, the genitalia are very different from those of all other copepods.[4] Some species have large, well-developed nauplius eyes, while others are basically blind.[citation needed]
Larval nauplial stages do not possess any discernible antennae, antenullae or mouth parts, but paired tube-shaped nourishing appendages to absorb nutrients from their host, which are also present in later copepodite stages that resemble the adult morphology; in adults, scars of these now discarded appendages remain as small processes on the cephalothorax.[5]
Taxonomy of genera and species descriptions are normally based on a few key characteristics: the length and setation-pattern of the antennulae,[6] presence/absence and morphology of the eyes, number and shape of caudal setae, and structure and setation-pattern of the fifth swimming leg in females/genital complex in males, respectively.[3]

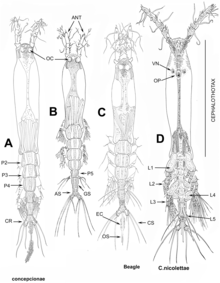

Distribution
[edit]Monstrilloids are distributed worldwide (including both the Arctic[7] and Antarctic), inhabiting coastal-neritic waters (0-200m depth).[8] Adults are regularly caught with plankton nets and are clearly pelagic organisms; however, the endoparasitic larval stages infect sessile benthic organisms and therefore are part of the epibenthos and hyperbenthos.[3]
Biology
[edit]Biologically and ecologically, our knowledge of the order is limited, although the life cycle differs from that of all other copepods:[9] Members of the Monstilloida are protelean parasites, meaning that their larval stages are parasitoids that kill their host to emerge as free-living subadults. Apparently, some hosts recover after the final subadult monstrilloid exits their body.[3] It is hypothesized, that the host's relative body size and the number and location of copepods parasitizing the same host determine whether it survives an infection.[3] The detailed life cycle may vary between different species, but generally follows a certain sequence: after a free-swimming, infective nauplius stage, the larvae develop inside benthic polychaetes, gastropods, sponges and bivalve mussels (They may be a pest in commercially important bivalve aquaculture),[10] from where the planktonic adults emerge. They do not possess functioning mouth-parts, their sole purpose is to reproduce.[11] In Contrast to holoplanktonic calanoid and cyclopoid copepods, Monstrilloids do not use their largest cephalic appendages, the antennulae, for locomotion, but to create a stream-line shaped corridor, rather using their four pairs of swimming legs to move in the water column. Sex determination depends on conspecifics infecting the same host individual. In case of 2-3 coexisting monstrilloids they become males, when there is only one parasite in a host, it develops into a female.[12]

Taxonomy
[edit]The taxonomy of the order and family is undergoing several revisions,[13] for instance, the family Thaumatopsyllidae was formerly included in the order, but is now usually placed in the Cyclopoida.[14] and the genus Strilloma is now considered a taxonomic synonym of Monstrilla, the largest genus.[15] In General, the Monstrilloida are taxonomically challenging, both regarding their relation to other copepod groups and species assignment within the order. Monstrilloida was placed as a sister taxa to the Siphonostomatoida, but a lack of mouth parts makes comparison based on homologies difficult. A more recent analysis placed the order nested within the fish-parasitizing caligiform groups of Siphonostomatoida. Consequently, they would have evolved from an ectoparasitic ancestor associated with fish; most parasitic copepods are not free-living as adults, so Monstrilloids presumably underwent a change in life cycle strategy, host selection and body morphology.[16] Yet the unique nature of the order Monstrilloida sister group of the Siphonostomatoida has been corroborated using modern molecular approaches.[17] So far, no ultimately satisfying copepod phylogeny has been proposed, and the placement of the monophyletic Monstrilloida remains unresolved.[5]
Because of their enigmatic life cycle, the morphology of most postnaupliar and copepodite stages is not known. Monstrilloids are not abundant in planktonic samples, and often only single specimens can be collected. Since many species occupy overlapping geographic ranges, males and females of different species collected in the same sample may be mistaken for conspecifics. Until now, both sexes were described for less than 25% of all known species.[5] To link males and females of a species, taxonomists have started to use molecular methods such as DNA Barcoding recently.[18]
As of 2019, the order Monstrilloida contains seven accepted genera with more than 160 species:[7][19]
- Monstrilla Dana, 1849
- Australomonstrillopsis Suárez-Morales & McKinnon, 2014
- Caromiobenella Jeon, Lee & Soh, 2018
- Cymbasoma Thompson, 1888
- Maemonstrilla Grygier & Ohtsuka, 2008
- Monstrillopsis Sars, 1921
- Spinomonstrilla Suárez-Morales, 2019
References
[edit]- ^ "Monstrillidae Dana, 1849". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved July 8, 2011.
- ^ a b "Monstrilloida Sars, 1901". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved July 8, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e Suárez-Morales, Eduardo (August 2018). "Monstrilloid Copepods: the Best of Three Worlds". Bulletin, Southern California Academy of Sciences. 117 (2): 92–103. doi:10.3160/3646.1. ISSN 0038-3872. S2CID 92446569.
- ^ Davis, Charles C. (1949). "A primary revision of the Monstrilloidea, with descriptions of two new species". Transactions of the American Microscopical Society. 68 (3): 245–255. doi:10.2307/3223221. JSTOR 3223221.
- ^ a b c Suárez-Morales, Eduardo (2011-08-10). Browman, Howard (ed.). "Diversity of the Monstrilloida (Crustacea: Copepoda)". PLOS ONE. 6 (8): e22915. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...622915S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022915. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3154257. PMID 21853055.
- ^ Grygier, Mark J.; Ohtsuka, Susumu (1995-10-01). "Sem Observation of the Nauplius of Monstrilla Hamatapex, New Species, from Japan and an Example of Upgraded Descriptive Standards for Monstrilloid Copepods". Journal of Crustacean Biology. 15 (4): 703–719. doi:10.1163/193724095X00118. ISSN 0278-0372.
- ^ a b Delaforge, Aurélie; Suárez-Morales, Eduardo; Walkusz, Wojciech; Campbell, Karley; Mundy, C. J. (2017-10-18). "A new species of Monstrillopsis (Crustacea, Copepoda, Monstrilloida) from the lower Northwest Passage of the Canadian Arctic". ZooKeys (709): 1–16. doi:10.3897/zookeys.709.20181. ISSN 1313-2970. PMC 5674165. PMID 29118635.
- ^ Suárez-Morales, Eduardo; Mckinnon, A. David (2014-03-17). "The Australian Monstrilloida (Crustacea: Copepoda) I. Monstrillopsis Sars, Maemonstrilla Grygier & Ohtsuka, and Australomonstrillopsis gen. nov". Zootaxa. 3779 (3): 301–340. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3779.3.1. ISSN 1175-5334. PMID 24871727.
- ^ Cristina de Oliveira Dias (1996). "Monstrilloida (Copepoda) off the Brazilian coast". Hydrobiologia. 324 (3): 253–256. doi:10.1007/BF00016397. S2CID 8233032.
- ^ Suárez-Morales, Eduardo; Scardua, Marcos Paiva; da Silva, Patricia Mirella (August 2010). "Occurrence and histopathological effects of Monstrilla sp. (Copepoda: Monstrilloida) and other parasites in the brown mussel Perna perna from Brazil". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 90 (5): 953–958. doi:10.1017/S0025315409991391. ISSN 0025-3154. S2CID 86117943.
- ^ E. Suárez-Morales & R. Palomares-García (1995). "A new species of Monstrilla (Copepoda: Monstrilloida) from a coastal system of the Baja California Peninsula, Mexico". Journal of Plankton Research. 17 (4): 745–752. doi:10.1093/plankt/17.4.745.
- ^ Malaquin, Alphonse (1901-09-01). "Le parasitisme évolutif des Monstrillides (Crustacés Copépodes)". Archives de zoologie expérimentale et générale. 9: 81–232.
- ^ E. Suárez-Morales & J. B. Escamilla (2001). "Taxonomic report on some monstrilloids (Copepoda, Monstrilloida) from southeast Mexico with the description of a new species of Monstrilla". Journal of Natural History. 35 (10): 1433–1445. doi:10.1080/002229301317067629. S2CID 85042857.
- ^ J. W. Martin & G. E. Davis (2001). An Updated Classification of the Recent Crustacea (PDF). Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. pp. 1–132.
- ^ Eduardo Suárez-Morales & Rebeca Gasca (2004). "On the invalidity of Strilloma Isaac (Copepoda: Monstrilloida): observations from the type species" (PDF). Zoological Studies. 43 (2): 292–299.
- ^ Huys, Rony; Llewellyn-Hughes, Julia; Conroy-Dalton, Sophie; Olson, Peter D.; Spinks, Jennifer N.; Johnston, David A. (May 2007). "Extraordinary host switching in siphonostomatoid copepods and the demise of the Monstrilloida: Integrating molecular data, ontogeny and antennulary morphology". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 43 (2): 368–378. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2007.02.004. PMID 17383905.
- ^ Khodami, Sahar; McArthur, J. Vaun; Blanco-Bercial, Leocadio; Martinez Arbizu, Pedro (2017-08-22). "Molecular Phylogeny and Revision of Copepod Orders (Crustacea: Copepoda)". Scientific Reports. 7 (1): 9164. Bibcode:2017NatSR...7.9164K. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-06656-4. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 5567239. PMID 28831035. (Retracted, see doi:10.1038/s41598-020-74404-2, PMID 33057148)
- ^ Baek, Su Youn; Jang, Kuem Hee; Choi, Eun Hwa; Ryu, Shi Hyun; Kim, Sang Ki; Lee, Jin Hee; Lim, Young Jin; Lee, Jimin; Jun, Jumin; Kwak, Myounghai; Lee, Young-Sup (2016-07-06). "DNA Barcoding of Metazoan Zooplankton Copepods from South Korea". PLOS ONE. 11 (7): e0157307. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1157307B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0157307. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4934703. PMID 27383475.
- ^ "The World of Copepods - Monstrillidae Dana, 1849". www.marinespecies.org. Retrieved 2020-04-19.

