Millennium Development Goals

In the United Nations, the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 created following the Millennium Summit, following the adoption of the United Nations Millennium Declaration. These were based on the OECD DAC International Development Goals agreed by Development Ministers in the "Shaping the 21st Century Strategy". The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) succeeded the MDGs in 2016.
All 191 United Nations member states, and at least 22 international organizations, committed to help achieve the following Millennium Development Goals by 2015:
- To eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
- To achieve universal primary education
- To promote gender equality and empower women
- To reduce child mortality
- To improve maternal health
- To combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases
- To ensure environmental sustainability[1]
- To develop a global partnership for development[1]
Each goal had specific targets, and dates for achieving those targets. The eight goals were measured by 21 targets. To accelerate progress, the G8 finance ministers agreed in June 2005 to provide enough funds to the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the African Development Bank (AfDB) to cancel $40 to $55 billion in debt owed by members of the heavily indebted poor countries (HIPC) to allow them to redirect resources to programs for improving health and education and for alleviating poverty.
Critics of the MDGs complained of a lack of analysis and justification behind the chosen objectives, and the difficulty or lack of measurements for some goals and uneven progress, among others. Although developed countries' aid for achieving the MDGs rose during the challenge period, more than half went for debt relief and much of the remainder going towards natural disaster relief and military aid, rather than further development.[citation needed]
As of 2013, progress towards the goals was uneven. Some countries achieved many goals, while others were not on track to realize any. A UN conference in September 2010 reviewed progress to date and adopted a global plan to achieve the eight goals by their target date. New commitments targeted women's and children's health, and new initiatives in the worldwide battle against poverty, hunger and disease.
Background
[edit]Origins
[edit]Following the end of the Cold War, a series of UN‑led conferences in the 1990s had focused on issues such as children, nutrition, human rights and women, producing commitments for combined international action on those matters. The 1995 World Summit on Social Development produced a Copenhagen Declaration on Social Development with a long and complex list of commitments by global leaders, including many adapted from the outcomes of previous conferences.[2] But international aid levels were falling and, in that same year, the Development Assistance Committee of the OECD set up a reflection process to review the future of development aid.[3] The resulting 1996 report, "Shaping the 21st Century", turned some of the Copenhagen commitments into six monitorable "International Development Goals", which had similar content and form to the eventual MDGs: halving poverty by 2015; universal primary education by 2015; eliminating gender disparity in schools by 2005; reductions in infant, child and maternal mortality by 2015, universal access to reproductive health services by 2015 and adequate national strategies for sustainable development in place everywhere by 2015.[4]
In late 1997, the UN General Assembly envisaged a special Millennium Assembly and forum as a focus for efforts to reform the UN system.[5] A year later, it specifically resolved to hold not only the Millennium Assembly but also a Millennium Summit, and mandated the Secretary-General, Kofi Annan, to come up with proposals for "a number of forward-looking and widely relevant topics", thus opening the possibility of going beyond the institutional questions of UN reform.[6] Annan's report, when published in April 2000 under the title "We the Peoples: The Role of the United Nations in the 21st Century", framed the questions of UN reform within the larger challenges facing the world, the chief of which was identified as "to ensure that globalization becomes a positive force for all the world's people, instead of leaving billions of them behind in squalor".[7] In the report Annan urged the forthcoming Millennium Summit to adopt certain key goals and objectives on many of the issues raised in the Copenhagen summit, other conferences of the 1990s, and the recently published Brahimi Report on international peace and security.[7]
The Millennium Summit and the General Assembly in September 2000 issued a Millennium Declaration echoing the agenda that Annan had set out.[8] This declaration did not specifically mention "Millennium Development Goals", but it does contain the substance – and much of the same wording – as the eventual goals. A process of selecting and refining the Goals from the content of the Declaration continued for some time. A crucial moment here was unification between discussions under the auspices of the United Nations and approaches being followed by the OECD based on "Shaping the 21st Century"; this unification was agreed at a meeting convened by the World Bank in March 2001.[3] In September 2001, Annan presented to the General Assembly a "Road map towards the implementation of the United Nations Millennium Declaration" which did contain a section specifically about "the Millennium Development Goals", enunciating some of them in their eventual wording, and indicating the remaining issues in formulating a definitive set.[9]
Human capital, infrastructure and human rights
[edit]The MDGs emphasized three areas: human capital, infrastructure and human rights (social, economic and political), with the intent of increasing living standards.[10] Human capital objectives include nutrition, healthcare (including child mortality, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria, and reproductive health) and education. Infrastructure objectives include access to safe drinking water, energy and modern information/communication technology; increased farm outputs using sustainable practices; transportation; and environment. Human rights objectives include empowering women, reducing violence, increasing political voice, ensuring equal access to public services and increasing security of property rights. The goals were intended to increase an individual's human capabilities and "advance the means to a productive life". The MDGs emphasize that each nation's policies should be tailored to that country's needs; therefore most policy suggestions are general.
Goals
[edit]
The MDGs were developed out of several commitments set forth in the Millennium Declaration, signed in September 2000. There are eight goals with 21 targets,[11] and a series of measurable health indicators and economic indicators for each target.[12][13]
Goal 1: Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
[edit]- Target 1A: Halve, between 1990 and 2015, the proportion of people living on less than $1.25 a day[14]
- Target 1B: Achieve Decent Employment for Women, Men, and Young People
- Target 1C: Halve, between 1990 and 2015, the proportion of people who suffer from hunger[15]
Goal 2: Achieve universal primary education
[edit]- Target 2A: By 2015, all children can complete a full course of Primary education/primary schooling, girls and boys[16]
MDG 2 focused on primary education and emphasizes enrollment and completion. In some countries, primary enrollment increased at the expense of achievement levels. In some cases, the emphasis on primary education has negatively affected secondary and post-secondary education.[17]
Goal 3: Promote gender equality and empower women
[edit]- Target 3A: Eliminate gender disparity in primary and secondary education preferably by 2005, and at all levels by 2015[18]
Goal 4: Reduce child mortality rates
[edit]- Target 4A: Reduce by two-thirds, between 1990 and 2015, the under-five mortality rate [19]
Achieving the MDGs does not depend on economic growth alone. In the case of MDG 4, developing countries such as Bangladesh have shown that it is possible to reduce child mortality with only modest growth with inexpensive yet effective interventions, such as measles immunization.[20] Still, government expenditure in many countries is not enough to meet the agreed spending targets.[21]
Goal 5: Improve maternal health
[edit]- Target 5A: Reduce by three-quarters, between 1990 and 2015, the maternal mortality ratio
- Target 5B: Achieve, by 2015, universal access to reproductive health[22]
Goal 6: Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases
[edit]- Target 6A: Have halted by 2015 and begun to reverse the spread of HIV/AIDS
- Target 6B: Achieve, by 2010, universal access to treatment for HIV/AIDS for all those who need it
- Target 6C: Have halted by 2015 and begun to reverse the incidence of malaria and other major diseases[23]
Research on health systems suggests that a "one size fits all" model will not sufficiently respond to the individual healthcare profiles of developing countries; however, a study found a common set of constraints in scaling up international health, including the lack of absorptive capacity, weak health systems, human resource limitations, and high costs. The study argued that the emphasis on coverage obscures the measures required for expanding health care. These measures include political, organizational, and functional dimensions of scaling up, and the need to nurture local organizations.[24]
Goal 7: Ensure environmental sustainability
[edit]- Target 7A: Integrate the principles of sustainable development into country policies and programs; reverse loss of environmental resources
- Target 7B: Reduce biodiversity loss, achieving, by 2010, a significant reduction in the rate of loss
- Target 7C: Halve, by 2015, the proportion of the population without sustainable access to safe drinking water and basic sanitation
- Target 7D: By 2020, to have achieved a significant improvement in the lives of at least 100 million slum-dwellers[25]
Goal 8: Develop a global partnership for development
[edit]- Target 8A: Develop further an open, rule-based, predictable, non-discriminatory trading and financial system
- Target 8B: Address the Special Needs of the Least Developed Countries (LDCs)
- Target 8C: Address the special needs of landlocked developing countries and small island developing States
- Target 8D: Deal comprehensively with the debt problems of developing countries through national and international measures in order to make debt sustainable in the long term
- Target 8E: In co-operation with pharmaceutical companies, provide access to affordable, essential drugs in developing countries
- Target 8F: In co-operation with the private sector, make available the benefits of new technologies, especially information and communications[26]
MDG 8 uniquely focused on donor achievements, rather than development successes. The Commitment to Development Index, published annually by the Center for Global Development in Washington, D.C., is considered the best numerical indicator for MDG 8.[27] It is a more comprehensive measure of donor progress than official development assistance, as it takes into account policies on a number of indicators that affect developing countries such as trade, migration and investment.
Progress
[edit]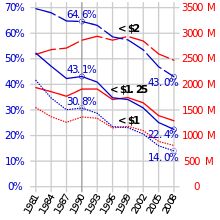
A major conference was held at UN headquarters in New York on 20–22 September 2010 to review progress. The conference concluded with the adoption of a global action plan to accelerate progress towards the eight anti-poverty goals. Major new commitments on women's and children's health, poverty, hunger and disease ensued.
Between 1990 and 2010 the population living on less than $1.25 a day in developing countries halved to 21%, or 1.2 billion people, achieving MDG 1A before the target date, although the biggest decline was in China, which took no notice of the goal. However, the child mortality and maternal mortality are down by less than half. Sanitation (MDG 7) and education (MDG 2) targets will also be missed.[28]
Fundamental issues such as gender, the divide between the humanitarian and development agendas and economic growth will determine whether or not the MDGs are achieved, according to researchers at the Overseas Development Institute (ODI).[29][30][31]
Example countries
[edit]Progress towards reaching the goals has been uneven across countries. Brazil achieved many of the goals,[32] while others, such as Benin, are not on track to realize any.[33] The major successful countries include China (whose poverty population declined from 452 million to 278 million) and India.[34] The World Bank estimated that MDG 1A (halving the proportion of people living on less than $1 a day) was achieved in 2008 mainly due to the results from these two countries and East Asia.[35]
In the early 1990s Nepal was one of the world's poorest countries and remains South Asia's poorest country. Doubling health spending and concentrating on its poorest areas halved maternal mortality between 1998 and 2006. Its Multidimensional Poverty Index has seen the largest decreases of any tracked country. Bangladesh has made some of the greatest improvements in infant and maternal mortality ever seen, despite modest income growth.[28]
Success factors
[edit]Scholars identified "six factors that have enabled or hindered MDG implementation" for particular countries.[36] These include path dependencies ("whether the MDGs are in line with the historical political orientation and tradition of a country"), government ownership of the MDGs, pressure from NGOs, availability of financial resources, "administrative capacity and level of economic development", and "support from international or bilateral donors".[36]
The researchers identified China as a successful country with the MDGs because it "had strong administrative capacities and economic development and could hence adopt effective national strategies aligned with the MDGs".[36]
Multilateral debt reduction
[edit]G‑8 Finance Ministers met in London in June 2005 in preparation for the Gleneagles Summit in July and agreed to provide enough funds to the World Bank, IMF and the African Development Bank (AfDB) to cancel the remaining HIPC multilateral debt ($40 to $55 billion). Recipients would theoretically re-channel debt payments to health and education.[37]
The Gleaneagles plan became the Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative (MDRI). Countries became eligible once their lending agency confirmed that the countries had continued to maintain the reforms they had implemented.[37]
While the World Bank and AfDB limited MDRI to countries that complete the HIPC program, the IMF's eligibility criteria were slightly less restrictive so as to comply with the IMF's unique "uniform treatment" requirement. Instead of limiting eligibility to HIPC countries, any country with per capita income of $380 or less qualified for debt cancellation. The IMF adopted the $380 threshold because it closely approximated the HIPC threshold.[37]
Sub-Saharan Africa
[edit]One success was to strengthen rice production in Sub-Saharan Africa. By the mid‑1990s, rice imports reached nearly $1 billion annually. Farmers had not found suitable rice varieties that produce high yields. New Rice for Africa (NERICA), a high-yielding and well adapted strain, was developed and introduced in areas including Congo Brazzaville, Côte d'Ivoire, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Guinea, Kenya, Mali, Nigeria, Togo and Uganda. Some 18 varieties of this strain became available, enabling African farmers to produce enough rice to feed their families and have extra to sell.[38]
The region also showed progress towards MDG 2. School fees that included Parent-Teacher Association and community contributions, textbook fees, compulsory uniforms and other charges took up nearly a quarter of a poor family's income and led countries including Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Tanzania, and Uganda to eliminate such fees, increasing enrollment. For instance, in Ghana, public school enrollment in the most deprived districts rose from 4.2 million to 5.4 million between 2004 and 2005. In Kenya, primary school enrollment added 1.2 million in 2003 and by 2004, the number had climbed to 7.2 million.[39]
Millennium Villages Project
[edit]Following the adoption of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), in 2000, Jeffrey Sachs of The Earth Institute at Columbia University was among the leading academic scholars and practitioners on the MDGs. He chaired the WHO Commission on Macroeconomics and Health (2000–01), which played a pivotal role in scaling up the financing of health care and disease control in the low-income countries to support MDGs 4, 5, and 6. He worked with UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan in 2000–2001 to design and launch The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria.[40] He also worked with senior officials of the George W. Bush administration to develop the PEPFAR program to fight HIV/AIDS, and the PMI to fight malaria. On behalf of Annan, from 2002 to 2006 he chaired the UN Millennium Project, which was tasked with developing a concrete action plan to achieve the MDGs. The UN General Assembly adopted the key recommendations of the UN Millennium Project at a special session in September 2005. The recommendations for rural Africa are currently being implemented and documented in the Millennium Villages, and in several national scale-up efforts such as in Nigeria.
The Millennium Villages Project, which Sachs directs, operates in more than a dozen African countries and covers more than 500,000 people. The MVP has engendered considerable controversy associated as critics have questioned both the design of the project and claims made for its success. In 2012 The Economist reviewed the project and concluded "the evidence does not yet support the claim that the millennium villages project is making a decisive impact."[41] Critics have pointed to the failure to include suitable controls that would allow an accurate determination of whether the Projects methods were responsible for any observed gains in economic development. A 2012 Lancet paper claiming a 3-fold increase in the rate of decline in childhood mortality was criticized for flawed methodology, and the authors later admitted that the claim was "unwarranted and misleading".[42]
Millennium Development Goal 3 (gender equality)
[edit]
Increased focus on gender issues could accelerate MDG progress, e.g. empowering women through access to paid work could help reduce child mortality.[43] In South Asian countries babies often suffered from low birth weight and high mortality due to limited access to healthcare and maternal malnutrition. Paid work could increase women's access to health care and better nutrition, reducing child mortality. Increasing female education and workforce participation increased these effects. Improved economic opportunities for women also decreased participation in the sex market, which decreased the spread of AIDS, MDG 6A.[43]
Although the resources, technology and knowledge exist to decrease poverty through improving gender equality, the political will is often missing.[44] If donor and developing countries focused on seven "priority areas", great progress could be made towards the MDG. These seven priority areas include: increasing girls' completion of secondary school, guaranteeing sexual and reproductive health rights, improving infrastructure to ease women's and girl's time burdens, guaranteeing women's property rights, reducing gender inequalities in employment, increasing seats held by women in government, and combating violence against women.[44]
It is thought by some women's rights' advocatess that the current MDGs targets do not place enough emphasis on tracking gender inequalities in poverty reduction and employment as there are only gender goals relating to health, education, and political representation.[43][45] Feminist writers such as Naila Kabeer have argued that in order to encourage women's empowerment and progress towards the MDGs, increased emphasis should be placed on gender mainstreaming development policies and collecting data based on gender.
According to MDG Monitor, the target under MDG 3 "To eliminate gender disparity in primary and secondary education by 2005, and in all levels of education by 2015" was met.[46]
However MDG monitor points out that while parity has been achieved across the developing world, there are regional and national differences favouring girls in some cases and boys in others. In secondary education in "Western Asia, Oceania, and sub-Saharan Africa, girls are still at a disadvantage, while the opposite is true in Latin America and the Caribbean – boys are at a disadvantage." Similarly in tertiary education there are disparities "at the expense of men in Northern Africa, Eastern Asia, and Latin America and the Caribbean" while conversely they are "at the expense of women in Southern Asia and sub-Saharan Africa."[46]
Funding commitment
[edit]Over the past 35 years, UN members have repeatedly "commit[ted] 0.7% of rich-countries' gross national income (GNI) to Official Development Assistance".[47] The commitment was first made in 1970 by the UN General Assembly.
The text of the commitment was: "Each economically advanced country will progressively increase its official development assistance to the developing countries and will exert its best efforts to reach a minimum net amount of 0.7 percent of its gross national product at market prices by the middle of the decade."[48]
The attention to well-being other than income helps bring funding to achieving MDGs.[49] Further MDGs prioritize interventions, establish obtainable objectives with useful measurements of progress despite measurement issues and increased the developed world's involvement in worldwide poverty reduction.[50] MDGs include gender and reproductive rights, environmental sustainability, and spread of technology. Prioritizing interventions helps developing countries with limited resources make decisions about allocating their resources. MDGs also strengthen the commitment of developed countries and encourage aid and information sharing.[49] The global commitment to the goals likely increases the likelihood of their success. They note that MDGs are the most broadly supported poverty reduction targets in world history.[51]
The International Health Partnership (IHP+) aimed to accelerate MDG progress by applying international principles for effective aid and development in the health sector. In developing countries, significant funding for health came from external sources requiring governments to coordinate with international development partners. As partner numbers increased variations in funding streams and bureaucratic demands followed. By encouraging support for a single national health strategy, a single monitoring and evaluation framework, and mutual accountability, IHP+ attempted to build confidence between government, civil society, development partners and other health stakeholders.[52]
European Union
[edit]In 2005 the European Union reaffirmed its commitment to the 0.7% aid targets, noting that "four out of the five countries, which exceed the UN target for ODA of 0.7%, of GNI are member states of the European Union".[53] Further, the UN "believe[s] that donors should commit to reaching the long-standing target of 0.7 percent of GNI by 2015".[48]
United States
[edit]However, the United States as well as other nations disputed the Monterrey Consensus that urged "developed countries that have not done so to make concrete efforts towards the target of 0.7% of gross national product (GNP) as ODA to developing countries".[54][55]
The US consistently opposed setting specific foreign-aid targets since the UN General Assembly first endorsed the 0.7% goal in 1970.[56]
OECD
[edit]Many Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) nations, did not donate 0.7% of their GNI. Some nations' contributions fell far short of 0.7%.[57]
The Australian government committed to providing 0.5% of GNI in International Development Assistance by 2015–2016.[58]
Criticism
[edit]General
[edit]General criticisms included a perceived lack of analytical power and justification behind the chosen objectives.[49] Some of the indicator definitions, baselines and targets were changed after their first adoption, to suggest that progress had been better than was really the case.[59]
Further criticism included their "money-metric and donor-centric view", their "unidirectional dimension and narrow focus on developing countries, with industrialized countries being deployed almost as their tutors", the "lack of stakeholder engagement in formulating the MDGs" and the "weak review mechanisms to measure performance".[36]
David Hulme and James Scott noted that the process of creating the MDGs was diffuse, having no single architect and "no clear start or end". They also commented that the process was driven by rich states rather than the countries that would be more the subject of MDG interventions.[3] The entire MDG process has been accused of lacking legitimacy as a result of failure to include, often, the voices of the very participants that the MDGs seek to assist.
The MDGs lacked strong objectives and indicators for within-country equality, despite significant disparities in many developing nations.[49][60]
The MDGs were attacked for insufficient emphasis on environmental sustainability.[49] Thus, they did not capture all elements needed to achieve the ideals set out in the Millennium Declaration.[60]
Human rights
[edit]The MDGs may under-emphasize local participation and empowerment (other than women's empowerment).[49] FIAN International, a human rights organization focusing on the right to adequate food, contributed to the Post 2015 process by pointing out a lack of: "primacy of human rights; qualifying policy coherence; and of human rights based monitoring and accountability. Without such accountability, no substantial change in national and international policies can be expected."[61]
Measurement difficulties
[edit]A publication from 2005 argued that goals related to maternal mortality, malaria and tuberculosis are impossible to measure and that current UN estimates lack scientific validity or are missing.[62] Household surveys are the primary measure for the health MDGs but may be poor and duplicative measurements that consume limited resources. Furthermore, countries with the highest levels of these conditions typically have the least reliable data collection. The study also argued that without accurate measures, it is impossible to determine the amount of progress, leaving MDGs as little more than a rhetorical call to arms.[62]
MDG proponents such as McArthur and Sachs countered that setting goals is still valid despite measurement difficulties, as they provide a political and operational framework to efforts. With an increase in the quantity and quality of healthcare systems in developing countries, more data could be collected.[63] They asserted that non-health related MDGs were often well measured, and that not all MDGs were made moot by lack of data.
Equity
[edit]Further developments in rethinking strategies and approaches to achieving the MDGs include research by the Overseas Development Institute into the role of equity.[64] Researchers at the ODI argued that progress could be accelerated due to recent breakthroughs in the role equity plays in creating a virtuous circle where rising equity ensures the poor participate in their country's development and creates reductions in poverty and financial stability.[64] Yet equity should not be understood purely as economic, but also as political. Examples abound, including Brazil's cash transfers, Uganda's eliminations of user fees and the subsequent huge increase in visits from the very poorest or else Mauritius's dual-track approach to liberalization (inclusive growth and inclusive development) aiding it on its road into the World Trade Organization.[64] Researchers at the ODI thus propose equity be measured in league tables in order to provide a clearer insight into how MDGs can be achieved more quickly; the ODI is working with partners to put forward league tables at the 2010 MDG review meeting.[64]
The effects of increasing drug use were noted by the International Journal of Drug Policy as a deterrent to the goal of the MDGs.[65]
Example activities and organizations
[edit]- The United Nations Millennium Campaign was launched to increase support for the Millennium Development Goals.[59][66] The Millennium Campaign targets intergovernmental, government, civil society organizations and media at global and regional levels.
- The Millennium Promise Alliance, Inc. (or simply the "Millennium Promise") is a U.S.-based non-profit organization founded in 2005 by Jeffrey Sachs and Ray Chambers.[67] Millennium Promise coordinated the Millennium Villages Project in partnership with Columbia's Earth Institute and UNDP; it aimed to demonstrate MDG feasibility through an integrated, community-led approach. The project ran from 2005 to 2015, operating in 15 sites across 11 countries in sub-Saharan Africa.[68]
- The Youth in Action EU Programme "Cartoons in Action" project[69] created animated videos about MDGs,[70] and videos about MDG targets using Arcade C64 videogames.[70][71]
Next set of goals (SDGs)
[edit]Although there have been major advancements and improvements achieving some of the MDGs even before the deadline of 2015, the progress has been uneven between the countries. In 2012 the UN Secretary-General established the "UN System Task Team on the Post-2015 UN Development Agenda", bringing together more than 60 UN agencies and international organizations to focus and work on sustainable development.[72]
At the MDG Summit, UN Member States discussed the Post-2015 Development Agenda and initiated a process of consultations. Civil society organizations also engaged in the post-2015 process, along with academia and other research institutions, including think tanks.[73]
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are the goals and targets relating to future sustainable development for 2030 once the MDGs expired at the end of 2015.
On 31 July 2012, Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon appointed 26 public and private leaders to advise him on the post-MDG agenda.[74]
In 2014, the UN's Commission on the Status of Women agreed on a document that called for the acceleration of progress towards achieving the millennium development goals, and confirmed the need for a stand-alone goal on gender equality and women's empowerment in post-2015 goals, and for gender equality to underpin all of the post-2015 goals.[75]
See also
[edit]- Declaration of Human Duties and Responsibilities
- Seoul Development Consensus
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
- Post-2015 Development Agenda
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Background", United Nations Millennium Development Goals, retrieved 16 June 2009.
- ^ "Copenhagen Declaration on Social Development Annex I" (PDF). United Nations. 14 March 1995. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ a b c Hulme, David; Scott, James (January 2010). The Political Economy of the MDGs : Retrospect and Prospect for the World's Biggest Promise. Manchester: University of Manchester. Brooks World Poverty Institute. pp. 3–5. ISBN 978-1-907247-09-5. OCLC 1099885941.
- ^ "Shaping the 21st century: The contribution of development co-operation" (PDF). OECD. May 1996. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ UN General Assembly (9 January 1998). "Renewing the United Nations: a programme for reform (Resolution 52/12 B of 19 December 1997)" (PDF). World Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ "The Millennium Assembly of the United Nations (Resolution 53/202 of 17 December 1998)". United Nations. 12 February 1999. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ a b Annan, Kofi A. "We the peoples: The role of the United Nations in the 21st century" (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ UN General Assembly (18 September 2000). "United Nations Millennium Declaration (Resolution 52/2 of 8 September 2000)" (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ Secretary-General, Un (6 September 2001). "Road map towards the implementation of the United Nations Millennium Declaration: Report of the Secretary-General". United Nations. Retrieved 27 April 2021.
- ^ "The Millennium Development Goals Report"
- ^ "United Nations Millennium Development Goals". Un.org. 20 May 2008. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "Tracking the Millennium Development Goals". Mdg Monitor. 16 May 2011. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "List of goals, targets, and indicators" (PDF). Siteresources.worldbank.org. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 15 April 2013. Retrieved 8 September 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Goal :: Eradicate Extreme Poverty and Hunger". Mdg Monitor. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "Goal :: Achieve Universal Primary Education". Mdg Monitor. 15 May 2011. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ Waage, Jeff; et al. (18 September 2010). "The Millennium Development Goals: a cross-sectoral analysis and principles for goal setting after 2015". The Lancet. 376 (9745): 991–1023. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(10)61196-8. PMC 7159303. PMID 20833426.(registration required)
- ^ "Goal :: Promote Gender Equality and Empower Women". Mdg Monitor. 30 April 2011. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "Goal :: Reduce Child Mortality". Mdg Monitor. 16 May 2011. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ [1] Archived 2 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The Feasibility of Financing Sectoral Development Targets" (PDF). Archived from the original on 5 October 2012. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ "Goal :: Improve Maternal Health". Mdg Monitor. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "Goal :: Combat HIV/AIDS, Malaria and Other Diseases". MDG Monitor. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ Subramanian, Savitha; Joseph Naimoli; Toru Matsubayashi; David Peters (2011). "Do We Have the Right Models for Scaling Up Health Services to Achieve the Millennium Development Goals?". BMC Health Services Research. 11 (336): 336. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-11-336. PMC 3260120. PMID 22168915.
- ^ "Goal :: Ensure Environmental Sustainability". Mdg Monitor. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "Goal :: Develop a Global Partnership for Development". Mdg Monitor. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2003" (PDF). The Millennium Project. United Nations Development Programme. Archived from the original on 27 March 2015. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ a b "Poverty: Growth or safety net?". The Economist. 21 September 2013. Retrieved 4 October 2013.
- ^ "Gender and the MDGs". ODI Briefing Paper. Overseas Development Institute. Retrieved 7 July 2011.
- ^ "MDGs and the humanitarian-development divide". ODI Briefing Paper. Overseas Development Institute. Retrieved 7 July 2011.
- ^ "Economic Growth and the MDGs". ODI Briefing Paper. Overseas Development Institute. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 7 July 2011.
- ^ "Brazil: Quick Facts". MDG Monitor. Archived from the original on 3 June 2013. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ "Benin: Quick Facts". MDG Monitor. Archived from the original on 16 December 2012. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ "Halving Global Poverty" (PDF). Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ Chen, Shaohua; Ravallion, Martin (29 February 2012). "An Update to the World Bank's Estimates of Consumption Poverty in the Developing World" (PDF). Development Research Group, World Bank. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 September 2012. Retrieved 14 August 2012.
- ^ a b c d Hickmann, Thomas; Biermann, Frank; Spinazzola, Matteo; Ballard, Charlotte; Bogers, Maya; Forestier, Oana; Kalfagianni, Agni; Kim, Rakhyun E.; Montesano, Francesco S.; Peek, Tom; Sénit, Carole‐Anne; van Driel, Melanie; Vijge, Marjanneke J.; Yunita, Abbie (2023). "Success factors of global goal‐setting for sustainable development: Learning from the Millennium Development Goals". Sustainable Development. 31 (3): 1214–1225. doi:10.1002/sd.2461. ISSN 0968-0802.
- ^ a b c E. Carrasco, C. McClellan, & J. Ro (2007) "Foreign Debt: Forgiveness and Repudiation" University of Iowa Center for International Finance and Development E-Book Archived 31 July 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Goal :: Tracking the Millennium Development Goals". Mdg Monitor. 1 November 2007. Archived from the original on 30 January 2012. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ "Goal: Tracking the Millennium Development Goals". MDG Monitor. 1 November 2007. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ Kidder, Tracy (2003). Mountains Beyond Mountains. New York: Random House. p. 257. ISBN 9780375506161.
- ^ "Jeffrey Sachs and the millennium villages: Millennium bugs". The Economist. 14 May 2012. Retrieved 10 September 2015.
- ^ "Does It Take a Village?". 24 June 2013.
- ^ a b c Kabeer, Naila. 2003. Gender Mainstreaming in Poverty Eradication and the Millennium Development Goals: A Handbook for Policy-Makers and Other Stakeholders. Commonwealth Secretariat.
- ^ a b Grown, Caren (2005). "Answering the Skeptics: Achieving Gender Equality and the Millennium Development Goals". Development. 48 (3): 82–86. doi:10.1057/palgrave.development.1100170. S2CID 83769004.
- ^ Noeleen Heyzer. 2005. "Making the Links: Women's Rights and Empowerment Are Key to Achieving the Millennium Development Goals". Gender and Development, Vol. 13, No. 1, Millennium Development Goals (March 2005), pp. 9–12
- ^ a b "MDG 3: Promote gender equality and empower women". 15 November 2016. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
Gender disparity has reduced dramatically at all levels of education in the developing regions since 2000, hitting the MDG target.
- ^ "Press Archive". UN Millennium Project. Archived from the original on 18 February 2015. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ a b "Publications". UN Millennium Project. 1 January 2007. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f Deneulin, Séverine; Shahani, Lila (2009). An introduction to the human development and capability approach freedom and agency. Sterling, Virginia Ottawa, Ontario: Earthscan International Development Research Centre. ISBN 978-1844078066.
- ^ Andy Haines and Andrew Cassels. 2004. "Can The Millennium Development Goals Be Attained?" BMJ: British Medical Journal, Vol. 329, No. 7462 (14 August 2004), pp. 394–397
- ^ United Nations. 2006. "The Millennium Development Goals Report: 2006." United Nations Development Programme, www.undp.org/publications/MDGReport2006.pdf (accessed 2 January 2008).
- ^ "History". UHC2030. Archived from the original on 1 October 2017. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ^ "External Relations Council, Brussels 24 May 2005" (PDF). Unmillenniumproject.org. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "United Nations Report of the International Conference on Financing for Development" (PDF). Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ [2] Archived 8 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Engardio, Pete (2 September 2005). "Bush Balks at Pact to Fight Poverty" (PDF). BusinessWeek online. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ "Poverty Can Be Halved If Efforts Are Coupled with Better Governance, says TI" (PDF). UN Millennium Project. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ [3] Archived 1 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Hikel, Jason (21 August 2014). "Exposing the great 'poverty reduction' lie". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ a b Can the MDGs provide a pathway to social justice?: The challenge of intersecting inequalities. 2010. Naila Kabeer for Institute of Development Studies.
- ^ FIAN International. "Post 2015 Thematic Consultation". Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 7 October 2013.
- ^ a b Attaran, Amir (October 2005). "An Immeasurable Crisis? A Criticism of the Millennium Development Goals and Why They Cannot Be Measured". PLOS Medicine. 2 (10): 318. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0020318. PMC 1201695. PMID 16156696.
- ^ McArthur, J. W.; Sachs, J. D.; Schmidt-Traub, G. (2005). "Response to Amir Attaran". PLOS Medicine. 2 (11): e379. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0020379. PMC 1297542. PMID 16288557.
- ^ a b c d MDGs Targets for 2005 and 2015 Achieving the Millennium Development Goals, IIED
- ^ Singer, M (2008). "Drugs and Development: The Global Impact of Drug Use and Trafficking on Social and Economic Development". International Journal of Drug Policy. 19 (6): 467–478. doi:10.1016/j.drugpo.2006.12.007. PMID 19038724.
- ^ "Kofi Annan and the Transition to Sustainable Development Goals". IISD. 6 December 2018. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ "Overview". Millennium Promise. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "Millennium villages". Millennium Promise Alliance. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ "Cartoons in action Progetto Gioventù in Azione finanziato dallANG – Agenzia Nazionale per i Giovani Youth in Action EU Programme. Il presente progetto è finanziato con il sostegno della Commissione europea. | Wix.com". Socialab.wix.com. Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ a b R.I.P. giovane e dolce Melissa. "Cartoons inAction". YouTube. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ "MDGs". YouTube. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ "Millennium Development Goals and post-2015 Development Agenda". The United Nations. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ "United Nations Millennium Development Goals". Un.org. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ "UN Secretary-General Appoints High-Level Panel on Post-2015 Development Agenda" (PDF). Un.org. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ Ford, Liz (23 March 2014). "Campaigners Welcome 'Milestone' Agreement at UN Gender Equality Talks." The Guardian. Retrieved from TheGuardian.com, 8 February 2019.
