2010 Maryland gubernatorial election
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 54.02% | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
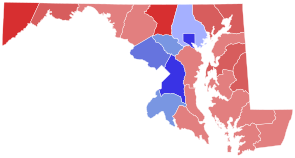 County results O'Malley: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 80–90% Ehrlich: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Maryland |
|---|
 |
|
|
The 2010 Maryland gubernatorial election was held on November 2, 2010.[2] The date included the election of the governor, lieutenant governor, and all members of the Maryland General Assembly. Incumbent Democratic governor Martin O'Malley and lieutenant governor Anthony Brown won re-election to a second term in office, defeating Republican former governor Bob Ehrlich and his running mate Mary Kane.
Ehrlich had previously lost re-election to O'Malley in 2006. O'Malley and Brown became the first gubernatorial ticket in Maryland history to receive more than one million votes.[3][4]
While Ehrlich won a clear majority of Maryland's counties, he lost in the area between Baltimore and Washington, which accounts for more than 90% of the state's population. This allowed O’Malley to win by a relatively large margin of 14.4%.
Background
[edit]In his first term as governor of Maryland, Martin O'Malley had made accomplishments, including raising total state tax collections by 14%. In April 2009 he signed the traffic speed camera enforcement law. He had supported raising revenue to try to overcome an imminent state deficit. Through his strenuous lobbying, he also implemented on a statewide level, Maryland StateStat One, the same CitiStat system he used to manage the city of Baltimore as mayor. One off his first actions as governor was to close the Maryland House of Corrections in Jessup, a notoriously violent maximum-security prison. By 2010 O'Malley's approval ratings had reached 55%, making his chances of reelection very good.
Democratic primary
[edit]In the Democratic primary O'Malley faced J. P. Cusick and Ralph Jaffe, placing him in an unusual position, as he had run unopposed in the 2006 Democratic primary. He benefited from being the incumbent, and he handily defeated them in the primary. O'Malley received 86.3% of the vote. Cusick came in second with 9.7%, and Jaffe finished in last place with 5% of the vote. O'Malley again chose incumbent Democratic Lieutenant Governor Anthony Brown as his running mate.
Candidates
[edit]- J. P. Cusick
- Running mate: Michael Lange
- Ralph Jaffe, teacher and perennial candidate[5]
- Running mate: Freda Jaffe
- Martin O'Malley, incumbent governor
- Running mate: Anthony Brown, incumbent lieutenant governor
Results
[edit]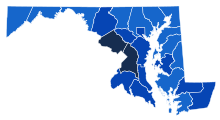
- O'Malley—≥90%
- O'Malley—80–90%
- O'Malley—70–80%
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Martin O'Malley (incumbent) | 414,595 | 86.28 | |
| Democratic | J. P. Cusick | 46,411 | 9.66 | |
| Democratic | Ralph Jaffe | 19,517 | 4.06 | |
| Total votes | 480,523 | 100 | ||
Republican primary
[edit]The frontrunner for the Republican primary was former Republican Governor (and O'Malley's predecessor) Bob Ehrlich. He faced Brian Murphy in the primary. Like O'Malley, Erlich had also run unopposed in the 2006 Republican primary. Ehrlich easily defeated Murphy in the Republican primary by a margin of 75.8%-24.2%. He chose his former Secretary of State Mary Kane as his running mate.
Candidates
[edit]- Bob Ehrlich, former governor[7]
- Running mate: Mary Kane, former Maryland Secretary of State
- Brian Murphy, businessman[8]
- Running mate: Mike Ryman, former federal and congressional inspector and candidate for the State Senate in 2006[9]
- Former running mate: Carmen Amedori, former State Delegate[9]
Results
[edit]
- Ehrlich—80–90%
- Ehrlich—70–80%
- Ehrlich—60–70%
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Bob Ehrlich | 211,428 | 75.84 | |
| Republican | Brian Murphy | 67,364 | 24.16 | |
| Total votes | 278,792 | 100 | ||
Minor party candidates
[edit]Constitution Party
[edit]- Eric Delano Knowles
- Running mate: Michael Hargadon
Green Party
[edit]- Maria Allwine
- Running mate: Ken Eidel
Libertarian Party
[edit]- Susan Gaztanaga
- Running mate: Doug McNeil
Endorsements
[edit]Ehrlich was endorsed by high-profile people. These include Terrapin basketball standout and Memphis Grizzlies NBA draft pick Greivis Vásquez and his former lieutenant governor who was then the chairman of the Republican National Committee, Michael Steele. He was also supported by former Massachusetts governor Mitt Romney and former New York city mayor Rudy Giuliani. The support of these individuals elevated support to his campaign.
General election
[edit]Predictions
[edit]| Source | Ranking | As of |
|---|---|---|
| Cook Political Report[10] | Tossup | October 14, 2010 |
| Rothenberg[11] | Likely D | October 28, 2010 |
| RealClearPolitics[12] | Likely D | November 1, 2010 |
| Sabato's Crystal Ball[13] | Likely D | October 28, 2010 |
| CQ Politics[14] | Lean D | October 28, 2010 |
Polling
[edit]Polling for the election overwhelmingly showed O'Malley would be reelected. The first poll taken in September 2009 showed him with an 11-point lead over Ehrlich. Throughout the election, only a few polls showed Ehrlich with a lead. By the last few months of the campaign, O'Malley held a strong double-digit lead over Ehrlich. The last poll taken showed him with a 10-point lead over Ehrlich: 52%-42%.
| Poll source | Dates administered | Bob Ehrlich (R) |
Martin O'Malley (D) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rasmussen Reports[15] | October 24, 2010 | 42% | 52% |
| Rasmussen Reports[16] | October 5, 2010 | 41% | 49% |
| Washington Post[17] | September 22–26, 2010 | 41% | 52% |
| Rasmussen Reports[16] | September 15, 2010 | 47% | 50% |
| Center Maryland/Opinion Works[18] | August 13–18, 2010 | 41% | 47% |
| Rasmussen Reports[19] | August 17, 2010 | 44% | 45% |
| Gonzales poll[20] | July 13–21, 2010 | 42% | 45% |
| Public Policy Polling[21] | July 10–12, 2010 | 42% | 45% |
| Rasmussen Reports[22] | July 12, 2010 | 47% | 46% |
| Magellan Strategies[23] | June 29, 2010 | 46% | 43% |
| The Polling Company[24] | June 8–10, 2010 | 43% | 44% |
| Rasmussen Reports[22] | June 8, 2010 | 45% | 45% |
| Washington Post[25] | May 3–6, 2010 | 41% | 49% |
| Rasmussen Reports[26] | April 20, 2010 | 44% | 47% |
| Rasmussen Reports[27] | February 23, 2010 | 43% | 49% |
| Gonzales poll[28] | September 17, 2009 | 38% | 49% |
Results
[edit]On election night, Ehrlich won a majority of Maryland counties, but O'Malley's strong showing in the highly populated counties allowed him to win in a landslide over Ehrlich. He significantly increased his margin from 2006. In a year when Republicans made significant gains over Democrats, O'Malley received 56.2% of the vote while Ehrlich received 41.8%. The only county to flip from one party to another was Baltimore County, which Ehrlich had carried in 2006, but O'Malley carried by a narrow margin in 2010. O'Malley was certified as the winner, and was sworn in for his second term in January 2011.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Martin O'Malley (incumbent) | 1,044,961 | 56.24% | +3.54% | |
| Republican | Bob Ehrlich | 776,319 | 41.79% | −4.41% | |
| Libertarian | Susan Gaztanaga | 14,137 | 0.76% | ||
| Green | Maria Allwine | 11,825 | 0.64% | −0.26% | |
| Constitution | Eric Knowles | 8,612 | 0.46% | ||
| Write-ins | 2,026 | 0.11% | |||
| Majority | 268,642 | 14.45% | +7.92% | ||
| Turnout | 1,857,880 | ||||
| Democratic hold | Swing | ||||
Counties that flipped from Republican to Democratic
- Baltimore County (largest municipality: Dundalk)
Ehrlich campaign robocall controversy
[edit]In the summer before the election, Ehrlich's campaign hired a consultant who advised that "the first and most desired outcome is voter suppression", in the form of having "African-American voters stay home."[30] To that end, the Republicans placed thousands of Election Day robocalls to Democratic voters, telling them that O'Malley had won, although in fact the polls were still open for some two more hours.[31] The Republicans' call, worded to seem as if it came from Democrats, told the voters, "Relax. Everything's fine. The only thing left is to watch it on TV tonight."[30] The calls reached 112,000 voters in majority-African American areas.[31] In 2011, Ehrlich's campaign manager, Paul Schurick, was convicted of fraud and other charges because of the calls.[30] Ehrlich denied knowing about the calls.[30]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "2010 Gubernatorial Primary Election - Voter Turnout". elections.maryland.gov. Maryland State Board of Elections. Retrieved May 1, 2022.
- ^ "Maryland Elections, forthcoming". Msa.md.gov. November 6, 1956. Retrieved August 21, 2010.
- ^ "State Gubernatorial Term Limits". Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved September 9, 2007.
- ^ "Maryland State Board of Elections". www.elections.state.md.us. Archived from the original on June 14, 2012.
- ^ "2010 Gubernatorial Primary Election" (PDF). Maryland State Board of Elections.
- ^ a b "Maryland Gubernatorial Primary Results". Maryland State Board of Elections. September 19, 2010. Retrieved September 19, 2010.
- ^ "Ehrlich Announces Run For Maryland Governor". wjz.com. March 31, 2010. Archived from the original on April 4, 2010. Retrieved August 21, 2010.
- ^ "Brian Murphy for Governor of Maryland. Leading a Return to Principled Governance". Brianmurphy2010.com. Archived from the original on August 14, 2010. Retrieved August 21, 2010.
- ^ a b Wagner, John (July 6, 2010). "Maryland Politics – GOP hopeful Murphy offers second running mate". Voices.washingtonpost.com. Archived from the original on October 3, 2012. Retrieved August 21, 2010.
- ^ "2010 Governors Race Ratings". Cook Political Report. Archived from the original on October 28, 2010. Retrieved October 28, 2010.
- ^ "Governor Ratings". Rothenberg Political Report. Retrieved October 28, 2010.
- ^ "2010 Governor Races". RealClearPolitics. Retrieved October 28, 2010.
- ^ "THE CRYSTAL BALL'S FINAL CALLS". Sabato's Crystal Ball. Retrieved October 28, 2010.
- ^ "Race Ratings Chart: Governor". CQ Politics. Archived from the original on October 5, 2010. Retrieved October 28, 2010.
- ^ Rasmussen Reports
- ^ a b Rasmussen Reports
- ^ Washington Post
- ^ Center Maryland/Opinion Works Archived 2010-09-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Rasmussen Reports
- ^ Gonzales poll
- ^ Public Policy Polling
- ^ a b Rasmussen Reports
- ^ Magellan Strategies
- ^ The Polling Company
- ^ Washington Post
- ^ Rasmussen Reports
- ^ Rasmussen Reports
- ^ Gonzales poll
- ^ "2010 General Election Official Results".
- ^ a b c d Broadwater, Luke (December 6, 2011), "Schurick guilty of election fraud in robocall case", The Baltimore Sun, archived from the original on January 11, 2014, retrieved December 7, 2011
- ^ a b Wagner, John (December 6, 2011), "Ex-Ehrlich campaign manager Schurick convicted in robocall case", The Washington Post, retrieved December 8, 2011
External links
[edit]- Maryland State Board of Elections
- Maryland Governor Candidates at Project Vote Smart
- Campaign contributions for 2010 Maryland Governor from Follow the Money
- Maryland Governor 2010 from OurCampaigns.com
- 2010 Maryland Governor General Election: Bob Ehrlich (R) vs Martin O'Malley (D) graph of multiple polls from Pollster.com
- Election 2010: Maryland Governor from Rasmussen Reports
- 2010 Maryland Governor – Ehrlich vs. O'Malley from Real Clear Politics
- 2010 Maryland Governor's Race[permanent dead link] from CQ Politics
- Race Profile in The New York Times
- Candidate blogs Archived 2011-06-29 at the Wayback Machine at The Baltimore Sun
Official campaign websites (Archived)


