Mangala Fossa
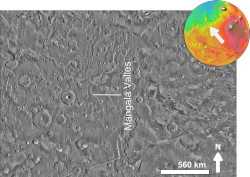 Mangala Fossa and Mangala Valles (THEMIS image) | |
| Coordinates | 11°36′S 151°00′W / 11.6°S 151.0°W |
|---|---|
| Length | 828.0 km |
Mangala Fossa is a graben in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars, located near 11°36′S 151°00′W / 11.6°S 151.0°W, which originated in the Hesperian and Amazonian epochs. The graben is located at the head of the outflow channel Mangala Valles, which is thought to have been formed by at least two catastrophic flood events during the same geological period, leading to the release of vast quantities of water from Mangala Fossa onto the Martian surface. The flooding was probably initiated by the emplacement of a dike radiating from the volcano Arsia Mons, resulting in the formation of the graben, Mangala Fossa, at the channels' head. This dike breached a pressurized aquifer trapped beneath a thick "cryosphere" (layer of frozen ground) beneath the surface. As the floor of the graben subsided, water found its way up one or both of the faults in the crust that defined the edges of the graben and spilled into the depression, eventually filling it and overflowing at the lowest point on the rim to erode the Mangala Valles channels.[1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
"Mangala" is the name for Mars in Jyotish (or Hindu) astrology.
Gallery
[edit]-
Mangala Fossa and Mangala Valles
(THEMIS) -
Graben in Memnonia Fossae – possible result of magmatic dikes, rather than regional tectonic stretching as seen by HiRISE
-
Mangala Valles - head region
(THEMIS)
See also
[edit]Further reading
[edit]- Leask, H. J., L. Wilson, and K. L. Mitchell (2006), Formation of Ravi Vallis outflow channel, Mars: Morphological development, water discharge, and duration estimates, J. Geophys. Res., 111, E08070, doi:10.1029/2005JE002550.
- Wilson, L.; Head, J.W.; Leask, H.J.; Ghatan, G.; Mitchell, K.L. (2004), Factors Controlling Water Volumes and Release Rates in Martian Outflow Channels, Lunar and Planetary Science XXXV (2004).
References
[edit]- ^ "Mars Channels and Valleys". Msss.com. Retrieved 13 January 2015.
- ^ Michael H. Carr (2006). The surface of Mars. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-87201-0. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ^ Carr, M. 1979. Formation of martian flood features by release of water from confined aquifers. Journal of Geophysical Research 84: 2995-3007.
- ^ Hanna, J. and R. Phillips. 2005. Tectonic pressurization of aquifers in the formation of Mangala and Athabasca Valles on Mars. LPSC XXXVI. Abstract 2261.
- ^ Ghatan, Gil J.; Head, James W.; Wilson, L.; Leask, H.J. (2004). "Mangala Valles, Mars: Investigations of the Source of Flood Water and Early Stages of Flooding - Lunar and Planetary Science XXXV (2004)" (PDF). Lunar and Planetary Institute. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
- ^ Leask, Harald J.; Wilson, Lionel; Mitchell, Karl L. (24 February 2007). "Formation of Mangala Fossa, the source of the Mangala Valles, Mars: Morphological development as a result of volcano-cryosphere interactions" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research. 112 (E02011): E02011. Bibcode:2007JGRE..112.2011L. doi:10.1029/2005JE002644.
- ^ Leask, Harald J.; Wilson, Lionel; Mitchell, Karl L. (4 August 2007). "Formation of Mangala Valles outflow channel, Mars: Morphological development and water discharge and duration estimates" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research. 112 (E08003): E08003. Bibcode:2007JGRE..112.8003L. doi:10.1029/2006JE002851.