Keratic precipitate
Appearance
| Keratic precipitate | |
|---|---|
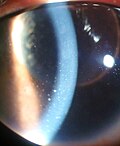 | |
| Keratic precipitate due to Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease |
Keratic precipitate (KP) is an inflammatory cellular deposit seen on corneal endothelium. Acute KPs are white and round in shape whereas old KPs are faded and irregular in shape. Mutton-fat KPs are large in shape and are greasy-white in color and are formed from macrophages and epithelioid cells. They are indicative of inflammatory disease.[1] Mutton fat KPs are due to granulomatous iridocyclitis.[2] Another variant called red KPs may be seen in hemorrhagic uveitis.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ Brightbill, Frederick S. (2009). Corneal Surgery: Theory, Technique and Tissue. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 102. ISBN 978-0323048354. Retrieved 11 November 2017.
- ^ Tandon, Radhika (2014). Parson's Diseases of the Eye - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 616. ISBN 9788131238196. Retrieved 11 November 2017.
