History of the Aztecs: Difference between revisions
typo |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==The Aztecs arrive in the Valley of Mexico== |
==The Aztecs arrive in the Valley of Mexico== |
||
In the 13th century in the [[Valley of Mexico]], there existed many city-states including [[Chalco]], [[Xochimilco]], [[Tlacopan]], [[Culhuacan]], and [[Atzcapotzalco]]. The most powerful were Culhuacan on the south shore of [[Lake Texcoco]] and Azcapotzalco on the west shore. |
In the 13th century in the [[Valley of Mexico]], there existed many city-states including [[Chalco]], [[Xochimilco]], [[Tlacopan]], [[Culhuacan]], and [[Atzcapotzalco]]. The most powerful were Culhuacan on the south shore of [[Lake Texcoco]] and Azcapotzalco on the west shore. hi |
||
As a result, when the Mexica arrived in the Valley of Mexico as a semi-nomadic tribe, they had nowhere to go. In roughly 1248,<ref> Smith (1984) p. 173. In arriving at 1248, Smith averages together dates from [[Fernando de Alva Cortés Ixtlilxochitl]] (1246), the [[Annals of Tlatelolco]] (1257), the [[Annals of Cuauhtitlan]] (1246), [[Fernando Alvarado Tezozomoc]] (1247), and [[Diego Duran]] (1245). </ref> they first settled on Chapultepec, a hill on the west shore of [[Lake Texcoco]], the site of numerous springs. |
As a result, when the Mexica arrived in the Valley of Mexico as a semi-nomadic tribe, they had nowhere to go. In roughly 1248,<ref> Smith (1984) p. 173. In arriving at 1248, Smith averages together dates from [[Fernando de Alva Cortés Ixtlilxochitl]] (1246), the [[Annals of Tlatelolco]] (1257), the [[Annals of Cuauhtitlan]] (1246), [[Fernando Alvarado Tezozomoc]] (1247), and [[Diego Duran]] (1245). </ref> they first settled on Chapultepec, a hill on the west shore of [[Lake Texcoco]], the site of numerous springs. |
||
Revision as of 16:35, 6 May 2009
The Aztecs were a Pre-Columbian Mesoamerican people of central Mexico in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. They called themselves Mexica ([pronunciation?]). The Republic of Mexico and its capital, Mexico City, derive their names from the word "Mexica".
The capital of the Aztec empire was Tenochtitlan, built on raised island in Lake Texcoco. Mexico City is built on the ruins of Tenochtitlan. The Spanish colonization of the Americas reached the mainland during the reign of Huey Tlatoani , Moctezuma II (Montezuma II). In 1521 Hernan Cortés and an allied army of American Indians that far outnumbered the defending Aztecs, conquered the Aztecs through germ warfare, siege warfare, psychological warfare, and direct combat. [1]
Origins of the Aztecs
The Aztecs' legendary home was Aztlan, a Nahuatl word likely meaning "place of the heron". It is generally thought that Aztlan was somewhere to the north of the Valley of Mexico; some experts have placed it as far north as Northwestern Mexico and the US Southwest, while others suggest is a mythical place, since Aztlan can also be translated as "the place of the origin".
Whatever caused them to leave Aztlan, the Mexica, as the Aztecs called themselves, came to the Valley of Mexico in the mid-13th century. The mythical story of these travels is recorded in a number of Aztec codices.

The Aztecs arrive in the Valley of Mexico
In the 13th century in the Valley of Mexico, there existed many city-states including Chalco, Xochimilco, Tlacopan, Culhuacan, and Atzcapotzalco. The most powerful were Culhuacan on the south shore of Lake Texcoco and Azcapotzalco on the west shore. hi
As a result, when the Mexica arrived in the Valley of Mexico as a semi-nomadic tribe, they had nowhere to go. In roughly 1248,[2] they first settled on Chapultepec, a hill on the west shore of Lake Texcoco, the site of numerous springs.
In time, the Tepanecs of Azcapotzalco ousted the Mexica from Chapultepec and the ruler of Culhuacan, Cocoxtli, gave the Mexica permission to settle in the empty barrens of Tizaapan in 1299. There they married and assimilated into Culhuacan culture.
In 1323, they asked the new ruler of Culhuacan, Achicometl, for his daughter, in order to make her the goddess Yaocihuatl. Unbeknownst to the king, the Mexica actually planned to sacrifice her. The Mexica believed that by doing this the princess would join the gods as a deity. As the story goes, during a festival dinner, a priest came out wearing her flayed skin as part of the ritual. Upon seeing this, the king and the people of Culhuacan were horrified and expelled the Mexica.
Forced to flee, in 1325 they went to a small island on the west side of Lake Texcoco, where they began to build their city Tenochtitlan, eventually creating a large artificial island. It is said that the Aztec god, Huitzlipochtli, instructed the Aztecs to found their city at the location where they saw an eagle, on a cactus, with a snake in its talons. The Aztecs, apparently, saw this vision on the small island where Tenochtitlan was founded.
Another Mexica group settled on the north side of this island: this would become the city of Tlatelolco. Originally, this was an independent Mexica kingdom, but eventually it was absorbed by Tenochtitlan, and treated as a "fifth" quadrant. The famous marketplace described by Hernan Cortés and Bernal Diaz del Castillo was actually located in Tlatelolco.
In 1376, the Mexica elected their first tlatoani, Acamapichtli, following customs learned from the Culhuacan.
Rise of the Aztecs
Initially, the Mexica hired themselves out as mercenaries in wars between the different Nahua states.
From 1376 until 1427, the Mexica were a tributary of Azcapotzalco. The Aztec rulers Acamapichtli, Huitzilihuitl and Chimalpopoca were, in fact, vassals of Tezozomoc, the Tepanec ruler of Azcapotzalco.
When Tezozomoc died in 1426, his son Maxtla ascended to the throne of Azcapotzalco. Shortly thereafter, Maxtla assassinated Chimalpopoca, the Aztec ruler. In an effort to defeat Maxtla, Chimalpopoca's successor, Itzcoatl, allied with Nezahualcoyotl, the exiled ruler of Texcoco. This coalition became the foundation of the Aztec Triple Alliance.
Itzcoatl and Nezahualcoyotl and their allies subsequently besieged Azcapotzalco, took Maxtla captive, and sacrificed him.
Aztec Triple Alliance
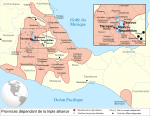
The Triple Alliance of Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan would, in the next 100 years, come to dominate the Valley of Mexico and extend its power to both the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific shores. From the beginning of the Triple Alliance, Tenochtitlan was mostly in charge of the military and conquest, whereas the other two cities had other responsibilities. This military dominance of Tenochtitlan gradually led to this city becoming the dominant power in the alliance.
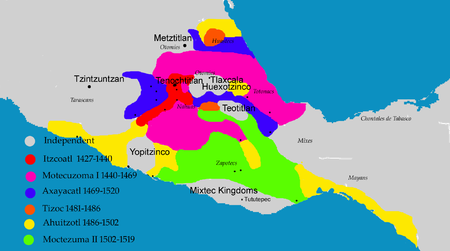
The reign of Itzcoatl 1427-1440
The first Tlatoani of the Triple Alliance was Itzcoatl and he, along with his Texcocan co-ruler Nezahualcoyotl, began expanding the territory dominated by the alliance towards the south conquering Nahua speaking cities like Cuauhnahuac (now Cuernavaca) and towards Huexotla, Coatlinchan, and Tepoztlan in the modern-day state of Morelos which was then dominated by the Tlahuica. During this period the Nahuan cities immediately on the lakeside such as Xochimilco, Culhuacan and Mixquic were also subdued.
Moctezuma I and Tlacaelel 1440-1469
Two of the primary architects of the Aztec empire were the half-brothers Tlacaelel and Moctezuma I. They were sons of Huitzilíhuitl, the 3rd Hueyi Tlatoani, half-brothers to Chimalpopoca, the 4th Hueyi Tlatoani, and nephews of Itzcoatl, the 5th. Moctezuma I succeeded Itzcoatl as the 6th Hueyi Tlatoani in 1449. Tlacaelel became the power behind the throne and reformed both the Aztec state and the Aztec religion.
Moctezuma I began the expansion in earnest. First he had to reconquer towns first conquered by Itzcoatl but which had rebelled. He asked a number of smaller cities to contribute to the construction of a new Great Temple, and only Chalco refused, which caused Moctezuma to start a war against them which lasted for several years. He then conquered Huastec territory under a pretext of securing Aztec merchants in that area, and then he went to war against the Mixtecs of Coixtlahuaca. Coixtlahuaca was successfully conquered although the Mixtec ruler Atonal received military assistance from the Nahua states of Tlaxcala and Huexotzinco, by now enemies of the Aztecs. After the defeat of Coixtlahuaca many Mixtec artisans were relocated to the Aztec capital [4]. Later Moctezuma marched upon the Totonacan cities of Vera Cruz and conquered Xalapa, Cosamaloapan, Cotaxtla (modern day Cuetlachtlan), Ahuilizapan (Modern day Orizaba) and north into Huastec territory conquering Tuxpan and Xilotepec.
Tlacaelel
Tlacaelel was one of the primary architects of the Aztec empire. Rising to prominence during the war against the Tepanec in the late 1420s, Tlacaelel wielded power as something of a Grand Vizier during the reigns of four Hueyi Tlatoani, until his death in 1487.
Tlacaelel recast or strengthened the concept of the Aztecs as a chosen people and elevated the tribal god/hero Huitzilopochtli to the top of the pantheon of gods. In tandem with this, Tlacaelel increased the level and prevalence of human sacrifice, particularly during a period of natural disasters that started in 1446 (according to Durán). During the reign of Moctezuma I, he instigated the flower wars in which the Aztecs fought Tlaxcala and other Nahuan city-states.
To strengthen the Aztec nobility, he helped create and enforce sumptuary laws, prohibiting commoners from wearing certain adornments such as lip plugs, gold armbands, and cotton cloaks.
At the start of Tlacaelel's tenure, the Mexica were vassals. By the end, they had become the Aztecs, rulers of a socially stratified and expansionistic empire.
The reigns of Axayacatl 1469-1481 and Tizoc 1481-1486
Moctezuma I's son, Axayacatl, ascended to the throne in 1469. During his reign, Tenochtitlan absorbed the kingdom of Tlatelolco. Axayacatl's sister was married to the tlatoani of Tlatelolco, and, as a pretext for war, Axayacatl declared that she was mistreated.
He went on to conquer the Matlatzinca and Mazahua cities of Tollocan, Ocuillan, and Malinalco west of the Valley of Mexico.
At this point Tenochtitlan experienced a brief "Civil war" when the small city of Tlatelolco, considered a part of Tenochtitlan by the Aztecs, rebelled under their Tlatoani Moquihuix, who sought to ally himself with the longstanding enemies of the Tenochca, the Chalca, Tlaxcalteca, Chololteca and Huexotzinca. The Tlatelolca were defeated and Axayacatl then ordered the execution of all the rulers who had aided him, including the ruler of Xochimilco.
Continuing campaigns in the west in 1479, he suffered an unprecedented defeat by the Tarascans at Tzintzuntzan. This was the Aztec's first great defeat; once recovered he had to consolidate control of the Huasteca region which had already been conquered by his predecessor.
In 1481 Axayacatl's son Tizoc ruled briefly, but his rule was marred by the humiliation he received in his coronation war: fighting the Otomies at Metztitlan he brought home only 40 prisoners for sacrifice at his coronation ceremony [5]. After this defeat Tizoc had to fight principally to maintain control of the already conquered territories, and failing to subdue new towns he was replaced, possibly poisoned, by his younger brother Ahuitzotl.
Ahuitzotl's reign 1486-1502
The expansionist policies of the empire culminated during Ahuitzotl's reign. In his coronation war, he fought the Chontales in the territories west of Mexico defeating Toluca, Malinalco and Xilotepec. He invited the rulers of the still independent states of the Tarascans, Tlaxcaltecs and Huexotzinca to the dedication ceremony of the enlarged Great Temple, all of whom witnessed an unprecedented increase of human sacrifices and gift-givings. He then conducted punitive expeditions to rebellious cities on the Gulf Coast. He also conquered vast territories in the isthmus of Tehuantepec, and as far south as Xoconosco in present day Chiapas. He constructed a series of fortifications and garrisons on the frontiers of the independent kingdoms of the Tlaxcaltecs and Tarascans. Some archaeological remains exist of these fortifications, for example at Oztuma in Guerrero, Quauhquechula in Puebla and the best preserved Aztec site, the one at Malinalco in the state of Mexico.
The reign of Motecuhzoma II Xocoyotzin
Moctezuma II was, although many sources depict him otherwise, a notable warrior who extended the tributary system, and consolidated the conquests made by his predecessors as well as conquering new territories. His campaigns reached as far south as Tapachula in the Soconusco region and the Chontal Maya states of Xicallanco in Tabasco. Only the Aztec archenemies of Tlaxcala, Huexotzinco and the Tarascans remained undefeated, as well as the Mixtec kingdoms of Tututepec and Yopitzinco which didn't interest the Aztecs. Thus the Aztec empire had its largest geographical extent when the Spaniards arrived in 1519. In some sources, it claims that Moctezuma II, and the Aztecs, believed the arriving Spanish to linked to the supposed return of an exiled god, Quetzlcoatl, who was supposed to return pale and bearded.
Fall of the Aztec Empire
- For more on the conquest of Mexico by Spain, see also Spanish Conquest of Mexico, Siege of Tenochtitlan, and Hernán Cortés.
The Aztecs were conquered by Spain in 1521 after a long siege of the capital, Tenochtitlan, where much of the population died from hunger and smallpox. Cortés, with up to 500 Spaniards, did not fight alone but with as many as 150,000 or 200,000 allies from Tlaxcala, and eventually other Aztec tributary states. It was not difficult for Cortes to find allies to fight with him, the Aztecs were not generally liked by the neighbouring city-states. Cuauhtémoc, the last Hueyi Tlatoani surrendered to Cortés on August 13, 1521.
It took nearly another 60 years of war before the Spaniards completed the conquest of Mesoamerica (the Chichimeca wars), a process that could have taken longer were it not for three separate epidemics that took a heavy toll on the Native American population. The Spanish conquest of Yucatán took almost 170 years.
After the fall of Tenochtitlan, most of the other Mesoamerican cultures remained intact. In fact, the conquest of the Aztec empire did not have an immediate impact on other Mesoamerican cultures. If anything, the freedom from Aztec domination was probably considered a positive development by most of the other cultures.
As allies of the Spaniards, the Tlaxcalans gained the most. The Spaniards would eventually break the alliance, but not until decades later.
The fate of the Aztec empire under Spanish rule
Cortés stated intention was to maintain the structure of the Aztec empire. Initially, it seemed that the Aztec empire could survive under Spanish rule. The upper classes of the Aztec empire were initially considered as noblemen (to this day, the title of Duke of Moctezuma is held by a Spanish noble family). The upper classes learned Spanish, and several learned to write in Roman characters. Some of their surviving writings are crucial to our knowledge of the Aztecs. In addition, the first missionaries tried to learn Nahuatl and some, like Bernardino de Sahagún, set out to learn as much as they could of the Aztec culture.
All that changed rapidly. Eventually, the indigenous peoples were not only forbidden to learn of their cultures, but were also forbidden to learn to read and write in Spanish, and, under the law, they were reduced to the status of minors.
The impact of epidemics on the Aztec Empire
The first epidemic, an outbreak of smallpox occurred from 1520-1521 and decimated the population of Tenochtitlan and was decisive in the fall of the city. The other two epidemics, of smallpox (1545-1548) and typhus (1576-1581) killed up to 75% of the population of Mesoamerica. [citation needed]
Whole towns disappeared, lands were deserted, roads were closed and armies were destroyed. The Spaniards, trying to make more of the diminishing population, merged the survivors from small towns into the bigger ones. This broke the power of the upper classes and dissolved the coherence of the indigenous society. In addition, the indigenous peoples collected in the larger towns were more susceptible to epidemics due to the higher population density.
The population before the time of the conquest is estimated at 15 million; by 1550, the estimated population was 4 million and less than two million by 1581. Thus, the "New Spain" of the 17th century was a depopulated country and many Mesoamerican cultures were wiped out.
In order to have an adequate supply of labor, the Spaniards began to import black slaves, although most of them eventually merged with the population.
Notable rulers
- Acamapichtli - 'Handful of Arrows', 1st ruler. First Aztec ruler during the early construction of Tenochtitlán and local conquests
- Itzcoatl - 'Obsidian Serpent', 4th Ruler. Formed a coalition with other lakeside people against the Tepanecs, brought an end to the Tepanec Domination of the basin of Mexico by sacking the city of Azcapotzalco, and founded the empire of the Triple Alliance
- Ahuitzotl - 'Water Beast', 8th ruler. Was a fierce warrior, rebuilt the Great Temple, sacrificed 2,000 victims at temple's opening ceremony, and extended the empire from coast to coast
- Moctezuma II - 'Angry Lord, The Younger', 9th Ruler. Was the emperor of the Aztecs during the time of the three Spanish expeditions, the third of which was led by Hernán Cortés. He was captured by Cortés when the Spaniards, after being welcomed into the city, took him hostage because of the fear of an uprising. Accounts of his death vary: according to some he was killed by his own people later (stoned to death) when Cortés used him to try to quell the uprising, according to others the Spaniards killed him when he had proved to be unable to control the uprising.
Footnotes
- ^ Woods, 2000
- ^ Smith (1984) p. 173. In arriving at 1248, Smith averages together dates from Fernando de Alva Cortés Ixtlilxochitl (1246), the Annals of Tlatelolco (1257), the Annals of Cuauhtitlan (1246), Fernando Alvarado Tezozomoc (1247), and Diego Duran (1245).
- ^ Based onto the maps by Ross Hassig in "Aztec Warfare"
- ^ According to Richard Townsends "The Aztecs" pp88. Thames and Hudson 1992.
- ^ Townsend, Richard 1992. pp 96.
References
- Berdan, Frances F. (2005) The Aztecs of Central Mexico: An Imperial Society. 2nd ed. Thomson-Wadsworth, Belmont, CA.
- Berdan, Frances F., Richard E. Blanton, Elizabeth H. Boone, Mary G. Hodge, Michael E. Smith and Emily Umberger (1996) Aztec Imperial Strategies. Dumbarton Oaks, Washington, DC.
- Boone, Elizabeth H. 1989. "Incarnations of the Aztec Supernatural: The Image of Huitzilopochtli in Mexico and Europe." Transactions of the American Philosophical Society, New Ser., Vol. 79, No. 2., pp. i-iv+1-107.
- Boone, Elizabeth H. (2000) Stories in Red and Black: Pictorial Histories of the Aztecs and Mixtecs. University of Texas Press, Austin.
- Carrasco, Davíd (1999) City of Sacrifice: The Aztec Empire and the Role of Violence in Civilization. Beacon Press, Boston.
- Carrasco, Pedro (1999) The Tenochca Empire of Ancient Mexico: The Triple Alliance of Tenochtitlan, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan. University of Oklahoma Press, Norman.
- Clendinnen, Inga (1991) Aztecs: An Interpretation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
- Davies, Nigel (1973) The Aztecs: A History. University of Oklahoma, Norman.
- Gillespie, Susan D. (1989) The Aztec Kings: The Construction of Rulership in Mexica History'. University of Arizona Press, Tucson.
- Graulich, Michel (1997) Myths of Ancient Mexico. Translated by Bernard R. Ortiz de Montellano and Thelma Ortiz de Montellano. University of Oklahoma Press, Norman.
- Guggenheim Museum (editor) (2004) The Aztec Empire (Curated by Felipe Solís). Guggenheim Museum, New York.
- Hassig, Ross (1988) Aztec Warfare: Imperial Expansion and Political Control. University of Oklahoma Press, Norman.
- León-Portilla, Miguel (Ed.) (1992) [1959]. The Broken Spears: The Aztec Account of the Conquest of Mexico. Ángel María Garibay K. (Nahuatl-Spanish trans.), Lysander Kemp (Spanish-English trans.), Alberto Beltran (illus.) (Expanded and updated edition ed.). Boston: Beacon Press. ISBN 0-807-05501-8.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - León-Portilla, Miguel (1963) Aztec Thought and Culture: A Study of the Ancient Náhuatl Mind. University of Oklahoma Press, Norman.
- López Luján, Leonardo (2005) The Offerings of the Templo Mayor of Tenochtitlan. Revised ed. Translated by Bernard R. Ortiz de Montellano and Thelma Ortiz de Montellano. University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque.
- Matos Moctezuma, Eduardo (1988) The Great Temple of the Aztecs. Thames and Hudson, New York.
- Matos Moctezuma, Eduardo and Felipe R. Solís Olguín (editors) (2002) Aztecs. Royal Academy of Arts, London.
- Ortiz de Montellano, Bernard R. (1990) Aztec Medicine, Health, and Nutrition. Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick.
- Smith, Michael E. (1984); "The Aztlan Migrations of Nahuatl Chronicles: Myth or History?", in Ethnohistory 31(3): 153 - 186.
- Smith, Michael E. (2003) The Aztecs. 2nd ed. Blackwell Publishers, Oxford.
- Smith, Michael E, "Life in the Provinces of the Aztec Empire", Scientific American.
- Soustelle, J., (1961) The Daily life of the Aztecs, London, WI
- Woods, M., (2000) "Conquistadors", Ubuversity of California Press Berkeley and Los Angeles, California.
- Townsend, Richard F. (2000) The Aztecs. revised ed. Thames and Hudson, New York.