Halazone
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
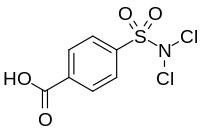
4-(Dichlorosulfamoyl)benzoic acid | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.140 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1479 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H5Cl2NO4S | |
| Molar mass | 270.08 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Fine white powder with an odor of chlorine[2] |
| Melting point | 213 °C (415 °F; 486 K);[3] 196 °C with decomposition.[4] |
| Less than 1 g/L at 70 °F [2] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319 | |
| P264, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Halazone (4-(dichlorosulfamoyl)benzoic acid) is a chemical compound whose formula can be written as either C
7H
5Cl
2NO
4S or (HOOC)(C
6H
4)(SO
2)(NCl
2). It has been widely used to disinfect drinking water.
Other names for this compound include p-sulfondichloramidobenzoic acid, 4-[(dichloroamino)sulfonyl]benzoic acid, and Pantocide.
Uses
[edit]Halazone tablets have been used to disinfect water for drinking, especially where treated tap water is not available. A typical dosage is 4 mg/L.[5][6]
Halazone tablets were commonly used during World War II by U.S. soldiers for portable water purification, even being included in accessory packs for C-rations until 1945.[7]
Halazone was widely used by Marine infantry units during the Vietnam War. Halazone has largely been replaced in that use by sodium dichloroisocyanurate. The primary limitation of halazone tablets was the very short usable life of opened bottles, typically three days or less, unlike iodine-based tablets which have a usable open bottle life of three months.[citation needed]
Dilute halazone solutions (4 to 8 ppm of available chlorine) has also been used to disinfect contact lenses,[8] and as a spermicide.
Mechanism of action
[edit]Halazone's disinfecting activity is mainly due to the hypochlorous acid (HClO) released by hydrolysis of the chlorine-nitrogen bonds when the product is dissolved in water:[8]
- (R1)(R2)NCl + H
2O → HOCl + (R1)(R2)NH
The hypochlorous acid is a powerful oxidizer and chlorinating agent that destroys or denatures many organic compounds.
Production
[edit]Halazone can be prepared by chlorination of p-sulfonamidobenzoic acid.[4]
Another synthesis route is the oxidation of dichloramine-T with potassium permanganate in a mild alkaline medium.[4]
See also
[edit]- Bleach
- Chlorine-releasing compound
- Chloramine-T (tosylchloramide sodium salt), another water disinfection agent.
- Water chlorination
References
[edit]- ^ a b PubChem: "Halazone". Accessed on 2018-06-18.
- ^ a b NTP (1992), cited by PubChem
- ^ Jean-Claude Bradley: Open Melting Point Dataset. Quoted by Chemspider.
- ^ a b c Saljoughian, M.; Sadeghi, M. T. (1986). "An improved procedure for the synthesis ofp-(dichlorosulfamoyl)benzoic acid (Halazone)". Monatshefte für Chemie. 117 (4): 553. doi:10.1007/BF00810903.
- ^ Gripo Laboratories: "Water purification range: Halazone USP based Chlorine Tablets Archived 2020-06-27 at the Wayback Machine". Product page, accessed on 2018-06-18
- ^ Precise Health Care PVT LTD: "Halazone tablets Archived 2021-09-01 at the Wayback Machine". Product page, accessed on 2018-06-18
- ^ Hlavatá, L; Aguilaniu, H; Pichová, A; Nyström, T (2003). "The oncogenic RAS2val19 mutation locks respiration, independently of PKA, in a mode prone to generate ROS". The EMBO Journal. 22 (13): 3337–3345. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg314. PMC 165639. PMID 12839995.
- ^ a b Rosenthal, Ruth Ann; Schlitzen, Ronald L; McNamee, Linda S; Dassanayake, Nissanake L; Amass, Roger (1992). "Antimicrobial activity of organic chlorine releasing compounds". Journal of the British Contact Lens Association. 15 (2): 81. doi:10.1016/0141-7037(92)80044-Z.
