HD 93486
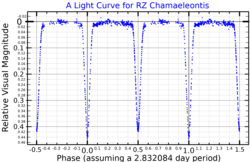 A visual band light curve for RZ Chamaeleontis, plotted from data published by Jørgensen & Gyldenkerne (1975)[1] | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Chamaeleon |
| Right ascension | 10h 42m 24.10884s[2] |
| Declination | −82° 02′ 14.1832″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.1 – 8.5[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F5 IV-V (both components)[4] |
| B−V color index | +0.45[5] |
| Variable type | Algol[6] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 20±0.6[7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −13.536 mas/yr[2] Dec.: −45.153 mas/yr[2] |
| Parallax (π) | 5.7404 ± 0.0186 mas[2] |
| Distance | 568 ± 2 ly (174.2 ± 0.6 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +1.72[8] (combined) |
| Orbit[4] | |
| Primary | RZ Cha A |
| Companion | RZ Cha B |
| Period (P) | 2.8321 d |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 12.2 AU[9] |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.00 |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2,441,402.4791 JD |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 0.00° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 108.2±0.6 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 107.6±0.9 km/s |
| Details | |
| combined/mean | |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.91±0.01[4] cgs |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.23±0.10[10] dex |
| Details | |
| A | |
| Mass | 1.51[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 2.29[11] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 7.94+0.77 −0.70[10] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.900±0.013[12] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,450±150[11] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 39±1[4] km/s |
| Age | 2.11[11] Gyr |
| B | |
| Mass | 1.40[11] M☉ |
| Radius | 2.21[11] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 7.94+0.77 −0.70[10] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.902±0.014[12] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,450±150[11] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 41±3[4] km/s |
| Age | 3.03[11] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
HD 93486, also known as HIP 52381, is a binary star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon near the border with Octans. Its variable star designation is RZ Chamaeleontis (RZ Cha). It has an apparent magnitude ranging from 8.2 to 9.1,[6] which is below the limit for naked eye visibility. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements place the system 568 light years away,[2] and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 20 km/s.[7] At its current distance, HD 93486's average brightness is diminished by 0.53 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.[14] The system has a combined absolute magnitude of +1.72.[8]
In 1964, HD 93486 was discovered to be an eclipsing binary by astronomer W. Strohmeier and colleagues. [15] Four years later, the system was found to be an Algol variable[16] and was given the variable star designation RZ Chamaeleontis in 1974.[17] J. Andersen et al. (1975) calculated a circular orbit of 2.8321 days,[4] which is also its variability period. During this time, RZ Cha drops from photographic magnitude 8.2 to 9.1 when the smaller component is eclipsed, and to 8.8 when the larger one is eclipsed.[6]
Both components have a stellar classification of F5 IV-V, indicating that they are slightly evolved F-type stars with luminosity classes intermediate between a subgiant and a main-sequence star. The primary has 151% the mass of the Sun[9] and 2.29 times the Sun's radius.[11] The secondary has 140% the mass of the Sun and 2.21 times the radius of the Sun.[11] Together, both stars radiate 7.94 times the luminosity of the Sun[18] from their photospheres at an effective temperature of 6,450 K, giving it a combined yellowish-white hue. The system is metal enriched with an iron abundance and is estimated to be 2 to 3 billion years old.[11] Both stars spin modestly, with projected rotational velocities of 39 km/s and 41 km/s respectively.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Jørgensen, H. E.; Gyldenkerne, K. (November 1975). "Four-colour photometry of eclipsing binaries. II. RZ Cha, light curves, photometric elements and determination of helium content". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 44: 343–347. Bibcode:1975A&A....44..343J. Retrieved 16 February 2023.
- ^ a b c d e Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ Giuricin, G.; Mardirossian, F.; Mezzetti, M.; Predolin, F. (1980). "Revised photometric elements of the detached eclipsing binaries RS Cha, RZ Cha, HS Hya". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 85: 259. Bibcode:1980A&A....85..259G.
- ^ a b c d e f g Andersen, J.; Gjerloff, H.; Imbert, M. (November 1975). "Spectroscopic observations of eclipsing binaries II: Absolute dimensions, evolutionary state, and helium content of RZ Chamaeleontis". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 44: 349-353. Bibcode:1975A&A....44..349A. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (March 2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27 – L30. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ a b c Samus’, N. N.; Kazarovets, E. V.; Durlevich, O. V.; Kireeva, N. N.; Pastukhova, E. N. (January 2017). "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1". Astronomy Reports. 61 (1): 80–88. Bibcode:2017ARep...61...80S. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. eISSN 1562-6881. ISSN 1063-7729. S2CID 125853869.
- ^ a b Pourbaix, D.; Tokovinin, A. A.; Batten, A. H.; Fekel, F. C.; Hartkopf, W. I.; Levato, H.; Morrell, N. I.; Torres, G.; Udry, S. (23 August 2004). "SB9: The ninth catalogue of spectroscopic binary orbits". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 424 (2): 727–732. arXiv:astro-ph/0406573. Bibcode:2004A&A...424..727P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041213. eISSN 1432-0746. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ a b Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (May 2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331–346. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. eISSN 1562-6873. ISSN 1063-7737. S2CID 119257644.
- ^ a b c Kraicheva, Z.; Popova, E.; Tutukov, A.; Yungelson, L. (July 1980). "Catalogue of physical parameters of spectroscopic binary stars". Bull. Inf. Centre Données Stellaires. 19: 71. Bibcode:1980BICDS..19...71K.
- ^ a b c Kovaleva, D. A. (December 2001). "Age and metallicity estimates for moderate-mass stars in eclipsing binaries". Astronomy Reports. 45 (12): 972–983. Bibcode:2001ARep...45..972K. doi:10.1134/1.1426128. eISSN 1562-6881. ISSN 1063-7729. S2CID 121028634.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Brown, Timothy M. (4 January 2010). "Radii of Rapidly Rotating Stars, with Application to Transiting-Planet Hosts". The Astrophysical Journal. 709 (1): 535–545. arXiv:0912.1639. Bibcode:2010ApJ...709..535B. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/709/1/535. eISSN 1538-4357. ISSN 0004-637X.
- ^ a b Eker, Z.; Bilir, S.; Soydugan, F.; Gökçe, E. Yaz; Soydugan, E.; Tüysüz, M.; Şenyüz, T.; Demircan, O. (2014). "The Catalogue of Stellar Parameters from the Detached Double-Lined Eclipsing Binaries in the Milky Way". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia. 31. arXiv:1403.1583. Bibcode:2014PASA...31...24E. doi:10.1017/pasa.2014.17. eISSN 1448-6083. ISSN 1323-3580.
- ^ "RZ Cha". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved February 13, 2023.
- ^ Gontcharov, George A.; Mosenkov, Aleksandr V. (28 September 2017). "Verifying reddening and extinction for Gaia DR1 TGAS main sequence stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 472 (4): 3805–3820. arXiv:1709.01160. Bibcode:2017MNRAS.472.3805G. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx2219. eISSN 1365-2966. ISSN 0035-8711.
- ^ Strohmeier, W.; Knigge, R.; Ott, H. (September 1964). "Bright Southern BV-Stars". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars. 66: 1. Bibcode:1964IBVS...66....1S. ISSN 0374-0676.
- ^ Strohmeier, W.; Mauder, H. (1969). "Discovery and study of bright variable stars". Sky and Telescope. 37 (1): 1. Bibcode:1969S&T....37a...1S. ISSN 0037-6604.
- ^ Geyer, E. H.; Knigge, R. (October 1974). "Improved Light Elements for the Eclipsing Binaries RZ Cha, YZ Cha and DZ Mus". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars. 941: 1. Bibcode:1974IBVS..941....1G. ISSN 0374-0676.
- ^ Malkov, O. Yu. (January 1993). "Catalogue of astrophysical parameters of binary systems". Bulletin d'Information du Centre de Donnees Stellaires. 42: 27. Bibcode:1993BICDS..42...27M. ISSN 1169-8837.
Further reading
[edit]- Dryomova, G. N.; Svechnikov, M. A. (April 2007). "Effect of tidal evolution in determining the ages of eclipsing-variable early main sequence close binary systems". Astrophysics. 50 (2): 239–253. Bibcode:2007Ap.....50..239D. doi:10.1007/s10511-007-0023-9. eISSN 1573-8191. ISSN 0571-7256. S2CID 121459015.
