Germanium monosulfide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Germanium(II) sulfide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.536 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| GeS | |
| Molar mass | 104.69 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Carbon monosulfide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Germanium monosulfide or Germanium(II) sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula GeS. It is a chalcogenide glass and a semiconductor.[1] Germanium sulfide is described as a red-brown powder or black crystals.[2] Germanium(II) sulfide when dry is stable in air, hydrolyzes slowly in moist air but rapidly reacts in water forming Ge(OH)2 and then GeO.[3] It is one of a few sulfides that can be sublimed under vacuum without decomposition.[4]
Preparation
[edit]First made by Winkler by reducing GeS2 with Ge.[3] Other methods include reduction in a stream of H2 gas,[3] or with an excess of H3PO2 followed by vacuum sublimation.[2]
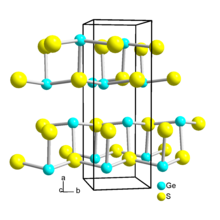
Structure
[edit]It has a layer structure similar to that of black phosphorus.[2] The Ge-S distances range from 247 to 300 pm.[3] Molecular GeS in the gas phase has a Ge-S bond length of 201.21 pm.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ Sutter, Eli; Zhang, Bo; Sun, Muhua; Sutter, Peter (2019-08-27). "Few-Layer to Multilayer Germanium(II) Sulfide: Synthesis, Structure, Stability, and Optoelectronics". ACS Nano. 13 (8): 9352–9362. doi:10.1021/acsnano.9b03986. ISSN 1936-0851. PMID 31305983.
- ^ a b c Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b c d E. G. Rochow, E. W. Abel ,1973, The Chemistry of Germanium Tin and Lead, Pergamon Press, ISBN 0-08-018854-0
- ^ Michael Binnewies, Robert Glaum, Marcus Schmidt, Peer Schmidt, 2012, Chemical Vapor Transport Reactions, De Gruyter, ISBN 978-3-11-025464-8
- ^ Lide, David R., ed. (2006). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0487-3.
