Foreign policy of Donald Trump during the 2016 presidential election
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Business and personal 45th & 47th President of the United States Tenure
Impeachments Civil and criminal prosecutions  |
||

This article describes the foreign policy positions taken by Donald Trump during his 2016 presidential campaign (announced June 16, 2015).
Overview
[edit]In a New York Times interview in July 2016, Presidential Nominee Trump "repeatedly defined American global interests almost purely in economic terms," with the nation's "roles as a peacekeeper, as a provider of a nuclear deterrent against adversaries like North Korea, as an advocate of human rights and as a guarantor of allies' borders" being "quickly reduced to questions of economic benefit to the United States."[1]
A 68-page document likely written by and under the direction of the Trump administration's national security adviser, Lt. Gen. H.R. McMaster was released by the Trump administration in December 2017,[2] which has been referred to as outlining the administration's doctrine pertaining to foreign policy goals.[3]
United States Armed Forces and defense spending
[edit]Trump stated in a December 2015 Republican primary debate that "Our military is a disaster," and in a July 2016 on-air radio broadcast described the United States Armed Forces as "depleted and in horrible shape."[4][5]
In July 2016, retired U.S. Marine Corps General John R. Allen, who supports Trump's opponent Hillary Clinton, gave a forceful speech against Trump at the 2016 Democratic National Convention.[6] Trump responded by calling the four-star military leader "a failed general" and saying that he had never met him.[7][8]
Trump has stated on several occasions that if elected president, he "would increase [spending] on the military."[9] Trump claims that the United States Armed Forces will be "funded beautifully" if he was elected president.[10] While Trump has not offered specifics on defense spending under a Trump presidency, he has repeatedly called for a U.S. military buildup and has criticized President Barack Obama's military spending strategy.[11][12][13] Trump has criticized the decline in the numbers of active-duty armed forces, Navy ships and Air Force planes since the end of the Cold War.[11] Trump has pledged to rein in wasteful spending in the military.[12]
In an interview with Fox News in June 2015, Trump claimed: "There's nobody bigger or better at the military than I am."[14] In an interview with The Washington Post, Trump said that he would not reveal his military plans for fear of informing the enemy: "I don't want them to know what I'm thinking, does that make sense? I want people to be guessing ... I don't want people to figure it out. I don't want people to know what my plan is. I have plans. I have plans! But I don't want to do it."[15]
Diplomacy and U.S. allies
[edit]Trump has stated his intention to provide presidential leadership with strong diplomacy to restore "respect" for the United States around the world. He supports a robust national defense.[16][17][18] In an interview with Bill O'Reilly, Trump claimed that he had a proven record in negotiating with foreign countries. "I've made a fortune with foreign countries."[14]
Trump has stated, "We Americans are laughed at around the world for losing a hundred and fifty billion dollars year after year, for defending wealthy nations for nothing, nations that would be wiped off the face of the earth in about 15 minutes if it weren't for us. Our 'allies' are making billions screwing us."[19] Trump has called for allied countries, including Germany, Israel, Japan, Saudi Arabia, and South Korea to pay the United States for helping protect their nations.[20][21][22]
Foreign policy advisors
[edit]Trump unveiled a list of foreign policy advisors in April 2016: Joseph E. Schmitz, Walid Phares, Keith Kellogg, Carter Page,[23] Bert Mizusawa, Gary Harrell, Chuck Kubic and George Papadopoulos.[24][25] Retired Lt. General Michael Flynn is also a Trump foreign policy advisor (and was reportedly on Trump's shortlist for running mate).[26][27][28] Politico noted that several of those cited on the list "are complete unknowns; others have mixed reputations among GOP national security pros."[29] According to Duke political science professor Peter Feaver, the list "looks more like an ad hoc coalition of the willing than any deliberate effort to reflect a particular candidate's vision of America's role in the world."[30] After it was reported that Carter Page was being investigated for allegedly meeting with Kremlin officials over the summer of 2016, a Trump campaign spokesman denied that Page had ever been part of the campaign, except as an "informal adviser".[31]
Two of the advisors on the list "view Islamic Sharia law within the U.S. as a dire threat—even though many conservatives consider the issue a fringe obsession."[29] One of the advisors "has accused the State Department's top official for Ukraine and Russia, Victoria Nuland, of "fomenting" the 2014 revolution that overthrew Ukraine's government."[29] According to a former colleague, Flynn has argued for a more aggressive approach to U.S. interests around the world.[26][27] A review of Flynn's book The Field of Fight (2016) by Will McCants of the Brookings Institution describes Flynn's vision as a combination of neoconservatism (his insistence on destroying what he sees an alliance of tyranny, dictatorships, and radical Islamist regimes) and realism (support for working with "friendly tyrants").[32] However, like Trump, Flynn has been a critic of the U.S.'s military involvement in Iraq[33] and Libya[34] as well as its support for the Syrian opposition, and has advocated for closer ties with Russia.[35] Flynn has said that Trump's strategic approach is to "start really, really high and really, really hard, OK? And then, be prepared to get down to where you think you can actually negotiate." Flynn also disputed the notion that Trump would order the military to kill the families of terrorists and complimented Trump's ability to surround himself with good people.[27]
Previously when asked about who he was consulting with on foreign policy during an interview on MSNBC's Morning Joe, Trump responded with "I'm speaking with myself, number one, because I have a very good brain and I've said a lot of things".[36] Some of Trump's foreign policy ideas have been met with opposition by the foreign policy establishment of the Republican Party (GOP).[37] The Economist Intelligence Unit placed a Trump victory in the 2016 United States presidential election fifth in their list of ten global risks for 2016, citing his foreign policy positions which increase the risk of trade war, him being used as a potent recruitment tool for jihadi groups and weakened efforts to contain Russia's expansionist tendencies.[38]
Post-inauguration, President Trump has been accused of "abandoning the foreign policy that brought him victory" and "as a disappointment for those who hoped for a break from the liberal interventionist/neoconservative synthesis. ... It doesn't appear that he has any foreign policy realists around him, or anyone with a restrained view of America's international responsibilities."[39] (See Appointments section in the article Foreign policy of the first Donald Trump administration.)
Americas
[edit]Cuba
[edit]In September 2016, Trump expressed his opposition to the restoration of full diplomatic relations between the United States and Cuba achieved in July 2015.[40] As part of the restoration of full diplomatic relations, the United States embargo against Cuba remains in place, but a series of regulations have been loosened to allow more American companies to sell their products in Cuba.[40] Trump said that he would only restore full diplomatic relations with Cuba if the Cuban regime met his demands to restore political freedoms and free political prisoners.[40] This is a shift from the position expressed in September 2015 when he said that the opening with Cuba was "fine. But we should have made a better deal."[40]
In February 2016, Trump said that he opposed the Cuban Adjustment Act, which allows any Cuban who reaches U.S. soil to remain in the country legally and apply for residency.[41] Trump said, "I don't think that's fair. I mean, why would that be a fair thing?"[41]
On the first day of the Donald Trump presidential campaign, 2000, Trump held an event in Miami where he vowed to maintain the embargo on Cuba and never spend his or his companies' money in Cuba until Fidel Castro was removed from power.[42] However, according to reporting by Newsweek in September 2016, Trump had conducted business in Cuba in violation of the embargo seven months before his vow.[42] Bloomberg News reported in July 2016 that Trump Organization executives and advisers traveled to Havana in late 2012 or early 2013 to explore golf-course developments in Cuba, possibly a violation of the embargo.[43]
Mexico
[edit]Trump has emphasized U.S. border security as well as illegal immigration to the United States as a campaign issue.[44][45] During his announcement speech he stated in part, "When Mexico sends its people, they're not sending their best. They're not sending you. They're sending people that have lots of problems, and they're bringing those problems. ... They're bringing drugs. They're bringing crime. They're rapists. And some, I assume, are good people."[17] On July 6, 2015, Trump issued a written statement[46] to clarify his position on illegal immigration which drew a reaction from critics. It read in part:
The Mexican Government is forcing their most unwanted people into the United States. They are, in many cases, criminals, drug dealers, rapists, etc. This was evident just this week when, as an example, a young woman in San Francisco was viciously killed by a 5-time deported Mexican with a long criminal record, who was forced back into the United States because they didn't want him in Mexico. This is merely one of thousands of similar incidents throughout the United States. In other words, the worst elements in Mexico are being pushed into the United States by the Mexican government. The largest suppliers of heroin, cocaine and other illicit drugs are Mexican cartels that arrange to have Mexican immigrants trying to cross the borders and smuggle in the drugs. The Border Patrol knows this. Likewise, tremendous infectious disease is pouring across the border. The United States has become a dumping ground for Mexico and, in fact, for many other parts of the world. On the other hand, many fabulous people come in from Mexico and our country is better for it. But these people are here legally, and are severely hurt by those coming in illegally. I am proud to say that I know many hard working Mexicans—many of them are working for and with me ... and, just like our country, my organization is better for it.[47]
A study published in Social Science Quarterly in May 2016 tested Trump's claim that immigrants are responsible for higher levels of violent and drug-related crime in the United States.[48] It found no evidence that links Mexican or undocumented Mexican immigrants specifically to violent or drug-related crime.[48] It did however find a small but significant association between undocumented immigrant populations (including non-Mexican undocumented immigrants) and drug-related arrests.[48]
Trump has repeatedly pledged to build a wall along the U.S.'s southern border and has said that Mexico would pay for it through increased border-crossing fees and NAFTA tariffs.[49] In his speech announcing his candidacy, Trump pledged to "build a great, great wall on our southern border. And I will have Mexico pay for that wall. Mark my words."[50][51] Trump also said "nobody builds walls better than me, believe me, and I'll build them very inexpensively."[51] The concept for building a barrier to keep illegal immigrants out of the U.S. is not new; 670 miles of fencing (about one-third of the border) was erected under the Secure Fence Act of 2006, at a cost of $2.4 billion.[51] Trump said later that his proposed wall would be "a real wall. Not a toy wall like we have now."[52] In his 2015 book, Trump cites the Israeli West Bank barrier as a successful example of a border wall.[53] "Trump has at times suggested building a wall across the nearly 2,000-mile border and at other times indicated more selective placement."[54] After a meeting with Mexican President Enrique Peña Nieto on August 31, 2016, Trump said that they "didn't discuss" who would pay for the border wall that Trump has made a centerpiece of his presidential campaign.[55] Nieto contradicted that later that day, saying that he at the start of the meeting "made it clear that Mexico will not pay for the wall".[56] Later that day, Trump reiterated his position that Mexico will pay to build an "impenetrable" wall on the Southern border.[57]
According to experts and analyses, the actual cost to construct a wall along the remaining 1,300 miles of the border could be as high as $16 million per mile, with a total cost of up to $25 billion, with the cost of private land acquisitions and fence maintenance pushing up the total cost further.[54] Maintenance of the wall cost could up to $750 million a year, and if the Border Patrol agents were to patrol the wall, additional funds would have to be expended.[54] Rough and remote terrain on many parts of the border, such as deserts and mountains, would make construction and maintenance of a wall expensive, and such terrain may be a greater deterrent than a wall in any case.[54] Experts also note that on federally protected wilderness areas and Native American reservations, the Department of Homeland Security may have only limited construction authority, and a wall could cause environmental damage.[54]
Critics of Trump's plan question whether a wall would be effective at stopping unauthorized crossings, noting that walls are of limited use unless they are patrolled by agents and to intercept those climbing over or tunneling under the wall.[54] Experts also note that approximately half of illegal immigrants in the U.S. did not surreptitiously enter, but rather "entered through official crossing points, either by overstaying visas, using fraudulent documents, or being smuggled past the border."[54]
Trump has vowed to impose tariffs—in the range of 15 to 35 percent—on companies that move their operations to Mexico.[58] He has specifically criticized the Ford Motor Co.,[citation needed] Carrier Corporation,[citation needed] and Mondelez International.[58][59] Trump has pledged a 35% tariff on "every car, every truck and every part manufactured in [Ford's Mexico plant] that comes across the border."[60] Tariffs at that level would be far higher than the international norms (which are around 2.67 percent for the U.S. and most other advanced economies and under 10 percent for most developing countries).[citation needed] In August 2015, in response to Oreo maker Mondelez International's announcement that it would move manufacturing to Mexico, Trump said that he would boycott Oreos.[59]
According to economic experts canvassed by PolitiFact, the tariffs could help create new manufacturing jobs and lead to some concessions from the U.S.'s foreign trading partners, but consumer costs and production costs would almost certainly rise, the stock market would fall, interest rates could rise, and trade wars could occur.[61] PolitiFact noted that lower-income consumers in the United States would be hurt the most.[61]
In a 60 Minutes interview in September 2015, Trump condemned the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), saying that if elected president, "We will either renegotiate it, or we will break it."[62][63] A range of trade experts have said that pulling out of NAFTA as Trump proposed would have a range of unintended consequences for the U.S., including reduced access to the U.S.'s biggest export markets, a reduction in economic growth, and increased prices for gasoline, cars, fruits, and vegetables.[64] The Washington Post fact-checker furthermore noted that a Congressional Research Service review of the academic literature on NAFTA concluded that the "net overall effect of NAFTA on the U.S. economy appears to have been relatively modest, primarily because trade with Canada and Mexico accounts for a small percentage of U.S. GDP."[citation needed]
According to an analysis by the Peterson Institute for International Economics, Trump's proposed tariff increases on China and Mexico could, if China and Mexico retaliate with their own tariff increases, push the U.S. into recession and cost 5 million U.S. jobs.[65] Even more limited retaliation by China and Mexico, or an aborted trade war (the Trump administration backs down from its tariff increases one year into them) would hit the U.S. economy hard.[65] Gary Clyde Hufbauer, senior fellow at PIIE, notes that there is ample precedent and scope for a U.S. president to unilaterally raise tariffs as Trump has vowed to do, and that efforts to block Trump's actions through the courts, or by amending the authorizing statutes in Congress, would be difficult and time-consuming.[66]
Asia
[edit]Claims of currency devaluation were leveled against Japan and China by Trump.[67]
According to New Republic,[68] the Daily Beast,[69] and Vox,[70] Asians have been singled out for criticism and attacks by Trump, and it has been suggested that the ultimate intent is a racial conflict.
China
[edit]Background
[edit]Speaking on the Piers Morgan Tonight talk show in February 2011 about ″what a President Trump would do to revive America's prosperity″, in responding to Piers Morgan′s questions about how to deal with the Chinese and whether they are Americans′ friends, Donald Trump said, ″I don't think they're friends. I think they're enemies. ... I understand the Chinese and I deal with them all the time. ... They consider our leaders extremely stupid people. They cannot believe what they get away with. ... They're never going to treat us well unless we do something strong. ... We have very, very unfair trade. I call it unfair trade. I would tax them 25 percent. They would come to the table immediately.″[71] In August 2011, he said that he would "send [China] a bill for the value of the secrets that they've stolen," referring to alleged Chinese theft of American stealth technology.[72]
In November 2015, Trump promised to designate People's Republic of China a currency manipulator on his first day in office.[73] He pledged "swift, robust and unequivocal" action against Chinese piracy, counterfeit American goods, and theft of U.S. trade secrets and intellectual property; and has condemned China's "illegal export subsidies and lax labor and environmental standards."[73]
In January 2016, Trump proposed a 45 percent tariff on Chinese exports to the United States to give "American workers a level playing field."[74][75] When asked about potential Chinese retaliation to the implementation of tariffs, such as sales of U.S. bonds, Trump judged such scenario unlikely: "They won't crash our currency. They will crash their economy. That's what they are going to do if they start playing that."[76] In a May 2016 speech, Trump responded to concerns regarding a potential trade war with China: "We're losing $500 billion in trade with China. Who the hell cares if there's a trade war?"[77]
Trump Administration (2017–2021)
[edit]On January 23, speaking about China's claims to sovereignty over the Spratly Islands in the South China Sea, White House spokesman Sean Spicer said, "It's a question of if those islands are in fact in international waters and not part of China proper, then yeah, we're going to make sure that we defend international territories from being taken over by one country."[78]
On February 4, on a visit to Japan, U.S. Defense Secretary James Mattis reaffirmed Washington's commitment under the Treaty of Mutual Cooperation and Security between the United States and Japan to defending Japan, including the Senkaku Islands (the East China Sea) that are claimed by China.[79]
In an interview with The Atlantic, the U.S. Deputy Secretary for the Middle East Michael Mulroy explained that the Department of Defense was concerned about China's desire to erode U.S. military advantages, as well as China's push for access and basing, use of economics to intimidate through the One Belt One Road initiative (which is a worldwide campaign of infrastructure investment) and technology and intellectual property theft, acquisition and penetration.[80] This was followed by U.S. Army General Mark Milley's testimony during his Senate confirmation hearing to be the next Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff where he said that China was the United States' primary challenge and they were outspending the U.S. in research, development and procurement.[81]
India
[edit]Trump has spoken favorably of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi and of a closer alliance with India.[82] He told a campaign rally of Indian-Americans that under his administration, relations with India would be "the best ever".[83] The Trump Organization has extensive business ventures in India, involving at least 16 Indian partnerships and corporations.[83]
North Korea
[edit]Trump has "declined to share details of his plans to deal with North Korea"[84] but has said that he would be willing to meet North Korean supreme leader Kim Jong-un, saying that he would have "no problem" doing so.[84][85] Trump described Kim as a "maniac" but also claimed that Kim deserves "credit" for being able to overcome his rivals in order to succeed his father.[86] Trump has advocated placing greater pressure on China, including through restrictions on trade, to rein in its ally North Korea in the wake of the January 2016 North Korean nuclear test,[87] saying that China has "total control" over North Korea[87] and the U.S. has "tremendous" economic power over China.[85] In the September 2016 Presidential Debate, Trump said, "China should solve that [North Korea] problem for us. China should go into North Korea. China is totally powerful as it relates to North Korea."[88] He also argued that the Iran nuclear deal should have included a component about Iran–North Korea relations.[88]
An editorial in North Korean state media hailed Trump as a "wise politician" and "far-sighted presidential candidate" who could be good for North Korea.[89] The editorial suggested that a statement from Trump that he did not want to get involved in any conflict between North and South Korea was "fortunate from North Koreans' perspective".[89]
Experts warned in December 2017 that Trump's calls for additional sanctions on North Korea, including a request that China cease oil shipments, would lead to famine within North Korea without seriously curbing their nuclear capabilities.[90]
Taiwan
[edit]President-elect Trump's telephone conversation with the President of Taiwan Tsai Ing-wen on December 2, 2016, the first such contact with Taiwan by a U.S. president-elect or president since 1979, provoked the People's Republic of China to lodge a diplomatic protest ("stern representations").[91][92] Trump went on to clarify his move by telling the Fox News, "I fully understand the 'one China' policy, but I don't know why we have to be bound by a 'one China' policy unless we make a deal with China having to do with other things, including trade."[92]
Pakistan
[edit]In 2015, Trump said Pakistan is "the most dangerous country in the world" and should denuclearize.[93] But according to the Pakistan government, in a cordial post-election telephone conversation with Pakistan's Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif, Trump lavished praise on Pakistan and its "fantastic" people, said he would love to visit the country, and offered to help Pakistan solve any outstanding problems.[94] After taking office, President Trump indicated that Pakistan will be among the countries whose citizens will have to go through an "extreme vetting" process before entering the United States.[95]
Philippines
[edit]In December 2016, Trump reportedly praised Philippines President Rodrigo Duterte's controversial war on drugs, describing it as the "right way" and wishing Duterte success with his efforts. Later that month, Duterte praised Trump for abandoning the Trans-Pacific Partnership.[96]
In January 2017, Tillerson advocated blocking islands from China.[97] When Rex Tillerson threatened China's positions on the islands, the Philippines said that Tillerson was speaking for the USA only in the USA's interest and prerogatives and not that of the Philippines.[98] Delfin Lorenzana, the Defense Secretary rejected the possibility of war against China over the islands in the South China Sea.[99]
In January 2017, Duterte again praised President Trump and First Lady Melania Trump, stating that "I envy him."[100]
Middle East and North Africa
[edit]Afghanistan
[edit]On October 6, 2015, Trump stated that the United States "made a terrible mistake getting involved [in Afghanistan] in the first place."[101] When asked again about Afghanistan on October 20, 2015, Trump reversed his position, claiming to have never characterized U.S. entry into Afghanistan as a mistake.[101] Trump stated that the War in Afghanistan was necessary and that he supported keeping a limited number of troops there.[101]
Egypt
[edit]On February 10, 2011, the day prior to the overthrow of Hosni Mubarak, Trump stated that he had no sympathy for Mubarak and expressed optimism that events in Egypt will not affect the world economy.[102] At the time, Trump offered neither criticism nor praise for how President Barack Obama dealt with the Egyptian crisis, saying it was out of Obama's hands.[102] Later, in August 2011, Trump criticized the Obama administration for not helping Mubarak keep power, citing Mubarak's positive relationship with Israel and the negative effect that Mubarak's removal would have on other allies' faith in the United States.[103][104] In 2012, Trump reiterated his criticisms of the Obama administration's handling of Mubarak and asserted that "Egypt is now our enemy" and that "Israel is in trouble."[105]
In September 2016, Trump first met the President of Egypt, Abdel Fattah el-Sisi, describing him as a "fantastic guy", praising his handling of the Egyptian coup d'état of 2013 that removed former President Mohamed Morsi from power.[106] Trump said that there was a "good feeling between [them]".[106] Sisi later said he had "no doubt" that Trump would be a strong leader if elected.[107]
In April 2017, President Trump invited President Sisi to the White House, a privilege that was not afforded to Sisi under the Obama administration. There, Trump clarified his stance on U.S.-Egypt relations: "I just want to let everybody know in case there was any doubt that we are very much behind President el-Sisi. He's done a fantastic job in a very difficult situation. We are very much behind Egypt and the people of Egypt. The United States has, believe me, backing, and we have strong backing." Sisi responded by saying "you will find Egypt and myself always beside you in bringing about an effective strategy in the counterterrorism effort," and pledged to support Trump's Israel-Palestine peace efforts, stating he hoped they would "find a solution to the problem of the century in the deal of the century."[108]
Iran
[edit]In June 2016, Trump maintained that "Iran is now the dominant Islamic power in the Middle East and on the road to nuclear weapons."[109] Trump opposes the international nuclear agreement with Iran (negotiated with the United States and five other world powers) that was made in 2015, calling it "terrible" and saying that the Obama administration negotiated the agreement "from desperation."[110] Trump has claimed that he has "studied this issue in great detail ... actually greater by far than anybody else."[111] Trump opposed the sanctions relief in the agreement, saying: "we're giving them billions of dollars in this deal, which we shouldn't have given them. We should have kept the money."[110] Trump has claimed that the United States gives Iran $150 billion as part of the Iran deal, a statement rated false by FactCheck.org.[112] FactCheck.org notes that the Iranian assets that were unfrozen as part of the deal were held mostly by banks and other financial institutions outside the United States, and that the value of the assets is estimated to be between $25 billion and $56 billion.[112] Trump has claimed that "when those restrictions expire (in the Iran nuclear deal), Iran will have an industrial-size military nuclear capability ready to go," a statement rated "false" by PolitiFact.com.[111] Trump was critical of State Department officials as they negotiated the Iran deal, saying that "It's a one-day deal. This whole thing should have taken a day."[113]
In July 2015, when explaining his opposition to the Iran agreement, Trump cited four American prisoners being held prisoner in the country.[110] When the four prisoners were released in January 2016, after the agreement went into effect, Trump claimed credit for the release, an assertion that was termed "dubious" by CBS News.[114]
In August 2015, Trump had said that despite opposing the content of the deal, he would attempt to enforce it rather than abrogate it.[115] In a speech to the American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC) in March 2016, however, Trump said that his "number-one priority is to dismantle the disastrous deal with Iran."[116] In July 2016, Trump foreign policy adviser Walid Phares claimed Trump would not "get rid of" the Iran deal and would instead seek to "renegotiate" it.[117]
In September 2015, Trump told CNN that he believed the agreement would compel the United States to side with Iran in the event of war: "There's something in the Iran deal that people I don't think really understand or know about, and nobody's able to explain it, that if somebody attacks Iran, we have to come to their defense. So if Israel attacks Iran, according to that deal, I believe the way it reads ... that we have to fight with Iran against Israel."[118] Trump's statement is based on his interpretation of a provision in the agreement that "the U.S. and other partners are prepared, as appropriate, to cooperate with training to strengthen Iran's ability to protect against and respond to nuclear security threats, including sabotage." PolitiFact rated Trump's statement "false" and the Obama administration disagrees with Trump's interpretation.[119]
During an interview with Bill O'Reilly, Trump was asked whether he would negotiate a new deal with Iran. Trump responded that, with the current deal, "Iran is doing nuclear. They're going nuclear." He would "put on the sanctions big league. I'd double and triple up the sanctions and make a deal from strength."[14] According to Trump, nuclear weapons, not global warming, is the world's biggest problem.[14] Trump said that any deal with Iran should stipulate that inspectors have 24-hour-a-day access immediately to all nuclear sites and made reference to American nationals imprisoned the country.[110]
In the September 2016 Presidential Debate, Trump said that the Iran deal should have contained provisions that Iran must "do something with respect to North Korea. And they should have done something with respect to Yemen and all these other places."[120]
In October 2016, it was reported that despite Trump's denouncement of Iran as a "big enemy" and assertions that donations from foreign governments to the Clinton Foundation charity amounted to evidence of corruption, the Trump Organization did business with one of Iran's largest state-controlled banks from 1998 to 2003.[121] The Trump Organization kept the bank on as a tenant for four more years after the United States Department of the Treasury designated the bank in 1999 as being controlled by the Iranian government.[121] U.S. authorities also alleged that the bank had been used between 2002 and 2006 to funnel money to a unit of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps that has sponsored terrorist attacks—a period that overlapped with the time the bank rented office space from Trump.[121]
Also in April 2019, the U.S. designated the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) as a foreign terrorist organization under the State Department's maximum pressure campaign.[122] This designation was done over the opposition of the Central Intelligence Agency and the Department of Defense.[123][124][125] United States Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense Mick Mulroy stated that this terrorist designation did not grant any additional authorities to the DoD and that they were not seeking any and that the DoD did not believe the Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Terrorists could be applied to Iran.[126]
Iraq
[edit]Support
[edit]Donald Trump had stated many times that George H. W. Bush should have removed Saddam Hussein from power in the Gulf War of 1991 according to 1999 Fox News interview with Tony Snow and 2000 book, “The America We Deserve,” by Donald Trump and Dave Shiflett.[127]
In his 2000 book, “The America We Deserve,” by Donald Trump and Dave Shiflett, he suggested that he would be in favor of a pre-emptive strike if Iraq was viewed as a threat to national security. “I’m no warmonger,” Trump wrote. “But the fact is, if we decide a strike against Iraq is necessary, it is madness not to carry the mission to its conclusion.” He went on to compare a decision to invade with the “quick, secret, decisive moves in order to gain a negotiating advantage” in a business deal. "[128]
On September 11, 2002, when asked by radio talk-show host Howard Stern if he supported an invasion of Iraq, Trump responded, "Yeah, I guess so." He then referenced the Persian Gulf War of 1991 in which Saddam Hussein still remained in power. "You know I wish the first time it was done correctly."[129][130][131] In a January 28, 2003 interview with Neil Cavuto, on the night of President George W. Bush's 2003 State of the Union Address, Trump said that he expected to hear "a lot of talk about Iraq" and urged Bush to make a decision on Iraq—"Either you attack or you don't attack".[132] When asked whether Bush should be more focused on Iraq or the economy, Trump said:
Well, he has either got to do something or not do something, perhaps, because perhaps he shouldn't be doing it yet and perhaps we should be waiting for the United Nations, you know. He's under a lot of pressure. I think he's doing a very good job. But, of course, if you look at the polls, a lot of people are getting a little tired. I think the Iraqi situation is a problem. And I think the economy is a much bigger problem as far as the president is concerned. Well, I'm starting to think that people are much more focused now on the economy. They're getting a little bit tired of hearing "We're going in, we're not going in." Whatever happened to the days of Douglas MacArthur? Either do it or don't do it.[133][134]
On March 21, 2003, one day into the Iraq War, Trump was interviewed by Fox News' Neil Cavuto. Trump said that the war appeared to be "a tremendous success from a military standpoint", and expressed hope that it would continue to be so.[135] Later that week he publicly called the war a "mess".[136][137]
Opposition during 2016 campaign
[edit]According to a February 2016 statement by Sean Hannity, "I battled him at the time. He did not want us to go to Iraq. He was dead set against it."[138] There are no transcripts or audio to confirm Hannity's claim,[139] and Hannity says that Trump opposed an invasion of Iraq during telephone calls following Hannity's show.[140]
Trump first directly criticized the Iraq War in an April 2004 conversation with Howard Stern, which was more than one year after the invasion of Iraq.[141] Later, Trump publicly and explicitly criticized the war in an interview published in Esquire in August 2004, sixteen months after the invasion.[142] Trump said: "Look at the war in Iraq and the mess that we're in," criticized the George W. Bush administration's handling of the war, dismissed the idea of Iraq becoming functionally democratic, and predicted that "Two minutes after we leave, there's going to be a revolution, and the meanest, toughest, smartest, most vicious guy will take over. And he'll have weapons of mass destruction, which Saddam didn't have."[142][143]
On the campaign trail in 2015 and 2016, Trump has repeatedly said that he was "against the war from the very beginning."[142][144]
Israel and Israeli–Palestinian conflict
[edit]Trump has been critical of the Obama administration's treatment of Israel, stating that "Israel has been totally mistreated."[109] Trump has also claimed that Israel has been the victim of bias at the United Nations, and announced the United States' departure from the UN Commission on Human Rights for this reason.[145]
Israel-related causes
[edit]In 2001, Trump lent his personal jet to then-New York City Mayor Rudy Giuliani so that the latter could show solidarity for terror victims in Israel, and in 2004 Trump was the grand marshal of the Celebrate Israel Parade in New York City.[146] Speaking in 2006, Trump called Israel "a great country" and one of his favorite countries, adding: "I know that you've been through a lot recently."[147] Trump released a video endorsing Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu during the 2013 Israeli elections.[148][149] In February 2015, Trump stated: "We love Israel, we will fight for Israel 100 percent, 1000 percent, it will be there forever."[150][151] Trump has made multimillion-dollar donations to the establishment of new settlements in Israel, to house Israeli families who were evacuated from Gush Katif in 2005, and to house families evacuated from settlements in the Sinai Peninsula in 1980. As a result, his name is listed on the top of the plaque of the major contributors to the development of Dekel in the Southern District.[152] Trump has also donated to the West Bank settlement of Beit El.[153]
Proposed Muslim ban and cancelled Israel visit
[edit]After Trump proposed in December 2015 to temporarily exclude Muslims from travel to the United States, numerous world leaders, including Prime Minister of Israel Benjamin Netanyahu,[154] criticized Trump's proposal. Netanyahu released a statement saying: "The State of Israel respects all religions and strictly guarantees the rights of all its citizens." Several dozen Israeli Knesset members, many of whom are Muslim themselves, signed a petition urging Netanyahu not to meet with Trump later that month;[155] a day later, Trump postponed his visit to Israel until "a later date after I become President of the U.S.",[156] stating that he did not want to put Netanyahu "under pressure".[154]
Settlements
[edit]During his presidential campaign, Trump broke with long-standing bipartisan U.S. policy on the construction of Israeli settlements in the West Bank as a precursor to negotiations with the Palestinians, saying that Israel "have to keep going" and "I don't think there should be a pause."[157] Ynetnews noted: "If elected, Trump's seemingly broad support of settlement development would constitute a dramatic shift in U.S. foreign policy, as both Democratic and Republican U.S. presidents have stated in the past that the settlements are illegal and no further building in them should be allowed."[157]
U.S. aid to Israel
[edit]At a press conference in March 2016, Trump said that as president, he would require U.S. allies to pay the U.S. back for the defense spending and foreign aid that the U.S. has spent on their behalf. When specifically asked whether his previously stated stance on charging U.S. allies for defense spending would extend to Israel, he replied "I think Israel would do that also. There are many countries that can pay, and they can pay big-league."[158] However, immediately after the press conference, Trump reversed himself on aid to Israel, adding, "They [Israel] help us greatly."[159]
Israeli-Palestinian peace process
[edit]In February 2017, Trump said that he could live with either a two-state solution or a one-state solution to the Israeli–Palestinian conflict.[160] This is a break with the previous bipartisan foreign policy consensus on support for the two-state solution.[160] Middle East experts have warned that the policy change could reduce the likelihood of resolving the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.[160]
Trump has previously said that he would not take sides in any Israeli-Palestinian agreement in order to be a neutral negotiator in the peace talks, although he also added that he was "totally pro-Israel."[161] In December 2015, Trump told the Associated Press that an Israeli-Palestinian peace accord would depend very much upon Israel, remarking: "I have a real question as to whether or not both sides want to" come to a peace accord. "A lot will have to do with Israel and whether or not Israel wants to make the deal—whether or not Israel's willing to sacrifice certain things."[162]
Trump has vowed that as president he will veto a United Nations-imposed Israel-Palestine peace agreement, stating: "When I'm president, believe me, I will veto any attempt by the U.N. to impose its will on the Jewish state. It will be vetoed 100 percent."[163] He added that "The Palestinians must come to the table knowing that the bond between the United States and Israel is absolutely, totally unbreakable."[163]
Trump has criticized the Palestinian National Authority for the absence of peace, saying: "the Palestinian Authority has to recognize Israel's right to exist as a Jewish state. ... [and they] have to stop the terror, stop the attacks, stop the teaching of hatred ... They have to stop the teaching of children to aspire to grow up as terrorists, which is a real problem. Of course, the recognition of Israel's right to exist as a Jewish state is also a major sticking point, with the current Palestinian leadership repeatedly refusing to meet that basic condition."[164]
Capital of Israel
[edit]Trump has said on more than one occasion that if elected president he will move the U.S. embassy in Israel from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem, which he described as the "eternal capital of the Jewish people."[165][166] In an earlier speech before the Republican Jewish Coalition, Trump had refused to say whether he supports Israel's position that Jerusalem is its undivided capital.[162] Meeting with Benjamin Netanyahu in September 2016, Trump's statement said that "under a Trump administration, [we] will finally accept the long-standing Congressional mandate to recognize Jerusalem as the undivided capital of the State of Israel."[167] On December 6, 2017, Trump officially recognized Jerusalem as the capital of Israel, despite objections from Palestinian leaders. Trump added that he would initiate the process of establishing a new U.S. embassy in Jerusalem.[168]
Deal of the Century
[edit]The Deal of the Century is a proposal[169] intended to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. It is a peace plan for the Middle East made ready by United States President Donald Trump.[170] After 18 months of planning, Israel's officials have developed the proposal by visiting the four Arab capitals. However it is not ready to be presented to the public officially.[171] Palestinian leader Mahmoud Abbas described the deal as the "slap of the century."[172][173]
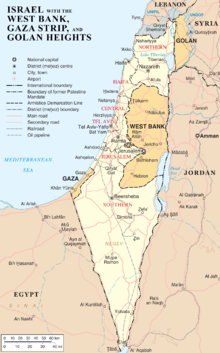
The United States tried to work on the latest "peace plan." The Palestinian Authority had been supported by the United States and its allies.[174] In fact, According to the Balfour Declaration, a national homeland for Jewish people was determined in Palestine in 1917.[175] Israel took Jerusalem from Jordan in the Six-Day War.[176] On November 29, 1947, the international community recognized the legitimacy of the establishment of an independent Palestinian state according to the UN partition plan.[177]
The term "Deal of the Century" shares a name with a 1983 American comedy film Deal of the Century which features a group of arms dealers that compete to sell weapons to a South American dictator.[171]
When Donald Trump was elected US president in November 2016, he talked about the peaceful resolution of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. He named the plan for bringing peace to Israel and Palestine the "deal of the century".[178] In September 2017, while at the UN General Assembly, US President Donald Trump and Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas had a meeting. Abbas, President of the Palestinian Authority, said that their meeting showed the US administration's efforts "to achieve the deal of the century in the Middle East during this year or in the coming months." After 76 days, that deal was canceled. Trump's decision to recognize Jerusalem as Israel's capital and move its embassy there from Tel Aviv illustrates the effect of Washington on any peace settlement.[179] In January 2018, Mahmoud Abbas gave a lecture in Ramallah and said the deal of the century presented by Trump was the peaceful solution, but when the US selected Jerusalem as Israel's capital, it turned into the slap of century.[180]
The effect returns to 40 years to the Camp David Accords. Based on this peace treaty that signed between Egypt and Israel, the request for establishing Palestinian self-government in the West Bank and Gaza was offered. After the Gulf war in 1991, President George H W Bush managed a summit of Arabs and Israelis in Madrid and a historic handshake on the White House between the Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and Chairman of the Palestinian Liberation Organization, Yasser Arafat happened. After a while President Obama's Secretary of State John Kerry try to make a better relationship between Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Abbas.[179]
The detail of deal has not been published officially but is equipped with the 35-page document from the Saudis. As Palestinian officials reported, the context of the deal is to establish a new Jerusalem for Palestinians and the security of the border would be prepared by Israel forces. The deal would provide the Palestine state with the provisional borders on half of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, without Jerusalem.[181]
Based on the poll done by Haaretz newspaper, in the result, 44 percent of the participants believe that the deal is in favor of Israelis while 7 percent believe that the deal favors Palestinians.[170][182]
Palestinian leader Mahmoud Abbas stated the aim of the deal is disarming Hamas. He also said the selection of Jerusalem as Israel's capital is the solution presented in the Deal of the Century.[183] When he met with Russia's president, Vladimir Putin, he described the deal as the "slap of the century."[172] He previously said he would reject any peace deal which was drawn up by the United States as Palestinians believe Washington's neutrality is compromised.[172]
The Iran supreme leader, Ali Khamenei, said that the deal will never be realized.[184]
Libya
[edit]In 2009, Libyan dictator Muammar Gaddafi rented space through intermediaries on Trump's Seven Springs estate in the suburb of Bedford, New York. Gaddafi rented Trump's land to camp in a "Bedouin-style" tent while in the United States to attend the UN General Assembly. The situation created controversy when the tents were raised on the property, and Trump forced Gaddafi off the property saying that he was unaware of the arrangement.[185][186][187] In 2011, Trump told Fox News that he had "screwed" Gaddafi on the deal, touting the affair as evidence of foreign-policy experience.[186]
Support for 2011 intervention
[edit]Trump was a strong supporter of the 2011 military intervention in Libya, arguing "fervently" on a number of occasions that U.S. military intervention was necessary to advert humanitarian disaster in Libya and warning that it would be "a major, major black eye for this country [the U.S.]" if it failed to depose Gaddafi.[188][189] In a February 2011 video blog, Trump said: "I can't believe what our country is doing. Qaddafi in Libya is killing thousands of people, nobody knows how bad it is, and we're sitting around we have soldiers all have the Middle East, and we're not bringing them in to stop this horrible carnage ... Now we should go in, we should stop this guy, which would be very easy and very quick."[189] Trump made similar comments in a March 2011 appearance on Piers Morgan Tonight.[189] In 2011, Trump also advocated U.S. seizure of Libyan oil.[190]
Opposition during 2016 campaign
[edit]While campaigning for the presidency in 2016, Trump reversed his earlier position, stating on several occasions that the U.S. would be "so much better off" or "100% better off" if Gaddafi remained in charge of Libya.[191][192] At a Republican primary debate in February 2016, Trump claimed that he "never discussed" the Libyan intervention at the time it occurred; Politifact noted that this assertion was "patently inaccurate" and gave it its "Pants on Fire" rating.[191] In June 2016, Trump again reversed course, saying on CBS' Face the Nation that he would have supported "surgical" bombing, against Gaddafi in particular.[193] However, during both an NBC presidential forum and a presidential debate in September 2016, Trump once again reversed his position, criticizing Hillary Clinton for her support for the 2011 military intervention.[194][195]
In May 2016, Trump suggested that the United States should bomb ISIL in Libya.[196]
Saudi Arabia
[edit]In December 2015, Trump said that the days of the Saudi Royal Family buying off American politicians will end if he is elected president.[197]
In February 2016, Trump blamed Saudi Arabia for the September 11 attacks, saying: "Who blew up the World Trade Center? It wasn't the Iraqis, it was Saudi – take a look at Saudi Arabia, open the documents."[198]
Trump has called for Saudi Arabia to pay for the costs of American troops stationed there: "They should pay us. ... The primary reason we're with Saudi Arabia is because we need the oil. Now we don't need the oil so much ...".[199] He has argued that regional allies of the United States, such as Saudi Arabia should provide troops in the fight against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL). Trump said he would halt oil imports from Saudi Arabia unless the Saudi government provide ground troops to defeat ISIL.[200]
In June 2016, Trump demanded that Hillary Clinton should give back donations the Clinton Foundation had accepted from Saudi Arabia. Trump wrote: "Saudi Arabia and many of the countries that gave vast amounts of money to the Clinton Foundation want women as slaves and to kill gays. Hillary must return all money from such countries!"[201]
Syrian Civil War, Iraq and ISIL
[edit]Trump's positions on defeating the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) frequently changed throughout his presidential campaign.[202] Trump has claimed that he would "bomb the hell" out of Iraqi oil fields controlled by ISIL.[14][203] In the aftermath of the November 2015 Paris attacks, which were committed by ISIL, Trump reiterated his statements about ISIL from November 12, 2015, when he stated he would "bomb the shit out of 'em"[204] and said "I'd blow up the [oil] pipes, I'd blow up the refineries, and you know what, you'll get Exxon to come in there in two months ... and I'd take the oil."[205] Trump said in an interview with Anderson Cooper "There is no Iraq. Their leaders are corrupt."[204] In 2015 when asked how he would deal with Iraq's condemnation of strikes on their oil fields, Trump replied that Iraq is a corrupt country that is not deserving of his respect.[14] Trump said that to combat ISIL, "I would find you a proper general. I would find a Patton or a McArthur. I would hit them so hard your head would spin."[14]
Trump's first post-announcement interview on June 17, 2015, was with Bill O'Reilly on The O'Reilly Factor.[14] One of several issues he highlighted was his proposed strategy in dealing with the Syrian Civil War.[14] In the interview, Trump stated: "Iran and Russia are protecting Syria and it's sort of amazing that we're in there fighting ISIS in Syria so we're helping the head of Syria [Bashar al-Assad] who is not supposed to be our friend although he looks a lot better than some of our so-called friends."[14] Instead of fighting ISIL in Syria, Trump suggested "maybe Syria should be a free zone for ISIS, let them fight and then you pick up the remnants."[14]
In a Republican primary debate in November 2015, Trump said he "got to know [Vladimir Putin] very well because we were both on '60 Minutes', we were stable mates, we did well that night." Trump said he approved of the Russian military intervention in Syria, stating: "If Putin wants to knock the hell out of ISIS, I'm all for it 100 percent and I can't understand how anybody would be against that ... He's going in and we can go in and everybody should go in."[206] During his speech at the Oklahoma State Fair, Trump accused his opponents of wanting to "start World War III over Syria."[15]
Trump stated in November 2015, "I know more about ISIS than the generals do. Believe me."[207]
When asked in the March 11 CNN debate if he would send ground troops to fight ISIL, Trump answered, "We really have no choice. We have to knock out ISIS."[208] When pressed on specific numbers, Trump answered, "I would listen to the generals, but I'm hearing numbers of 20,000 to 30,000. We have to knock them out fast."[208] Later that month, he retracted that statement, saying that he would "never ever" deploy 20,000 to 30,000 U.S. troops to combat ISIL.[209] In June 2016, Trump stated that he "[likes] the idea of using NATO and also neighbors that aren't in NATO" to "take [ISIL] out" and that "it's very possible that we should use NATO" to fight ISIL.[210]
In an interview, Trump stated "You have to take out their families, when you get these terrorists, you have to take out their families. ... When they say they don't care about their lives, you have to take out their families." When pressed on what "take out" meant, Trump said the U.S. should "wipe out their homes" and "where they came from."[211] The intentional targeting of non-combatants is a violation of the Geneva Conventions and other aspects of the international law of war.[212] Jonathan Russell, head of policy for the anti-radicalization think tank Quilliam, warned that Trump's "anti-Muslim rhetoric" helps ISIL's narrative, saying "Trump will contribute to Islamist radicalization as his comments will make Muslims feel unwelcome in America. This grievance will fuel their identity crisis, which when combined are a potent combination for the vulnerability that ISIS is so adept at exploiting with their Islamist narrative."[213]
During his presidential campaign, Trump has repeatedly criticized the battle to liberate Mosul from ISIL control, saying that the United States is "not going to benefit" from dislodging ISIL from the Iraqi city. Trump has repeatedly asserted that U.S. and Iraqi military leaders should have used "the element of surprise" to attack Mosul rather than announcing plans beforehand. He also said that U.S. military planners were "a group of losers" for not doing so.[214][215] U.S. military officials "strongly rebuked" Trump's comments, noting that "it is nearly impossible to move tens of thousands of troops into position without alerting the enemy" and that it was vital to warn civilians of impending military action.[214]
During the presidential debate on October 9, 2016, Trump suggested he differed on his vice-presidential nominee Mike Pence's support for airstrikes against the Syrian regime, stating "he and I haven't spoken and I disagree."[216]
On February 16, 2017, President Trump's Secretary of Defense, James Mattis, declared that the United States was not currently prepared to collaborate with Russia on military matters – including future anti-ISIL US operations.[217]
The Trump administration has taken a different stance from the previous Obama administration on the issue of the Syrian Civil War, with UN Ambassador Nikki Haley and Secretary of State Rex Tillerson both stating in March 2017 that the United States would no longer prioritize the removal of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad from office, in line with Trump's stance during his campaign.[218]
During a joint press conference on April 5, 2017, with King Abdullah II of Jordan in the aftermath of the 2017 Khan Shaykhun chemical attack, Trump stated "my attitude toward Syria and Assad has changed very much" and that the attack "crossed many, many lines." He accused the Obama administration's decision not to follow through with its proposed 2013 military intervention against the Assad regime in Syria of having led to the chemical attack.[219]
On April 7, 2017, Trump ordered the United States Navy to launch cruise missiles at Shayrat Air Base in response to the Khan Shaykhun chemical attack. The response had wide international support[220] and was highly praised by the majority of Republicans as well as Democratic senators,[221] and many countries, however it drew criticism from Russia, who the United States had warned in advance about the attack. Although Russian anti-missile defenses such as S-300's failed to deter the missile attack, Russian forces suffered minimal damage, as the United States had intended to avoid striking areas of the base used by Russia.[222] Russian Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev called the strike "good news for terrorists".[223]
Many right-wing/leaning populist media figures who supported Trump during the election criticized Trump's reversal of policy towards war in Syria and the Middle East.[224][225][226][227] Ann Coulter pointed out that Trump "campaigned on not getting involved in Mideast" and this was one of the reasons many voted for him.[224]
Accusations regarding Obama administration's role
[edit]In the aftermath of the Orlando nightclub shooting in June 2016, Trump accused the Obama administration that it has actively "supported" the Islamic extremist group that became ISIL, an assertion rated "Pants on Fire" by PolitiFact (which quoted experts describing the claim as a "transparently fallacious conspiracy theory") and given "Four Pinocchios" by The Washington Post fact-checker (which described it as a "bizarre claim").[228][229]
In August 2016, Trump repeatedly and falsely asserted that President Barack Obama was the "founder" of ISIL.[230][231][232] In an interview with conservative radio host Hugh Hewitt, Trump responded to Hewitt's attempt to reframe Trump's comment as one that said Obama's foreign policy created the conditions in Iraq and Syria that allowed ISIL to thrive, by saying "No, I meant he's the founder of ISIS. I do. ... He was the founder. The way he got out of Iraq—that was the founding of ISIS, OK?"[229][233][a] The Associated Press noted that the claim is "patently false," ISIL expert Joby Warrick referred to it as a "ludicrous claim,"[230] and PolitiFact rated the claim as "Pants on Fire" false, calling it "ridiculous."[232] ISIL in fact predates the Obama presidency,[230][232] with roots beginning in 2004.[232] Former U.S. Ambassador to Russia Michael McFaul wrote that Trump's accusation that the United States created ISIL "echoes exactly a myth propagated by Russian state-controlled media and bloggers."[233] Two days after Trump said that Obama had founded ISIL, and a day after he insisted that he meant what he said, Trump said that he was being sarcastic.[234] Later that day, Trump muddied his meaning, saying both that he was "being sarcastic. But not that sarcastic, to be honest with you."[235]
On April 7, 2017, the United States launched 59 cruise missiles at Shayrat Air Base.[236]
Many right-wing/-leaning populist media figures criticized Trump's reversal of policy towards war in Syria and the Middle East.[224][225][226][227] Ann Coulter pointed out that Trump "campaigned on not getting involved in Mideast" and this was one of the reasons many voted for him.[224]
Turkey
[edit]Regarding the 2016 coup attempt in Turkey, Trump said in a July 2016 interview, "I give great credit to [Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan] for being able to turn that around."[1] When asked if Erdoğan was exploiting the coup attempt to purge his political enemies, Trump did not call for the Turkish leader to observe the rule of law, or offer other cautions for restraint. He said that the United States had to "fix our own mess" before trying to change the behavior of other countries.[1]
Trump stated in the July 2016 interview that he believed he could persuade Erdoğan to step up efforts against ISIL.[1] When asked how he would solve the problem of Turkish attacks on Kurds who are fighting ISIL, Trump said "Meetings."[1]
In May 2017, Turkish state bodyguards attacked U.S. protestors in Washington, D.C. The bodyguards responsible were not charged with crimes until nearly a month later, and the charges were dropped in March 2018 before a meeting between Rex Tillerson and Erdogan.[237][238]
EU and Europe
[edit]European Union
[edit]In a July 2016 interview, Trump said of the European Union, "the reason that it got together was like a consortium so that it could compete with the United States."[239] U.S. foreign-policy experts such as Strobe Talbott and Amie Kreppel noted that this was incorrect, pointing out that while the EU was established in part to rebuild the European economies after World War II, it was not created specifically to compete with the United States. In fact the United States sanctioned the EU's creation to foster peace, prevent another catastrophic war, and create a "strong European market to consume American-made goods to help fuel American economic growth."[240]
France
[edit]In their first telephone call, President Trump told French President François Hollande that he "loved France" and that there was "no more beautiful country than France".[241] However, in his 2017 CPAC speech, President Trump said, "France is no longer France" because of terrorism.[241][242] In response, President Hollande said allies should not criticize each other,[242] and he invited him to visit Disneyland Paris.[241]
Germany
[edit]During the campaign Trump was critical of German chancellor Angela Merkel and her handling of the European migrant crisis, saying "Everyone thought she was a really great leader and now she's turned out to be this catastrophic leader. And she'll be out if they don't have a revolution."[243] In July 2016, German Foreign Minister Frank-Walter Steinmeier stated that he was concerned about what he sees as Trump's contradictory promises to "make America strong again" while simultaneously reducing involvement overseas.[244] Steinmeier said that Trump's proposed policies "would be dangerous not only for the United States, but for Europe and the rest of the world as well".[244]
After becoming president, Trump met with Merkel at the White House on March 17, 2017. The meeting was described as "awkward"; Trump failed to shake hands with Merkel for a photo op, and he made a joke about wiretapping.[245][246] The two "politely disagreed on everything from immigration to free trade and the value of seeking multinational agreements."[247]
Ireland
[edit]United Kingdom
[edit]In regards to British voters voting to leave the European Union, Trump stated, "I think it's a great thing that happened ... Basically they took back their country. That's a good thing."[248] One reason that Trump was enthusiastic about the outcome of the vote was that it lowered the value of the British pound, which was good for business at his golf course in Scotland.[249] Trump had expressed support for the "leave" side during the Brexit campaign.[250][251][252] In an interview with Piers Morgan in May 2016, Trump said that UK withdrawal would make no difference to a potential bilateral trade deal between the United Kingdom and the United States if he became president: "I am going to treat everybody fairly but it wouldn't make any difference to me whether they were in the EU or not. ... You would certainly not be back of the queue, that I can tell you."[253]
Trump said in May 2016 that if elected president, he would be unlikely "to have a very good relationship" with then-British Prime Minister David Cameron, citing Cameron's criticism of him.[84][254] Trump subsequently said "I'm sure I'll have a good relationship with him."[84]
At a Trump rally in August 2016, Nigel Farage, a former leader of the UK Independence Party and the Brexit campaign in the UK, compared the support that Trump has received in the United States with the movement that led to the vote by the UK to withdraw from the EU.[255]
In November 2017, Trump retweeted provocative and false information from Jayda Fransen, deputy leader of far-right nationalist party Britain First, drawing condemnation from all political parties in the United Kingdom. Trump later tweeted to Prime Minister May, suggesting that she not worry about what he retweeted and focuses on supposed problems stemming from Muslim immigration to the United Kingdom.[256]
Russia and Ukraine
[edit]Russia
[edit]Background
[edit]In a July 2016 interview, Trump stated that he would consider recognizing Crimea as Russian territory and lifting sanctions on Russia that were imposed after Russia began aiding self-proclaimed separatist republics in eastern Ukraine seeking to undermine the new, pro-Western Ukrainian government.[257] He added that Russia could help the United States in fighting the ISIS terror organization.[258] In another July 2016 interview he added to this "You know the people of Crimea, from what I've heard, would rather be with Russia than where they were, and you have to look at that also."[259] Former NSA director and CIA director Michael Hayden denounced Trump's comments as "devoid of facts and divorced from traditional American, traditionally European policy."[260]
Trump has praised Russian President Vladimir Putin over a series of years, developing what CNN called a "long-established track record of ... fondness for the autocratic Russian leader."[261] In October 2007, Trump told Larry King that Putin was doing a "great job in rebuilding the image of Russia and also rebuilding Russia period."[261] In December 2011, Trump published his book Time to Get Tough, in which he praised Putin's "intelligence" and "non-nonsense" and expressed "respect" for Putin and the Russians.[261] In July 2016, Trump called Putin "a better leader" than U.S. President Barack Obama.[262] In 2013, Trump wondered over Twitter whether Putin would attend the Miss Universe 2013 pageant in Moscow and "become my new best friend."[261] In October 2013, Trump said that Putin was outsmarting the United States[261] On multiple occasions in 2015, Trump said that he would "get along very well" with Putin.[261] Beginning in 2015, Trump also stated of Putin, "I got to know him very well because we were both on 60 Minutes, we were stablemates." Trump repeated the "stablemates" characterization in a number of interviews and rallies, although the two men were interviewed at different times in different countries.[261]
Putin has praised Trump, saying in December 2015: "He is a very bright and talented man, no doubt about that." Trump has repeatedly claimed that Putin has called him a "genius," a mischaracterization based on an incorrect translation;[263] in fact, Putin used the Russian word яркий (yarkii), meaning "bright" in the sense of colorful, vivid, or flamboyant.[264][265] Trump returned the praise (saying "It is always a great honor to be so nicely complimented by a man so highly respected within his own country and beyond") and shrugged off allegations of Putin's alleged assassination of journalists and dissidents by saying that Putin is "running his country and at least he's a leader, unlike what we have in this country. I think our country does plenty of killing also."[261][266]
In response to a question in October 2015 about the Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 shootdown and the U.S. intelligence community's "confident" assessment that pro-Russian separatists shot it down, Trump responded, "Putin and Russia say they didn't do it, the other side said they did, no one really knows who did it, probably Putin knows who did it. Possibly it was Russia but they are totally denying it."[267] In the second presidential debate, Trump said that he did not know whether Russia is trying to influence the U.S. presidential election through hacking; he was however personally briefed on Russia's role in the hacks by U.S. officials.[268] In the first presidential debate, Trump pondered that "it could be Russia, but it could also be China"; he had at that time also been briefed about and discussed extensively with US intelligence officials the Russian government's attempts to interfere in the 2016 election.[268]
Rossiya 1 (Russian state TV) has backed Trump, hailing him as an "anti-establishment" candidate who is ready to cooperate with Moscow.[269] Trump has also been praised by RT (formerly Russia Today), a Russian government-funded TV network.[270] In October 2016, Trump recited a falsified story that may have originated in the Russian government-controlled news agency Sputnik—which "has a reasonably large [U.S.] audience"—at a rally to attack Hillary Clinton; according to Jon Passatino of BuzzFeed, however, "the source of Trump's comments ... may have been a tweet from earlier in the day which included the precise language Trump read" rather than Sputnik.[271][272][273]
Trump chose the Center for the National Interest, which is viewed as one "of the most Kremlin-sympathetic institutions in the nation's capital," as the venue for his first major foreign-policy speech.[274] In the speech, Trump "made no mention of the threat Russia poses in Europe although he made a vague reference to 'serious differences' with Russia and China."[275]
Trump has argued that a "lack of respect" by the Russians for President Barack Obama encourages the Russians to engage in seemingly hostile air maneuvers against the U.S. in European waters.[276] Trump has stated that the U.S. should open fire on Russian planes if Russia rejects calls to stop the approaches. Secretary of State John Kerry has indicated that the U.S. would be within its rights to do so.[276]
Trump criticized former Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev as not having "a firm enough hand" controlling Russia, mentioning China for effectively handling the situation during the Tiananmen Square massacre, saying: "they were horrible, but they put it down with strength. That shows you the power of strength."[277]
The Politico Magazine in August 2016 wrote that Trump's stance on Russia's involvement in Ukraine might have been changed in 2016 as a result of counsel he drew from newcomers to his orbit who were said to be "sympathetic to Russian influence in Ukraine", such as Paul Manafort, Carter Page, and Henry Kissinger.[278] Manafort formerly provided public relations services to Viktor Yanukovych, the pro-Russian president of Ukraine who was deposed in the 2014 Ukrainian revolution.[279][280][281] In August 2016, The New York Times reported that Manafort received $12.7 million in undisclosed cash payments from Yanukovych's political party from 2007 to 2012.[282] The Associated Press reported that Manafort secretly routed at least $2.2 million (~$2.89 million in 2023) in payments to two prominent Washington lobbying firms in 2012 for Yanukovych's part, and did so in a way that effectively obscured the foreign political party's efforts to influence U.S. policy.[283] Manafort joined Trump's campaign in late March 2016, became campaign chairman in May, took control of Trump's campaign in June (following the firing of campaign chairman Corey Lewandowski), and resigned from the campaign in August, following scrutiny over his Ukraine ties.[284][285] Another Trump foreign policy advisor, retired Lt. General Michael T. Flynn, appeared in a photograph with Putin at a banquet celebrating the RT network.[279][280][281][286] Richard Burt reportedly helped shape Donald Trump's first foreign policy speech; Burt was at the same time working as a lobbyist on behalf of a Moscow-controlled gas company.[287]
Trump viewed as under Putin's influence
[edit]The Steele dossier alleges that the Russians possess kompromat on Trump which can be used to blackmail him, and that the Kremlin promised him that the kompromat will not be used as long as he continues his cooperation with them.[288][289] Trump's actions at the Helsinki summit in 2018 "led many to conclude that Steele's report was more accurate than not.... Trump sided with the Russians over the U.S. intelligence community's assessment that Moscow had waged an all-out attack on the 2016 election,... The joint news conference,.. cemented fears among some that Trump was in Putin's pocket and prompted bipartisan backlash."[290]
At the joint news conference, when asked directly about the subject, Putin denied that he had any kompromat on Trump. Even though Trump was reportedly given a "gift from Putin" the weekend of the pageant, Putin argued "that he did not even know Trump was in Russia for the Miss Universe pageant in 2013 when, according to the Steele dossier, video of Trump was secretly recorded to blackmail him."[291]
In reaction to Trump's actions at the summit, Senator Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.) spoke in the Senate:
Millions of Americans will continue to wonder if the only possible explanation for this dangerous and inexplicable behavior is the possibility—the very real possibility—that President Putin holds damaging information over President Trump.[292]
Several operatives and lawyers in the U.S. intelligence community reacted strongly to Trump's performance at the summit. They described it as "subservien[ce] to Putin" and a "fervent defense of Russia's military and cyber aggression around the world, and its violation of international law in Ukraine" which they saw as "harmful to US interests". They also suggested that he was either a "Russian asset" or a "useful idiot" for Putin,[293] and that he looked like "Putin's puppet".[294] Former Director of National Intelligence James Clapper wondered "if Russians have something on Trump",[295] and former CIA director John O. Brennan, who has accused Trump of "treason", tweeted: "He is wholly in the pocket of Putin."[296]
Former acting CIA director Michael Morell has called Trump "an unwitting agent of the Russian federation", and former CIA director Michael V. Hayden said Trump was a "useful fool" who is "manipulated by Moscow".[297] House Speaker Nancy Pelosi questioned Trump's loyalty when she asked him: "[Why do] all roads lead to Putin?"[298]
Ynet, an Israeli online news site, reported on January 12, 2017, that U.S. intelligence advised Israeli intelligence officers to be cautious about sharing information with the incoming Trump administration, until the possibility of Russian influence over Trump, suggested by Steele's report, has been fully investigated.[299]
Trump Administration (2017–2021)
[edit]On February 6, 2017, talking to Bill O'Reilly on the Fox News Trump questioned the veracity O'Reilly's claim that ″within 24 hours of you on the phone with the Russian leader, the pro-Russian forces step[ed] up the violence in Ukraine″, said he ″respected″ Putin and dismissed O'Reilly's statement that Putin was a ″killer″,[300][301] which prompted CNN to opine that Trump had "appeared to equate U.S. actions with the authoritarian regime of Russian President Vladimir Putin."[302]
On February 16, Secretary of State Rex Tillerson had a meeting with his Russian counterpart Sergey Lavrov in Bonn, Germany; Tillerson told the press afterwards, "As we search for new common ground, we expect Russia to honor its commitment to the Minsk agreements and work to de-escalate the violence in Ukraine".[303] Sergey Lavrov said the meeting was productive, and added that Moscow was ready to work with Washington on all issues as soon as Donald Trump's foreign policy team was fully formed.[citation needed]
Ukraine
[edit]At the Conservative Political Action Conference in March 2014, Trump stated that Putin was taking "the heart and soul" of Ukraine because he believed Crimea was "where all the money is" and went on to predict "the rest of Ukraine will fall and it's predicted to fall fairly quickly."[304] Later that month, Trump stated that the Russian takeover of Crimea "should never have happened."[304]
In July 2015 Trump opposed U.S. involvement in the Ukrainian crisis (in a rally in July 2016 he implied that this could have led to World War III[305]), describing Crimea as "Europe's problem."[306] In July 2016, Trump stated that he would "look into" recognizing Crimea as Russian territory.[307] In a subsequent interview in July 2016, Trump claimed that Putin isn't going to go into Ukraine, saying "He's not going into Ukraine, okay, just so you understand. He's not gonna go into Ukraine, all right? You can mark it down."[259] When informed that the Russian military has intervened in Ukraine since 2014, Trump responded, "Okay, well, he's there in a certain way".[259] In the same interview Trump also again stated he would "look into" recognizing Crimea as a Russian territory and added to this "You know the people of Crimea, from what I've heard, would rather be with Russia than where they were, and you have to look at that also."[259]
In August 2015 Trump stated he "did not care" about Ukrainian membership in NATO,[308] saying that both membership and non-membership would be "great."[309]
Speaking to the Yalta European Strategy conference in September 2015, Trump criticized Germany and other European countries for not doing enough to support Ukraine in its conflict with Russia, saying, Ukrainians are "not being treated right."[308] He also stated that because Russian President Putin did not respect President Obama Russia had pursued an aggressive policy in Ukraine.[309] In March 2016 Trump again claimed that Germany and other NATO countries "they're not doing anything" while the U.S. was "doing all of the lifting" even though "Ukraine is a country that affects us far less than it affects other countries in Nato".[310] In February 2017 Trump stated in a tweet that Crimea was taken by Russia by force and asked whether Obama was too soft on Russia.[311]
On December 22, 2017, the U.S. agreed to supply Ukraine with more lethal weapons, including Javelin anti-tank missiles.[312] A Russian diplomat said the move will fuel the conflict in the country's east.[313]
The Balkans
[edit]Trump opposed the 1995 NATO intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina.[314]
In an interview on October 8, 1999, Trump criticized the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, saying that he "would have done it a little bit differently," instead advocating a military intervention involving ground troops.[315] In his 2000 book, The America We Deserve, he questioned the necessity of the intervention itself, claiming there was a possibility of a diplomatic solution with the Serbs prior to their invasion of Kosovo and noting "we could have been in deep trouble in Kosovo."[316] However, in October 2015, he indicated he had no objection to the intervention when asked about his views on it, stating "it's OK, sure."[317]
In July 2018, Trump was asked a question on the United States being required to defend fellow NATO member Montenegro if they were attacked. Trump described Montenegrins as "very aggressive people. They may get aggressive, and congratulations, you're in World War Three".[318]
NATO
[edit]In his 2000 book, The America We Deserve, Trump argued that European countries used NATO as a pathway to place the burden of international responsibility on the United States while "their conflicts are not worth American lives. Pulling back from Europe would save this country millions of dollars annually."[309]
In a March 2016 interview with CNN, Trump called for a "rethink" of American involvement in NATO, stating that the United States pays too much to ensure the security of allies, stating that "NATO is costing us a fortune, and yes, we're protecting Europe with NATO, but we're spending a lot of money".[319] Later in the same interview, he stated that the U.S. should not "decrease its role" in NATO but rather should decrease U.S. spending in regards to the organization.[320] In May 2016, based on his previous statements, the Annenberg Public Policy Center's FactCheck.org has assessed that Trump might be willing to leave NATO unless changes are made to the alliance.[321]
In a July 2016 interview, Trump "explicitly raised new questions about his commitment to automatically defend NATO allies," questioning whether he, as president, would automatically extend security guarantees to NATO members.[1] Asked about a prospective Russia attack on NATO's Baltic members, Trump stated that he would decide whether to come to their aid only after reviewing whether those nations "have fulfilled their obligations to us."[1] This would represent a sharp break with U.S. foreign traditions.[1][322]
Trump's remarks on NATO alarmed U.S. allies in Europe as well as experts such as Michael McFaul, who stated that "We have had decades of bipartisan commitment to NATO, which has made it the greatest alliance in history. Trump is now threatening that."[323] A number of experts said that Trump's suggested limitations on the collective security (Article 5) provision of the NATO treaty risk unraveling the alliance or making it obsolete.[323]
On September 28, when Trump met with the Polish National Alliance, Trump stated: "As president I will honor Poland's sacrifices for freedom. We're committed to a strong Poland, very committed, totally committed, and a strong Eastern Europe as a bulwark for freedom and security." Along with stating: "We want NATO to be strong which means we want more nations to follow the example of Poland."[324]
One day after his first meeting with German Chancellor Angela Merkel Trump tweeted, "Germany owes vast sums of money to NATO & the United States must be paid more for the powerful, and very expensive, defense it provides to Germany!"[325]
United Nations
[edit]In 2005, Trump praised the United Nations, saying he was "a big fan, a very big fan, of the United Nations and all it stands for".[326] In March 2016, Trump criticized the United Nations, saying that it was weak, incompetent, and "not a friend of democracy ... freedom ... the United States ... Israel".[326]
On October 13, 2017, President Donald Trump made the decision to withdraw by the end 2018 from U.N.'s cultural heritage Organization UNESCO, citing it as 'Anti-Israel Bias."[327] The State department stated that it will remain as a nonmember observer state, allowing the United States to engage in UNESCO activities but not be able to vote.[328] The U.S. has already stopped funding the organization in 2011 due to the admission of Palestine as a full member of the UNESCO.[327]
Nuclear proliferation
[edit]Japan and South Korea
[edit]Trump has expressed support for South Korea and Japan having nuclear weapons if they would be unwilling to pay the United States for security.[329][330][331][332] He has also deemed it inevitable, "It's going to happen anyway. It's only a question of time. They're going to start having them or we have to get rid of them entirely."[329]
Political scientists Gene Gerzhoy and Nick Miller write that the idea the nuclear proliferation is inevitable and good for the United States flies "in the face of a wide range of recent scholarship."[333] Richard Nephew, a fellow with the Center on Global Energy Policy at Columbia University, states: "The prevailing, bipartisan and fairly settled academic judgment has been that the risk of loose nukes or accidental nuclear war means that every additional nuclear weapon is a potential cataclysm waiting to happen. I'm not aware of anyone that I'd deem to be a serious policy proponent or thinker who has seriously advocated this in a while."[334]
When asked in a March 2016 interview with The New York Times whether he would object if Japan and South Korea "got their own nuclear arsenal, given the threat that they face from North Korea and China", Trump said that if the United States could no longer pay for protecting the two states, it could mean that Japan and South Korea would go nuclear.[330] Trump added, "if Japan had that nuclear threat, I'm not sure that would be a bad thing for us."[330] In an interview with Fox News, Trump said that "maybe they would in fact be better off if they defend themselves from North Korea ... including with nukes."[331] Referring to a Japan armed with nuclear weapons, Trump said, "the case could be made, that let them protect themselves against North Korea. They'd probably wipe them out pretty quick."[332]
In June 2016, after Hillary Clinton said that Trump had "encouraged" Japan to have nuclear weapons, Trump reversed himself on the issue, saying that he did not favor Japanese acquisition of nuclear weapons and accusing Clinton of misrepresenting his position.[335] PolitiFact reported that Clinton's statement was "mostly true," stating that: "Trump used vague and contradictory language, but it's a fair reading to say his words amounted to encouragement. On more than one occasion, Trump publicly said that Japan, and the United States, might be better off if Japan had nuclear weapons, and he declined multiple attempts by interviewers to backtrack from that view."[334]
Saudi Arabia
[edit]In March 2016, Anderson Cooper asked, "Saudi Arabia, nuclear weapons?" Trump answered: "Saudi Arabia, absolutely." Cooper then asked, "You would be fine with them having nuclear weapons?" Trump responded, "No, not nuclear weapons, but they have to protect themselves or they have to pay us."[329]
Pakistan
[edit]Trump has been critical of Pakistan, comparing it to North Korea, calling it "probably the most dangerous country" in the world, and claiming that Pakistan's nuclear weapons posed a "serious problem." He has advocated improving relations with India as a supposed "check" to Pakistan. He has said that his government will fully cooperate with India in doing so.[336]
Other security topics
[edit]Internet and computer security
[edit]Trump said in a December 2015 rally, "We have to see Bill Gates and a lot of different people that really understand what's happening. We have to talk to them about, maybe in certain areas, closing that Internet up in some ways. Somebody will say, 'Oh freedom of speech, freedom of speech.' These are foolish people."[337][338] In a Republican debate in December 2015, Trump said that the Internet should be shut off to countries that have a majority of their territory controlled by terrorist organizations.[339]
Nuclear weapons
[edit]In his announcement speech, Trump said that the U.S.'s control is getting weaker and that its nuclear arsenal is old and does not work, although he appeared to be unfamiliar with the term "nuclear triad" when asked by Hugh Hewitt in a December 2015 debate what specific improvements he would make.[340] Trump's answers in the September 28 debate to Lester Holt's questions were perceived as being ambiguous and confusing "first strike" and "first use".[341][342][343]
When asked in a March 2016 town hall meeting with MSNBC's Chris Matthews whether he would rule out the use of nuclear weapons, Trump answered that the option of using nuclear weapons should never be taken off the table.[344][345][346]
Seizure of other nations' oil reserves
[edit]Before his campaign for the presidency, during the campaign and after taking office, Trump has spoken in favor of seizing the oil reserves of other countries. In 2011, he advocated U.S. seizure of Libyan oil.[190] In November 2015, he seizing the oil fields controlled by ISIS in Iraq: "I'd blow up the [oil] pipes, I'd blow up the refineries, and you know what, you'll get Exxon to come in there in two months ... and I'd take the oil."[347] In September 2016, he advocated that the United States should "take the oil" in Iraq as part of the "spoils of war" and to keep it out of the hands of ISIS.[348] He elaborated, "You're not stealing anything," Trump said. "We're reimbursing ourselves ... at a minimum, and I say more. We're taking back $1.5tn to reimburse ourselves."[349]
Trump reiterated his support for seizing other nations' oil after taking office as president. In January 2017, he said that the United States "should have kept the oil" after the Iraq invasion and "maybe we'll have another chance".[350] In February 2017, Trump reiterated his support for seizing other nations' oil: "We've spent $6 trillion ... in the Middle East ... We've got nothing. We've got nothing. We never even kept a small, even a tiny oil well. Not one little oil well. I said, 'Keep the oil.'"[351]
Experts note that seizing the oil wealth of sovereign nations is a violation of the Geneva Convention and would be considered a war crime. It would also require a considerable ground troops presence, and most likely increase the local population's hostility towards the United States.[348][349][350]
Waterboarding, torture, and interrogation
[edit]During 2016, Trump has called for the resumption of waterboarding,[352][353][354][355][356] and has repeatedly expressed support for the use of torture by the U.S. for the purpose of trying to get information from terrorists,[352][353][357] if Congress allows it.[357][358] On one occasion, Trump has called waterboarding "your minimal form of torture";[352] on another occasion he has said, "Nobody knows if it's torture".[359] Whether waterboarding is torture or not, Trump supports broadening the laws to allow waterboarding.[357][358][360] Many experts believe that waterboarding would be illegal without a change in the laws, including a group of foreign policy experts who published a letter in Foreign Policy magazine to that effect in March 2016.[361]
On the effectiveness of torture, Trump has said: "Don't tell me it doesn't work—torture works"[353] and "we have to beat the savages".[357] Trump has also said:
I'd go through a process and get it declassified [as a war crime], certainly waterboarding at a minimum. They're chopping off heads of Christians and many other people in the Middle East. ... They laugh at us when they hear that we're not going to approve waterboarding ... I have no doubt that it does work in terms of information and other things, and maybe not always, but nothing works always.[355][362]
Moreover, he says, if waterboarding "doesn't work, they deserve it anyway, for what they're doing".[363] Trump's statement that "torture works" runs counter to a 2014 Senate Intelligence Committee report on CIA torture, in which a majority of the committee's members concluded that the CIA's use of enhanced interrogation techniques was "not an effective means of acquiring intelligence or gaining cooperation from detainees".[364] But, there is strong public support for the proposition that torture can be justified to obtain information about terrorism.[365] Many people in the CIA favor interrogation that goes beyond the current limitations in the United States Army Field Manuals, and they find it ironic that the U.S. has softened interrogations of terrorists while increasingly killing them by drone strikes, though others in the CIA are unwilling to risk more fallout from coercive interrogations.[366]
At a Republican primary debate in March 2016, when asked whether the U.S. military would obey orders to torture in violation of international law, Trump stated: "Frankly, when I say they'll do as I tell them, they'll do as I tell them".[358] The following day, Trump said that he would "not order military or other officials to violate those laws and will seek their advice on such matters".[358] Several weeks later, Trump called for a change in the law to legalize "the waterboarding thing". Trump referred to those who "came up with this international law" as "eggheads" and said that the current legal limitations were "probably a political decision" rather than based upon military advice.[358][360]
Trump is in favor of sending terrorist suspects to Guantanamo Bay.[367] Trump has said he would like to "load it up with bad dudes."[367]
Action against terrorists' families
[edit]In a 2015 interview, Trump stated "You have to take out their families, when you get these terrorists, you have to take out their families. ... When they say they don't care about their lives, you have to take out their families." When pressed on what "take out" meant, Trump said the United States should "wipe out their homes" and "where they came from."[211] The intentional targeting of non-combatants is a violation of the Geneva Conventions and other aspects of the international law of war.[212]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h Sanger, David E.; Haberman, Maggie (July 21, 2016). "Donald Trump Sets Conditions for Defending NATO Allies Against Attack". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved July 21, 2016.
- ^ Seldin, Jeff (December 18, 2017). "Trump National Security Strategy Aims to 'Regain Momentum'". VOA.
- ^ The Editorial Board (December 19, 2017). "The Trump Doctrine, in Theory". Wall Street Journal.
- ^ C. Eugene Emery Jr., Hillary Clinton says Donald Trump has called the U.S. military 'a disaster', PolitiFact (July 29, 2016).
- ^ Louis Jacobson, Rear Adm. John Hutson says Donald Trump 'called the military that I served in a disaster', PolitiFact (July 27, 2016).
- ^ Tyler Pager, Gen. John Allen backs Clinton in hawkish rebuke of Trump, Politico (July 28, 2016).
- ^ Jose A. DelReal, A retired general spoke forcefully for Clinton. Now Trump is attacking him, The Washington Post (July 30, 2016).
- ^ Cristiano Lima, Trump rips 'failed' Gen. Allen in rebuttal to DNC criticism, Politico (July 29, 2016).
- ^ "'Hannity on the Road': Donald Trump". Fox News. March 9, 2016. Retrieved July 24, 2016.
- ^ "Transcript: Donald Trump's Foreign Policy Speech". The New York Times. April 27, 2016. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved July 14, 2016.
- ^ a b Leo Shane III (April 27, 2016). "Trump promises to rebuild the military, make allies pay more". Military Times.
- ^ a b Ellen Mitchell (June 9, 2016). "Trump convenes meeting with top defense lobbyists". Politico.
- ^ "Trump's military spending flip-flop". Politico. August 5, 2016. Retrieved August 5, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Donald Trump running for President". The O'Reilly Factor. June 17, 2015. Retrieved September 29, 2015.
- ^ a b Johnson, Jenna (September 25, 2015). "Donald Trump: Let Russia fight the Islamic State in Syria". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Donald Trump: "I want to make the country great again"". The Kelly File. Fox News. May 21, 2015. Archived from the original on July 13, 2016. Retrieved January 25, 2017.
- ^ a b Trump, Donald (June 16, 2015). "Full text: Donald Trump announces a presidential bid". The Washington Post.
- ^ Trump sets record for longest 2016 GOP announcement speech . Fox News Channel, June 16, 2015
- ^ Thomas Wright (January 20, 2016). "Trump's 19th Century Foreign Policy". Politico.
- ^ "Japan-U.S. security alliance not fair, Donald Trump says". The Japan Times. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ "Donald Trump says South Korea doesn't pay United States for troop presence". PolitiFact. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ Hensch, Mark (January 5, 2016). "Trump: 'I would want to protect Saudi Arabia'". The Hill.
- ^ Trump's New Russia Adviser Has Deep Ties to Kremlin's Gazprom March 30, 2016
- ^ "Here's who Donald Trump is taking foreign policy advice from". Los Angeles Times. ISSN 0458-3035. Retrieved May 31, 2016.
- ^ Rappeport, Alan (March 22, 2016). "Top Experts Confounded by Advisers to Donald Trump". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved May 31, 2016.
- ^ a b "Trump being advised by ex-U.S. Lieutenant General who favors closer Russia ties". Reuters. February 26, 2016. Retrieved July 20, 2016.
- ^ a b c "Lt. Gen. Flynn: I'm trying to improve Trump's foreign policy talk". Politico. May 19, 2016. Retrieved July 20, 2016.
- ^ "A curveball in Trump's Veep search: He's seriously considering a retired general". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 20, 2016.
- ^ a b c "Trump's foreign policy team baffles GOP experts". Politico. March 21, 2016. Retrieved May 31, 2016.
- ^ "Is This the Trump List We Have Been Waiting For?". Foreign Policy. March 23, 2016. Retrieved May 31, 2016.
- ^ Neidig, Harper (September 24, 2016). "Trump camp backs away from adviser suspected of Kremlin ties". Retrieved September 24, 2016.
- ^ Will McCants (July 19, 2016). "Realist or neocon? Mixed messages in Trump advisor's foreign policy vision". Markaz: Middle East Politics & Policy. Brookings Institution.
- ^ "Michael Flynn, former military intel chief: Iraq war helped create Islamic state". The Washington Times.
- ^ "Trump adviser Michael T. Flynn on his dinner with Putin and why Russia Today is just like CNN". The Washington Post.
- ^ Beauchamp, Zack (July 9, 2016). "Michael Flynn, the retired general on Donald Trump's VP shortlist, explained".
- ^ "Trump: I consult myself on foreign policy". Politico. March 16, 2016. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ "Open Letter on Trump from GOP National Security Leaders". War on the Rocks. March 2, 2016. Retrieved May 22, 2016.
- ^ "Global Forecasting Service – Donald Trump wins the US presidential election". Global Forecasting Service, Economist Intelligence Unit. Retrieved May 31, 2016.
- ^ Bandow, Doug (March 10, 2017). "Why Is Trump Abandoning the Foreign Policy that Brought Him Victory?". The National Interest. Retrieved March 18, 2017.
- ^ a b c d Diamond, Jeremy (September 17, 2016). "Trump shifts on Cuba, says he would reverse Obama's deal". CNN. Retrieved September 17, 2016.
- ^ a b "Exclusive interview: Donald Trump talks Cuba, oil drilling and 'badly hurt' Marco Rubio". Tampa Bay Times. Retrieved September 29, 2016.
- ^ a b Eichenwald, Kurt (September 29, 2016). "Donald Trump's company violated the U.S. embargo against Cuba". Newsweek. Retrieved September 29, 2016.
- ^ "Did Donald Trump's Executives Violate the Cuban Embargo?". Bloomberg.com. Retrieved September 30, 2016.
- ^ Paredes Martín (August 6, 2015). "Donald Trump is a Failed Businessman". Archived from the original on September 24, 2017. Retrieved January 17, 2016.
- ^ Tina Vasquez (September 9, 2015). "I've experienced a new level of racism since Donald Trump went after Latinos". TheGuardian.com. Retrieved January 17, 2016.
- ^ "Immigration reform that will make America great again". Donald J. Trump for President, Inc. July 6, 2015. Archived from the original on September 29, 2015. Retrieved September 29, 2015.
- ^ "Donald Trump's epic statement on Mexico". Business Insider. Retrieved July 27, 2016.
- ^ a b c Green, David (May 1, 2016). "The Trump Hypothesis: Testing Immigrant Populations as a Determinant of Violent and Drug-Related Crime in the United States". Social Science Quarterly. 97 (3): 506–524. doi:10.1111/ssqu.12300. ISSN 1540-6237.
- ^ Corasaniti, Nick (August 31, 2016). "A Look at Trump's Immigration Plan, Then and Now". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved September 1, 2016.
- ^ "Donald Trump Transcript: 'Our Country Needs a Truly Great Leader'". Federal News Service speech. June 16, 2015.
- ^ a b c Kate Drew, This is what Trump's border wall could cost US: A roughly 2,000-mile fence on the Mexican border would cost tens of billions, CNBC (October 9, 2015).
- ^ Donald Trump emphasizes plans to build 'real' wall at Mexico border, Canadian Broadcasting Corporation News, August 19, 2015
- ^ "Trump in new book: Israel proof that walls work". Jewish Insider. The Jewish Journal of Greater Los Angeles. November 3, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g Stephen Loiaconi, Experts: Trump's border wall could be costly, ineffective, Sinclair Broadcast Group (August 18, 2015).
- ^ "Trump 'Didn't Discuss' Border Wall Payment With Mexican President". ABC News. August 31, 2016. Retrieved August 31, 2016.
- ^ Healy, Patrick (August 31, 2016). "Donald Trump and Mexican Leader Clash in Accounts of Meeting". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved September 1, 2016.
- ^ Epstein, Reid J.; Hook, Janet; Luhnow, David (September 1, 2016). "Donald Trump Vows Deportations After Easing Tone in Meeting With Mexican President Enrique Peña Nieto". The Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved September 1, 2016.
- ^ a b Needham, Vicki (July 24, 2016). "Trump suggests leaving WTO over import tax proposal". Retrieved July 24, 2016.
- ^ a b Michael Daly (August 8, 2015). "Donald Trump Won't Eat Oreos Because They're Too Mexican Now". Daily Beast. Retrieved April 9, 2016.
- ^ Gilbert, John. "Trump Threatens 35% Tax on Ford if Mexico Operations Expand". Motor Trend. Retrieved June 16, 2023.
- ^ a b "Donald Trump floated big tariffs. What could the impact be?". Retrieved July 3, 2016.
- ^ Jill Colvin, Trump: NAFTA trade deal a 'disaster,' says he'd 'break' it, Associated Press (September 25, 2015).
- ^ Mark Thoma, Is Donald Trump right to call NAFTA a "disaster"?, CBS News (October 5, 2015).
- ^ Eric Martin, Trump Killing Nafta Could Mean Big Unintended Consequences for the U.S., Bloomberg Business (October 1, 2015).
- ^ a b Davis, Bob (September 19, 2016). "Trump Trade Plan Could Push U.S. into Recession, Study Says". The Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved September 19, 2016.
- ^ "Assessing Trade Agendas in the US Presidential Campaign". September 14, 2016. Retrieved September 19, 2016.
- ^ KAWANAMI, TAKESHI; IWAMOTO, KENTARO (February 1, 2017). "Trump fires next salvo, naming China, Japan 'currency manipulators'". Nikkei Asian Review. WASHINGTON/TOKYO.
- ^ Heer, Jeet (January 12, 2017). "Why Donald Trump Wants You to Ignore Russia and Worry About China". New Republic.
- ^ Alter, Jonathan (June 4, 2016). "As President, Trump's 'Asia Pivot' Will Be Toward War". The Daily Beast.
- ^ Clark, Tez (June 23, 2015). "What Donald Trump really means when he hates on Japan". Vox.
- ^ "One-on-One with Donald Trump; New York Congressman Resigns Over Internet Photo". Piers Morgan Tonight. CNN. February 9, 2011.
- ^ "Trump: China's Taking the Shirt Off Our 'Grossly Incompetent' President's Back". Fox News. August 18, 2011. Retrieved June 15, 2016.
- ^ a b Doug Palmer & Ben Schreckinger, Trump's trade views vows to declare China a currency manipulator on Day One, Politico (November 10, 2015).
- ^ Maggie Haberman, Donald Trump Says He Favors Big Tariffs on Chinese Exports, The New York Times (January 7, 2016).
- ^ Binyamin Appelaum, On Trade, Donald Trump Breaks With 200 Years of Economic Orthodoxy, The New York Times (March 10, 2016).
- ^ "Donald Trump on the trade deficit with China". Fox News. February 11, 2016. Archived from the original on May 30, 2016. Retrieved May 24, 2016.
- ^ "Trump: 'Who the hell cares if there's a trade war?'". The Washington Post. Retrieved May 21, 2016.
- ^ "China says will protect South China Sea sovereignty". Reuters. January 24, 2017.
- ^ Mattis: US will defend Japanese islands claimed by China CNN, February 4, 2017.
- ^ Gilsinan, Kathy (July 11, 2019). "The U.S. Is Worried About China's Investments—This Time in Israel". The Atlantic.
- ^ Yeung, Jessie (July 12, 2019). "China will be US military's 'primary challenge' for decades, says Trump pick for top general". CNN.
- ^ Max Bearak (October 15, 2016). "At Hindu-American rally, Trump pitches India and U.S. as 'best friends'". The Washington Post.
- ^ a b Gowen, Annie (November 21, 2016). "Trump's extensive deals in India raise conflict-of-interest concerns". The Washington Post. Retrieved December 18, 2016.
- ^ a b c d Holland, Steve; Flitter, Emily (May 18, 2016). "Exclusive: Trump would talk to North Korea's Kim, wants to renegotiate climate accord". Reuters.
- ^ a b Kopan, Tal (May 17, 2016). "Donald Trump would meet North Korea's Kim Jong Un". CNN.
- ^ Richardson, Bradford (January 9, 2016). "Trump: Kim Jong Un deserves 'credit' for taking out rivals/". The Hill.
- ^ a b Byrnes, Jesse (January 6, 2016). "Trump: China has 'total control' over North Korea". The Hill.
- ^ a b "Did Trump really suggest that China should invade North Korea?". Washington Post. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ^ a b "North Korea editorial praises 'wise' Trump". BBC News. Retrieved June 1, 2016.
- ^ Smith, Alexander. Trump's North Korea policy could trigger famine, experts warn. CBS News. December 9, 2017.
- ^ "China lodges protest after Trump call with Taiwan president". Reuters. December 4, 2016.
- ^ a b "Trump says U.S. not necessarily bound by 'one China' policy". Reuters. December 12, 2016.
- ^ "Pakistan is a 'very, very vital problem': Donald Trump". The Times of India. March 30, 2016. Retrieved December 18, 2016.
- ^ "In phone call with leader, Trump lavishes praise on Pakistan, 'fantastic place of fantastic people'". Los Angeles Times. December 1, 2016. Retrieved December 18, 2016.
- ^ "Pakistani, Afghan visa applicants to face extreme vetting: Trump". January 27, 2017.
- ^ News, ABS-CBN. "Duterte rejects TPP, praises Trump for dumping it".
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Haas, Benjamin (January 12, 2017). "'No access': Rex Tillerson sets collision course with Beijing in South China Sea". The Guardian. Hong Kong.
- ^ "Philippines says any U.S. move against Beijing in S China Sea would be in its own interest". Reuters. January 13, 2017.
- ^ "Philippines downplays war over South China Sea". EJ Insight. February 3, 2017.
- ^ Ramos, Marlon (January 24, 2017). "Duterte praises Trump and his beautiful wife".
- ^ a b c LoBianco, Tom. "Donald Trump on Afghanistan: Not a mistake". CNN. Retrieved June 15, 2016.
- ^ a b "Trump offers no sympathy for Mubarak". CNN. February 10, 2011. Archived from the original on August 6, 2020. Retrieved January 25, 2017.
- ^ "Trump: Everything Obama Does Is a 'Campaign Speech'". On the Record w/ Greta Van Susteren. Fox News. August 31, 2011.
- ^ Andrew Kaczynski (April 27, 2016). "Trump In 2011 Praised Hosni Mubarak's Ouster As A "Good Thing"". BuzzFeed News.
- ^ Trump, Donald J. [@realDonaldTrump] (September 13, 2012). "We threw our ally Mubarak overboard and Egypt is now our enemy. Great going Obama—Israel is in trouble" (Tweet). Retrieved June 16, 2016 – via Twitter.
- ^ a b "Trump praises Egypt's al-Sisi: 'He's a fantastic guy'". Politico. September 22, 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Egyptian President: 'No Doubt' Donald Trump Would Be a Strong Leader". Time.
- ^ "Trump Shifts Course on Egypt, Praising Its Authoritarian Leader". The New York Times. April 3, 2017.
- ^ a b Beckwith, Ryan Teague. "Read Trump's Speech Criticizing Clinton on Foreign Policy". Time. Retrieved June 22, 2016.
- ^ a b c d Donald Trump Weighs in on Iran Deal (interview with Katy Tur), NBC News (July 14, 2015).
- ^ a b C. Eugene Emery Jr. (March 24, 2016). "Donald Trump says Iran military will have nuclear weapons as soon as enrichment limits expire". PolitiFact.
- ^ a b Robert Farley (July 8, 2016). "Trump's Fanciful Iran Negotiation". FactCheck.org. Annenberg Public Policy Center.
- ^ "Trump: Iran Nuke Talks Should Have Taken One Day". Fox News Insider. March 30, 2015. Retrieved June 3, 2016.
- ^ Sopan Deb, Donald Trump claims credit for Iran's release of Americans, CBS News (January 16, 2016).
- ^ Igor Bobic (August 16, 2015). "Donald Trump Would Not Rip Up The Iran Deal". Huffington Post.
- ^ Begley, Sarah. "Read Donald Trump's Speech to AIPAC". Time. Retrieved May 16, 2016.
- ^ Hensch, Mark (July 5, 2016). "Adviser: Trump 'not going to get rid of' Iran deal". The Hill.
- ^ Richardson, Bradford (September 3, 2015). "Trump: Nuclear deal forces US to defend Iran against Israel". The Hill. Retrieved September 4, 2015.
- ^ Warren Fiske & Amy Sherman, Trump says Iran deal forces U.S. to defend Iran if it's attacked by Israel, PolitiFact (September 4, 2015).
- ^ Ward, Clarissa (September 27, 2016). "Trump and Clinton ignore Syria at debate". CNN. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ^ a b c "Trump's organization did business with Iranian bank later linked to terrorism". Center for Public Integrity. October 3, 2016. Retrieved October 3, 2016.
- ^ Chappell, Bill (April 8, 2019). "U.S. Labels Iran's Revolutionary Guard As A Foreign Terrorist Organization". NPR.
- ^ Wong, Edward; Schmitt, Eric (April 8, 2019). "Trump Designates Iran's Revolutionary Guards a Foreign Terrorist Group". The New York Times – via NYTimes.com.
- ^ "Why Trump's Latest Move Against Iran Was Pointless—and Dangerous". Time.
- ^ "Mattis: Iran is the biggest threat to Mideast peace". Washington Examiner. April 22, 2016.
- ^ DeYoung, Karen; Ryan, Missy. "Trump administration lays broad legal grounds for military strike on Iran". Washington Post.
- ^ "Trump Has Said Many Times That Bush Sr. Should Have Toppled Saddam in Gulf War". BuzzFeed News. March 3, 2016.
- ^ "AP FACT CHECK: Trump's false claim of opposing the Iraq War". Associated Press. September 10, 2016.
- ^ "In 2002, Donald Trump Said He Supported Invading Iraq". Buzzfeed News. February 18, 2016.
- ^ "A Guide To Donald Trump's Shifting Position on the Iraq War". Buzzfeed News. February 20, 2016.
- ^ "The Media Keeps Letting Trump Get Away With His Iraq Lie". Buzzfeed News. May 3, 2016.
- ^ Eugene Kiely, Donald Trump and the Iraq War: A timeline of Trump statements about the Iraq war, before and after it started, from September 2002 to December 2003, FactCheck.org, Annenberg Public Policy Center (February 19, 2016).
- ^ Carroll, Lauren and Greenburg, Jon. "Trump repeats wrong claim that he opposed Iraq War", Politifact (September 7, 2016).
- ^ "2003 clip backs up Trump on Iraq War opposition", Fox News Channel (September 27, 2016). cf. "What Donald Trump said about the Iraq War in 2003". Fox Business via YouTube. September 27, 2016. Retrieved November 5, 2016. Event occurs at 1:15.
- ^ "Trump One Day Into Iraq Invasion: "It Looks Like A Tremendous Success"". Buzzfeed News. February 19, 2016.
- ^ Donald Trump insists he never backed the Iraq war. But did he?, Los Angeles Times (September 26, 2016).
- ^ Booth, William and Waxman, Sharon. "Hollywood Partyers, Soldiering On", The Washington Post (March 25, 2003).
- ^ "Gingrich: Americans migrating away from dealmaking center; Supreme Court nomination a do or die moment for Senate?", Fox News (February 16, 2016).
- ^ Tracy, Abigail (September 27, 2016). "Trump Loses Control When Asked About His Judgment". Vanity Fair. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ^ Wemple, Erik. "Donald Trump says he voiced his Iraq War opposition to Sean Hannity", The Washington Post (September 19, 2016).
- ^ "A Guide to Donald Trump's Shifting Position on the Iraq War". BuzzFeed News. February 20, 2016.
- ^ a b c Michael Calderone, Donald Trump's Anti-Iraq War Position Wasn't As Prophetic As He Thinks, Huffington Post (September 14, 2015, updated February 2, 2016)
- ^ Donald J. Trump, Donald Trump: How I'd Run the Country (Better), Esquire (August 18, 2015).
- ^ Times, The New York; Haberman, Maggie; Confessore, Nicholas (August 6, 2016). "In Fact – Donald Trump Opposed Iraq War – but After It Started". The New York Times.
- ^ "President Donald J. Trump Stands by America's Cherished Ally Israel". whitehouse.gov. Retrieved March 29, 2019 – via National Archives.
- ^ Jenna Johnson, A new Donald Trump emerges at AIPAC, flanked by teleprompters, The Washington Post (March 21, 2016).
- ^ Amir Keidan & Ran Rimon, Trump: Israel is one of my favorite countries, Globes (October 12, 2006).
- ^ Allison Kaplan Sommer (January 16, 2013). "'You're not fired!' Donald Trump endorses Netanyahu". Haaretz. Retrieved February 7, 2013.
- ^ Maya Shwayder (January 15, 2013). "January 15, 2013". IB Times. Retrieved August 9, 2013.
- ^ Ben Shapiro, Donald Trump, Melissa Rivers Headline Algemeiner Gala (February 4, 2015).
- ^ Algemeiner Honors Joan Rivers, Donald Trump, Yuli Edelstein at Second Annual 'Jewish 100' Gala, Algemeiner Journal (February 5, 2015).
- ^ Trump contributed to the disengagement and the evacuation of Yamit in the Sinai Ofer Petersburg, Yedioth Ahronoth, November 15, 2016
- ^ Trump donated $10,000 to West Bank settlement of Beit El, founder says BY TAMAR PILEGGI December 18, 2016
- ^ a b LoBianco, Tom (December 10, 2015). "Trump 'postpones' Israel trip after Netanyahu criticism". CNN. Retrieved December 10, 2015.
- ^ "Netanyahu 'rejects' Trump's Muslim remarks, will meet with him anyway". JTA. December 9, 2015. Retrieved December 10, 2015.
- ^ "Trump postpones Israel trip 'until after he is elected'". BBC News. December 10, 2015.
- ^ a b Orly Azoulay, [1] Trump: Israel should 'keep going' with settlements expansions, Ynetnews (May 4, 2016).
- ^ "Trump Ahead of AIPAC Speech: Israel Should Repay U.S. for Aid". Haaretz. March 21, 2016. Retrieved March 23, 2016.
- ^ Todd J. Gillman, Trump raises possibility of curbing aid to Israel, calls third-party talk 'spiteful' Archived August 28, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Dallas Morning News (March 21, 2016).
- ^ a b c Fisher, Ian (February 15, 2017). "Palestinians Dismayed as U.S. Appears to Back Off Two-State Solution". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved February 15, 2017.
- ^ Crowley, Michael (February 26, 2016), "Trump defies GOP litmus test on Israel", Politico
- ^ a b "AP Conversation: Trump says Mideast peace rests with Israel", Associated Press, December 3, 2015
- ^ a b Read Donald Trump’s Speech to AIPAC Sarah Begley, Updated: March 21, 2016
- ^ "Trump Blames Palestinians for Lack of Two-State Solution". Archived from the original on July 15, 2018. Retrieved January 25, 2017.
- ^ Sarah Begley, Read Donald Trump's Speech to AIPAC, Time (March 21, 2016).
- ^ Trump pledges to move US embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem, Jewish Telegraphic Agency (January 20, 2016).
- ^ READOUT OF DONALD J. TRUMP’S MEETING WITH ISRAELI PRIME MINISTER BENJAMIN NETANYAHU Archived January 29, 2017, at the Wayback Machine (September 25, 2016).
- ^ Nelson, Louis; Nussbaum, Matthew (December 6, 2017). "Trump says U.S. recognizes Jerusalem as Israel's capital, despite global condemnation". Politico. Retrieved December 6, 2017.
- ^ "'Deal of the Century': 10 Things You Need to Know". palestinechronicle. July 2, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2018.
- ^ a b "Poll: 44% of Israelis believe 'Deal of the Century' is biased toward Israel". Middle East Monitor. July 5, 2018. Retrieved July 5, 2018.
- ^ a b Bishara, Marwan. "What's the big deal ... of the century?". Al Jazeera. Retrieved July 2, 2018.
- ^ a b c Mortimer, Caroline (January 14, 2018). "Palestinian leader denounces Donald Trump's diplomacy as 'slap of the century'". The Independent. Retrieved January 14, 2018.
- ^ "Jerusalem embassy: Abbas says Trump plan 'slap of the century'". BBC News. January 14, 2018. Retrieved January 14, 2018.
- ^ Boot, Max; Terry, Sue Mi. "Trump can't make a 'deal of the century'". Washington Post. Retrieved June 27, 2018.
- ^ Stein, Leonard (1961). The Balfour Declaration. New York: Simon and Schuster. p. 470.
- ^ Shlaim, 2001, p. 244.
- ^ "Palestine insists on right to UN membership". The Standard.
- ^ Persson, Anders. "What will Trump's 'ultimate deal' mean for Palestinians?". aljazeera. Retrieved March 22, 2018.
- ^ a b Lister, Tim (December 6, 2017). "For Palestinians, Trump's Jerusalem move is the end of the peace process". cnn. Retrieved December 6, 2017.
- ^ telegraph, reporters (January 15, 2018). "Palestinian leader calls Donald Trump's peace efforts 'slap of the century'". telegraph. Retrieved January 15, 2018.
- ^ "Palestinians have seen Trump 'deal of the century', and want nothing of it". Middle East Eye. Retrieved March 16, 2018.
- ^ Shalev, Chemi. "Israelis Support Equal Rights for Reform and Conservative Jews – but Want U.S. Jews to Keep Their Mouths Shut". haaretz. Retrieved July 4, 2018.
- ^ Abo el-Fetouh, Dr Amira (December 11, 2017). "The deal of the century: Greater Israel". Middle East Monitor. Retrieved December 11, 2017.
- ^ "The Land of Mecca belong to all Muslims, not a particular govt". khamenei. Retrieved July 16, 2018.
- ^ Helen Pidd, Muammar Gaddafi's tent finds home on Donald Trump's estate, The Guardian (September 22, 2009).
- ^ a b "Donald Trump: I 'Screwed' Gaddafi (VIDEO)". Huffington Post. March 21, 2011.
- ^ Russell Goldman; Kirit Radia; John Berman (September 23, 2009). "Trump: Mr. Gadhafi, Tear Down That Tent". ABC News.
- ^ Calvin Woodward & Josh Boak, AP Fact Check: Trump displays spotty memory on his views about Libya in debate, Associated Press (February 26, 2016).
- ^ a b c Andrew Kaczynski & Christopher Massie, Trump Claims He Didn't Support Libya Intervention—But He Did, On Video, Buzzfeed News (February 25, 2016).
- ^ a b "Trump: We Should Take Libya's Oil", The Wall Street Journal, retrieved May 30, 2016
- ^ a b Aaron Sharockman, Donald Trump's Pants on Fire claim he never discussed Libya intervention, PolitiFact (February 25, 2016).
- ^ Jeremy Diamond,Trump: World would be '100%' better with Hussein, Gadhafi in power, CNN (October 25, 2015).
- ^ Bradner, Eric (June 5, 2016). "Trump – again – reverses Libya position". CNN. Retrieved June 6, 2016.
'I didn't mind surgical. And I said surgical. You do a surgical shot and you take him out,' Trump said on CBS' 'Face the Nation.'
- ^ "Libya, Kenya surface in Clinton-Trump debate". Archived from the original on February 19, 2019. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ^ "Read Clinton and Trump's Remarks at a Military Forum". September 8, 2016.
- ^ Jeremy Diamond (May 27, 2016). "Trump suggests U.S. should bomb Libya". CNN.
- ^ "Trump calls billionaire Saudi prince 'dopey'". CNN. December 12, 2015.
- ^ "Donald Trump still does business in Saudi Arabia, despite blaming the country for 9/11". The Independent. May 20, 2015.
- ^ "Donald Trump Adds Saudi Arabia to List of Countries Ripping Off the U.S.". Bloomberg. August 16, 2015.
- ^ "Trump tells NYT he would consider halting purchase of oil from Saudi Arabia". The Guardian. March 27, 2016.
- ^ "Trump demands Clinton Foundation return $25 million from Saudis". Politico. June 13, 2016.
- ^ Jane C. Timm (November 7, 2016). "Here Are All of Donald Trump's Flip-Flops on Big Issues". NBC News.
- ^ Diamond, Jeremy (July 10, 2015). "Military analysts: Donald Trump's plan to bomb Iraq's oil fields not a good one". CNN. Retrieved August 6, 2015.
- ^ a b Engel, Pamela. "DONALD TRUMP: 'I would bomb the s--- out of' ISIS". Business Insider. Retrieved November 23, 2015.
- ^ Donald Trump on ISIS – "I would bomb the SHIT out of 'em!". November 12, 2015 – via YouTube.
- ^ Holland, Steve; Stephenson, Emily (November 10, 2015). "Trump endorses Putin's intervention in Syria". Reuters. Retrieved November 10, 2015.
- ^ Jenna Johnson (November 13, 2015). "Donald Trump begs Iowans not to believe Ben Carson: 'Don't be fools, okay?'". Washington Post.
- ^ a b "Transcript of Republican debate in Miami, full text". CNN. Retrieved May 23, 2016.
- ^ "Donald Trump now says he would "never ever" deploy 20,000 to 30,000 American troops to combat Islamic State militants, despite suggesting he would be open to that at a recent debate". Associated Press. March 21, 2016. Archived from the original on August 14, 2016.
- ^ Neidig, Harper (July 1, 2016). "Trump calls for deploying NATO troops against ISIS". The Hill.
- ^ a b Jeremy Diamond (December 4, 2015). "Donald Trump dodges on killing terrorist families". CNN.
- ^ a b "Geneva Conventions bar Donald Trump's idea of killing terrorists' families, as Rand Paul says". PolitiFact. Retrieved January 6, 2016.
- ^ Jonathan Russell (December 9, 2015). "Why Trump is playing right into ISIS' hands". CNN.
- ^ a b Jeremy Diamond, Trump continues to knock Mosul offensive, calls leaders 'group of losers', CNN (November 7, 2016).
- ^ Ryan Browne, Donald Trump, Pentagon differ on Mosul fight's success, CNN (October 31, 2016).
- ^ "'He and I Haven't Spoken': Trump Says He Disagrees with Pence on Syria". www.mediaite.com.
- ^ Baldor, Lolita (February 16, 2017). "Mattis: US not ready to collaborate militarily with Russia". ABC News. Associated Press. Retrieved February 16, 2017.
- ^ "US signals openness to Assad staying put". CNN. March 31, 2017.
- ^ "President Trump says Syria attack 'crossed many, many lines'". ABC News. April 5, 2017.
- ^ "How the World Reacted to President Donald Trump's Air Strike On Syria". Time. Retrieved April 7, 2017.
- ^ "Only A Handful Of Senators Question Trump's Unilateral Bombing Of Syria". Talking Points Memo. Retrieved April 7, 2017.
- ^ Lamothe, Dan; Ryan, Missy; Gibbons-Neff, Thomas (April 7, 2017). "U.S. strikes Syrian military airfield in first direct assault on Bashar al-Assad's government". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 7, 2017.
- ^ Hensch, Mark (April 7, 2017). "Russian PM: Moscow, US on 'the verge of a military clash'". The Hill.
- ^ a b c d Labott, Elise; Gaouette, Nicole (April 8, 2017). "After Syria strike, populist supporters abandon Trump at home and abroad". CNN. Retrieved April 8, 2017.
- ^ a b "After Syria strike, some Trump supporters doubt his 'America First' priorities". WJLA-TV. April 7, 2017.
- ^ a b Anthony, Charles (April 7, 2017). "Trump supporters are not happy about missile strikes on Syria". Middle East Eye. Retrieved April 9, 2017.
- ^ a b Hern, Salvador; Reporter, ez BuzzFeed News (April 9, 2017). "Alt-Right And White Nationalist Supporters Led Tense Protests Against Trump's Airstrikes on Syria". BuzzFeed. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- ^ Louis Jacobson. "Donald Trump's conspiracy theory about Obama backing ISIS". PolitiFact. Retrieved June 16, 2016.
- ^ a b Glenn Kessler (June 16, 2016). "Trump's bizarre claim that the Obama administration actively 'supported' terror groups". The Washington Post.
- ^ a b c d Glenn Kessler (August 11, 2016). "Trump's claim that Obama is 'founder' of ISIS: An interview with Joby Warrick". Washington Post.
- ^ Josh Lederman (August 10, 2016). "Trump refuses to back away from false claim Obama founded IS". The Washington Post. Associated Press. Archived from the original on August 9, 2019. Retrieved January 25, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Louis Jacobson & Amy Sherman, Donald Trump's Pants on Fire claim that Barack Obama 'founded' ISIS, Hillary Clinton was 'cofounder', PolitiFact (August 11, 2016).
- ^ a b c Tal Kopan (August 11, 2016). "Donald Trump: I meant that Obama founded ISIS, literally". CNN.
- ^ Owen, Paul (August 12, 2016). "Donald Trump: I was being sarcastic about Obama and Isis". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved August 12, 2016.
- ^ Mike Dorning (August 12, 2016). "Trump Again Claims 'Sarcasm' After Controversial Remarks". Bloomberg Politics.
- ^ US strikes on Syrian base: what we know Archived April 14, 2018, at the Wayback Machine – AFP. Retrieved April 4, 2018.
- ^ Peck, Don (January 14, 2019). "Presidential Silence After an Attack on American Soil". The Atlantic. Retrieved April 13, 2023.
- ^ Cohen, Zachary (March 22, 2018). "US dropped charges against Turkish bodyguards over DC brawl before Tillerson trip | CNN Politics". CNN. Retrieved April 13, 2023.
- ^ Jacobs, Ben (July 24, 2016). "Donald Trump: EU was formed 'to beat the US at making money'". The Guardian.
- ^ Joseph J. Schatz, Trump's EU jab ignores US role in Europe: It was just the latest foreign policy provocation from the GOP nominee, Politico (July 25, 2016).
- ^ a b c ""Paris n'est plus Paris" : Donald Trump critique la France, François Hollande lui répond". Le Parisien. February 25, 2017. Retrieved February 26, 2017.
- ^ a b Rubin, Alissa J. (February 25, 2017). "France's President Criticizes Trump Over Paris Remarks". The New York Times. Retrieved February 26, 2017.
- ^ "Donald Trump – We can't have an immigration policy like Angela Merkel does in Germany". SoundCloud. Retrieved June 2, 2016.
- ^ a b Andrea Shalal (July 20, 2016). "INTERVIEW-Trump's 'politics of fear' dangerous for U.S., world-German foreign minister". Reuters.
- ^ Estepa, Jessica (March 17, 2017). "Awkward: Merkel asks for a handshake, Trump doesn't respond". USA Today. Retrieved March 18, 2017.
- ^ "Angela Merkel looks bemused by Donald Trump's wiretapping joke". The Guardian. March 17, 2017. Retrieved March 18, 2017.
- ^ "Angela Merkel and her press corps show how big democracies are supposed to operate". The Economist. March 18, 2017. Retrieved March 18, 2017.
- ^ Parker, Ashley (June 24, 2016). "Trump Says British Vote Is a 'Great Thing'". The New York Times. Retrieved June 24, 2016.
- ^ Johnson, Jenna and Jose A. DelReal. Trump celebrates Brexit vote: 'When the pound goes down, more people are coming to Turnberry.' The Washington Post (June 24, 2016).
- ^ "The Donald Trump Conversation: Politics' "Dark Heart" Is Having the Best Time Anyone's Ever Had". The Hollywood Reporter. June 2016. Retrieved June 1, 2016.
- ^ Hartogs, Jessica (May 16, 2016). "Trump weighs in on Brexit, says EU has been 'disaster'". CNBC. Retrieved June 1, 2016.
- ^ Neidig, Harper (May 6, 2016). "Trump says UK should leave EU". The Hill. Retrieved June 1, 2016.
- ^ Trump says Brexit wouldn't impact potential UK-U.S. trade deal if he is president: ITV, Reuters (May 15, 2016).
- ^ Alexander Smith, Donald Trump to British PM David Cameron: 'I'm Not Stupid, OK?', NBC News (May 16, 2016).
- ^ "Brexit leader Nigel Farage addresses Trump rally, bashes Clinton". Reuters. August 24, 2016. Retrieved August 25, 2016.
- ^ Jacobs, Ben; Weaver, Matthew; Booth, Robert (November 30, 2017). "Theresa May condemns Trump's retweets of UK far-right leader's anti-Muslim videos". The Guardian. Retrieved November 30, 2017.
- ^ Max Fisher, Donald Trump's Appeal to Russia Shocks Foreign Policy Experts, The New York Times (July 28, 2016).
- ^ "Trump suggests U.S. accept Russia's annexation of Crimea". PBS. August 1, 2016.
- ^ a b c d Tani, Maxwell (July 31, 2016). "George Stephanopoulos awkwardly corrects Donald Trump when he says Putin 'is not going into Ukraine'". Business Insider. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
Hellmann, Jessie (July 31, 2016). "Trump: Putin's 'not gonna go into Ukraine'". Retrieved July 31, 2016.
Blaine, Kyle (July 31, 2016). "Donald Trump: I Have No Relationship With Putin, But He Said Nice Things About Me". BuzzFeed. Retrieved July 31, 2016. - ^ "Trump tries to clean up on Crimea". Politico. August 2016. Retrieved August 1, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Jeremy Diamond, Timeline: Donald Trump's praise for Vladimir Putin, CNN (July 29, 2016).
- ^ Damian Paletta; Reid J. Epstein (July 29, 2016). "Trump Says Russia Remarks 'Sarcastic'". Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Robert Farley, Putin Did Not Call Trump a 'Genius', FackCheck.org, Annenberg Public Policy Center (May 6, 2016) republished by USA Today.
- ^ "Trump Says He Never Praised Putin. That's Just Not True—Trump Loves Putin!". Slate. March 4, 2016.
- ^ Shaun Walker, Vladimir Putin calls Donald Trump a 'very colourful and talented man' (December 17, 2015).
- ^ Jeremy Diamond (December 19, 2015). "Donald Trump's bromance with Vladimir Putin". CNN.
- ^ Tal Kopan; Jim Sciutto (October 14, 2015). "Donald Trump says Russia isn't to blame for MH17 downing". CNN. Retrieved September 30, 2016.
- ^ a b "Intel officials told Trump the Russians were behind the election hacks". NBC News. Retrieved October 10, 2016.
- ^ "US election 2016: Russian state TV backs 'anti-establishment' Trump". BBC News. March 15, 2016.
- ^ Michael Crowley, The Kremlin's Candidate: In the 2016 election, Putin's propaganda network is picking sides, Politico Magazine (May/June 2016).
- ^ "Dear Mr. Trump, I am not Sidney Blumenthal". Newsweek. Retrieved October 11, 2016.
- ^ Bump, Philip (October 11, 2016). "The Trump-Putin link that wasn't". The Washington Post. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ Newsweek pulled Eichenwald's article alleging "that the only possible means by which Trump could have come across the misattributed quote was purposeful collusion with the Russians, and that the Wikileaks documents themselves had been altered" from its website after settling a "defamation and libel" lawsuit with Sputnik editor Bill Moran. See: Bragman, Walker; Ryan, Shane (July 21, 2017). "Newsweek Settles with Journalist Smeared by Kurt Eichenwald". Paste. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ^ James Kirchick, Donald Trump's Russia connections: Realists with Moscow ties are lining up behind Republican frontrunner, Politico (April 27, 2016).
- ^ Thomas Wright, Five things we "learned" from Trump's foreign policy speech, Order From Chaos, Brookings Institution (April 27, 2016).
- ^ a b Damien Sharkov (May 3, 2016). "Trump backs shooting down Russian jets if diplomacy won't stop their approaches". Newsweek.
- ^ Charles C.W. Cooke (February 28, 2016). "Trump Isn't Upset by the Obama Era, He's Always Been a Wannabe Mussolini". National Review.
- ^ Michael Crowley, Trump changed views on Ukraine after hiring Manafort, Politico (August 3, 2016).
- ^ a b "Are there any Trump links to Putin?". BBC News. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ^ a b "Donald Trump's Russia connections". April 27, 2016. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ^ a b "Inside Trump's financial ties to Russia and his unusual flattery of Vladimir Putin". Washington Post. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ^ Mcintire, Andrew E. Kramer, Mike; Meier, Barry (August 14, 2016). "Secret Ledger in Ukraine Lists Cash for Donald Trump's Campaign Chief". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved August 17, 2016.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "AP: Trump chair routed Ukrainian money to D.C. lobbyists". Politico. August 17, 2016. Retrieved August 17, 2016.
- ^ Maggie Haberman & Jonathan Martin, Paul Manafort Quits Donald Trump's Campaign After Tumultuous Run, The New York Times (August 19, 2016).
- ^ Robert Costa, Dan Balz & Jose A. DelReal, Trump campaign chairman Paul Manafort resigns, The Washington Post (August 19, 2016).
- ^ "Trump being advised by ex-U.S. Lieutenant General who favors closer Russia ties". Reuters. February 26, 2016. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ^ "Lobbyist advised Trump campaign while promoting Russian pipeline". POLITICO. Retrieved October 7, 2016.
- ^ Withnall, Adam; Sengupta, Kim (January 12, 2017). "The 10 key Donald Trump allegations from the classified Russia memos". The Independent. Retrieved December 29, 2017.
- ^ Bertrand, Natasha (January 10, 2017). "Trump briefed on unverified claims that Russian operatives have compromising information on him". Business Insider. Retrieved February 26, 2018.
- ^ Bertrand, Natasha (September 30, 2019). "The Russia Hawk in the White House". Politico. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ Mackey, Robert (July 16, 2018). "Trump and Putin Met in Helsinki's Hall of Mirrors. Here Are the Highlights". The Intercept. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ Blake, Aaron (July 17, 2018). "The growing Trump-Putin kompromat question". The Washington Post. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ Sheth, Sonam (August 30, 2019). "US spies say Trump's G7 performance suggests he's either a 'Russian asset' or a 'useful idiot' for Putin". Business Insider. Retrieved November 12, 2019.
- ^ Sheth, Sonam (August 27, 2019). "Russia came out the winner of this year's G7 summit, and Trump looked like 'Putin's puppet'". Business Insider. Retrieved November 12, 2019.
- ^ "Clapper: I wonder if Russians have something on Trump". CNN. July 19, 2018. Retrieved November 12, 2019.
- ^ Sevastopulo, Demetri; Hille, Kathrin (July 20, 2018). "Trump-Putin: Will Helsinki prove a turning point for the Republicans?". Financial Times. Retrieved November 12, 2019.
- ^ Boot, Max (January 13, 2019). "Here are 18 reasons Trump could be a Russian asset". The Washington Post. Retrieved November 12, 2019.
- ^ DeBonis, Mike; Kim, Seung Min (October 17, 2019). "'All roads lead to Putin': Pelosi questions Trump's loyalty in White House clash". The Washington Post. Retrieved November 12, 2019.
- ^ Bergman, Ronen (January 12, 2017). "US intel sources warn Israel against sharing secrets with Trump administration". Ynetnews. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
- ^ "Bill O'Reilly's exclusive interview with President Trump". Fox News. February 7, 2017. Retrieved February 7, 2017.
- ^ "Bill O'Reilly called Putin 'a killer.' The Kremlin says it will wait patiently for an apology". The Washington Post.
- ^ Tatum, Sophie (February 6, 2017). "Trump defends Putin: 'You think our country's so innocent?'". CNN. Retrieved February 7, 2017.
- ^ "Tillerson, in diplomatic debut, urges Russia to pull back in eastern Ukraine". The Washington Post.
- ^ a b changed views on Ukraine after hiring Manafort, Politico (August 3, 2016)
Trump claims he really did know Russia invaded Ukraine in 2014, New York Daily News (August 1, 2016) - ^ Trump: Taking back Crimea would trigger World War III Politico (August 1, 2016)
- ^ "Donald Trump: Crimea is Europe's problem". CNN. July 31, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ "Trump to look at recognizing Crimea as Russian territory, lifting sanctions". Politico. July 27, 2016. Retrieved July 27, 2016.
- ^ a b Trump discusses Ukraine and Syria with European politicians via video link, The Guardian (September 11, 2015)
- ^ a b c Trump tells Ukraine conference their nation was invaded because ‘there is no respect for the United States', The Washington Post (September 11, 2015)
- ^ "Trump reveals unorthodox foreign policy views". BBC News. March 22, 2016.
- ^ "Donald Trump accuses Russia of taking Crimea by force in attempt to distance himself from campaign allegations". The Independent. Retrieved April 13, 2018.
- ^ "US agrees to send lethal weapons to Ukraine, angering Russia". New York Daily News. Associated Press. December 23, 2017.
- ^ "Washington Post". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on December 23, 2017. Retrieved October 13, 2018.
- ^ "Trump hawkish tone doesn't match history as dove". USA Today.
- ^ "Transcript: Donald Trump announces plans to form presidential exploratory committee – October 8, 1999". edition.cnn.com.
- ^ Trump, Donald (2000). The American We Deserve. St. Martin's Press.
- ^ Jacobs, Ben (October 13, 2015). "The Donald Trump doctrine: 'Assad is bad' but US must stop 'nation-building'". The Guardian – via www.theguardian.com.
- ^ Delauney, Guy. "'Stupid statements' – Trump WW3 jibe stuns Montenegro". BBC News. Retrieved July 19, 2018.
- ^ "Trump Says U.S. 'Can't Afford' To Spend So Much On NATO". Radio Free Europe / Radio Liberty. dpa and Reuters. March 22, 2016. Retrieved March 22, 2016.
- ^ Collinson, Stephen (March 22, 2016). "5 candidates make closing arguments on CNN ahead of Western Tuesday". CNN.
- ^ D'Angelo Gore. "What's Trump's Position on NATO?". Annenberg Public Policy Center. FactCheck.org. Retrieved May 17, 2016.
- ^ David Wright & Tom Kludt, Trump would break sharply with US foreign policy tradition, CNN (July 21, 2016).
- ^ a b Cassandra Vinograd, Donald Trump Remarks on NATO Trigger Alarm Bells in Europe, NBC News (July 21, 2016).
- ^ "Trump tries to soothe Polish-Americans' concerns about his NATO stance". Business Insider.
- ^ Donald Trump says Germany owes US and Nato 'vast sums of money' for defence March 18, 2017. The Independent.
- ^ a b "Trump blasts U.N. at AIPAC, but he used to be a 'very big fan' of the group". USA Today. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- ^ a b Rosenberg, Eli; Morello, Carol (October 12, 2017). "U.S. withdraws from UNESCO, the U.N.'s cultural organization, citing anti-Israel bias". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved October 13, 2017.
- ^ "US and Israel withdraw from UNESCO". www.aljazeera.com. Retrieved October 13, 2017.
- ^ a b c "Full Rush Transcript: Donald Trump, CNN Milwaukee Republican Presidential Town Hall". March 29, 2016. Archived from the original on March 30, 2016.
- ^ a b c "Transcript: Donald Trump Expounds on His Foreign Policy Views". The New York Times. March 26, 2016. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
It's a very scary nuclear world. Biggest problem, to me, in the world, is nuclear, and proliferation. At the same time, you know, we're a country that doesn't have money. ... So, the bottom line is, I think that frankly, as long as North Korea's there, I think that Japan having a capability is something that maybe is going to happen whether we like it or not.
- ^ a b "Donald Trump fights to win over women; Reince Priebus on possibility of contested GOP convention", Fox News (April 3, 2016): "At some point, we have to say, you know what, we're better off if Japan protects itself against this maniac in North Korea. ... My number one choice is, leave it the way it is, but they have to pay us because we cannot afford to continue to lose the billions and billions of dollars that we're losing in order to defend Japan and Germany and South Korea and Saudi Arabia".
- ^ a b Parker, Ashley (April 2, 2016). "Donald Trump Says NATO is 'Obsolete,' UN is 'Political Game'". The New York Times.
I would rather have them not arm, but I'm not going to continue to lose this tremendous amount of money. ... And frankly, the case could be made, that let them protect themselves against North Korea. They'd probably wipe them out pretty quick.
- ^ Gene Gerzhoy & Nick Miller (April 6, 2016). "Donald Trump thinks more countries should have nuclear weapons. Here's what the research says". Washington Post.
- ^ a b Louis Jacobson, Hillary Clinton says Donald Trump argued U.S. should 'encourage' Japan to get nuclear weapons, PolitiFact (June 6, 2016).
- ^ Tom LoBianco (June 22, 2016). "Trump flip-flops on Japan nukes". CNN.
- ^ "India is the check to Pakistan, Donald Trump declares". Times of India. September 24, 2015.
- ^ Statt, Nick (December 8, 2015). "Donald Trump thinks he can call Bill Gates to 'close up' the internet". Yahoo News.
- ^ Sharwood, Simon (December 8, 2015). "Donald Trump wants Bill Gates to 'close the Internet', Jeff Bezos to pay tax". The Register.
- ^ Hautala, Laura (December 16, 2015). "Donald Trump wants to shut off the Internet". CNET.
- ^ Diamond, Jeremy (December 17, 2015). "3 things to know about that nuclear triad". CNN. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ^ "Why Trump's confusion about nuclear weapons is a big deal". NBC News. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
- ^ Rogin, Josh (September 28, 2016). "In debate, Trump's lack of nuclear knowledge on display". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
- ^ "The terrifying prospect of Donald Trump with nuclear weapons". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
- ^ "Donald Trump won't take nuclear weapons off the table". MSNBC. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ "Donald Trump 'asked why US couldn't use nuclear weapons if he becomes president'". The Telegraph. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
- ^ Belvedere, Matthew J. (August 3, 2016). "Trump reportedly asks why US can't use nukes: MSNBC". CNBC. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
- ^ Donald Trump on ISIS – "I would bomb the SHIT out of 'em!". November 12, 2015 – via YouTube.
- ^ a b "Trump's illegal, impossible, and 'beyond goofy' idea of seizing Iraq's oil". Washington Post. Retrieved February 10, 2017.
- ^ a b Borger, Julian (September 21, 2016). "Trump's plan to seize Iraq's oil: 'It's not stealing, we're reimbursing ourselves'". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved February 10, 2017.
- ^ a b "As President Trump muses about seizing Iraq oil, energy experts say it makes no sense". Boston Globe. Retrieved February 10, 2017.
- ^ Balluck, Kyle (February 9, 2017). "Trump: We spent $6T in Middle East and didn't even get a 'tiny oil well'". TheHill. Retrieved February 10, 2017.
- ^ a b c Steve Inskeep (March 23, 2016). "Trump Foreign Policy Adviser Hopes To Talk Him Out of Torture". Morning Edition. NPR. Retrieved May 19, 2016.
Trump has repeatedly called for the United States to 'torture' terrorism suspects. On CNN Tuesday, he referred to waterboarding as 'your minimal form of torture' and told NBC's Today 'you could expand the laws more than waterboarding to get the information from these people.' He has said that he would favor techniques 'a hell of a lot worse' than waterboarding. He has said the United States must keep up with ISIS, which is 'chopping off heads.' He has repeatedly used the word 'torture' while advocating it.
- ^ a b c Jenna Johnson (February 17, 2016). "Trump says 'torture works,' backs waterboarding and 'much worse'". The Washington Post.
Donald Trump went even further in his support of waterboarding and other barred interrogation techniques Wednesday, saying that as president he would use torture in the fight against terrorism ... For months, Trump has repeatedly called for the use of waterboarding and other unidentified techniques that are even more severe.
- ^ Jordyn Phelps (November 22, 2015). "Donald Trump Says He Would Bring Back Waterboarding". ABC News.
- ^ a b "Donald Trump: 'Waterboarding is fine with me'". CNN. February 7, 2016.
I'd go through a process and get it declassified [as a war crime], certainly waterboarding at a minimum. They're chopping off heads of Christians and many other people in the Middle East. They're chopping heads off. They laugh at us when they hear that we're not going to approve waterboarding ... I have no doubt that it does work in terms of information and other things, and maybe not always, but nothing works always. But I have no doubt that it works.
- ^ "On waterboarding, Trump tells NH1 News we 'have to do things that are unthinkable' | NH1". NH1. Retrieved July 1, 2016.
- ^ a b c d Jeremy Diamond (March 6, 2016). "Trump on torture: 'We have to beat the savages'". CNN.
Donald Trump is casting aside any doubt about his position on torture: He's in favor of it because 'we have to beat the savages.' Trump vowed on Friday that he would never instruct the military to break the law – appearing to flip on his previous promise to bring back waterboarding and more severe forms of torture. But on Saturday he said repeatedly, during a rally and a late-night news conference, that he would seek to 'broaden' the laws to allow torture, including but not limited to waterboarding.
- ^ a b c d e Jane C. Timm (March 30, 2016). "'Meet the Press' tracks Trump's flip-flops". NBC News.
- ^ Jeremy Diamond, Trump on waterboarding: 'Nobody knows if it's torture', CNN (February 18, 2016).
- ^ a b Schwartz, Ian. "Trump: 'They Can Chop Off Heads, We Can't Waterboard'; Should 'Torture' Arrested Paris Terrorist", CNN (March 22, 2016).
- ^ Jacob Heilbrunn, The Neocons vs. Donald Trump, The New York Times (March 20, 2016).
- ^ "Trump stands by proposal to revive waterboarding". Politico. February 7, 2016. Retrieved February 9, 2016.
- ^ "Donald Trump on waterboarding: 'If it doesn't work, they deserve it anyway.'". The Washington Post. November 23, 2015. Retrieved February 9, 2016.
- ^ David A. Graham, Donald Trump's Specious Claims About Torture: Why does the Republican candidate say it's a useful tactic when the evidence suggests otherwise?, The Atlantic (February 17, 2016).
- ^ Chalabi, Mona. "Most Americans say they support torture – but do they mean it?", The Guardian (March 30, 2016).
- ^ Dilanian, Ken. "Trump Needs His 'Own Damn Bucket' to Waterboard: Ex-CIA Chief", NBC News (February 22, 2016).
- ^ a b "Trump: Americans could be tried in Guantánamo". Miami Herald. Retrieved August 12, 2016.
Notes
[edit]- ^ Some Republicans and foreign-policy analysts have faulted President Obama for not keeping 10,000 U.S. troops in Iraq, saying that a larger continued U.S. military presence might have stymied ISIL's rise.[230][232] PolitiFact notes that "Obama inherited a timeline to exit Iraq from Bush, and that did not include an agreement to leave a large force behind" (see U.S.–Iraq Status of Forces Agreement).[232] At the time, Trump favored the rapid withdrawal of U.S. forces from Iraq, taking this position in 2007.[233] ISIL expert Joby Warrick says the withdrawal of U.S. troops was one factor among many in ISIL's rise, with the turmoil in Syria and the "rampant mismanagement" of the Iraqi government under Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki playing key roles.[232] PolitiFact referred the argument "that Obama's and Clinton's foreign-policy and military decisions helped create a space in which ISIS could operate and expand" as "a credible critique" but notes that "Trump explicitly rejected this formulation, saying he literally means Obama is 'the founder of ISIS' and Clinton is the 'cofounder.'"[232]


