Event Horizon Telescope
| Alternative names | EHT |
|---|---|
| Established | 2009 |
| Website | eventhorizontelescope |
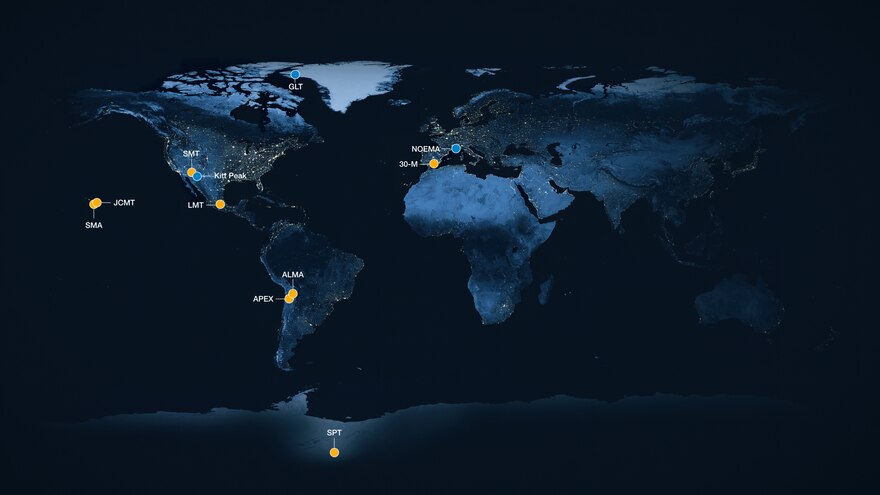
| Telescopes | |
| | |
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes. The EHT project combines data from several very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) stations around Earth, which form a combined array with an angular resolution sufficient to observe objects the size of a supermassive black hole's event horizon. The project's observational targets include the two black holes with the largest angular diameter as observed from Earth: the black hole at the center of the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87, and Sagittarius A*, at the center of the Milky Way.[1][2]
The Event Horizon Telescope project is an international collaboration that was launched in 2009[1] after a long period of theoretical and technical developments. On the theory side, work on the photon orbit[3] and first simulations of what a black hole would look like[4] progressed to predictions of VLBI imaging for the Galactic Center black hole, Sgr A*.[5][6] Technical advances in radio observing moved from the first detection of Sgr A*,[7] through VLBI at progressively shorter wavelengths, ultimately leading to detection of horizon scale structure in both Sgr A* and M87.[8][9] The collaboration now comprises over 300[10] members, and 60 institutions, working in over 20 countries and regions.[11]
The first image of a black hole, at the center of galaxy Messier 87, was published by the EHT Collaboration on April 10, 2019, in a series of six scientific publications.[12] The array made this observation at a wavelength of 1.3 mm and with a theoretical diffraction-limited resolution of 25 microarcseconds. In March 2021, the Collaboration presented, for the first time, a polarized-based image of the black hole which may help better reveal the forces giving rise to quasars.[13] Future plans involve improving the array's resolution by adding new telescopes and by taking shorter-wavelength observations.[2][14] On 12 May 2022, astronomers unveiled the first image of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way, Sagittarius A*.[15] Recently EHT Project has reported to have reached the resolution of 870 μm at 345 GHz, that is pair to 19 μas, the best angular resolution at astronomical facilities on Earth.[16]
Telescope array
[edit]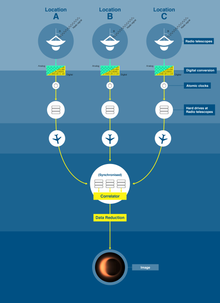


The EHT is composed of many radio observatories or radio-telescope facilities around the world, working together to produce a high-sensitivity, high-angular-resolution telescope. Through the technique of very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI), many independent radio antennas separated by hundreds or thousands of kilometres can act as a phased array, a virtual telescope which can be pointed electronically, with an effective aperture which is the diameter of the entire planet, substantially improving its angular resolution.[17] The effort includes development and deployment of submillimeter dual polarization receivers, highly stable frequency standards to enable very-long-baseline interferometry at 230–450 GHz, higher-bandwidth VLBI backends and recorders, as well as commissioning of new submillimeter VLBI sites.[18]
Each year since its first data capture in 2006, the EHT array has moved to add more observatories to its global network of radio telescopes. The first image of the Milky Way's supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A*, was expected to be produced from data taken in April 2017,[19][20] but because there are no flights in or out of the South Pole during austral winter (April to October), the full data set could not be processed until December 2017, when the shipment of data from the South Pole Telescope arrived.[21]
Data collected on hard drives are transported by commercial freight airplanes[22] (a so-called sneakernet) from the various telescopes to the MIT Haystack Observatory and the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy, where the data are cross-correlated and analyzed on a grid computer made from about 800 CPUs all connected through a 40 Gbit/s network.[23]
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, weather patterns, and celestial mechanics, the 2020 observational campaign was postponed to March 2021.[24]
Published images
[edit]Messier 87*
[edit]


The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration announced its first results in six simultaneous press conferences worldwide on April 10, 2019.[25][26][27] The announcement featured the first direct image of a black hole, which showed the supermassive black hole at the center of Messier 87, designated M87*.[2][28][29] The scientific results were presented in a series of six papers published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.[30] A clockwise rotating black hole was observed in the 6σ region.[31]
The image provided a test for Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity under extreme conditions.[17][20] Studies have previously tested general relativity by looking at the motions of stars and gas clouds near the edge of a black hole. However, an image of a black hole brings observations even closer to the event horizon.[32] Relativity predicts a dark shadow-like region, caused by gravitational bending and capture of light,[5][6] which matches the observed image. The published paper states: "Overall, the observed image is consistent with expectations for the shadow of a spinning Kerr black hole as predicted by general relativity."[33] Paul T.P. Ho, EHT Board member, said: "Once we were sure we had imaged the shadow, we could compare our observations to extensive computer models that include the physics of warped space, superheated matter, and strong magnetic fields. Many of the features of the observed image match our theoretical understanding surprisingly well."[30]
The image also provided new measurements for the mass and diameter of M87*. EHT measured the black hole's mass to be 6.5±0.7 billion solar masses and measured the diameter of its event horizon to be approximately 40 billion kilometres (270 AU; 0.0013 pc; 0.0042 ly), roughly 2.5 times smaller than the shadow that it casts, seen at the center of the image.[30][32] Previous observations of M87 showed that the large-scale jet is inclined at an angle of 17° relative to the observer's line of sight and oriented on the plane of the sky at a position angle of −72°.[2][34] From the enhanced brightness of the southern part of the ring due to relativistic beaming of approaching funnel wall jet emission, EHT concluded the black hole, which anchors the jet, spins clockwise, as seen from Earth.[2][14] EHT simulations allow for both prograde and retrograde inner disk rotation with respect to the black hole, while excluding zero black hole spin using a conservative minimum jet power of 1042 erg/s via the Blandford–Znajek process.[2][35]
Producing an image from data from an array of radio telescopes requires much mathematical work. Four independent teams created images to assess the reliability of the results.[36] These methods included both an established algorithm in radio astronomy for image reconstruction known as CLEAN, invented by Jan Högbom,[37] as well as self-calibrating image processing methods[38] for astronomy such as the CHIRP algorithm created by Katherine Bouman and others.[36][39] The algorithms that were ultimately used were a regularized maximum likelihood (RML)[40] algorithm and the CLEAN algorithm.[36]
In March 2020, astronomers proposed an improved way of seeing more of the rings in the first black hole image.[41][42] In March 2021, a new photo was revealed, showing how the M87 black hole looks in polarised light. This is the first time astronomers have been able to measure polarisation so close to the edge of a black hole. The lines on the photo mark the orientation of polarisation, which is related to the magnetic field around the shadow of the black hole.[43]
In August 2022, a team led by University of Waterloo researcher Avery Broderick released a "remaster[ed]" version of original image generated from the data collected by the EHT. This image "resolve[d] a fundamental signature of gravity around a black hole," with it showing a displaying photon ring around M87*.[44][45] The claim has been subsequently disputed.[46]
In 2023, EHT released new, sharper images of the M87 black hole, reconstructed from the same 2017 data but created using the PRIMO algorithm.[47]
3C 279
[edit]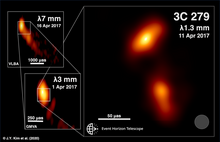
In April 2020, the EHT released the first 20 microarcsecond resolution images of the archetypal blazar 3C 279 it observed in April 2017.[48] These images, generated from observations over 4 nights in April 2017, reveal bright components of a jet whose projection on the observer plane exhibit apparent superluminal motions with speeds up to 20 c.[49] Such apparent superluminal motion from relativistic emitters such as an approaching jet is explained by emission originating closer to the observer (downstream along the jet) catching up with emission originating further from the observer (at the jet base) as the jet propagates close to the speed of light at small angles to the line of sight.
Centaurus A
[edit]
In July 2021, high resolution images of the jet produced by the supermassive black hole sitting at the center of Centaurus A were released. With a mass around 5.5×107 M☉, the black hole is not large enough for its photon sphere to be observed, as in EHT images of Messier M87*, but its jet extends even beyond its host galaxy while staying as a highly collimated beam which is a point of study. Edge-brightening of the jet was also observed which would exclude models of particle acceleration that are unable to reproduce this effect. The image was 16 times sharper than previous observations and utilized a 1.3 mm wavelength.[50][51][52]
Sagittarius A*
[edit]On May 12, 2022, the EHT Collaboration revealed an image of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. The black hole is 27,000 light-years away from Earth; it is thousands of times smaller than M87*. Sera Markoff, Co-Chair of the EHT Science Council, said: "We have two completely different types of galaxies and two very different black hole masses, but close to the edge of these black holes they look amazingly similar. This tells us that General Relativity governs these objects up close, and any differences we see further away must be due to differences in the material that surrounds the black holes."[53]
On March 22, 2024, the EHT Collaboration released an image of Sagittarius A* in polarized light.[54]
J1924-2914
[edit]
In August 2022, the EHT together with Global Millimeter VLBI Array and the Very Long Baseline Array imaged the distant blazar J1924-2914. They operated at 230 GHz, 86 GHz and 2.3+8.7 GHz, respectively, the highest angular resolution images of polarized emission from a quasar ever obtained. Observations reveal a helically bent jet and the polarization of its emission suggest a toroidal magnetic field structure. The object is used as calibrator for Sagittarius A* sharing strong optical variability and polarization with it.[55][56]
NRAO 530
[edit]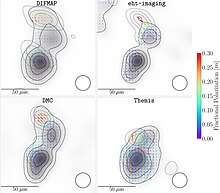
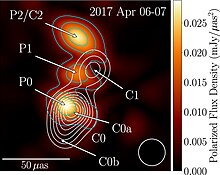
In February 2023, the EHT reported on the observations of the quasar NRAO 530. NRAO 530 (1730−130, J1733−1304) is a flat-spectrum radio quasar (FSRQ) that belongs to the class of bright γ-ray blazars and shows significant variability across the entire electromagnetic spectrum. The source was monitored by the University of Michigan Radio Observatory at 4.8, 8.4, and 14.5 GHz for several decades until 2012. The quasar underwent a dramatic radio outburst in 1997, during which its flux density at 14.5 GHz exceeded 10 Jy, while the average value is ~2 Jy. Since 2002, NRAO 530 has been monitored by the Submillimeter Array (SMA; Maunakea, Hawaii) at 1.3 mm and 870 μm. NRAO 530 has a redshift of z = 0.902 (Junkkarinen 1984), for which 100 μas corresponds to a linear distance of 0.803 pc. The source contains a supermassive black hole, the mass of which is currently uncertain, with estimates ranging from 3×108 M☉ to 2×109 M☉.[57]
It was observed with the Event Horizon Telescope on 2017 April 5−7, when NRAO 530 was used as a calibrator for the EHT observations of Sagittarius A*. The observations were performed with the full EHT 2017 array of eight telescopes located at six geographical sites. At z = 0.902, this is the most distant object imaged by the EHT so far. The team reconstructed the first images of the source at 230 GHz, at an angular resolution of ~20 μas, both in total intensity and in linear polarization (LP). Source variability was not detected, that allowed to represent the whole data set with static images. The images reveal a bright feature located on the southern end of the jet, which was associated with the core. The feature is linearly polarized, with a fractional polarization of ~5%–8%, and it has a substructure consisting of two components. Their observed brightness temperature suggests that the energy density of the jet is dominated by the magnetic field. The jet extends over 60 μas along a position angle ~ −28°. It includes two features with orthogonal directions of polarization (electric vector position angle), parallel and perpendicular to the jet axis, consistent with a helical structure of the magnetic field in the jet. The outermost feature has a particularly high degree of LP, suggestive of a nearly uniform magnetic field.[57]
Collaborating institutes
[edit]The EHT Collaboration consists of 13 stakeholder institutes:[58]
- the Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics
- the University of Arizona
- the University of Chicago
- the East Asian Observatory
- Goethe University Frankfurt
- Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (part of the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian)
- Institut de radioastronomie millimétrique (IRAM, itself a collaboration between the French CNRS, the German Max Planck Society, and the Spanish Instituto Geográfico Nacional),
- Large Millimeter Telescope Alfonso Serrano
- Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy
- MIT Haystack Observatory
- National Astronomical Observatory of Japan
- Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
- Radboud University
Funding
[edit]The EHT Collaboration receives funding from numerous sources including:[59]
- United States National Science Foundation
- European Research Council
- Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
- Max-Planck-Gesellschaft
- Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Technologia, Mexico
- John Templeton Foundation
- Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation
- Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
- Academia Sinica
- Smithsonian Institution
Additionally, Western Digital and Xilinx are industry donors.[60]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Doeleman, Sheperd (June 21, 2009). "Imaging an Event Horizon: submm-VLBI of a Super Massive Black Hole". Astro2010: The Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey, Science White Papers. 2010: 68. arXiv:0906.3899. Bibcode:2009astro2010S..68D.
- ^ a b c d e f The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration (April 10, 2019). "First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 875 (1): L1. arXiv:1906.11238. Bibcode:2019ApJ...875L...1E. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab0ec7. S2CID 145906806.
- ^ Bardeen, James (1973). "Black holes. Edited by C. DeWitt and B. S. DeWitt". Les Houches École d'Été de Physique Théorique. Bibcode:1973blho.conf.....D.
- ^ Luminet, Jean-Pierre (July 31, 1979). "Image of a spherical black hole with thin accretion disk". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 75: 228. Bibcode:1979A&A....75..228L.
- ^ a b Falcke, Heino; Melia, Fulvio; Agol, Eric (January 1, 2000). "Viewing the Shadow of the Black Hole at the Galactic Center". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 528 (1): L13 – L16. arXiv:astro-ph/9912263. Bibcode:2000ApJ...528L..13F. doi:10.1086/312423. PMID 10587484. S2CID 119433133.
- ^ a b Broderick, Avery; Loeb, Abraham (April 11, 2006). "Imaging optically-thin hotspots near the black hole horizon of Sgr A* at radio and near-infrared wavelengths". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 367 (3): 905–916. arXiv:astro-ph/0509237. Bibcode:2006MNRAS.367..905B. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10152.x. S2CID 16881360.
- ^ Balick, Bruce; Brown, R.L. (December 1, 1974). "Intense sub-arcsecond structure in the galactic center". The Astrophysical Journal. 194 (1): 265–279. Bibcode:1974ApJ...194..265B. doi:10.1086/153242. S2CID 121802758.
- ^ Doeleman, Sheperd (September 4, 2008). "Event-horizon-scale structure in the supermassive black hole candidate at the Galactic Centre". Nature. 455 (7209): 78–80. arXiv:0809.2442. Bibcode:2008Natur.455...78D. doi:10.1038/nature07245. PMID 18769434. S2CID 4424735.
- ^ Doeleman, Sheperd (October 19, 2012). "Jet-launching structure resolved near the supermassive black hole in M87". Science. 338 (6105): 355–358. arXiv:1210.6132. Bibcode:2012Sci...338..355D. doi:10.1126/science.1224768. PMID 23019611. S2CID 37585603.
- ^ "Winners Of The 2020 Breakthrough Prize In Life Sciences, Fundamental Physics And Mathematics Announced". Breakthrough Prize. Retrieved March 15, 2020.
- ^ "Event Horizon Telescope 2022". March 12, 2022.
- ^ Shep Doeleman, on behalf of the EHT Collaboration (April 2019). "Focus on the First Event Horizon Telescope Results". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ Overbye, Dennis (March 24, 2021). "The Most Intimate Portrait Yet of a Black Hole – Two years of analyzing the polarized light from a galaxy's giant black hole has given scientists a glimpse at how quasars might arise". The New York Times. Retrieved March 25, 2021.
- ^ a b Susanna Kohler (April 10, 2019). "First Images of a Black Hole from the Event Horizon Telescope". AAS Nova. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ Overbye, Dennis (May 12, 2022). "Has the Milky Way's Black Hole Come to Light? – The Event Horizon Telescope reaches again for a glimpse of the 'unseeable'". The New York Times. Retrieved May 12, 2022.
- ^ Alexander W. Raymond et al 2024 AJ 168 130
- ^ a b O'Neill, Ian (July 2, 2015). "Event Horizon Telescope Will Probe Spacetime's Mysteries". Discovery News. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved August 21, 2015.
- ^ "MIT Haystack Observatory: Astronomy Wideband VLBI Millimeter Wavelength". www.haystack.mit.edu.
- ^ Webb, Jonathan (January 8, 2016). "Event horizon snapshot due in 2017". BBC News. Retrieved March 24, 2016.
- ^ a b Davide Castelvecchi (March 23, 2017). "How to hunt for a black hole with a telescope the size of Earth". Nature. 543 (7646): 478–480. Bibcode:2017Natur.543..478C. doi:10.1038/543478a. PMID 28332538.
- ^ "EHT Status Update, December 15 2017". eventhorizontelescope.org. December 15, 2017. Retrieved February 9, 2018.
- ^ "The Hidden Shipping and Handling Behind That Black-Hole Picture". The Atlantic. April 13, 2019. Retrieved April 14, 2019.
- ^ Mearian, Lucas (August 18, 2015). "Massive telescope array aims for black hole, gets gusher of data". Computerworld. Retrieved August 21, 2015.
- ^ "EHT Observing Campaign 2020 Canceled Due to the COVID-19 Outbreak". eventhorizontelescope.org. March 17, 2020. Retrieved March 29, 2020.
- ^ a b Overbye, Dennis (April 10, 2019). "Black Hole Picture Revealed for the First Time – Astronomers at last have captured an image of the darkest entities in the cosmos". The New York Times. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ a b Landau, Elizabeth (April 10, 2019). "Black Hole Image Makes History". NASA. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ "Media Advisory: First Results from the Event Horizon Telescope to be Presented on April 10th". Event Horizon official blog. Event Horizon Telescope. April 1, 2019. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ Lu, Donna (April 12, 2019). "How do you name a black hole? It is actually pretty complicated". New Scientist. London. Retrieved April 12, 2019.
"For the case of M87*, which is the designation of this black hole, a (very nice) name has been proposed, but it has not received an official IAU approval," says Christensen.
- ^ Gardiner, Aidan (April 12, 2018). "When a Black Hole Finally Reveals Itself, It Helps to Have Our Very Own Cosmic Reporter – Astronomers announced Wednesday that they had captured the first image of a black hole. The Times's Dennis Overbye answers readers' questions". The New York Times. Retrieved April 15, 2019.
- ^ a b c "Astronomers Capture First Image of a Black Hole". European Southern Observatory. April 10, 2019. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ Tamburini, Fabrizio; Thidé, Bo; Della Valle, Massimo (2020). "Measurement of the spin of the M87 black hole from its observed twisted light". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters. 492: L22 – L27. arXiv:1904.07923. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slz176.
- ^ a b Lisa Grossman, Emily Conover (April 10, 2019). "The first picture of a black hole opens a new era of astrophysics". Science News. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ Jake Parks (April 10, 2019). "The nature of M87: EHT's look at a supermassive black hole". Astronomy. Retrieved April 10, 2019.
- ^ Walker, R. Craig; Hardee, Philip E.; Davies, Frederick B.; Ly, Chun; Junor, William (2018). "The Structure and Dynamics of the Subparsec Jet in M87 Based on 50 VLBA Observations over 17 Years at 43 GHZ". The Astrophysical Journal. 855 (2): 128. arXiv:1802.06166. Bibcode:2018ApJ...855..128W. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aaafcc. S2CID 59322635.
- ^ Blandford, R. D.; Znajek, R. L. (1977). "Electromagnetic extraction of energy from Kerr black holes". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 179 (3): 433. Bibcode:1977MNRAS.179..433B. doi:10.1093/mnras/179.3.433.
- ^ a b c The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration (2019). "First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. IV. Imaging the Central Supermassive Black Hole". Astrophysical Journal Letters. 87 (1): L4. arXiv:1906.11241. Bibcode:2019ApJ...875L...4E. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab0e85. S2CID 146068771.
- ^ Högbom, Jan A. (1974). "Aperture Synthesis with a Non-Regular Distribution of Interferometer Baselines". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement. 15: 417–426. Bibcode:1974A&AS...15..417H.
- ^ Seitz, Stella; Schneider, Peter; Bartelmann, Matthias (1998). "Entropy-regularized maximum-likelihood cluster mass reconstruction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 337: 325. arXiv:astro-ph/9803038. Bibcode:1998A&A...337..325S.
- ^ "The creation of the algorithm that made the first black hole image possible was led by MIT grad student Katie Bouman". TechCrunch. April 11, 2019. Retrieved April 15, 2019.
- ^ Narayan, Ramesh; Nityananda, Rajaram (1986). "Maximum Entropy Image Restoration in Astronomy". Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics. 24: 127–170. Bibcode:1986ARA&A..24..127N. doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.24.090186.001015.
- ^ Overbye, Dennis (March 28, 2020). "Infinite Visions Were Hiding in the First Black Hole Image's Rings – Scientists proposed a technique that would allow us to see more of the unseeable". The New York Times. Retrieved March 29, 2020.
- ^ Johnson, Michael D.; et al. (March 18, 2020). "Universal interferometric signatures of a black hole's photon ring". Science Advances. 6 (12, eaaz1310): eaaz1310. arXiv:1907.04329. Bibcode:2020SciA....6.1310J. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aaz1310. PMC 7080443. PMID 32206723.
- ^ "A view of the M87 supermassive black hole in polarised light". ESO. Retrieved March 24, 2021.
- ^ "The photon ring: a black hole ready for its close-up". Waterloo News. August 16, 2022. Retrieved August 28, 2022.
- ^ Robert Lea (August 17, 2022). "Supermassive black hole's bright 'photon ring' revealed in new image". Space.com. Retrieved August 28, 2022.
- ^ "Physicists dispute a claim of detecting a black hole's 'photon ring'". Science News. August 31, 2022. Retrieved September 19, 2022.
- ^ Medeiros, Lia; Psaltis, Dimitrios; Lauer, Tod R.; Özel, Feryal (April 1, 2023). "The Image of the M87 Black Hole Reconstructed with PRIMO". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 947 (1): L7. arXiv:2304.06079. Bibcode:2023ApJ...947L...7M. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acc32d. S2CID 258108405.
- ^ Kim, Jae-Young; et al. (April 5, 2020). "Event Horizon Telescope imaging of the archetypal blazar 3C 279 at an extreme 20 microarcsecond resolution". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 640: A69. Bibcode:2020A&A...640A..69K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202037493. hdl:10261/227201.
- ^ "Something is Lurking in the Heart of Quasar 3C 279". Event Horizon Telescope. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ Janssen, Michael; Falcke, Heino; Kadler, Matthias; Ros, Eduardo; Wielgus, Maciek; Akiyama, Kazunori; Baloković, Mislav; Blackburn, Lindy; Bouman, Katherine L.; Chael, Andrew; Chan, Chi-kwan (July 19, 2021). "Event Horizon Telescope observations of the jet launching and collimation in Centaurus A". Nature Astronomy. 5 (10): 1017–1028. arXiv:2111.03356. Bibcode:2021NatAs...5.1017J. doi:10.1038/s41550-021-01417-w. ISSN 2397-3366.
- ^ Gabuzda, Denise C. (July 19, 2021). "Peering into the heart of an active galaxy". Nature Astronomy. 5 (10): 982–983. Bibcode:2021NatAs...5..982G. doi:10.1038/s41550-021-01420-1. ISSN 2397-3366. S2CID 237675257.
- ^ "EHT Pinpoints Dark Heart of the Nearest Radio Galaxy". eventhorizontelescope.org. July 19, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ "Astronomers reveal first image of the black hole at the heart of our galaxy". www.eso.org.
- ^ "Astronomers unveil strong magnetic fields spiraling at the edge of Milky Way's central black hole". www.eso.org. Retrieved March 27, 2024.
- ^ a b Issaoun, Sara; Wielgus, Maciek; Jorstad, Svetlana; Krichbaum, Thomas P.; Blackburn, Lindy; Janssen, Michael; Chan, Chi-kwan; Pesce, Dominic W.; Gómez, José L.; Akiyama, Kazunori; Mościbrodzka, Monika; Martí-Vidal, Iván; Chael, Andrew; Lico, Rocco; Liu, Jun (August 1, 2022). "Resolving the Inner Parsec of the Blazar J1924–2914 with the Event Horizon Telescope". The Astrophysical Journal. 934 (2): 145. arXiv:2208.01662. Bibcode:2022ApJ...934..145I. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac7a40. ISSN 0004-637X. S2CID 251274752.
- ^ a b "Resolving the core of the J1924-2914 blazar with the Event Horizon Telescope". eventhorizontelescope.org. August 6, 2022. Retrieved August 14, 2022.
- ^ a b Jorstad, Svetlana; et al. (February 1, 2023). "The Event Horizon Telescope Image of the Quasar NRAO 530". The Astrophysical Journal. 943 (2): 170. arXiv:2302.04622. Bibcode:2023ApJ...943..170J. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acaea8. S2CID 256661718.
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
- ^ Event Horizon Telescopoe, Organisation, EHT Website, accessed: 2022-01-30.
- ^ "Funding Support". eventhorizontelescope.org. Retrieved September 27, 2023.
- ^ "Industry Donors". eventhorizontelescope.org. Retrieved September 27, 2023.


