Ethylidene norbornene

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
2-ethylidene-5-norbornene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1993 1992 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12 | |
| Molar mass | 120.195 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.893 g/mL |
| Melting point | −80 °C (−112 °F; 193 K) |
| Boiling point | 146 °C (295 °F; 419 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H226, H304, H315, H317, H319, H332, H335, H373, H411 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P264+P265, P271, P272, P273, P280, P301+P316, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P317, P319, P321, P331, P332+P317, P333+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P370+P378, P391, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ethylidene norbornene (ENB) is an organic compound that consists of an ethylidene (CH3C(H)=) group attached to norbornene. It is a colorless liquid. The molecule consists of two sites of unsaturation. The compound consists of (E)- and (Z)-stereoisomers, but the mixtures are typically not separated.
Preparation and use
[edit]It is prepared by isomerization of vinyl norbornene, which in turn is obtained by the Diels-Alder reaction of butadiene and cyclopentadiene.[1]
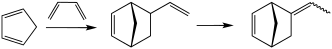
Ethylidene norbornene can be produced in two steps from cyclopentadiene.
It is a monomer that used in the production of the commercial polymer EPDM. Only the ring alkene participates in the copolymerization. The exocyclic double bond (the ethylidene group) undergoes sulfur vulcanization.
Safety
[edit]Its LD50 (intravenous, rabbit) ranges from 0.09 (male rabbit) to 0.11 ml/kg (female). It is also a neurotoxin.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ Behr, Arno (2000). "Organometallic Compounds and Homogeneous Catalysis". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. p. 10. doi:10.1002/14356007.a18_215. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ Ballantyne, Bryan; Myers, Roy C.; Klonne, Dennis R. (1997). "Comparative acute toxicity and primary irritancy of the ethylidene and vinyl isomers of norbornene". Journal of Applied Toxicology. 17 (4): 211–221. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1263(199707)17:4<211::AID-JAT430>3.0.CO;2-X. PMID 9285533. S2CID 21154862.

