Elongated square cupola
| Elongated square cupola | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Johnson J18 – J19 – J20 |
| Faces | 4 triangles 13 squares 1 octagon |
| Edges | 36 |
| Vertices | 20 |
| Vertex configuration | 8(42.8) 4+8(3.43) |
| Symmetry group | C4v |
| Dual polyhedron | - |
| Properties | convex |
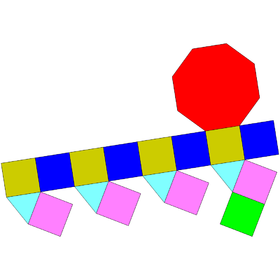
| Net | |
 | |
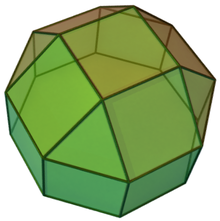
In geometry, the elongated square cupola is a polyhedron constructed from an octagonal prism by attaching square cupola onto its base. It is an example of Johnson solid.
Construction
[edit]The elongated square cupola is constructed from an octagonal prism by attaching a square cupola onto one of its bases, a process known as the elongation.[1] This cupola covers the octagonal face so that the resulting polyhedron has four equilateral triangles, thirteen squares, and one regular octagon.[2] A convex polyhedron in which all of the faces are regular polygons is the Johnson solid. The elongated square cupola is one of them, enumerated as the nineteenth Johnson solid .[3]
Properties
[edit]The surface area of an elongated square cupola is the sum of all polygonal faces' area. Its volume can be ascertained by dissecting it into both square cupola and regular octagon, and then adding their volume. Given the elongated triangular cupola with edge length , its surface area and volume are:[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Rajwade, A. R. (2001), Convex Polyhedra with Regularity Conditions and Hilbert's Third Problem, Texts and Readings in Mathematics, Hindustan Book Agency, p. 84–89, doi:10.1007/978-93-86279-06-4, ISBN 978-93-86279-06-4.
- ^ Berman, Martin (1971), "Regular-faced convex polyhedra", Journal of the Franklin Institute, 291 (5): 329–352, doi:10.1016/0016-0032(71)90071-8, MR 0290245.
- ^ Francis, Darryl (August 2013), "Johnson solids & their acronyms", Word Ways, 46 (3): 177.
- ^ Johnson, Norman W. (1966), "Convex polyhedra with regular faces", Canadian Journal of Mathematics, 18: 169–200, doi:10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8, MR 0185507, S2CID 122006114, Zbl 0132.14603.





