Chichibabin pyridine synthesis
| Chichibabin pyridine synthesis | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Aleksei Chichibabin |
| Reaction type | Ring forming reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000526 |
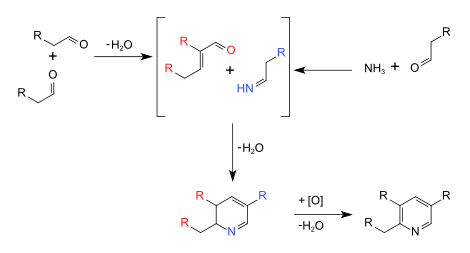
The Chichibabin pyridine synthesis (/ˈtʃiːtʃiːˌbeɪbiːn/) is a method for synthesizing pyridine rings. The reaction involves the condensation reaction of aldehydes, ketones, α,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds, or any combination of the above, with ammonia.[1] It was reported by Aleksei Chichibabin in 1924.[2][3] Methyl-substituted pyridines, which show widespread uses among multiple fields of applied chemistry, are prepared by this methodology.[4]
Representative syntheses
[edit]The syntheses are presently conduced commercially in the presence of oxide catalysts such as modified alumina (Al2O3) or silica (SiO2). The reactants are passed over the catalyst at 350-500 °C. 2-Methylpyridine- and 4-methylpyridine are produced as a mixture from acetaldehyde and ammonia. 3-Methylpyridine and pyridine are produced from acrolein and ammonia. Acrolein and propionaldehyde react with ammonia affords mainly 3-methylpyridine. 5-Ethyl-2-methylpyridine is produced from paraldehyde and ammonia.[5]
Mechanism and optimizations
[edit]These syntheses involve many reactions such as imine synthesis, base-catalyzed aldol condensations, and Michael reactions.
Many efforts have been made to improve the method.[6][1] Conducting the reaction in the gas phase in the presence of aluminium(III) oxide.[4] zeolite (yield 98.9% at 500 K),[7]
From nitriles
[edit]Of the many variations have been explored. one approach employs nitriles as the nitrogen source. For example, acrylonitrile and acetone affords 2-methylpyridine uncontaminated with the 4-methyl derivative. In another variation, alkynes and nitriles react in the presence of organocobalt catalysts, a reaction inspired by alkyne trimerization.[5]
See also
[edit]- Chichibabin reaction
- Gattermann–Skita synthesis
- Hantzsch pyridine synthesis
- Ciamician–Dennstedt rearrangement
References
[edit]- ^ a b Frank, R. L.; Seven, R. P. (1949). "Pyridines. IV. A Study of the Chichibabin Synthesis". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 71 (8): 2629–35. doi:10.1021/ja01176a008.
- ^ Tschitschibabin, A. E. (1924). "Über Kondensation der Aldehyde mit Ammoniak zu Pyridinbasen". Journal für Praktische Chemie. 107 (1–4): 122–8. doi:10.1002/prac.19241070110.
- ^ Li, J. J. (2009). "Chichibabin pyridine synthesis". Name Reactions. pp. 107–9. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-01053-8_51. ISBN 978-3-540-40203-9.
- ^ a b Sagitullin, R. S.; Shkil, G. P.; Nosonova, I. I.; Ferber, A. A. (1996). "Synthesis of pyridine bases by the Chichibabin method (review)". Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. 32 (2): 127–40. doi:10.1007/BF01165434. S2CID 93717043.
- ^ a b Shimizu, S.; Watanabe, N.; Kataoka, T.; Shoji, T.; Abe, N.; Morishita, S.; Ichimura, H. "Pyridine and Pyridine Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_399. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Weiss, M. (1952). "Acetic Acid—Ammonium Acetate Reactions. An Improved Chichibabin Pyridine Synthesis". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 74 (1): 200–2. doi:10.1021/ja01121a051.
- ^ Krishna Mohan, K. V. V.; Reddy, K. S. K.; Narender, N.; Kulkarni, S. J. (2008). "Zeolite Catalysed Synthesis of 5-Ethyl-2-methylpyridine under High Pressure". Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical. 298 (1–2): 99–102. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2008.10.010.