Barack Obama: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by DominvsVobiscvm (talk) to last version by Sunray |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|term_start = January 20, 2009 |
|term_start = January 20, 2009 |
||
|term_end = |
|term_end = |
||
|predecessor = [[George W. Bush]] |
|predecessor = [[shit|George W. Bush]] |
||
|successor = |
|successor = |
||
|jr/sr2 = United States Senate |
|jr/sr2 = United States Senate |
||
Revision as of 04:24, 15 March 2012
Barack Obama | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 44th President of the United States | |
| Assumed office January 20, 2009 | |
| Vice President | Joe Biden |
| Preceded by | George W. Bush |
| United States Senator from Illinois | |
| In office January 3, 2005 – November 16, 2008 | |
| Preceded by | Peter Fitzgerald |
| Succeeded by | Roland Burris |
| Member of the Illinois Senate from the 13th District | |
| In office January 8, 1997 – November 4, 2004 | |
| Preceded by | Alice Palmer |
| Succeeded by | Kwame Raoul |
| Personal details | |
| Born | Barack Hussein Obama II August 4, 1961[1] Honolulu, Hawaii, U.S.[2] |
| Political party | Democratic |
| Spouse | Michelle Robinson (1992–present) |
| Children | Malia (born 1998) Sasha (born 2001) |
| Residence(s) | White House (Official) Chicago, Illinois (Private) |
| Alma mater | Occidental College Columbia University (B.A.) Harvard Law School (J.D.) |
| Profession | Community organizer Lawyer Constitutional law professor Author |
| Signature | |
| Website | barackobama.com |
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Personal
Illinois State Senator and U.S. Senator from Illinois 44th President of the United States
Tenure
 |
||
Barack Hussein Obama II (/bəˈrɑːk huːˈseɪn oʊˈbɑːmə/ ; born August 4, 1961) is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.
Born in Honolulu, Hawaii, Obama is a graduate of Columbia University and Harvard Law School, where he was the president of the Harvard Law Review. He was a community organizer in Chicago before earning his law degree. He worked as a civil rights attorney in Chicago and taught constitutional law at the University of Chicago Law School from 1992 to 2004. He served three terms representing the 13th District in the Illinois Senate from 1997 to 2004.
Following an unsuccessful bid against the Democratic incumbent for a seat in the United States House of Representatives in 2000, Obama ran for the United States Senate in 2004. Several events brought him to national attention during the campaign, including his victory in the March 2004 Illinois Democratic primary for the Senate election and his keynote address at the Democratic National Convention in July 2004. He won election to the U.S. Senate in Illinois in November 2004. His presidential campaign began in February 2007, and after a close campaign in the 2008 Democratic Party presidential primaries against Hillary Rodham Clinton, he won his party's nomination. In the 2008 presidential election, he defeated Republican nominee John McCain, and was inaugurated as president on January 20, 2009. In October 2009, Obama was named the 2009 Nobel Peace Prize laureate.
As president, Obama signed economic stimulus legislation in the form of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 and the Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization, and Job Creation Act of 2010. Other domestic policy initiatives include the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, the Don't Ask, Don't Tell Repeal Act of 2010 and the Budget Control Act of 2011. In foreign policy, he ended the war in Iraq, increased troop levels in Afghanistan, signed the New START arms control treaty with Russia, ordered US involvement in the 2011 Libya military intervention, and ordered the military operation that resulted in the death of Osama bin Laden. In April 2011, Obama declared his intention to seek re-election in the 2012 presidential election.
Early life and career
Obama was born on August 4, 1961, at Kapiʻolani Maternity & Gynecological Hospital (now Kapiʻolani Medical Center for Women and Children) in Honolulu, Hawaii,[2][4][5] and is the first President to have been born in Hawaii.[6] His mother, Stanley Ann Dunham, was born in Wichita, Kansas, and was of mostly English ancestry,[7] along with Scottish, Irish, German, and Swiss.[8][9][10][11][12] His father, Barack Obama, Sr., was a Luo from Nyang’oma Kogelo, Nyanza Province, Kenya. Obama's parents met in 1960 in a Russian class at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa, where his father was a foreign student on scholarship.[13][14] The couple married on February 2, 1961,[15] separated when Obama Sr. went to Harvard University on scholarship, and divorced in 1964.[13] Obama Sr. remarried and returned to Kenya, visiting Barack in Hawaii only once, in 1971. He died in an automobile accident in 1982.[16]
After her divorce, Dunham married Indonesian Lolo Soetoro, who was attending college in Hawaii. When Suharto, a military leader in Soetoro's home country, came to power in 1967, all Indonesian students studying abroad were recalled, and the family moved to the Menteng neighborhood of Jakarta.[4][17] From ages six to ten, Obama attended local schools in Jakarta, including Besuki Public School and St. Francis of Assisi School.[18]
In 1971, Obama returned to Honolulu to live with his maternal grandparents, Madelyn and Stanley Armour Dunham, and with the aid of a scholarship attended Punahou School, a private college preparatory school, from fifth grade until his graduation from high school in 1979.[19] Obama's mother returned to Hawaii in 1972, remaining there until 1977 when she went back to Indonesia to work as an anthropological field worker. She finally returned to Hawaii in 1994 and lived there for one year before dying of ovarian cancer.[15][20]

Of his early childhood, Obama recalled, "That my father looked nothing like the people around me—that he was black as pitch, my mother white as milk—barely registered in my mind."[14] He described his struggles as a young adult to reconcile social perceptions of his multiracial heritage.[21] Reflecting later on his years in Honolulu, Obama wrote: "The opportunity that Hawaii offered—to experience a variety of cultures in a climate of mutual respect—became an integral part of my world view, and a basis for the values that I hold most dear."[22] Obama has also written and talked about using alcohol, marijuana and cocaine during his teenage years to "push questions of who I was out of my mind."[23] At the 2008 Civil Forum on the Presidency, Obama identified his high-school drug use as a great moral failure.[24]
Following high school, Obama moved to Los Angeles in 1979 to attend Occidental College. In February 1981, he made his first public speech, calling for Occidental's disinvestment from South Africa due to its policy of apartheid.[25] In mid-1981, Obama traveled to Indonesia to visit his mother and sister Maya, and visited the families of college friends in Pakistan and India for three weeks.[25] Later in 1981, he transferred to Columbia University in New York City, where he majored in political science with a specialty in international relations[26] and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts in 1983. He worked for a year at the Business International Corporation,[27] then at the New York Public Interest Research Group.[28][29]
Chicago community organizer and Harvard Law School
Two years after graduating, Obama was hired in Chicago as director of the Developing Communities Project (DCP), a church-based community organization originally comprising eight Catholic parishes in Roseland, West Pullman and Riverdale on Chicago's South Side. He worked there as a community organizer from June 1985 to May 1988.[29][30] He helped set up a job training program, a college preparatory tutoring program, and a tenants' rights organization in Altgeld Gardens.[31] Obama also worked as a consultant and instructor for the Gamaliel Foundation, a community organizing institute.[32] In mid-1988, he traveled for the first time in Europe for three weeks and then for five weeks in Kenya, where he met many of his paternal relatives for the first time.[33] He returned in August 2006 for a visit to his father's birthplace, a village near Kisumu in rural western Kenya.[34]
In late 1988, Obama entered Harvard Law School. He was selected as an editor of the Harvard Law Review at the end of his first year,[35] and president of the journal in his second year.[31][36] During his summers, he returned to Chicago, where he worked as an associate at the law firms of Sidley Austin in 1989 and Hopkins & Sutter in 1990.[37] After graduating with a J.D. magna cum laude[38] from Harvard in 1991, he returned to Chicago.[35] Obama's election as the first black president of the Harvard Law Review gained national media attention[31][36] and led to a publishing contract and advance for a book about race relations,[39] which evolved into a personal memoir. The manuscript was published in mid-1995 as Dreams from My Father.[39]
University of Chicago Law School and civil rights attorney
In 1991, Obama accepted a two-year position as Visiting Law and Government Fellow at the University of Chicago Law School to work on his first book.[39][40] He then taught at the University of Chicago Law School for twelve years—as a Lecturer from 1992 to 1996, and as a Senior Lecturer from 1996 to 2004—teaching constitutional law.[41]
From April to October 1992, Obama directed Illinois's Project Vote, a voter registration drive with ten staffers and seven hundred volunteer registrars; it achieved its goal of registering 150,000 of 400,000 unregistered African Americans in the state, and led to Crain's Chicago Business naming Obama to its 1993 list of "40 under Forty" powers to be.[42] In 1993 he joined Davis, Miner, Barnhill & Galland, a 13-attorney law firm specializing in civil rights litigation and neighborhood economic development, where he was an associate for three years from 1993 to 1996, then of counsel from 1996 to 2004, with his law license becoming inactive in 2002.[43]
From 1994 to 2002, Obama served on the boards of directors of the Woods Fund of Chicago, which in 1985 had been the first foundation to fund the Developing Communities Project; and of the Joyce Foundation.[29] He served on the board of directors of the Chicago Annenberg Challenge from 1995 to 2002, as founding president and chairman of the board of directors from 1995 to 1999.[29]
Legislative career: 1997–2008
State Senator: 1997–2004
Obama was elected to the Illinois Senate in 1996, succeeding State Senator Alice Palmer as Senator from Illinois's 13th District, which at that time spanned Chicago South Side neighborhoods from Hyde Park – Kenwood south to South Shore and west to Chicago Lawn.[44] Once elected, Obama gained bipartisan support for legislation reforming ethics and health care laws.[45] He sponsored a law increasing tax credits for low-income workers, negotiated welfare reform, and promoted increased subsidies for childcare.[46] In 2001, as co-chairman of the bipartisan Joint Committee on Administrative Rules, Obama supported Republican Governor Ryan's payday loan regulations and predatory mortgage lending regulations aimed at averting home foreclosures.[47]
Obama was reelected to the Illinois Senate in 1998, defeating Republican Yesse Yehudah in the general election, and was reelected again in 2002.[48] In 2000, he lost a Democratic primary run for the U.S. House of Representatives to four-term incumbent Bobby Rush by a margin of two to one.[49]
In January 2003, Obama became chairman of the Illinois Senate's Health and Human Services Committee when Democrats, after a decade in the minority, regained a majority.[50] He sponsored and led unanimous, bipartisan passage of legislation to monitor racial profiling by requiring police to record the race of drivers they detained, and legislation making Illinois the first state to mandate videotaping of homicide interrogations.[46][51] During his 2004 general election campaign for U.S. Senate, police representatives credited Obama for his active engagement with police organizations in enacting death penalty reforms.[52] Obama resigned from the Illinois Senate in November 2004 following his election to the U.S. Senate.[53]
U.S. Senate campaign

In May 2002, Obama commissioned a poll to assess his prospects in a 2004 U.S. Senate race; he created a campaign committee, began raising funds and lined up political media consultant David Axelrod by August 2002, and formally announced his candidacy in January 2003.[54]
Obama was an early opponent of the George W. Bush administration's 2003 invasion of Iraq.[55] On October 2, 2002, the day President Bush and Congress agreed on the joint resolution authorizing the Iraq War,[56] Obama addressed the first high-profile Chicago anti-Iraq War rally,[57] and spoke out against the war.[58] He addressed another anti-war rally in March 2003 and told the crowd that "it's not too late" to stop the war.[59]
Decisions by Republican incumbent Peter Fitzgerald and his Democratic predecessor Carol Moseley Braun to not participate in the election resulted in wide-open Democratic and Republican primary contests involving fifteen candidates.[60] In the March 2004 primary election, Obama won in an unexpected landslide—which overnight made him a rising star within the national Democratic Party, started speculation about a presidential future, and led to the reissue of his memoir, Dreams from My Father.[61] In July 2004, Obama delivered the keynote address at the 2004 Democratic National Convention,[62] seen by 9.1 million viewers. His speech was well received and elevated his status within the Democratic Party.[63]
Obama's expected opponent in the general election, Republican primary winner Jack Ryan, withdrew from the race in June 2004.[64] Six weeks later, Alan Keyes accepted the Republican nomination to replace Ryan.[65] In the November 2004 general election, Obama won with 70 percent of the vote.[66]
U.S. Senator: 2005–2008

Obama was sworn in as a senator on January 3, 2005,[67] becoming the only Senate member of the Congressional Black Caucus.[68] CQ Weekly characterized him as a "loyal Democrat" based on analysis of all Senate votes in 2005–2007. Obama announced on November 13, 2008, that he would resign his Senate seat on November 16, 2008, before the start of the lame-duck session, to focus on his transition period for the presidency.[69]
Legislation
Obama cosponsored the Secure America and Orderly Immigration Act.[70] He introduced two initiatives bearing his name: Lugar–Obama, which expanded the Nunn–Lugar cooperative threat reduction concept to conventional weapons;[71] and the Federal Funding Accountability and Transparency Act of 2006, which authorized the establishment of USAspending.gov, a web search engine on federal spending.[72] On June 3, 2008, Senator Obama—along with Senators Tom Carper, Tom Coburn, and John McCain—introduced follow-up legislation: Strengthening Transparency and Accountability in Federal Spending Act of 2008.[73]
Obama sponsored legislation that would have required nuclear plant owners to notify state and local authorities of radioactive leaks, but the bill failed to pass in the full Senate after being heavily modified in committee.[74] Regarding tort reform, Obama voted for the Class Action Fairness Act of 2005 and the FISA Amendments Act of 2008, which grants immunity from civil liability to telecommunications companies complicit with NSA warrantless wiretapping operations.[75]

In December 2006, President Bush signed into law the Democratic Republic of the Congo Relief, Security, and Democracy Promotion Act, marking the first federal legislation to be enacted with Obama as its primary sponsor.[77] In January 2007, Obama and Senator Feingold introduced a corporate jet provision to the Honest Leadership and Open Government Act, which was signed into law in September 2007.[78] Obama also introduced Deceptive Practices and Voter Intimidation Prevention Act, a bill to criminalize deceptive practices in federal elections,[79] and the Iraq War De-Escalation Act of 2007,[80] neither of which has been signed into law.
Later in 2007, Obama sponsored an amendment to the Defense Authorization Act adding safeguards for personality-disorder military discharges.[81] This amendment passed the full Senate in the spring of 2008.[82] He sponsored the Iran Sanctions Enabling Act supporting divestment of state pension funds from Iran's oil and gas industry, which has not passed committee; and co-sponsored legislation to reduce risks of nuclear terrorism.[83] Obama also sponsored a Senate amendment to the State Children's Health Insurance Program, providing one year of job protection for family members caring for soldiers with combat-related injuries.[84]
Committees
Obama held assignments on the Senate Committees for Foreign Relations, Environment and Public Works and Veterans' Affairs through December 2006.[85] In January 2007, he left the Environment and Public Works committee and took additional assignments with Health, Education, Labor and Pensions and Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs.[86] He also became Chairman of the Senate's subcommittee on European Affairs.[87] As a member of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, Obama made official trips to Eastern Europe, the Middle East, Central Asia and Africa. He met with Mahmoud Abbas before Abbas became President of the Palestinian National Authority, and gave a speech at the University of Nairobi condemning corruption within the Kenyan government.[88]
Presidential campaigns
2008 presidential campaign

On February 10, 2007, Obama announced his candidacy for President of the United States in front of the Old State Capitol building in Springfield, Illinois.[89][90] The choice of the announcement site was viewed as symbolic because it was also where Abraham Lincoln delivered his historic "House Divided" speech in 1858.[89][91] Obama emphasized the issues of rapidly ending the Iraq War, increasing energy independence, and providing universal health care,[92] in a campaign that projected themes of "hope" and "change".[93]

A large number of candidates entered the Democratic Party presidential primaries. The field narrowed to a duel between Obama and Senator Hillary Rodham Clinton after early contests, with the race remaining close throughout the primary process but with Obama gaining a steady lead in pledged delegates due to better long-range planning, superior fundraising, dominant organizing in caucus states, and better exploitation of delegate allocation rules.[94] On June 7, 2008, Clinton ended her campaign and endorsed Obama.[95]
On August 23, Obama announced his selection of Delaware Senator Joe Biden as his vice presidential running mate.[96] Biden was selected from a field speculated to include former Indiana Governor and Senator Evan Bayh and Virginia Governor Tim Kaine.[97] At the Democratic National Convention in Denver, Colorado, Hillary Clinton called for her supporters to endorse Obama, and she and Bill Clinton gave convention speeches in his support.[98] Obama delivered his acceptance speech, not at the center where the Democratic National Convention was held, but at Invesco Field at Mile High to a crowd of over 75,000; the speech was viewed by over 38 million people worldwide.[99][100]
During both the primary process and the general election, Obama's campaign set numerous fundraising records, particularly in the quantity of small donations.[101] On June 19, 2008, Obama became the first major-party presidential candidate to turn down public financing in the general election since the system was created in 1976.[102]

McCain was nominated as the Republican candidate and the two engaged in three presidential debates in September and October 2008.[103] On November 4, Obama won the presidency with 365 electoral votes to 173 received by McCain.[104] Obama won 52.9 percent of the popular vote to McCain's 45.7 percent.[105] He became the first African American to be elected president.[106] Obama delivered his victory speech before hundreds of thousands of supporters in Chicago's Grant Park.[107]
2012 presidential campaign
On April 4, 2011, Obama announced his re-election campaign for 2012 in a video titled "It Begins with Us" that he posted on his website and filed election papers with the Federal Election Commission.[108][109][110]
Presidency
First days

The inauguration of Barack Obama as the 44th President, and Joe Biden as Vice President, took place on January 20, 2009. In his first few days in office Obama issued executive orders and presidential memoranda directing the U.S. military to develop plans to withdraw troops from Iraq.[111] He ordered the closing of the Guantanamo Bay detention camp "as soon as practicable and no later than" January 2010,[112] but during his first two years in office he has been unable to persuade Congress to appropriate funds required to accomplish the shutdown.[113][114][115] Obama reduced the secrecy given to presidential records[116] and changed procedures to promote disclosure under the Freedom of Information Act.[117] He also reversed George W. Bush's ban on federal funding to foreign establishments that allow abortions.[118]
Domestic policy
The first bill signed into law by Obama was the Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act of 2009, relaxing the statute of limitations for equal-pay lawsuits.[119] Five days later, he signed the reauthorization of the State Children's Health Insurance Program (SCHIP) to cover an additional 4 million uninsured children.[120] In March 2009, Obama reversed a Bush-era policy which had limited funding of embryonic stem cell research. Obama stated that he believed "sound science and moral values ... are not inconsistent" and pledged to develop "strict guidelines" on the research.[121]

Obama appointed two women to serve on the Supreme Court in the first two years of his Presidency. Sonia Sotomayor, nominated by Obama on May 26, 2009, to replace retiring Associate Justice David Souter, was confirmed on August 6, 2009,[122] becoming the first Hispanic to be a Supreme Court Justice.[123] Elena Kagan, nominated by Obama on May 10, 2010, to replace retiring Associate Justice John Paul Stevens, was confirmed on August 5, 2010, bringing the number of women sitting simultaneously on the Court to three, for the first time in American history.[124]
On September 30, 2009, the Obama administration proposed new regulations on power plants, factories and oil refineries in an attempt to limit greenhouse gas emissions and to curb global warming.[125][126]
On October 8, 2009, Obama signed the Matthew Shepard and James Byrd, Jr. Hate Crimes Prevention Act, a measure that expands the 1969 United States federal hate-crime law to include crimes motivated by a victim's actual or perceived gender, sexual orientation, gender identity, or disability.[127][128]
On March 30, 2010, Obama signed the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act, a reconciliation bill which ends the process of the federal government giving subsidies to private banks to give out federally insured loans, increases the Pell Grant scholarship award, and makes changes to the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.[129][130]
In a major space policy speech in April 2010, Obama announced a planned change in direction at NASA, the U.S. space agency. He ended plans for a return of human spaceflight to the moon and ended development of the Ares I rocket, Ares V rocket and Constellation program. He is focusing funding (which is expected to rise modestly) on Earth science projects and a new rocket type, as well as research and development for an eventual manned mission to Mars. Missions to the International Space Station are expected to continue until 2020.[131]
On December 22, 2010, Obama signed the Don't Ask, Don't Tell Repeal Act of 2010, a bill that provides for repeal of the Don't ask, don't tell policy of 1993 that has prevented gay and lesbian people from serving openly in the United States Armed Forces.[132] Repealing "Don't ask, don't tell" had been a key campaign promise that Obama had made during the 2008 presidential campaign.[133][134]
On January 25, 2011, in his 2011 State of the Union Address, President Obama focused strongly on the themes of education and innovation, stressing the importance of innovation economics in working to make the United States more competitive globally. Among other plans and goals, Obama spoke of enacting a five-year freeze in domestic spending, eliminating tax breaks for oil companies and tax cuts for the wealthiest two percent of Americans, banning congressional earmarks, and reducing healthcare costs. Looking to the future, Obama promised that by 2015, the United States would have one million electric vehicles on the road and by 2035, clean-energy sources would be providing 80 percent of U.S. electricity.[135][136]
Economic policy

On February 17, 2009, Obama signed the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, a $787 billion economic stimulus package aimed at helping the economy recover from the deepening worldwide recession.[137] The act includes increased federal spending for health care, infrastructure, education, various tax breaks and incentives, and direct assistance to individuals,[138] which is being distributed over the course of several years.

In March, Obama's Treasury Secretary, Timothy Geithner, took further steps to manage the financial crisis, including introducing the Public-Private Investment Program for Legacy Assets, which contains provisions for buying up to $2 trillion in depreciated real estate assets.[141] Obama intervened in the troubled automotive industry[142] in March 2009, renewing loans for General Motors and Chrysler to continue operations while reorganizing. Over the following months the White House set terms for both firms' bankruptcies, including the sale of Chrysler to Italian automaker Fiat[143] and a reorganization of GM giving the U.S. government a temporary 60 percent equity stake in the company, with the Canadian government shouldering a 12 percent stake.[144] In June 2009, dissatisfied with the pace of economic stimulus, Obama called on his cabinet to accelerate the investment.[145] He signed into law the Car Allowance Rebate System, known colloquially as "Cash for Clunkers", that temporarily boosted the economy.[146][147][148]
Although spending and loan guarantees from the Federal Reserve and the Treasury Department authorized by the Bush and Obama administrations totaled about $11.5 trillion, only $3 trillion had been spent by the end of November 2009.[149] However, Obama and the Congressional Budget Office predicted that the 2010 budget deficit will be $1.5 trillion or 10.6 percent of the nation's gross domestic product (GDP) compared to the 2009 deficit of $1.4 trillion or 9.9 percent of GDP.[150][151] For 2011, the administration predicted the deficit will slightly shrink to $1.34 trillion, while the 10-year deficit will increase to $8.53 trillion or 90 percent of GDP.[152] The most recent increase in the U.S. debt ceiling to $14.3 trillion was signed into law on February 12, 2010.[153] On August 2, 2011, after a lengthy congressional debate over whether to raise the nation's debt limit, Obama signed the bipartisan Budget Control Act of 2011. The legislation enforces limits on discretionary spending until 2021, establishes a procedure to increase the debt limit, creates a Congressional Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction to propose further deficit reduction with a stated goal of achieving at least $1.5 trillion in budgetary savings over 10 years, and establishes automatic procedures for reducing spending by as much as $1.2 trillion if legislation originating with the new joint select committee does not achieve such savings.[154] By passing the legislation, Congress was able to prevent an unprecedented U.S. government default on its obligations.[155]
The unemployment rate rose in 2009, reaching a peak in October at 10.1 percent and averaging 10.0 percent in the fourth quarter. Following a decrease to 9.7 percent in the first quarter of 2010, the unemployment rate fell to 9.6 percent in the second quarter, where it remained for the rest of the year.[156] Between February and December 2010, employment rose by 0.8 percent, which was less than the average of 1.9 percent experienced during comparable periods in the past four employment recoveries.[157] GDP growth returned in the third quarter of 2009, expanding at a rate of 1.6 percent, followed by a 5.0 percent increase in the fourth quarter.[158] Growth continued in 2010, posting an increase of 3.7 percent in the first quarter, with lesser gains throughout the rest of the year.[158] In July 2010, the Federal Reserve expressed that although economic activity continued to increase, its pace had slowed, and Chairman Ben Bernanke stated that the economic outlook was "unusually uncertain."[159] Overall, the economy expanded at a rate of 2.9 percent in 2010.[160]
The Congressional Budget Office and a broad range of economists credit Obama's stimulus plan for economic growth.[161][162] The CBO released a report stating that the stimulus bill increased employment by 1–2.1 million,[162][163][164][165] while conceding that "It is impossible to determine how many of the reported jobs would have existed in the absence of the stimulus package."[161] Although an April 2010 survey of members of the National Association for Business Economics showed an increase in job creation (over a similar January survey) for the first time in two years, 73 percent of 68 respondents believed that the stimulus bill has had no impact on employment.[166]
Within a month of the 2010 midterm elections, Obama announced a compromise deal with the Congressional Republican leadership that included a temporary, two-year extension of the 2001 and 2003 income tax rates, a one-year payroll tax reduction, continuation of unemployment benefits, and a new rate and exemption amount for estate taxes.[167] The compromise overcame opposition from some in both parties, and the resulting $858 billion Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization, and Job Creation Act of 2010 passed with bipartisan majorities in both houses of Congress before Obama signed it on December 17, 2010.[168]
Health care reform

Obama called for Congress to pass legislation reforming health care in the United States, a key campaign promise and a top legislative goal.[169] He proposed an expansion of health insurance coverage to cover the uninsured, to cap premium increases, and to allow people to retain their coverage when they leave or change jobs. His proposal was to spend $900 billion over 10 years and include a government insurance plan, also known as the public option, to compete with the corporate insurance sector as a main component to lowering costs and improving quality of health care. It would also make it illegal for insurers to drop sick people or deny them coverage for pre-existing conditions, and require every American carry health coverage. The plan also includes medical spending cuts and taxes on insurance companies that offer expensive plans.[170][171]
On July 14, 2009, House Democratic leaders introduced a 1,017-page plan for overhauling the U.S. health care system, which Obama wanted Congress to approve by the end of 2009.[169] After much public debate during the Congressional summer recess of 2009, Obama delivered a speech to a joint session of Congress on September 9 where he addressed concerns over the proposals.[172] In March 2009, Obama lifted a ban on stem cell research.[173]
On November 7, 2009, a health care bill featuring the public option was passed in the House.[174][175] On December 24, 2009, the Senate passed its own bill—without a public option—on a party-line vote of 60–39.[176] On March 21, 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act passed by the Senate in December was passed in the House by a vote of 219 to 212.[177] Obama signed the bill into law on March 23, 2010.[178]
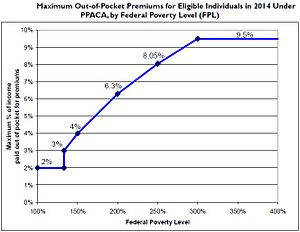
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act includes health-related provisions to take effect over four years, including expanding Medicaid eligibility for people making up to 133 percent of the federal poverty level (FPL) starting in 2014,[179] subsidizing insurance premiums for people making up to 400 percent of the FPL ($88,000 for family of four in 2010) so their maximum "out-of-pocket" payment for annual premiums will be from 2 to 9.5 percent of income,[180][181] providing incentives for businesses to provide health care benefits, prohibiting denial of coverage and denial of claims based on pre-existing conditions, establishing health insurance exchanges, prohibiting annual coverage caps, and support for medical research. According to White House and Congressional Budget Office figures, the maximum share of income that enrollees would have to pay would vary depending on their income relative to the federal poverty level.[180][182]
The costs of these provisions are offset by taxes, fees, and cost-saving measures, such as new Medicare taxes for those in high-income brackets, taxes on indoor tanning, cuts to the Medicare Advantage program in favor of traditional Medicare, and fees on medical devices and pharmaceutical companies;[183] there is also a tax penalty for those who do not obtain health insurance, unless they are exempt due to low income or other reasons.[184] The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the net effect of both laws will be a reduction in the federal deficit by $143 billion over the first decade.[185]
Gulf of Mexico oil spill
On April 20, 2010, an explosion destroyed an offshore drilling rig at the Macondo Prospect in the Gulf of Mexico, causing a major sustained oil leak. The well's operator, BP, initiated a containment and cleanup plan, and began drilling two relief wells intended to stop the flow. Obama visited the Gulf on May 2 among visits by members of his cabinet, and again on May 28 and June 4. On May 22 he announced a federal investigation and formed a bipartisan commission to recommend new safety standards, after a review by Secretary of the Interior Ken Salazar and concurrent Congressional hearings. On May 27, he announced a 6-month moratorium on new deepwater drilling permits and leases, pending regulatory review.[186] As multiple efforts by BP failed, some in the media and public expressed confusion and criticism over various aspects of the incident, and stated a desire for more involvement by Obama and the federal government.[187]
Foreign policy



In February and March, Vice President Joe Biden and Secretary of State Hillary Rodham Clinton made separate overseas trips to announce a "new era" in U.S. foreign relations with Russia and Europe, using the terms "break" and "reset" to signal major changes from the policies of the preceding administration.[188] Obama attempted to reach out to Arab leaders by granting his first interview to an Arab cable TV network, Al Arabiya.[189]
On March 19, Obama continued his outreach to the Muslim world, releasing a New Year's video message to the people and government of Iran.[190] This attempt at outreach was rebuffed by the Iranian leadership.[191] In April, Obama gave a speech in Ankara, Turkey, which was well received by many Arab governments.[192] On June 4, 2009, Obama delivered a speech at Cairo University in Egypt calling for "a new beginning" in relations between the Islamic world and the United States and promoting Middle East peace.[193]
On June 26, 2009, in response to the Iranian government's actions towards protesters following Iran's 2009 presidential election, Obama said: "The violence perpetrated against them is outrageous. We see it and we condemn it."[194] On July 7, while in Moscow, he responded to a Vice President Biden comment on a possible Israeli military strike on Iran by saying: "We have said directly to the Israelis that it is important to try and resolve this in an international setting in a way that does not create major conflict in the Middle East."[195]
On September 24, 2009, Obama became the first sitting U.S. president to preside over a meeting of the United Nations Security Council.[196]
In March 2010, Obama took a public stance against plans by the government of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to continue building Jewish housing projects in predominantly Arab neighborhoods of East Jerusalem.[197][198] During the same month, an agreement was reached with the administration of Russian President Dmitry Medvedev to replace the 1991 Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty with a new pact reducing the number of long-range nuclear weapons in the arsenals of both countries by about one-third.[199] The New START treaty was signed by Obama and Medvedev in April 2010, and was ratified by the U.S. Senate in December 2010.[200]
Iraq War
On February 27, 2009, Obama declared that combat operations in Iraq would end within 18 months. His remarks were made to a group of Marines preparing for deployment to Afghanistan. Obama said, "Let me say this as plainly as I can: By August 31, 2010, our combat mission in Iraq will end."[201] The Obama administration scheduled the withdrawal of combat troops to be completed by August 2010, decreasing troops levels from 142,000 while leaving a transitional force of 35,000 to 50,000 in Iraq until the end of 2011. On August 19, 2010, the last United States combat brigade exited Iraq. The plan is to transition the mission of the remaining troops from combat operations to counter-terrorism and the training, equipping, and advising of Iraqi security forces.[202][203] On August 31, 2010, Obama announced that the United States combat mission in Iraq was over.[204] On October 21, 2011 President Obama announced that all U.S. troops would leave Iraq in time to be, "home for the holidays".[205]
War in Afghanistan
Early in his presidency, Obama moved to bolster U.S. troop strength in Afghanistan.[206] He announced an increase to U.S. troop levels of 17,000 in February 2009 to "stabilize a deteriorating situation in Afghanistan", an area he said had not received the "strategic attention, direction and resources it urgently requires".[207] He replaced the military commander in Afghanistan, General David D. McKiernan, with former Special Forces commander Lt. Gen. Stanley A. McChrystal in May 2009, indicating that McChrystal's Special Forces experience would facilitate the use of counterinsurgency tactics in the war.[208] On December 1, 2009, Obama announced the deployment of an additional 30,000 military personnel to Afghanistan.[209] He also proposed to begin troop withdrawals 18 months from that date.[210][211] McChrystal was replaced by David Petraeus in June 2010, after McChrystal's staff criticized White House personnel in a magazine article.[212]
Israel

During the initial years of the Obama administration, the U.S. increased military cooperation with Israel, including a record number of U.S. troops participating in military exercises in the country, increased military aid, and the re-establishment of the U.S.-Israeli Joint Political Military Group and the Defense Policy Advisory Group. It was reported high-ranking defense officials from both countries had been making an unusual number of trips between the two countries, including Ehud Barak. Part of the military aid increase in 2010 was to fund Israel's missile defense shield. Before his retirement in September 2011, Adm. Mike Mullen, former Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, made four trips to Israel during his four-year tenure, two of them in 2010. Prior to 2007 no Chairman of the Joint Chiefs had done so for over ten years.[213]
In 2011, Obama's Ambassador to the United Nations vetoed a resolution condemning Israeli settlements, with the U.S. the only nation on the Security Council doing so.[214] Obama supports the two-state solution to the Arab-Israeli conflict based on the 1967 borders with land swaps.[215]
Libya
In March 2011, as forces loyal to Muammar Gaddafi advanced on rebels across Libya, calls for a no-fly zone came from around the world, including Europe, the Arab League, and a resolution[216] passed unanimously by the U.S. Senate.[217] In response to the unanimous passage of United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973 on March 17, Gaddafi who had previously vowed to "show no mercy" to the citizens of Benghazi[218]—announced an immediate cessation of military activities,[219] yet reports came in that his forces continued shelling Misrata.[220] The next day, on Obama's orders, the U.S. military took a lead role in air strikes to destroy the Libyan government's air defense capabilities in order to protect civilians and enforce a no-fly-zone,[221] including the use of Tomahawk missiles, B-2 Spirits, and fighter jets.[222][223][224] Six days later, on March 25, by unanimous vote of all of its 28 members, NATO took over leadership of the effort, dubbed Operation Unified Protector.[225] Some Representatives[226] questioned whether Obama had the constitutional authority to order military action in addition to questioning its cost, structure and aftermath.[227][228]

Osama bin Laden
Starting with information received in July 2010, intelligence developed by the CIA over the next several months determined what they believed to be the location of Osama bin Laden in a large compound in Abbottabad, Pakistan, a suburban area 35 miles from Islamabad.[229] CIA head Leon Panetta reported this intelligence to President Obama in March 2011.[229] Meeting with his national security advisers over the course of the next six weeks, Obama rejected a plan to bomb the compound, and authorized a "surgical raid" to be conducted by United States Navy SEALs.[229] The operation took place on May 1, 2011, resulting in the death of bin Laden and the seizure of papers and computer drives and disks from the compound.[230][231] Bin Laden's body was identified through DNA testing,[232] and buried at sea several hours later.[233] Within minutes of the President's announcement from Washington, DC, late in the evening on May 1, there were spontaneous celebrations around the country as crowds gathered outside the White House, and at New York City's Ground Zero and Times Square.[230][234] Reaction to the announcement was positive across party lines, including from former Presidents Bill Clinton and George W. Bush,[235] and from many countries around the world.[236]
2010 midterm election
Obama called the November 2, 2010 election, where the Democratic Party lost 63 seats in, and control of, the House of Representatives,[237] "humbling" and a "shellacking".[238] He said that the results came because not enough Americans had felt the effects of the economic recovery.[239]
Cultural and political image

Obama's family history, upbringing, and Ivy League education differ markedly from those of African American politicians who launched their careers in the 1960s through participation in the civil rights movement.[240] Obama is also not a descendant of American slaves.[241] Expressing puzzlement over questions about whether he is "black enough", Obama told an August 2007 meeting of the National Association of Black Journalists that "we're still locked in this notion that if you appeal to white folks then there must be something wrong".[242] Obama acknowledged his youthful image in an October 2007 campaign speech, saying: "I wouldn't be here if, time and again, the torch had not been passed to a new generation."[243]
Obama is frequently referred to as an exceptional orator.[244] During his pre-inauguration transition period and continuing into his presidency, Obama has delivered a series of weekly Internet video addresses.[245]
According to the Gallup Organization, Obama began his presidency with a 68 percent approval rating[246] before gradually declining for the rest of the year, and eventually bottoming out at 41 percent in August 2010,[247] a trend similar to Ronald Reagan's and Bill Clinton's first years in office.[248] He experienced a small poll bounce shortly after the death of Osama bin Laden, which lasted until around June 2011, when his approval numbers dropped back to where they were prior to the operation.[249][250][251] Polls show strong support for Obama in other countries,[252] and before being elected President he has met with prominent foreign figures including then-British Prime Minister Tony Blair,[253] Italy's Democratic Party leader and then Mayor of Rome Walter Veltroni,[254] and French President Nicolas Sarkozy.[255]

In a February 2009 poll conducted by Harris Interactive for France 24 and the International Herald Tribune, Obama was rated as the most respected world leader, as well as the most powerful.[257] In a similar poll conducted by Harris in May 2009, Obama was rated as the most popular world leader, as well as the one figure most people would pin their hopes on for pulling the world out of the economic downturn.[258][259]
Obama won Best Spoken Word Album Grammy Awards for abridged audiobook versions of Dreams from My Father in February 2006 and for The Audacity of Hope in February 2008.[260] His concession speech after the New Hampshire primary was set to music by independent artists as the music video "Yes We Can", which was viewed 10 million times on YouTube in its first month[261] and received a Daytime Emmy Award.[262] In December 2008, Time magazine named Obama as its Person of the Year for his historic candidacy and election, which it described as "the steady march of seemingly impossible accomplishments".[263]
On October 9, 2009, the Norwegian Nobel Committee announced that Obama had won the 2009 Nobel Peace Prize "for his extraordinary efforts to strengthen international diplomacy and cooperation between peoples".[264] Obama accepted this award in Oslo, Norway on December 10, 2009, with "deep gratitude and great humility."[265] The award drew a mixture of praise and criticism from world leaders and media figures.[266][267] Obama is the fourth U.S. president to be awarded the Nobel Peace Prize and the third to become a Nobel laureate while in office.
Family and personal life

In a 2006 interview, Obama highlighted the diversity of his extended family: "It's like a little mini-United Nations", he said. "I've got relatives who look like Bernie Mac, and I've got relatives who look like Margaret Thatcher."[268] Obama has a half-sister with whom he was raised, Maya Soetoro-Ng, the daughter of his mother and her Indonesian second husband and seven half-siblings from his Kenyan father's family – six of them living.[269] Obama's mother was survived by her Kansas-born mother, Madelyn Dunham,[270] until her death on November 2, 2008,[271] two days before his election to the Presidency. Obama also has roots in Ireland; he met with his Irish cousins in Moneygall in May 2011.[272] In Dreams from My Father, Obama ties his mother's family history to possible Native American ancestors and distant relatives of Jefferson Davis, President of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War.[273]
Obama was known as "Barry" in his youth, but asked to be addressed with his given name during his college years.[274] Besides his native English, Obama speaks Indonesian at the conversational level, which he learned during his four childhood years in Jakarta.[275] He plays basketball, a sport he participated in as a member of his high school's varsity team.[276]

Obama is a well known supporter of the Chicago White Sox, and threw out the first pitch at the 2005 ALCS when he was still a senator.[277] In 2009, he threw out the ceremonial first pitch at the all star game while wearing a White Sox jacket.[278] He is also primarily a Chicago Bears fan in the NFL, but in his childhood and adolescence was a fan of the Pittsburgh Steelers, and recently rooted for them ahead of their victory in Super Bowl XLIII 12 days after Obama took office as President.[279]
In June 1989, Obama met Michelle Robinson when he was employed as a summer associate at the Chicago law firm of Sidley Austin.[280] Assigned for three months as Obama's adviser at the firm, Robinson joined him at group social functions, but declined his initial requests to date.[281] They began dating later that summer, became engaged in 1991, and were married on October 3, 1992.[282] The couple's first daughter, Malia Ann, was born on July 4, 1998,[283] followed by a second daughter, Natasha ("Sasha"), on June 10, 2001.[284] The Obama daughters attended the private University of Chicago Laboratory Schools. When they moved to Washington, D.C., in January 2009, the girls started at the private Sidwell Friends School.[285] The Obamas have a Portuguese Water Dog named Bo, a gift from Senator Ted Kennedy.[286]
Applying the proceeds of a book deal, the family moved in 2005 from a Hyde Park, Chicago condominium to a $1.6 million house in neighboring Kenwood, Chicago.[287] The purchase of an adjacent lot—and sale of part of it to Obama by the wife of developer, campaign donor and friend Tony Rezko—attracted media attention because of Rezko's subsequent indictment and conviction on political corruption charges that were unrelated to Obama.[288]
In December 2007, Money magazine estimated the Obama family's net worth at $1.3 million.[289] Their 2009 tax return showed a household income of $5.5 million—up from about $4.2 million in 2007 and $1.6 million in 2005—mostly from sales of his books.[290][291] On his 2010 income of $1.7 million, he gave 14 percent to non-profit organizations, including $131,000 to Fisher House Foundation, a charity assisting wounded veterans' families, allowing them to reside near where the veteran is receiving medical treatments.[292][293]
Obama tried to quit smoking several times, sometimes using nicotine replacement therapy, and, in early 2010, Michelle Obama said that he had successfully quit smoking.[294][295]
Religious views
Obama is a Christian whose religious views developed in his adult life. He wrote in The Audacity of Hope that he "was not raised in a religious household". He described his mother, raised by non-religious parents (whom Obama has specified elsewhere as "non-practicing Methodists and Baptists"), to be detached from religion, yet "in many ways the most spiritually awakened person that I have ever known". He described his father as "raised a Muslim", but a "confirmed atheist" by the time his parents met, and his stepfather as "a man who saw religion as not particularly useful". Obama explained how, through working with black churches as a community organizer while in his twenties, he came to understand "the power of the African-American religious tradition to spur social change".[296]
In an interview with the evangelical periodical Christianity Today, Obama stated: "I am a Christian, and I am a devout Christian. I believe in the redemptive death and resurrection of Jesus Christ. I believe that that faith gives me a path to be cleansed of sin and have eternal life."[297]
On September 27, 2010, Obama released a statement commenting on his religious views saying "I'm a Christian by choice. My family didn't—frankly, they weren't folks who went to church every week. And my mother was one of the most spiritual people I knew, but she didn't raise me in the church. So I came to my Christian faith later in life, and it was because the precepts of Jesus Christ spoke to me in terms of the kind of life that I would want to lead—being my brothers' and sisters' keeper, treating others as they would treat me."[298][299]
Obama was baptized at the Trinity United Church of Christ, a black liberation church, in 1988, and was an active member there for two decades.[300] Obama resigned from Trinity during the Presidential campaign after controversial statements made by Rev. Jeremiah Wright became public.[301] After a prolonged effort to find a church to attend regularly in Washington, Obama announced in June 2009 that his primary place of worship would be the Evergreen Chapel at Camp David.[302]
Notes
- ^ "President Barack Obama". Washington, D.C.: The White House. 2008. Retrieved December 12, 2008.
- ^ a b "Certification of Live Birth: Barack Hussein Obama II, August 4, 1961, 7:24 pm, Honolulu" (PDF). Department of Health, State of Hawaii. The White House. April 27, 2011. Retrieved April 27, 2011.
- ^ "American President: Barack Obama". Charlottesville, VA: Miller Center of Public Affairs, University of Virginia. 2009. Retrieved January 23, 2009.
Religion: Christian
- "The Truth about Barack's Faith" (PDF). Obama for America. Retrieved April 8, 2011.
- Miller, Lisa (July 18, 2008). "Finding his faith". Newsweek. Retrieved February 4, 2010.
He is now a Christian, having been baptized in the early 1990s at Trinity United Church of Christ in Chicago.
- Barakat, Matthew (November 17, 2008). "Obama's church choice likely to be scrutinized; D.C. churches have started extending invitations to Obama and his family". MSNBC. Associated Press. Retrieved January 20, 2009.
The United Church of Christ, the denomination from which Obama resigned when he left Wright's church, issued a written invitation to join a UCC denomination in Washington and resume his connections to the church.
. - "Barack Obama, long time UCC member, inaugurated forty-fourth U.S. President". News. United Church of Christ. January 20, 2009. Retrieved January 21, 2009.
Barack Obama, who spent more than 20 years as a UCC member, is the forty-fourth President of the United States.
- Sullivan, Amy (June 29, 2009). "The Obama's find a church home—away from home". Time. Retrieved February 5, 2010.
instead of joining a congregation in Washington, D.C., he will follow in George W. Bush's footsteps and make his primary place of worship Evergreen Chapel, the nondenominational church at Camp David.
. - Kornblut, Anne E. (February 4, 2010). "Obama's spirituality is largely private, but it's influential, advisers say". The Washington Post. p. A6. Retrieved February 5, 2010.
Obama prays privately ... And when he takes his family to Camp David on the weekends, a Navy chaplain ministers to them, with the daughters attending a form of Sunday school there.
- ^ a b Maraniss, David (August 24, 2008). "Though Obama had to leave to find himself, it is Hawaii that made his rise possible". The Washington Post. p. A22. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Nakaso, Dan (December 22, 2008). "Twin sisters, Obama on parallel paths for years". The Honolulu Advertiser. p. B1. Retrieved January 22, 2011.
- ^ Rudin, Ken (December 23, 2009). "Today's Junkie segment On TOTN: a political review Of 2009". Talk of the Nation (Political Junkie blog). NPR. Retrieved April 18, 2010.
We began with the historic inauguration on January 20—yes, the first president ever born in Hawaii
- ^ for Stanley Ann's first name, see Obama (1995, 2004), p. 19.
- ^ Ewen MacAskill in Washington and Nicholas Watt (May 20, 2011). "Obama looks forward to rediscovering his Irish roots on European tour". The Guardian. London. Retrieved August 3, 2011.
- ^ Mason, Jeff (May 23, 2011). "Obama visits family roots in Ireland". Reuters. Retrieved August 3, 2011.
- ^ Obama urged to create own tartan. BBC News
- ^ Researchers: Obama has German roots. USATODAY.com]
- ^ Honorary citizenship papers sent to Obama. swissinfo
- ^ a b Jones, Tim (March 27, 2007). "Barack Obama: Mother not just a girl from Kansas; Stanley Ann Dunham shaped a future senator". Chicago Tribune. p. 1 (Tempo). Retrieved March 27, 2007.
- ^ a b Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 9–10.
- ^ a b Ripley, Amanda (April 9, 2008). "The story of Barack Obama's mother". Time. Retrieved April 9, 2007.
- ^ Ochieng, Philip (November 1, 2004). "From home squared to the US Senate: how Barack Obama was lost and found". The EastAfrican. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved June 25, 2008.
- Merida, Kevin (December 14, 2007). "The ghost of a father". The Washington Post. p. A12. Retrieved June 25, 2008.
- ^ Karana, Kinanti Pinta (December 9, 2009). "Statue of a young Obama to watch over Indonesian capital". Jakarta Globe. Retrieved December 8, 2009.
- Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 44–45.
- ^ Pickler, Nedra (January 24, 2007). "Obama debunks claim about Islamic school". The Washington Post. Associated Press. Retrieved December 31, 2009.
- "Statue of boy Obama erected in Jakarta". Xinhua News Agency. December 10, 2009. Retrieved December 31, 2009.
- ^ Serafin, Peter (March 21, 2004). "Punahou grad stirs up Illinois politics". Honolulu Star-Bulletin. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- Scott, Janny (March 14, 2008). "A free-spirited wanderer who set Obama's path". The New York Times. p. A1. Retrieved November 18, 2011.
- Obama (1995, 2004), Chapters 3 and 4.
- ^ Suryakusuma, Julia (November 29, 2006). "Obama for President... of Indonesia". The Jakarta Post. Retrieved June 25, 2008.
- ^ Serrano, Richard A. (March 11, 2007). "Obama's peers didn't see his angst". Los Angeles Times. p. A20. Retrieved March 13, 2007.
- Obama (1995, 2004), Chapters 4 and 5.
- ^ Reyes, B.J. (February 8, 2007). "Punahou left lasting impression on Obama". Honolulu Star-Bulletin. Retrieved February 10, 2007.
As a teenager, Obama went to parties and sometimes sought out gatherings on military bases or at the University of Hawaii that were mostly attended by blacks.
- ^ Elliott, Philip (November 21, 2007). "Obama gets blunt with N.H. students". The Boston Globe. Associated Press. p. 8A. Retrieved January 4, 2008.
- Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 93–94.
- for analysis of the political impact of the quote and Obama's more recent admission that he smoked marijuana as a teenager ("When I was a kid, I inhaled"), see:
- Seelye, Katharine Q. (October 24, 2006). "Obama offers more variations from the norm". The New York Times. p. A21. Retrieved October 29, 2006.
- Romano, Lois (January 3, 2007). "Effect of Obama's candor remains to be seen". The Washington Post. p. A1. Retrieved January 14, 2007.
- ^ Hornick, Ed (August 17, 2008). "Obama, McCain talk issues at pastor's forum". CNN. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ^ a b Gordon, Larry (January 29, 2007). "Occidental recalls 'Barry' Obama". Los Angeles Times. p. B1. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
- Possley, Maurice (March 30, 2007). "Activism blossomed in college". Chicago Tribune. p. 20. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
- Kovaleski, Serge F. (February 9, 2008). "Old friends say drugs played bit part in Obama's young life". The New York Times. p. A1. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
- Rohter, Larry (April 10, 2008). "Obama says real-life experience trumps rivals' foreign policy credits". The New York Times. p. A18. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
- Goldman, Adam; Tanner, Robert (May 15, 2008). "Old friends recall Obama's years in LA, NYC". USA Today. Associated Press. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Helman, Scott (August 25, 2008). "Small college awakened future senator to service". The Boston Globe. p. 1A. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
- Jackson, Brooks (June 5, 2009). "More 'birther' nonsense: Obama's 1981 Pakistan trip". FactCheck.org. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
- Remnick, David (2010). The Bridge: The Life and Rise of Barack Obama. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. pp. 98–112. ISBN 978-1-4000-4360-6.
- Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 92–112.
- Mendell (2007), pp. 55–62.
- ^ Boss-Bicak, Shira (January 2005). "Barack Obama '83". Columbia College Today. ISSN 0572-7820. Retrieved October 1, 2006.
- ^ Obama, Barack (1998). "Curriculum vitae". The University of Chicago Law School. Archived from the original on May 9, 2001. Retrieved October 1, 2006.
- Issenberg, Sasha (August 6, 2008). "Obama shows hints of his year in global finance; Tied markets to social aid". The Boston Globe. p. 1A. Retrieved August 6, 2008.
- ^ Scott, Janny (July 30, 2007). "Obama's account of New York often differs from what others say". The New York Times. p. B1. Retrieved July 31, 2007.
- Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 133–140.
- Mendell (2007), pp. 62–63.
- ^ a b c d Chassie, Karen, ed. (2007). Who's Who in America, 2008. New Providence, NJ: Marquis Who's Who. p. 3468. ISBN 978-0-8379-7011-0.
- ^ Lizza, Ryan (March 19, 2007). "The agitator: Barack Obama's unlikely political education". The New Republic. 236 (12): 22–26, 28–29. ISSN 0028-6583. Retrieved August 21, 2007.
- Secter, Bob; McCormick, John (March 30, 2007). "Portrait of a pragmatist". Chicago Tribune. p. 1. Retrieved April 8, 2007.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 140–295.
- Mendell (2007), pp. 63–83.
- Secter, Bob; McCormick, John (March 30, 2007). "Portrait of a pragmatist". Chicago Tribune. p. 1. Retrieved April 8, 2007.
- ^ a b c Matchan, Linda (February 15, 1990). "A Law Review breakthrough". The Boston Globe. p. 29. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- Corr, John (February 27, 1990). 27, 1990%20to%2002/27/1990)&p_field_advanced-0=Author&p_text_advanced-0=(John%20Corr)&xcal_numdocs=20&p_perpage=10&p_sort=_rank_:D&xcal_ranksort=4&xcal_useweights=yes "From mean streets to hallowed halls" (paid archive). The Philadelphia Inquirer. p. C01. Retrieved June 6, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Check|url=value (help)
- Corr, John (February 27, 1990). 27, 1990%20to%2002/27/1990)&p_field_advanced-0=Author&p_text_advanced-0=(John%20Corr)&xcal_numdocs=20&p_perpage=10&p_sort=_rank_:D&xcal_ranksort=4&xcal_useweights=yes "From mean streets to hallowed halls" (paid archive). The Philadelphia Inquirer. p. C01. Retrieved June 6, 2008.
- ^ Obama, Barack (1988). "Why organize? Problems and promise in the inner city". Illinois Issues. 14 (8–9): 40–42. ISSN 0738-9663.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) reprinted in:
Knoepfle, Peg, ed. (1990). After Alinsky: community organizing in Illinois. Springfield, IL: Sangamon State University. pp. 35–40. ISBN 0-9620873-3-5.He has also been a consultant and instructor for the Gamaliel Foundation, an organizing institute working throughout the Midwest.
- ^ Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 299–437.
- ^ Gnecchi, Nico (February 27, 2006). "Obama receives hero's welcome at his family's ancestral village in Kenya". Voice of America. Archived from the original on March 21, 2008. Retrieved June 25, 2008.
- ^ a b Levenson, Michael; Saltzman, Jonathan (January 28, 2007). "At Harvard Law, a unifying voice". The Boston Globe. p. 1A. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)- Kantor, Jodi (January 28, 2007). "In law school, Obama found political voice". The New York Times. p. A1. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- Mundy, Liza (August 12, 2007). "A series of fortunate events". The Washington Post. p. W10. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- Mendell (2007), pp. 80–92.
- ^ a b Butterfield, Fox (February 6, 1990). "First black elected to head Harvard's Law Review". The New York Times. p. A20. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- Ybarra, Michael J (February 7, 1990). "Activist in Chicago now heads Harvard Law Review". Chicago Tribune. p. 3. Retrieved October 29, 2011.
- Drummond, Tammerlin (March 12, 1990). "Barack Obama's law; Harvard Law Review's first black president plans a life of public service" (paid archive). Los Angeles Times. p. E1. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- Evans, Gaynelle (March 15, 1990). "Opening another door: The saga of Harvard's Barack H. Obama". Black Issues in Higher Education. 7 (1): 5. ISSN 0742-0277. Retrieved November 15, 2008.
- Pugh, Allison J. (April 18, 1990). 18, 1990%20to%2004/18/1990)&p_field_advanced-0=title&p_text_advanced-0=(Law%20Review's%20first%20black%20president%20aims%20to%20help%20poor)&xcal_numdocs=20&p_perpage=10&p_sort=_rank_:D&xcal_ranksort=4&xcal_useweights=yes "Law Review's first black president aims to help poor". The Miami Herald. Associated Press. p. C01. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Check|url=value (help)
- ^ Aguilar, Louis (July 11, 1990). "Survey: Law firms slow to add minority partners". Chicago Tribune. p. 1 (Business). Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- ^ Adams, Richard (May 9, 2007). "Barack Obama". The Guardian. London. Retrieved October 26, 2008.
- ^ a b c Scott, Janny (May 18, 2008). "The story of Obama, written by Obama". The New York Times. p. A1. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- Obama (1995, 2004), pp. xiii–xvii.
- ^ Merriner, James L. (June 2008). "The friends of O". Chicago. 57 (6): 74–79, 97–99. ISSN 0362-4595. Retrieved January 30, 2010.
- Zengerle, Jason (July 30, 2008). "Con law; What the University of Chicago right thinks of Obama". The New Republic. 239 (1): 7–8. ISSN 0028-6583. Retrieved January 30, 2010.
- Kantor, Jodi (July 30, 2008). "Teaching law, testing ideas, Obama stood slightly apart". The New York Times. p. A1. Retrieved January 30, 2010.
- Gray, Steven (September 10, 2008). "Taking professor Obama's class". Time. Retrieved January 30, 2010.
- Starr, Alexandra (September 21, 2008). "Case study". The New York Times Magazine. p. 76. Retrieved January 30, 2010.
- Hundley, Tom (March 22, 2009). "Ivory tower of power". Chicago Tribune Magazine. p. 6. Retrieved January 30, 2010.
- ^ "Statement regarding Barack Obama". University of Chicago Law School. March 27, 2008. Retrieved June 5, 2008.
- Miller, Joe (March 28, 2008). "Was Barack Obama really a constitutional law professor?". FactCheck.org. Retrieved June 10, 2008.
- Holan, Angie Drobnic (March 7, 2008). "Obama's 20 years of experience". PolitiFact.com. Retrieved June 10, 2008.
- ^ White, Jesse, ed. (2000). Illinois Blue Book, 2000, Millennium ed (PDF). Springfield, IL: Illinois Secretary of State. p. 83. OCLC 43923973. Archived from the original on April 16, 2004. Retrieved June 6, 2008.
- Jarrett, Vernon (August 11, 1992). "'Project Vote' brings power to the people" (paid archive). Chicago Sun-Times. p. 23. Retrieved June 6, 2008.
- Reynolds, Gretchen (1993). "Vote of confidence". Chicago. 42 (1): 53–54. ISSN 0362-4595. Retrieved June 6, 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Anderson, Veronica (1993). "40 under Forty: Barack Obama, Director, Illinois Project Vote". Crain's Chicago Business. 16 (39): 43. ISSN 0149-6956.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
- ^ Robinson, Mike (February 20, 2007). "Obama got start in civil rights practice". The Boston Globe. Associated Press. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- Pallasch, Abdon M. (December 17, 2007). 17, 2007%20to%2012/17/2007)&p_field_advanced-0=&p_text_advanced-0=(Pallasch)&xcal_numdocs=20&p_perpage=10&p_sort=YMD_date:D&xcal_useweights=no "As lawyer, Obama was strong, silent type; He was 'smart, innovative, relentless,' and he mostly let other lawyers do the talking" (paid archive). Chicago Sun-Times. p. 4. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Check|url=value (help) - Morain, Dan (April 6, 2008). "Obama's law days effective but brief". Los Angeles Times. p. A14. Retrieved February 14, 2010.
- "People" (paid archive). Chicago Tribune. June 27, 1993. p. 9 (Business). Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- "Business appointments" (paid archive). Chicago-Sun-Times. July 5, 1993. p. 40. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- Ripley, Amanda (November 3, 2004). "Obama's ascent". Time. Retrieved February 13, 2010.
- "About us". Miner, Barnhill & Galland – Chicago, Illinois. 2008. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- Reardon, Patrick T. (June 25, 2008). "Obama's Chicago". Chicago Tribune. p. 1 (Tempo). Retrieved February 13, 2010.
- Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 438–439.
- Mendell (2007), pp. 104–106.
- Pallasch, Abdon M. (December 17, 2007). 17, 2007%20to%2012/17/2007)&p_field_advanced-0=&p_text_advanced-0=(Pallasch)&xcal_numdocs=20&p_perpage=10&p_sort=YMD_date:D&xcal_useweights=no "As lawyer, Obama was strong, silent type; He was 'smart, innovative, relentless,' and he mostly let other lawyers do the talking" (paid archive). Chicago Sun-Times. p. 4. Retrieved June 15, 2008.
- ^ Jackson, David (April 3, 2007). "Obama Knows His Way Around a Ballot". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved January 14, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)White, Jesse (2001). "Legislative Districts of Cook County, 1991 Reapportionment". Illinois Blue Book 2001–2002. Springfield: Illinois Secretary of State. p. 65.{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) State Sen. District 13 = State Rep. Districts 25 & 26. - ^ Slevin, Peter (February 9, 2007). "Obama Forged Political Mettle in Illinois Capitol". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 20, 2008.Helman, Scott (September 23, 2007). "In Illinois, Obama dealt with Lobbyists". The Boston Globe. Retrieved April 20, 2008. See also:"Obama Record May Be Gold Mine for Critics". CBS News. Associated Press. January 17, 2007. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
- ^ a b Scott, Janny (July 30, 2007). "In Illinois, Obama Proved Pragmatic and Shrewd". The New York Times. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
- ^ Allison, Melissa (December 15, 2000). "State takes on predatory lending; Rules would halt single-premium life insurance financing" (paid archive). Chicago Tribune. p. 1 (Business). Retrieved June 1, 2008.Long, Ray; Allison, Melissa (April 18, 2001). "Illinois OKs predatory loan curbs; State aims to avert home foreclosures" (paid archive). Chicago Tribune. p. 1. Retrieved June 1, 2008.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "13th District: Barack Obama". Illinois State Senate Democrats. August 24, 2000. Archived from the original on April 12, 2000. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; August 24, 2000 suggested (help)"13th District: Barack Obama". Illinois State Senate Democrats. October 9, 2004. Archived from the original on August 2, 2004. Retrieved April 20, 2008. - ^ "Federal Elections 2000: U.S. House Results – Illinois". Federal Election Commission. Retrieved April 24, 2008.
- Gonyea, Dan (September 19, 2007). "Obama's Loss May Have Aided White House Bid". Retrieved January 30, 2011.
- Scott, Janny (September 9, 2007). "A Streetwise Veteran Schooled Young Obama". The New York Times. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
- McClelland, Edward (February 12, 2007). "How Obama Learned to Be a Natural". Salon. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
- Wolffe, Richard (July 16, 2007). "Across the Divide". Newsweek. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Helman, Scott (October 12, 2007). "Early Defeat Launched a Rapid Political Climb". The Boston Globe. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
- Wills, Christopher (October 24, 2007). "Obama learned from failed Congress run". USA Today. Retrieved November 15, 2010.
- ^ Calmes, Jackie (February 23, 2007). "Statehouse Yields Clues to Obama". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
- ^ Tavella, Anne Marie (April 14, 2003). 4, 2003%20to%204/4/2003)&p_field_date-0=YMD_date&p_params_date-0=date:B,E&p_text_date-0=4 April 2003%20to%204/4/2003)&xcal_numdocs=20&p_perpage=10&p_sort=YMD_date:D&xcal_useweights=no "Profiling, taping plans pass Senate" (paid archive). Daily Herald. p. 17. Retrieved June 1, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Check|url=value (help)Haynes, V. Dion (June 29, 2003). "Fight racial profiling at local level, lawmaker says; U.S. guidelines get mixed review" (paid archive). Chicago Tribune. p. 8. Retrieved June 1, 2008.Pearson, Rick (July 17, 2003). "Taped confessions to be law; State will be 1st to pass legislation" (paid archive). Chicago Tribune. p. 1 (Metro). Retrieved June 1, 2008. - ^ Youngman, Sam (March 14, 2007). "Obama's Crime Votes Are Fodder for Rivals". The Hill. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) See also:"US Presidential Candidate Obama Cites Work on State Death Penalty Reforms". International Herald Tribune. Associated Press. November 12, 2007. Retrieved April 20, 2008. - ^ Coffee, Melanie (November 6, 2004). "Attorney Chosen to Fill Obama's State Senate Seat". HPKCC. Associated Press. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
- ^ Helman, Scott (October 12, 2007). "Early defeat launched a rapid political climb". The Boston Globe. p. 1A. Retrieved April 13, 2008.
- ^ Strausberg, Chinta (September 26, 2002). "Opposition to war mounts" (paid archive). Chicago Defender. p. 1. Retrieved February 3, 2008.
- ^ Office of the Press Secretary (October 2, 2002). "President, House leadership agree on Iraq resolution". The White House. Retrieved February 18, 2008.
- Tackett, Michael (October 3, 2002). "Bush, House OK Iraq deal; Congress marches with Bush" (paid archive). Chicago Tribune. p. 1. Retrieved February 3, 2008.
- ^ Glauber, Bill (October 3, 2003). "War protesters gentler, but passion still burns" (paid archive). Chicago Tribune. p. 1. Retrieved February 3, 2008.
- Strausberg, Chinta (October 3, 2002). "War with Iraq undermines U.N". Chicago Defender. p. 1. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
Photo caption: Left Photo: Sen. Barack Obama along with Rev. Jesse Jackson spoke to nearly 3,000 anti-war protestors (below) during a rally at Federal Plaza Wednesday.
- Katz, Marilyn (October 2, 2007). "Five years since our first action". Chicagoans Against War & Injustice. Archived from the original on July 21, 2011. Retrieved February 18, 2008.
- Bryant, Greg; Vaughn, Jane B. (October 3, 2002). "300 attend rally against Iraq war" (paid archive). Daily Herald (Arlington Heights). p. 8. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Mendell (2007), pp. 172–177.
- Strausberg, Chinta (October 3, 2002). "War with Iraq undermines U.N". Chicago Defender. p. 1. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Obama, Barack (October 2, 2002). "Remarks of Illinois State Sen. Barack Obama against going to war with Iraq". BarackObama.com. Archived from the original on January 30, 2008. Retrieved February 3, 2008.
- McCormick, John (October 3, 2007). "Obama marks '02 war speech; Contender highlights his early opposition in effort to distinguish him from his rivals" (paid archive). Chicago Tribune. p. 7. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
The top strategist for Sen. Barack Obama has just 14 seconds of video of what is one of the most pivotal moments of the presidential candidate's political career. The video, obtained from a Chicago TV station, is of Obama's 2002 speech in opposition to the impending Iraq invasion.
- Pallasch, Abdon M. (October 3, 2007). "Obama touts anti-war cred; Kicks off tour 5 years after speech critical of going to Iraq" (paid archive). Chicago Sun-Times. p. 26. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- McCormick, John (October 3, 2007). "Obama marks '02 war speech; Contender highlights his early opposition in effort to distinguish him from his rivals" (paid archive). Chicago Tribune. p. 7. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Ritter, Jim (March 17, 2003). "Anti-war rally here draws thousands" (paid archive). Chicago Sun-Times. p. 3. Retrieved February 3, 2008.
- Office of the Press Secretary (March 16, 2003). "President Bush: Monday 'moment of truth' for world on Iraq". The White House. Retrieved February 18, 2008.
- ^ Davey, Monica (March 7, 2004). "Closely watched Illinois Senate race attracts 7 candidates in millionaire range". The New York Times. p. 19. Archived from the original on May 14, 2006. Retrieved April 13, 2008.
- ^ Mendell, David (March 17, 2004). "Obama routs Democratic foes; Ryan tops crowded GOP field; Hynes, Hull fall far short across state". Chicago Tribune. p. 1. Retrieved March 1, 2009.
- Davey, Monica (March 18, 2004). "As quickly as overnight, a Democratic star is born". The New York Times. p. A20. Retrieved March 1, 2009.
- Howlett, Debbie (March 19, 2004). "Dems see a rising star in Illinois Senate candidate". USA Today. p. A04. Retrieved March 1, 2009.
- Scheiber, Noam (May 31, 2004). "Race against history. Barack Obama's miraculous campaign". The New Republic. 230 (20): 21–22, 24–26 (cover story). Retrieved March 24, 2009.
- Finnegan, William (May 31, 2004). "The Candidate. How far can Barack Obama go?". The New Yorker. 20 (14): 32–38. Retrieved March 24, 2009.
- Dionne Jr., E.J. (June 25, 2004). "In Illinois, a star prepares". The Washington Post. p. A29. Retrieved March 24, 2009.
- Scott, Janny (May 18, 2008). "The story of Obama, written by Obama". The New York Times. p. A1. Retrieved January 9, 2010.
- Mendell (2007), pp. 235–259.
- ^ Bernstein, David (June 2007). "The Speech". Chicago Magazine. Retrieved April 13, 2008.
- ^ "Star Power. Showtime: Some are on the rise; others have long been fixtures in the firmament. A galaxy of bright Democratic lights". Newsweek. August 2, 2004. pp. 48–51. Retrieved November 15, 2008.
- Samuel, Terence (August 2, 2004). "A shining star named Obama. How a most unlikely politician became a darling of the Democrats". U.S. News & World Report. p. 25. Retrieved November 15, 2008.
- Lizza, Ryan (2004). "Why is Barack Obama generating more excitement among Democrats than John Kerry?". The Atlantic Monthly. pp. 30, 33. Retrieved November 15, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Davey, Monica (July 26, 2004). "A surprise Senate contender reaches his biggest stage yet". The New York Times. p. A1. Retrieved November 25, 2010.
- Leibovich, Mark (July 27, 2004). "The other man of the hour". The Washington Post. p. C1. Retrieved November 15, 2008.
- Milligan, Susan (July 27, 2004). "In Obama, Democrats see their future". The Boston Globe. p. B8. Retrieved November 15, 2008.
- Seelye, Katharine Q. (July 28, 2004). "Illinois Senate nominee speaks of encompassing unity". The New York Times. p. A1. Archived from the original on June 24, 2006. Retrieved November 15, 2008.
- Broder, David S. (July 28, 2004). "Democrats focus on healing divisions; Addressing convention, newcomers set themes". The Washington Post. p. A1. Retrieved November 15, 2008.
- Bing, Jonathan; McClintock, Pamela (July 29, 2004). "Auds resist charms of Dem stars". Daily Variety. p. 1. Retrieved November 15, 2008.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Mendell (2007), pp. 272–285.
- ^ "Ryan drops out of Senate race in Illinois". CNN. June 25, 2004. Retrieved April 13, 2008.
- Mendell (2007), pp. 260–271.
- ^ Lannan, Maura Kelly (August 9, 2004). "Alan Keyes enters U.S. Senate race in Illinois against rising Democratic star". Union-Tribune. San Diego. Associated Press. Retrieved April 13, 2008.
- ^ "America Votes 2004: U.S. Senate / Illinois". CNN. 2005. Retrieved April 13, 2008.
- Slevin, Peter (November 13, 2007). "For Obama, a handsome payoff in political gambles". The Washington Post. p. A3. Retrieved April 13, 2008.
- Chase, John; Mendell, David (November 3, 2004). "Obama scores a record landslide" (PDF). Chicago Tribune. p. 1. Retrieved April 3, 2009.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Fornek, Scott (November 3, 2004). "Obama takes Senate seat in a landslide". Chicago Sun-Times. p. 6. Retrieved April 3, 2009.
- ^ United States Congress. "Barack Obama (id: o000167)". Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Retrieved October 12, 2011.
- ^ "Member Info". Congressional Black Caucus. Archived from the original on July 9, 2008. Retrieved June 25, 2008.
- ^ Mason, Jeff (November 16, 2008). "Obama resigns Senate seat, thanks Illinois". Reuters. Retrieved March 10, 2009.
- Sidoti, Liz (November 13, 2008). "Obama to Resign Senate Seat on Sunday". Time. Time Inc. Retrieved November 22, 2008.
- ^ U.S. Senate, 109th Congress, 1st Session (May 12, 2005). "S. 1033, Secure America and Orderly Immigration Act". Thomas. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Lugar–Obama Nonproliferation Legislation Signed into Law by the President". Richard Lugar U.S. Senate Office. January 11, 2007. Archived from the original on December 18, 2008. Retrieved April 27, 2008. See also:Lugar, Richard G. (December 3, 2005). "Junkyard Dogs of War". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ McCormack, John (December 21, 2007). "Google Government Gone Viral". Weekly Standard. Retrieved April 27, 2008. See also:"President Bush Signs Coburn–Obama Transparency Act". Tom Coburn U.S. Senate Office. September 26, 2006. Archived from the original on May 1, 2008. Retrieved April 27, 2008. and USAspending.gov
- ^ S. 3077: Strengthening Transparency and Accountability in Federal Spending Act of 2008 Govtrack.us, 2007–2008 (110th Congress)
- ^ McIntire, Mike (February 3, 2008). "Nuclear Leaks and Response Tested Obama in Senate". The New York Times. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- ^ Fisher, Daniel (August 11, 2008). "November Election A Lawyer's Delight". Forbes. Retrieved January 11, 2009.
- ^ "Nunn–Lugar Report" (PDF). Richard Lugar U.S. Senate Office. 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 1, 2008. Retrieved April 30, 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "Democratic Republic of the Congo". United States Conference of Catholic Bishops. 2006. Archived from the original on January 8, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)"The IRC Welcomes New U.S. Law on Congo". International Rescue Committee. January 5, 2007. Retrieved April 27, 2008. - ^ Weixel, Nathaniel (November 15, 2007). "Feingold, Obama Go After Corporate Jet Travel". The Hill. Retrieved April 27, 2008.Weixel, Nathaniel (December 5, 2007). "Lawmakers Press FEC on Bundling Regulation". The Hill. Retrieved April 27, 2008. See also:"Federal Election Commission Announces Plans to Issue New Regulations to Implement the Honest Leadership and Open Government Act of 2007". Federal Election Commission. September 24, 2007. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- ^ Stern, Seth (January 31, 2007). "Obama–Schumer Bill Proposal Would Criminalize Voter Intimidation". CQPolitics.com. Retrieved April 27, 2008.U.S. Senate, 110th Congress, 1st Session (January 31, 2007). "S. 453, Deceptive Practices and Voter Intimidation Prevention Act of 2007". Thomas. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) See also:"Honesty in Elections" (editorial). The New York Times. January 31, 2007. Retrieved April 27, 2008. - ^ Krystin, E. Kasak (February 7, 2007). "Obama Introduces Measure to Bring Troops Home". Medill News Service. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- ^ "Obama, Bond Hail New Safeguards on Military Personality Disorder Discharges, Urge Further Action". Kit Bond U.S. Senate Office. October 1, 2007. Archived from the original on December 5, 2010. Retrieved April 27, 2008. See also:Dine, Philip (December 23, 2007). "Bond Calls for Review of Military Discharges". St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- ^ "Obama, Bond Applaud Senate Passage of Amendment to Expedite the Review of Personality Disorder Discharge Cases". March 14, 2008. Archived from the original on December 18, 2008.
- ^ "Obama, Schiff Provision to Create Nuclear Threat Reduction Plan Approved". Barack Obama U.S. Senate Office. December 20, 2007. Archived from the original on December 18, 2008. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- ^ "Senate Passes Obama, McCaskill Legislation to Provide Safety Net for Families of Wounded Service Members". Barack Obama U.S. Senate Office. August 2, 2007. Archived from the original on December 18, 2008. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- ^ "Committee Assignments". Barack Obama U.S. Senate Office. December 9, 2006. Archived from the original on December 9, 2006. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- ^ "Obama Gets New Committee Assignments". Barack Obama U.S. Senate Office. Associated Press. November 15, 2006. Archived from the original on December 18, 2008. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- ^ Baldwin, Tom (December 21, 2007). "Stay-At-Home Barack Obama Comes Under Fire for a Lack of Foreign Experience". Sunday Times (UK). Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- ^ Larson, Christina (September 2006). "Hoosier Daddy: What Rising Democratic Star Barack Obama Can Learn from an Old Lion of the GOP". Washington Monthly. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- Goudie, Chuck (January 12, 2006). "Obama Meets with Arafat's Successor". WLS-TV. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- "Obama Slates Kenya for Fraud". News24.com. August 28, 2006. Archived from the original on June 5, 2008. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- Wamalwa, Chris (September 2, 2006). "Envoy Hits at Obama Over Graft Remark". The Standard (Nairobi). Archived from the original on October 10, 2007. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
- Moracha, Vincent (September 4, 2006). "Leaders Support Obama on Graft Claims". The Standard (Nairobi). Archived from the original on October 7, 2007. Retrieved April 27, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- ^ a b Pearson, Rick (February 10, 2007). "Obama: I'm running for president". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved September 20, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Obama Launches Presidential Bid". BBC News. February 10, 2007. Retrieved January 14, 2008.
- ^ Parsons, Christi (February 10, 2007). "Obama's launch site: Symbolic Springfield: Announcement venue evokes Lincoln legacy". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved June 12, 2009.
- ^ "Barack Obama on the Issues: What Would Be Your Top Three Overall Priorities If Elected?". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 14, 2008. See also:
- Thomas, Evan (2009). A Long Time Coming. New York: PublicAffairs. p. 74. ISBN 978-1-58648-607-5.
- Falcone, Michael (December 21, 2007). "Obama's 'One Thing'". The New York Times. Retrieved April 14, 2008.
- ^ "The Obama promise of hope and change". The Independent. London. November 1, 2008. Archived from the original on May 15, 2011. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ Tumulty, Karen (May 8, 2008). "The Five Mistakes Clinton Made". Time. Retrieved November 11, 2008.
- Baker, Peter and Rutenberg, Jim (June 8, 2008). "The Long Road to a Clinton Exit". The New York Times. Retrieved November 29, 2008.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Baker, Peter and Rutenberg, Jim (June 8, 2008). "The Long Road to a Clinton Exit". The New York Times. Retrieved November 29, 2008.
- ^ Nagourney, Adam; Zeleny, Jeff (June 5, 2008). "Clinton to End Bid and Endorse Obama". The New York Times. Retrieved November 20, 2010.
- ^ Nagourney, Adam; Zeleny, Jeff (August 23, 2008). "Obama Chooses Biden as Running Mate". The New York Times. Retrieved September 20, 2008.
- ^ "Sources: High court selection process down to finalists". CNN. May 13, 2009.
- ^ Tom Baldwin (August 27, 2008). "Hillary Clinton: 'Barack is my candidate'". The Times. London. Retrieved August 27, 2008.
- Nagourney, Adam (August 27, 2008). "Obama Wins Nomination as Biden and Bill Clinton Rally the Party". The New York Times. Retrieved August 27, 2008.
- ^ Liasson, Mara; Norris, Michele (July 7, 2008). "Obama To Accept Nomination At Mile High Stadium". NPR. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Obama accepts Democrat nomination". BBC News. August 29, 2008. Retrieved August 29, 2008.
- Marks, Alexandra (August 29, 2008). "Soaring speech from Obama, plus some specifics". The Christian Science Monitor. Archived from the original on March 14, 2010. Retrieved September 20, 2008.
- ^ Malone, Jim (July 2, 2007). "Obama Fundraising Suggests Close Race for Party Nomination". Voice of America. Archived from the original on September 14, 2007. Retrieved January 14, 2008.
- Cummings, Jeanne (September 26, 2007). "Small Donors Rewrite Fundraising Handbook". Politico. Retrieved January 14, 2008.
- Cadei, Emily (February 21, 2008). "Obama Outshines Other Candidates in January Fundraising". CQ Politics. Archived from the original on June 13, 2008. Retrieved February 24, 2008.
- ^ Salant, Jonathan D. (June 19, 2008). "Obama Won't Accept Public Money in Election Campaign". Bloomberg. Retrieved June 19, 2008.
- ^ "Commission on Presidential Debates Announces Sites, Dates, Formats and Candidate Selection Criteria for 2008 General Election". Commission on Presidential Debates. November 19, 2007. Archived from the original on July 6, 2008. Retrieved July 6, 2008.
- "Gun Ruling Reverberates". Hartford Courant. June 27, 2008. Retrieved July 6, 2008.
- ^ Johnson, Alex (November 4, 2008). "Barack Obama elected 44th president". MSNBC. Retrieved February 20, 2009.
- "CNN Electoral Map Calculator—Election Center 2008". CNN. 2008. Retrieved December 14, 2008.
- ^ "General Election: McCain vs. Obama". Real Clear Politics. Retrieved February 20, 2009.
- ^ "Obama wins historic US election". BBC. November 5, 2008. Retrieved November 5, 2008.
- Nagourney, Adam (November 4, 2008). "Obama Elected President as Racial Barrier Falls". The New York Times. Retrieved November 5, 2008.
- "Obama: 'This is your victory'". CNN. November 5, 2008. Retrieved November 5, 2008.
- ^ Johnson, Wesley (November 5, 2008). "Change has come, says President-elect Obama". The Independent (UK). Retrieved November 5, 2008.
- ^ Shear, Michael D. (April 4, 2011). "Obama Begins Re-Election Facing New Political Challenges". The New York Times. Retrieved April 5, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|separator=ignored (help) - ^ "Obama announces re-election bid". United Press International. April 4, 2011. Retrieved April 5, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|separator=ignored (help) - ^ Zeleny, Jeff; Calmes, Jackie (April 4, 2011). "Obama Opens 2012 Campaign, With Eye on Money and Independent Voters". The New York Times. Retrieved April 5, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|separator=ignored (help) - ^ "Obama asks Pentagon for responsible Iraq drawdown". China Daily. January 23, 2009. Retrieved September 4, 2009.
- ^ Glaberson, William (January 21, 2009). "Obama Orders Halt to Prosecutions at Guantánamo". The New York Times. Retrieved February 3, 2009.
- ^ "Senate blocks transfer of Gitmo detainees". MSNBC. Associated Press. May 20, 2009. Retrieved March 22, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|separator=ignored (help) - ^ Obama, Barack (December 15, 2009). "Presidential Memorandum—Closure of Detention Facilities at the Guantanamo Bay Naval Base". whitehouse.gov. Retrieved March 22, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|separator=ignored (help) - ^ Serbu, Jared (January 7, 2011). "Obama signs Defense authorization bill". Federal News Radio. Retrieved March 22, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|separator=ignored (help) - ^ "Executive Order—Presidential Records". Retrieved January 22, 2009.
- ^ Doyle, Michael (January 23, 2009). "Obama restores some of the 'Freedom' to FOIA". McClatchy Newspapers. Retrieved January 24, 2009.
- ^ Gerstein, Josh (January 24, 2009). "Obama: End Abortion 'Politicization'". Politico.com.
- ^ "Obama Signs Equal-Pay Legislation". The New York Times. January 30, 2009. Retrieved June 15, 2009.
- ^ Levey, Noam N. "Obama signs into law expansion of SCHIP health-care program for children". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved June 15, 2009.
- ^ "Obama overturns Bush policy on stem cells". CNN. March 9, 2009. Retrieved April 18, 2010.
- ^ "Senate confirms Sotomayor for Supreme Court". CNN. August 6, 2009. Retrieved August 6, 2009.
- ^ Obama nominates Sotomayor to Supreme Court, CNN, accessed May 26, 2009.
- ^ Sherman, Mark (October 4, 2010). "New Era Begins on High Court: Kagan Takes Place as Third Woman". Associated Press. Retrieved November 13, 2010.
- ^ Broder, John M. (October 1, 2009). "E.P.A. Moves to Curtail Greenhouse Gas Emissions". The New York Times.
- ^ "US moves to limit industrial greenhouse gas emissions". Google. October 1, 2009. Retrieved April 18, 2010.
- ^ "President Barack Obama signs hate crimes legislation into law". Bay Windows. October 28, 2009. Archived from the original on July 22, 2011. Retrieved October 12, 2011.
- ^ "Obama signs hate crimes bill into law". CNN. October 28, 2009. Retrieved October 12, 2011.
- ^ Parsons, Christi (March 30, 2010). "Obama signs student loan reforms into law". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved April 18, 2010.
- ^ Branigin, William. "Obama signs higher-education measure into law". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- ^ Robert Block and Mark K. Matthews (January 27, 2010). "White House won't fund NASA moon program". LA Times. Retrieved January 30, 2011.
President Obama's budget proposal includes no money for the Ares I and Ares V rocket or Constellation program. Instead, NASA would be asked to monitor climate change and develop a new rocket
- ^ Jesse Lee. "The President Signs Repeal of "Don't Ask Don't Tell": "Out of Many, We Are One"". Whitehouse.gov. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ "'Don't ask, don't tell' repealed as Obama signs landmark law". The Guardian. London. December 22, 2010. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ "Obama to delay 'don't ask, don't tell' repeal". Washington Times. November 21, 2008. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ Albanesius, Chloe (January 25, 2011). "Obama Pushes Innovation in Tech-Heavy State of the Union". PCMag.com. Retrieved May 17, 2011.
- ^ Kornblut, Anne E. (January 26, 2011). "State of the Union 2011: 'Win the future,' Obama says". The Washington Post. Retrieved May 18, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Stimulus package en route to Obama's desk". CNN. February 14, 2009. Retrieved March 29, 2009.
- ^ "Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget, Stimulus Watch". Retrieved April 9, 2011.
- "Obama's remarks on signing the stimulus plan". CNN. February 17, 2009. Retrieved February 17, 2009.
- ^ "Unemployment Rate". Bureau of Labor Statistics. Retrieved February 6, 2012.
- ^ "Unemployment Rate". Bureau of Labor Statistics. Retrieved February 16, 2012.
- ^ Andrews, Edmund L.; Dash, Eric (March 23, 2009). "U.S. Expands Plan to Buy Banks' Troubled Assets". The New York Times. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- "Wall Street soars 7% on bank plan debut". REUTERS. March 23, 2009.
- ^ "White House questions viability of GM, Chrysler". The Huffington Post. March 30, 2009.
- ^ Bunkley, Nick; Vlasic, Bill (April 27, 2009). "Chrysler and Union Agree to Deal Before Federal Deadline". The New York Times. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- ^ John Hughes, Caroline Salas, Jeff Green, and Bob Van Voris (June 1, 2009). "GM Begins Bankruptcy Process With Filing for Affiliate". Bloomberg.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Conkey, Christopher; Radnofsky, Louise (June 9, 2009). "Obama Presses Cabinet to Speed Stimulus Spending". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Dana Hedgpeth (August 21, 2009). "U.S. Says 'Cash for Clunkers' Program Will End on Monday". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- ^ Joseph R. Szczesny (August 26, 2009). "Was Cash for Clunkers a Success?". Time. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- ^ Mian, Atif R.; Sufi, Amir (September 1, 2010). "The Effects of Fiscal Stimulus: Evidence from the 2009 'Cash for Clunkers' Program". SSRN Electronic Journal. SSRN. doi:10.2139/ssrn.1670759. Retrieved September 9, 2010.
- ^ Goldman, David (April 6, 2009). "CNNMoney.com's bailout tracker". Bailout tracker. 06: 20. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- ^ Montgomery, Lori (July 24, 2010). "Federal budget deficit to exceed $1.4 trillion in 2010 and 2011". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 29, 2010.
- ^ Bull, Alister; Mason, Jeff (February 1, 2010). "Obama's 2010 budget: deficit soars amid job spending". Reuters. Retrieved July 29, 2010.
- ^ Dickson, David M. (March 26, 2010). "CBO report: Debt will rise to 90% of GDP". Washington Times. Associated Press. Retrieved July 29, 2010.
- ^ "Obama signs debt limit-paygo bill into law" (February 12, 2010). Reuters [website]. Retrieved February 9, 2011.
- ^ By NBC's Sylvie Stein. "First Read — A breakdown of the debt-limit legislation". MSNBC. Retrieved August 3, 2011.
- ^ "House passes debt ceiling bill". MSNBC. March 8, 2011. Retrieved August 3, 2011.
- ^ Theodossiou, Eleni; Hipple, Steven F. (2011). "Unemployment Remains High in 2010" (PDF). Monthly Labor Review. 134 (3). Bureau of Labor Statistics: 3–22. Retrieved April 7, 2011.
- ^ Eddlemon, John P. (2011). "Payroll Employment Turns the Corner in 2010" (PDF). Monthly Labor Review. 134 (3). Bureau of Labor Statistics: 23–32. Retrieved April 7, 2011.
- ^ a b "Percent Change in Real Gross Domestic Product (Quarterly)". National Income and Product Accounts Table. Bureau of Economic Analysis. Retrieved April 7, 2011.
- ^ Harding, Robin (July 28, 2010). "Beige Book survey reports signs of slowdown". Financial Times. Retrieved July 29, 2010.
- ^ "Percent Change in Real Gross Domestic Product (Annual)". National Income and Product Accounts Table. Bureau of Economic Analysis. Retrieved April 7, 2011.
- ^ a b "Estimated Impact of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act on Employment and Economic Output". Congressional Budget Office. Retrieved February 21, 2012.
- ^ a b Calmes, Jackie; Cooper, Michael (November 20, 2009). "New Consensus Sees Stimulus Package as Worthy Step". The New York Times. Retrieved December 21, 2010.
- ^ "CBO: Stimulus created as many as 2.1 million jobs". February 23, 2010. Retrieved April 25, 2010.
- ^ Krugman, Paul (November 2, 2009). "Too Little of a Good Thing". The New York Times. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ Isidore, Chris (January 29, 2010). "Best economic growth in six years". CNN. Retrieved April 18, 2010.
- ^ "New NABE Survey Shows Business Recovery Gaining Momentum, with More Jobs Ahead". Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ^ Herszenhorn, David M.; Stolberg, Sheryl Gay (December 7, 2010). "Democrats Skeptical of Obama on New Tax Plan". The New York Times.
- ^ "Obama signs tax deal into law". CNN. December 17, 2010. Retrieved December 17, 2010.
- ^ a b Sweet, Lynn, "Obama July 22, 2009 press conference. Transcript", Chicago Sun-Times, July 22, 2009
- ^ Stolberg, Sheryl Gay; Zeleny, Jeff (September 9, 2009). "Obama, Armed With Details, Says Health Plan Is Necessary". The New York Times.
- ^ "Obama will hedge on public option". Politico.com. Retrieved September 9, 2009.
- ^ "Obama calls for Congress to face health care challenge". CNN. September 9, 2009. Retrieved September 9, 2009.
- ^ Stem cell retrieved March 19, 2011
- ^ Hulse, Carl (November 7, 2009). "Sweeping Health Care Plan Passes House". The New York Times. Retrieved November 8, 2009.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Herszenhorn, David M. (December 7, 2009). "Abortion Was at Heart of Wrangling". The New York Times. Retrieved December 6, 2009.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Hensley, Scott (December 24, 2009). "Senate Says Yes To Landmark Health Bill". NPR. Retrieved December 24, 2009.
- ^ "Health Care Reform, at Last". The New York Times. March 21, 2010. Retrieved March 22, 2010.
- ^ Gay Stolberg, Sheryl (March 23, 2010). "Obama Signs Landmark Health Care Bill". The New York Times. Retrieved March 23, 2010.
- ^ "5 key things to remember about health care reform". CNN. March 25, 2010.
- ^ a b "Policies to Improve Affordability and Accountability". The White House.
- ^ "Health Care Reform Bill 101". The Christian Science Monitor.
- ^ "An Analysis of Health Insurance Premiums Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act" (PDF).
- ^ Peter Grier, Health care reform bill 101: Who will pay for reform?, Christian Science Monitor (March 21, 2010).
- ^ Grier, Peter (March 19, 2010). "Health care reform bill 101: Who must buy insurance?". The Christian Science Monitor. Washington, D.C. Retrieved April 7, 2010.
- ^ Congressional Budget Office, Cost Estimates for H.R. 4872, Reconciliation Act of 2010 (Final Health Care Legislation) (March 20, 2010).
- ^ "Obama Halts Drilling Projects, Defends Actions". National Public Radio. May 27, 2010.
- ^ Jonsson, Patrik (May 29, 2010). "Gulf oil spill: Obama's big political test". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved June 6, 2010.
- ^ "Biden vows break with Bush era foreign policy". Retrieved June 15, 2009.
- Ghattas, Kim (March 8, 2009). "Clinton's gaffes and gains on tour". BBC News. Retrieved June 15, 2009.
- ^ "Obama reaches out to Muslim world on TV". MSNBC. Retrieved June 15, 2009.
- ^ DeYoung, Karen (April 9, 2009). "Nation U.S. to Join Talks on Iran's Nuclear Program". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 15, 2009.
- ^ "Iranian Leaders Ignore Obama's Outstretched Hand". Fox News Channel. March 20, 2009. Retrieved June 15, 2009.
- ^ "Obama speech draws praise in Mideast". The Guardian. London. January 23, 2008. Retrieved June 15, 2009.
- ^ "Obama in Egypt reaches out to Muslim world". CNN. June 4, 2009. Retrieved January 30, 2011.
- ^ "Obama dismisses Ahmadinejad apology request". The Washington Times. June 26, 2009.
- ^ Obama: No green light for Israel to attack Iran, CNN, July 7, 2009
- ^ Chidanand Rajghatta, "Barack 'No Bomb' Obama pushes for world without nukes", The Times of India, September 24, 2009.
- ^ Robert Berger, "Israel Refuses to Halt Construction in East Jerusalem", Voice of America, March 26, 2010.
- ^ Kershner, Isabel (March 24, 2010). "Israel Confirms New Building in East Jerusalem". The New York Times. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ^ Peter Baker, "Obama Seals Arms Control Deal With Russia", The New York Times, March 26, 2010.
- ^ Baker, Peter (December 22, 2010). "Senate Passes Arms Control Treaty With Russia, 71–26". The New York Times.
- ^ Feller, Ben (February 27, 2009). "Obama sets firm withdrawal timetable for Iraq". The Detroit News. Associated Press. Retrieved March 3, 2009.
- ^ Athena Johnes Obama announces Iraq plan. February 27, 2009. msnbc.com.
- ^ BBC News: Last US combat brigade exits Iraq, August 19, 2010 Last updated at 17:56 GMT.
- ^ MacAskill, Ewen (September 1, 2010). "Barack Obama ends the war in Iraq. 'Now it's time to turn the page'". The Guardian. London.
- ^ All U.S. troops out of Iraq by end of year, msnbc.com, October 21, 2011
- ^ "Obama Calls for U.S. Military to Renew Focus on Afghanistan". NewsHour with Jim Lehrer. PBS. July 15, 2008. Retrieved April 18, 2010.
- ^ Hodge, Amanda (February 19, 2009). "Obama launches Afghanistan Surge". The Australian.
- ^ "Top U.S. Commander in Afghanistan Is Fired". The Washington Post. May 12, 2009.
- "New U.S. Commander Brings Counterinsurgency Experience to Afghanistan". Fox News Channel. May 13, 2009.
- ^ "Obama to announce war strategy" Associated Press. msnbc.com. December 1, 2009.
- ^ "Obama details Afghan war plan, troop increases" Associated Press. msnbc.com. December 1, 2009.
- ^ President Obama's Afghanistan Speech pt.1, December 1, 2009 on YouTube
- ^ "Gates says he agrees with Obama decision on McChrystal". CNN. June 24, 2010. Retrieved September 18, 2010.
- ^ "U.S., Israel Build Military Cooperation", Charles Levinson. Wall Street Journal. August 14, 2010. Accessed March 1, 2011
- ^ "United States vetoes Security Council resolution on Israeli settlements", United Nations News Centre. February 18, 2011. Accessed March 1, 2011
- ^ Levy, Elior. "PA challenges Netanyahu to accept 1967 lines." Ynetnews. May 22, 2011. May 22, 2011.
- ^ "Floor Statement by Senator McCain Introducing the Senate Resolution Calling for a No-Fly Zone in Libya". Senate.gov. March 14, 2011. Retrieved March 28, 2011.
- ^ "Senate Passes Resolution Calling for No-Fly Zone Over Libya". National Journal. March 1, 2011. Retrieved March 28, 2011.
- ^ Winnett, Robert (March 17, 2011). "Libya: UN approves no-fly zone as British troops prepare for action". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved April 7, 2011.
- ^ "Libya declares ceasefire". New Statesman. UK. Retrieved July 16, 2011.
- ^ "Libya Live Blog — March 18". Al Jazeera. March 18, 2011.
- ^ "Obama: US to Transfer Lead Role in Libya". RTT Newswire. Retrieved March 22, 2011.
- ^ "Obama says US efforts in Libya have saved lives, control of operation can be turned over soon". Ventura County Star. Associated Press. Retrieved March 22, 2011.
- ^ Ian Pannell (March 21, 2011). "Gaddafi 'not targeted' by allied strikes". BBC. Retrieved July 3, 2011.
- ^ Jones, Sam (March 22, 2011). "F-15 fighter jet crashes in Libya". The Guardian. London. Retrieved March 23, 2011.
- ^ "NATO No-Fly Zone over Libya Operation UNIFIED PROTECTOR" (PDF). NATO. March 25, 2011.
- ^ Montopoli, Brian (March 22, 2011). "Is Obama's Libya offensive constitutional?". CBS News. Retrieved March 22, 2011.
- ^ Stein, Sam (March 21, 2011). "Obama's Libya Policy Makes Strange Bedfellows Of Congressional Critics". The Huffington Post. Retrieved March 26, 2011.
- ^ "Obama juggles Libya promises, realities". CNN. March 25, 2011. Retrieved March 26, 2011.
- ^ a b c Mazzetti, Mark (May 3, 2011). "Clues Gradually Led to the Location of Osama bin Laden". The New York Times. Retrieved May 4, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Osama bin Laden is killed by U.S. forces in Pakistan" – washingtonpost.com Retrieved May 2, 2011
- ^ "Official offers details of bin Laden raid" – newsday.com Retrieved May 2, 2011
- ^ Schabner, Dean (May 1, 2011). "Osama bin Laden Killed by U.S. Forces in Pakistan". ABC News. Retrieved May 3, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Baker, Peter (May 2, 2011). "Bin Laden Is Dead, Obama Says". The New York Times. Retrieved May 3, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Walsh, Declan (May 2, 2011). "Osama bin Laden is dead, Obama announces". The Guardian. London. Retrieved May 3, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Dorning, Mike (May 2, 2011). "Death of Bin Laden May Strengthen Obama's Hand in Domestic, Foreign Policy". Bloomberg News. Retrieved May 4, 2011.
- ^ "World Reaction To Osama Bin Laden's Death". NPR. May 2, 2011. Retrieved May 4, 2011.
- ^ Paul Harris in Oakland and Ewen MacAskill in Washington (November 3, 2010). "US midterm election results herald new political era as Republicans take House". The Guardian. London. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ "Obama calls midterm elections a 'shellacking' for Democrats". The Christian Science Monitor. November 4, 2010. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ "See Obama's first paragraph of his transcript". All Things Considered. NPR. November 3, 2010. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ Wallace-Wells, Benjamin (November 2004). "The Great Black Hope: What's Riding on Barack Obama?". Washington Monthly. Retrieved April 7, 2008. See also:Scott, Janny (December 28, 2007). "A Member of a New Generation, Obama Walks a Fine Line". International Herald Tribune. Retrieved April 7, 2008.
- ^ Harris, Paul (March 4, 2007). "Obama told of family's slave-owning history in deep South". The Observer. London. Retrieved April 18, 2010.
- ^ Payne, Les (August 19, 2007). "In One Country, a Dual Audience" (paid archive). Newsday. New York. Retrieved April 7, 2008.
- ^ Dorning, Mike (October 4, 2007). "Obama Reaches Across Decades to JFK" (paid archive). Chicago Tribune. Retrieved April 7, 2008. See also:Harnden, Toby (October 15, 2007). "Barack Obama is JFK Heir, Says Kennedy Aide". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved April 7, 2008.
- ^ Holmes, Stephanie (November 30, 2008). "Obama: Oratory and originality". The Age. Melbourne. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
- Gallo, Carmine (March 3, 2008). "How to Inspire People Like Obama Does". BusinessWeek. Retrieved February 21, 2009.
- Zlomislic, Diana (December 11, 2008). "New emotion dubbed 'elevation". Toronto Star. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
- Greene, Richard (January 25, 2011). "Obama Is America's Third Greatest Presidential Orator in Modern Era". The Huffington Post. Retrieved July 2, 2011.
- ^ "YouTube – ChangeDotGov's Channel". Youtube. Retrieved April 18, 2010.
- ^ "Obama Starts With 68% Job Approval". Gallup.com. January 24, 2009. Retrieved June 19, 2011.
- ^ "Obama hits low point in Gallup Poll – 41%". USA Today. April 15, 2011. Retrieved June 19, 2011.
- ^ Jon Terbush (December 9, 2010). "Approval By Numbers: How Obama Compares To Past Presidents". Tpmdc.talkingpointsmemo.com. Retrieved June 19, 2011.
- ^ "Bin Laden bounce? New poll shows jump in Obama approval", James Oliphant. Los Angeles Times. May 11, 2011. Accessed June 7, 2011
- ^ "Obama loses bin Laden bounce; Romney on the move among GOP contenders", Dan Balz. John Cohen. The Washington Post. June 6, 2011. Accessed June 7, 2011
- ^ "Washington Still Working Hard to Plug Gaps in The Bin Laden Story", Patrick Henningsen. 21st Century Wire. May 23, 2011. Accessed June 7, 2011
- ^ "World wants Obama as president: poll". ABC News. Reuters. September 9, 2008.
- ^ "Obama to visit nuclear, biological weapons destruction facilities in former Soviet Union" (Press release). Obama.senate.gov. August 24, 2005. Archived from the original on December 18, 2008. Retrieved October 12, 2011.
- ^ Scherer, Steve (September 12, 2007). "Rome Mayor's Leadership Bid May Lead to Early Italian Elections". Bloomberg. Retrieved May 21, 2011.
- ^ Pedder, Sophie (February 20, 2008). "Sarkozy, Obama and McCain". The Economist. Retrieved November 20, 2008.
- ^ President Obama Hangs Out With America, The White House, January 30, 2012.
- ^ Freed, John C. (February 6, 20009). "Poll shows Obama atop list of most respected". The New York Times. Retrieved January 22, 2012.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Obama Most Popular Leader, Poll Finds". The New York Times. May 29, 2009. Retrieved January 22, 2012.
- ^ "Obama remains a popular symbol of hope". France 24. June 2, 2009. Archived from the original on May 13, 2011. Retrieved January 22, 2012.
- ^ Goodman, Dean (February 10, 2008). "Obama or Clinton? Grammys go for Obama". Reuters. Retrieved November 24, 2008.
- ^ Strange, Hannah (March 5, 2008). "Celebrities join YouTube revolution". The Times. London. Retrieved December 18, 2008.
- ^ Wappler, Margaret (June 20, 2008). "Emmys give knuckle bump to will.i.am; more videos on the way". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on May 16, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
- ^ Von Drehle, David (December 16, 2008). "Why History Can't Wait". Time. Retrieved December 17, 2008.
- ^ "The Nobel Peace Prize 2009". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved October 9, 2009.
- ^ "Obama: 'Peace requires responsibility'". CNN. December 10, 2009. Retrieved May 21, 2011.
- ^ Philp, Catherine (October 10, 2009). "Barack Obama's peace prize starts a fight". The Times. UK. Retrieved October 10, 2009.
- ^ Samuelsohn, Darren (October 9, 2009). "Obama Wins Nobel Prize in Part for Confronting 'Great Climatic Challenges'". The New York Times. Greenwire. Retrieved April 18, 2010.
- ^ "Keeping Hope Alive: Barack Obama Puts Family First". The Oprah Winfrey Show. October 18, 2006. Retrieved June 24, 2008.
- ^ Fornek, Scott (September 9, 2007). "Half Siblings: 'A Complicated Family'". Chicago Sun-Times. Archived from the original on January 18, 2010. Retrieved June 24, 2008. See also:"Interactive Family Tree". Chicago Sun-Times. September 9, 2007. Archived from the original on July 3, 2008. Retrieved June 24, 2008.
- ^ Fornek, Scott (September 9, 2007). "Madelyn Payne Dunham: 'A Trailblazer'". Chicago Sun-Times. Archived from the original on May 14, 2009. Retrieved June 24, 2008.
- ^ "Obama's grandmother dies after battle with cancer". CNN. November 3, 2008. Retrieved November 4, 2008.
- ^ Smolenyak, Megan (May 9, 2011). "Tracing Barack Obama's Roots to Moneygall". The Huffington Post.
- ^ Obama (1995, 2004), p. 13. For reports on Obama's maternal genealogy, including slave owners, Irish connections, and common ancestors with George W. Bush, Dick Cheney, and Harry Truman, see:Nitkin, David (March 2, 2007). "A New Twist to an Intriguing Family History". Baltimore Sun. Archived from the original on September 30, 2007. Retrieved June 24, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)Jordan, Mary (May 13, 2007). "Tiny Irish Village Is Latest Place to Claim Obama as Its Own". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 24, 2008."Obama's Family Tree Has a Few Surprises". CBS 2 (Chicago). Associated Press. September 8, 2007. Archived from the original on June 2, 2008. Retrieved June 24, 2008. - ^ "When Barry Became Barack". Newsweek. March 31, 2008. Retrieved November 6, 2008.
- ^ Zimmer, Benjamin (2009). "Obama's Indonesian Redux". Language Log. Retrieved March 12, 2009.
- ^ Kantor, Jodi (June 1, 2007). "One Place Where Obama Goes Elbow to Elbow". The New York Times. Retrieved April 28, 2008. See also: "The Love of the Game" (video). Real Sports with Bryant Gumbel. HBO. April 15, 2008. Retrieved October 12, 2011.
- ^ "Barack Obama: White Sox 'serious' ball". The Swamp. August 25, 2008. Retrieved December 6, 2009.
- ^ "Barack Obama Explains White Sox Jacket, Talks Nats in All-Star Booth Visit". MLB Fanhouse. July 14, 2009. Retrieved December 6, 2009.
- ^ Branigin, William (January 30, 2009). "Steelers Win Obama's Approval". The Washington Post.
But other than the Bears, the Steelers are probably the team that's closest to my heart.
- ^ Obama (2006), pp. 327–332. See also:Brown, Sarah (December 7, 2005). "Obama '85 masters balancing act". The Daily Princetonian. Retrieved February 9, 2009.
- ^ Obama (2006), p. 329.
- ^ Fornek, Scott (October 3, 2007). "Michelle Obama: 'He Swept Me Off My Feet'". Chicago Sun-Times. Archived from the original on January 18, 2010. Retrieved April 28, 2008.
- ^ Martin, Jonathan (July 4, 2008). "Born on the 4th of July". The Politico. Retrieved July 10, 2008.
- ^ Obama (1995, 2004), p. 440, and Obama (2006), pp. 339–340. See also:"Election 2008 Information Center: Barack Obama". Gannett News Service. Retrieved April 28, 2008.
- ^ "Obamas choose private Sidwell Friends School", International Herald Tribune, November 22, 2008
- ^ Cooper, Helene (April 13, 2009). "One Obama Search Ends With a Puppy Named Bo". The New York Times. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ Zeleny, Jeff (December 24, 2005). "The first time around: Sen. Obama's freshman year". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved April 28, 2008.
- ^ Slevin, Peter (December 17, 2006). "Obama says he regrets land deal with fundraiser". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 10, 2008.
- Robinson, Mike (June 4, 2008). "Rezko found guilty in corruption case". MSNBC. Associated Press. Retrieved June 24, 2008.
- ^ Harris, Marlys (December 7, 2007). "Obama's Money". CNNMoney.com. Retrieved April 28, 2008.
See also:Goldfarb, Zachary A (March 24, 2007). "Measuring Wealth of the '08 Candidates". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 28, 2008. - ^ Zeleny, Jeff (April 17, 2008). "Book Sales Lifted Obamas' Income in 2007 to a Total of $4.2 Million". The New York Times. Retrieved April 28, 2008.
- ^ Shear, Michael D.; Hilzenrath, David S. (April 16, 2010). "Obamas report $5.5 million in income on 2009 tax return". The Washington Post. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ Solman, Paul (April 18, 2011). "How Much Did President Obama Make in 2010?". PBS NewsHour. Retrieved January 27, 2012.
- ^ Solman, Paul (April 27, 2011). "The Obamas Gave $131,000 to Fisher House Foundation in 2010; What Is It?". PBS NewsHour. Retrieved January 27, 2012.
- ^ Elsner, Alan (December 7, 2008). "Obama says he won't be smoking in White House". Reuters. Retrieved February 28, 2010.
- ^ Zengerle, Patricia (February 8, 2011). "Yes, he did: first lady says Obama quit smoking". Reuters. Retrieved May 9, 2011.
- ^ Christianity Today: "Q&A: Barack Obama" Interview by Sarah Pulliam and Ted Olsen, January 23, 2008
- ^ Obama 'Christian By Choice': President Responds To Questioner by Charles Babington and Darlene Superville, Associated Press, September 28, 2010
- ^ Video – President Obama: "I am a Christian By Choice" by ABC News, September 29, 2010
- ^ Kantor, Jodi (April 30, 2007). "Barack Obama's search for faith". The New York Times. Retrieved April 30, 2007.
- ^ "Obama's church choice likely to be scrutinized". MSNBC. Associated Press. November 17, 2008. Retrieved January 20, 2009.
- ^ Sullivan, Amy (June 29, 2009). "The Obamas Find a Church Home—Away from Home". Time. Retrieved December 14, 2009.
References
- Mendell, David (2007). Obama: From Promise to Power. New York: Amistad/HarperCollins. ISBN 0-06-085820-6.
- Obama, Barack (1995, 2004). Dreams from My Father: A Story of Race and Inheritance. New York: Three Rivers Press. ISBN 1-4000-8277-3.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|year=(help)CS1 maint: year (link) - Obama, Barack (2006). The Audacity of Hope: Thoughts on Reclaiming the American Dream. New York: Crown Publishing Group. ISBN 0-307-23769-9.
Further reading
- Graff, Garrett. "The Legend of Barack Obama", Washingtonian, November 1, 2006. Retrieved on January 14, 2008.
- Koltun, Dave (2005) "The 2004 Illinois Senate Race: Obama Wins Open Seat and Becomes National Political "Star"" in "The Road to Congress 2004" Editors: Sunil Ahuja (Youngstown State University) and Robert Dewhirst (Truman State University), Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, New York, 2005, ISBN 1-59454-360-7
- Lizza, Ryan. "Above the Fray", GQ, September 2007. Retrieved on October 27, 2010.
- MacFarquhar, Larissa. "The Conciliator: Where is Barack Obama Coming From?", New Yorker, May 7, 2007. Retrieved on January 14, 2008.
- McClelland, Edward, Young Mr. Obama: Chicago and the Making of a Black President, Bloomsbury Press, 2010.
- Zutter, Hank De. "What Makes Obama Run?", Chicago Reader, December 8, 1995. Retrieved on January 14, 2008.
External links
- Official
- President Barack Obama White House official website
- BarackObama.com (official re-election campaign website)
- Other
- Biography at the Biographical Directory of the United States Congress
- Financial information (federal office) at the Federal Election Commission
- Profile at Vote Smart
- Collected news and commentary at the Chicago Tribune
- Template:Dmoz
| Offices and distinctions |
|---|
Template:Link GA Template:Link GA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
- Barack Obama
- 1961 births
- African American academics
- African American lawyers
- African American memoirists
- African American United States presidential candidates
- African American United States Senators
- African-American Christians
- American civil rights lawyers
- American legal scholars
- American Nobel laureates
- American people of English descent
- American people of German descent
- American people of Irish descent
- American people of Kenyan descent
- American people of Welsh descent
- American political writers
- Audio book narrators
- Columbia University alumni
- Community organizers
- Current national leaders
- Democratic Party Presidents of the United States
- Democratic Party United States Senators
- Grammy Award winners
- Harvard Law School alumni
- Illinois Democrats
- Illinois lawyers
- Illinois State Senators
- Living people
- Luo people
- Nobel Peace Prize laureates
- Obama family
- Occidental College alumni
- People from Honolulu, Hawaii
- Politicians from Chicago, Illinois
- Presidents of the United Nations Security Council
- Punahou School alumni
- United Church of Christ members
- United States presidential candidates, 2008
- United States presidential candidates, 2012
- United States Senators from Illinois
- University of Chicago Law School faculty
- Writers from Chicago, Illinois
- Article Feedback 5 Additional Articles
- American people of Swiss descent


