Acetylleucine
Appearance
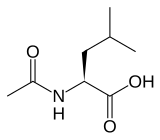 (S)-(−)-N-Acetyl-leucine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Acetamido-4-methylpentanoic acid[1]
| |
| Other names
N-Acetylleucine; N-Acetyl-L-Leucine
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1724849 (S)-(−) | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 985259 (S)-(−) | |
| KEGG |
|
| MeSH | acetylleucine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H15NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 173.212 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | −115 to −113 °C; −175 to −172 °F; 158 to 160 K |
| log P | −0.265 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.666 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 10.331 |
| Pharmacology | |
| N07CA04 (WHO) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
ENU |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Acetylleucine (N-acetyl-leucine) is a modified leucine amino acid.
Two forms are commercialized: N-acetyl-DL-leucine (sold under the brand Tanganil, among others, and used in the treatment of vertigo[2]) and N-acetyl-L-leucine (levacetylleucine, sold under the brand name Aqneursa, and used for the treatment of neurological manifestations of Niemann-Pick disease type C).[3]
References
[edit]- ^ "N-Acetyl-DL-leucine". PubChem Open Chemistry Database. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ "N07CA04 (acetylleucine)". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Norwegian Institute of Public Health. 19 December 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ Oertel WH, Janzen A, Henrich MT, Geibl FF, Sittig E, Meles SK, et al. (2 September 2024). "Acetyl-DL-leucine in two individuals with REM sleep behavior disorder improves symptoms, reverses loss of striatal dopamine-transporter binding and stabilizes pathological metabolic brain pattern—case reports". Nature Communications. 15 (1): 7619. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-51502-7. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 11369233. PMID 39223119.
