Accumulated winter season severity index
The accumulated winter season severity index or AWSSI provides a scientific way to compare the severity of a winter relative to its weather history. Points are assigned daily based on the maximum and minimum temperature, snowfall and snow depth for a specific site and accumulated through the winter.[1] The index can be used for historical comparisons,[2][3] road maintenance[4] and to understand how severe a current winter is.[5]
History
[edit]The AWSSI was originally developed in 2015 by researchers Barbara E. Mayes Boustead, Steven D. Hilberg, Martha D. Shulski and Kenneth G. Hubbard. The index was developed "to examine relationships to teleconnection patterns, determine trends, and create sector-specific applications, as well as to analyze an ongoing winter or any individual winter season to place its severity in context."[6]
Calculation
[edit]Values are assigned on a daily basis based on the maximum and minimum temperature, 24-hour snowfall and depth of snow on the ground. Values start being calculated at the start of winter. The start of winter is defined when any of these conditions are met: 1) daily maximum temperature ≤ 32 °F (0 °C), 2) first measurable snowfall or 3) it is December 1. Likewise, values stop being calculated at the end of winter – when the last of the following four conditions occurs: 1) daily maximum temperature ≤ 32 °F (0 °C) no longer occurs, 2) no daily measurable snowfall, 3) daily snow depth ≥ 1.0 in. (2.5 cm) is no longer observed, or 4) it is March 1.[7]
| AWSSI point thresholds | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Snow | |||
| Points | Max | Min | Snowfall | Snowdepth |
| 1 | 25 to 32 | 25 to 32 | 0.1 to 0.9 | 1 |
| 2 | 20 to 24 | 20 to 24 | 1.0 to 1.9 | 2 |
| 3 | 15 to 19 | 15 to 19 | 2.0 to 2.9 | 3 |
| 4 | 10 to 14 | 10 to 14 | 3.0 to 3.9 | 4 to 5 |
| 5 | 5 to 9 | 5 to 9 | – | 6 to 8 |
| 6 | 0 to 4 | 0 to 4 | 4.0 to 4.9 | 9 to 11 |
| 7 | −1 to −5 | −1 to −5 | 5.0 to 5.9 | 12 to 14 |
| 8 | −6 to −10 | −6 to −10 | – | 15 to 17 |
| 9 | −11 to −15 | −11 to −15 | 6.0 to 6.9 | 18 to 23 |
| 10 | −16 to −20 | −16 to −20 | 7.0 to 7.9 | 24 to 35 |
| 11 | – | −21 to −25 | – | – |
| 12 | – | – | 8.0 to 8.9 | – |
| 13 | – | – | 9.0 to 9.9 | – |
| 14 | – | – | 10.0 to 11.9 | – |
| 15 | <-20 | -26 to -35 | - | 36+ |
| 18 | - | - | 12.0 to 14.9 | - |
| 20 | - | <-35 | - | 36+ |
| 22 | - | - | 15.0 to 17.9 | - |
| 26 | - | - | 18.0 to 23.9 | - |
| 36 | - | - | 24.0 to 29.9 | - |
| 45 | - | - | >=30.0 | – |
AWSSI climatology
[edit]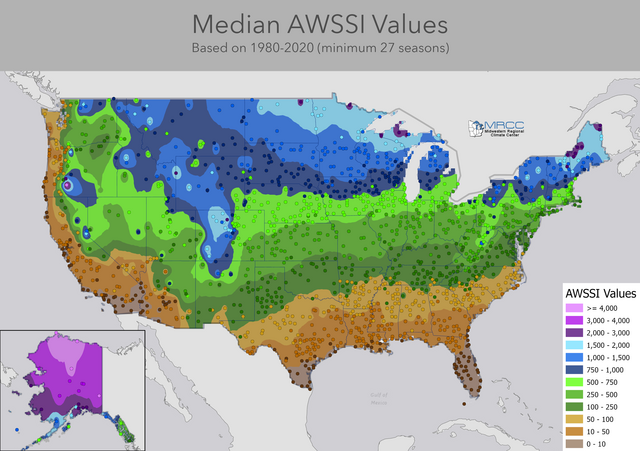
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "WeatherTalk Webinar #72". CoCoRaHS. Archived from the original on 2023-07-18. Retrieved 2023-07-18.
- ^ Boustead, Barb Mayes (n.d.). Awesome or Awful? Ranking Winter Severity with the Accumulated Winter Season Severity Index (AWSSI) (PDF) (Slide deck). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2023-07-18. Retrieved 2023-07-18.
- ^ Evans, Chad (27 December 2022). "Local Weather History: AWSSI or Winter Severity Ratings Since 1880". wlfi.com. Archived from the original on 18 July 2023. Retrieved 18 July 2023.
- ^ "Annual Survey of State Winter Maintenance Data". Clear Roads. Archived from the original on 2023-07-18. Retrieved 2023-07-18.
- ^ Erdman, Jonathan (27 November 2018). "It's Been One of the Most Miserable Starts to Winter on Record". The Weather Channel. Archived from the original on 2023-07-18. Retrieved 2023-07-18.
- ^ Mayes Boustead, Barbara E.; Hilberg, Steven D.; Shulski, Martha D.; Hubbard, Kenneth G. (2015). "The Accumulated Winter Season Severity Index (AWSSI)". Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology. 54 (8): 1693–1712. Bibcode:2015JApMC..54.1693M. doi:10.1175/JAMC-D-14-0217.1. S2CID 15847401. Archived from the original on 2023-12-19.
- ^ "Accumulated Winter Season Severity Index (AWSSI)". MRCC. Archived from the original on 2023-07-18. Retrieved 2023-07-18.
