Acacia bakeri
| Marblewood | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. bakeri
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia bakeri | |
| |
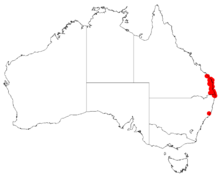
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Acacia bakeri, known as the marblewood, white marblewood, Baker's wattle, scrub wattle or white wattle, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is an erect or spreading tree with narrowly elliptic to lance-shaped phyllodes, spherical heads of pale yellow to cream-coloured flowers, and papery pods up to 200 mm (7.9 in) long. It is probably the largest species of Acacia in Australia
Description
[edit]Acacia bakeri is an erect or spreading tree that grows to a height of up to 40 m (130 ft), with a dbh of 90 cm (35 in), making it one of the largest Acacia species in Australia. At the time of its discovery, it was recorded as reaching about 50 m (160 ft), but now rarely exceeds 8 m (26 ft).[2][3][4] The bark is greyish-brown, the branchlets reddish and glabrous. Its phyllodes are narrowly elliptic to broadly elliptic or lance-shaped, 50–120 mm (2.0–4.7 in) long, mostly 15–30 mm (0.59–1.18 in) wide, thinly leathery and glabrous with two to four prominent veins on each side. The flowers are arranged in spherical heads in clusters of two to four 5–10 mm (0.20–0.39 in) long, each head with 10 to 20 pale yellow to cream-coloured flowers. Flowering occurs from about August to November, and the pods are papery, up to 200 mm (7.9 in) long and 10–16 mm (0.39–0.63 in) wide and constricted between the seeds. The seeds are oblong to broadly elliptic, dark brown and flattened, 6–10 mm (0.24–0.39 in) long.[2][3][4][5][6]
Taxonomy
[edit]Acacia bakeri was first formally described in 1896 by the botanist Joseph Maiden in the Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales from specimens collected near Mullumbimby by William Baeuerlen.[7][8] The specific epithet honours Richard Thomas Baker who worked for the Sydney Technological Museum and collected the type specimen.[5] This species is thought to be allied with A. binervata and part of a group of species closely related A. rothii.[3]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]Marblewood grows in lowland subtropical rainforest and in the margins of rainforest from near the Burrum River near Maryborough in south-east Queensland to Brunswick Heads and Mullumbimby in northeastern New South Wales.[2][3]
Ecology
[edit]The seeds of A. bakeri are unusual, in that they may begin to germinate before the pods fall from the tree.[4]
Conservation status
[edit]Acacia bakeri is listed as "vulnerable" under the New South Wales Government Office of Environment and Heritage Biodiversity Conservation Act 2016,[9] but as of "least concern" under the Queensland Government Nature Conservation Act 1992.[10] The species may be in danger of extinction, because of the extensive clearing of rainforest.[4] Most plants are on private property.[9]
Uses
[edit]The timber of A. bakeri is yellowish, hard and close-grained, making it suitable for flooring, cabinet work and tool handles.[4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Acacia adunca". Australian Plant Census. Retrieved 25 April 2024.
- ^ a b c Maslin, Bruce R. Kodela, Phillip G. (ed.). "Acacia bakeri". Flora of Australia. Australian Biological Resources Study, Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water: Canberra. Retrieved 6 March 2025.
- ^ a b c d "Acacia bakeri Maiden". Wattle - Acacias of Australia. Lucid Central. 2018. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- ^ a b c d e "Acacia bakeri". World Wide Wattle. Retrieved 6 March 2025.
- ^ a b Kodela, Phillip G.; Harden, Gwen J. " Acacia bakeri". Royal Botanic Garden, Sydney. Retrieved 6 March 2025.
- ^ Flloyd, Alex G. (1989). Rainforest Trees of Mainland South-eastern Australia. Terania Rainforest Publishing: Terania Rainforest Publishing. p. 210.
- ^ "Acacia bakeri". Australian Plant Name Index. Retrieved 5 March 2025.
- ^ Maiden, Joseph H. (1896). "A giant Acacia from the Brunswick River". Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales. 2. 10 (4): 337–339. Retrieved 5 March 2025.
- ^ a b "Marblewood - profile". New South Wales Government Office of Environment and Heritage. Retrieved 6 March 2025.
- ^ "Species profile—Acacia bakeri (marblewood)". Queensland Government Department of Education and Science. Retrieved 6 March 2025.
