2019 LF6
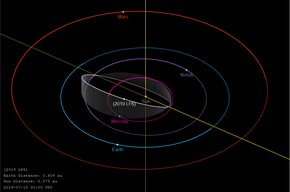 Highly inclined orbit of 2019 LF6 passing within Mercury's orbit, and slightly outside Venus's orbit | |
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Zwicky Transient Facility |
| Discovery site | Palomar Obs. |
| Discovery date | 10 June 2019 (first observed only) |
| Designations | |
| 2019 LF6 | |
| NEO · Atira [1] | |
| Orbital characteristics [2] | |
| Epoch 31 May 2020 (JD 2459000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 3 | |
| Observation arc | 358 days |
| Aphelion | 0.7938 AU |
| Perihelion | 0.3170 AU |
| 0.5554 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.42928 |
| 0.41 yr (151.2 d) | |
| 347.653° | |
| 2° 22m 51.74s / day | |
| Inclination | 29.506° |
| 179.029° | |
| 213.779° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.2608 AU |
| Physical characteristics | |
| 1–2 km (est. at 0.05–0.15) | |
| 17.200±0.398[2] | |
2019 LF6 is a near-Earth object of the Atira group. After 2021 PH27, it has the second-smallest semi-major axis among the known asteroids (0.555 AU), beating the previously-held record of 2019 AQ3.[3][4] It orbits the Sun in 151 days.[2] Discovered at only 19th magnitude, it is very difficult to see, never getting far from the sun and twilight.[5] It only occasionally brightens above 16th magnitude. Discovery was made using the Zwicky Transient Facility.[6]
2019 LF6 orbits the Sun at a distance of 0.3–0.8 AU once every 5 months (151 days; semi-major axis of 0.56 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.43 and an unusually high[6] inclination of 30° with respect to the ecliptic.[2] The asteroids 594913 ꞌAylóꞌchaxnim and 2019 AQ3 are the only known asteroids with closer aphelions. The orbital evolution of 2019 AQ3 is similar to that of 2019 LF6.[7]
References
[edit]- ^ a b "2019 LF6". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ^ a b c d "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2019 LF6)" (2019-07-05 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ^ "JPL Small-Body Database Search Engine: a > 0 (au) and a < 0.7 (au) and data-arc span > 3 (d)". JPL Solar System Dynamics. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ^ de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl (1 August 2019). "Understanding the evolution of Atira-class asteroid 2019 AQ3, a major step towards the future discovery of the Vatira population". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 487 (2): 2742–2752. arXiv:1905.08695. Bibcode:2019MNRAS.487.2742D. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz1437.
- ^ Hop Aboard 2019 LF6, The Asteroid With The Shortest Year Known Astrobob, 7/10/2019
- ^ a b Young, Monica (10 July 2019). "Sky-surveying Telescopes Sweep Up Near-Earth Asteroids". Sky & Telescope. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ^ de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl (25 July 2019). "Hot and Eccentric: The Discovery of 2019 LF6 as a New Step in the Quest for the Vatira Population". Research Notes of the American Astronomical Society. 3 (7): 106. Bibcode:2019RNAAS...3g.106D. doi:10.3847/2515-5172/ab346c. S2CID 201405666.
External links
[edit]- 2019 LF6 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- 2019 LF6 at the JPL Small-Body Database
