2012 East Azerbaijan earthquakes
| UTC time | Doublet earthquake: |
|---|---|
| A: 2012-08-11 12:23:17[1] | |
| B: 2012-08-11 12:34:36[2] | |
| ISC event | |
| A: 604084447 | |
| B: 604846898 | |
| USGS-ANSS | |
| A: ComCat | |
| B: ComCat | |
| Local date | August 11, 2012 |
| Local time | UTC+04.30 |
| A: 16:53 | |
| B: 17:04 | |
| Magnitude | 6.4 Mw |
| A: 6.2 Mw(GCMT) | |
| Depth | A: 9 km (5.6 mi)[1] B: 19 km (12 mi)[2] |
| Epicenter | 38°21′32″N 46°47′10″E / 38.359°N 46.786°E |
| Areas affected | Iran |
| Max. intensity | MMI VIII (Severe)[3] |
| Aftershocks | at least 60[4][5] |
| Casualties | 306 dead, 3,037 injured[6] |
The 2012 East Azerbaijan earthquakes – also known as the Ahar earthquakes – occurred on 11 August 2012, at 16:53 Iran Standard Time, near the cities of Ahar and Varzaqan in Iran's East Azerbaijan province, approximately 60 kilometers (37 miles) from Tabriz.[7] They comprised a doublet separated by eleven minutes, with magnitudes of 6.4 and 6.2 Mww.[8] At least 306 people died and more than 3,000 others were injured, primarily in the rural and mountainous areas to the northeast of Tabriz (though 45 died in the city of Ahar).[9] The shocks were felt in Armenia and the Republic of Azerbaijan, though no major damage was reported.[10]
Tectonic setting
[edit]Iran lies within the complex zone of continental collision between the Arabian plate and the Eurasian plate, which extends from the Bitlis-Zagros belt in the south to the Greater Caucasus Mountains, the Absheron-Balkan Sill and the Kopet Dag mountains in the north.[11] The collision between these plates deforms an area of ~ 3,000,000 km2 of continental crust. It is one of the largest convergent deformation regions on Earth.[12] In northwestern Iran, the Arabian plate is moving northwards at about 20 mm per year relative to the Eurasian plate, somewhat oblique to the plate boundary zone. The deformation in the area near Tabriz is dominated by the North Tabriz Fault, a WNW-ESE trending right-lateral strike-slip fault, which has been responsible for 7 historical earthquakes of magnitude greater than 6 since AD 858.[13] Other known active faults include a W-E trending fault between the cities of Ahar and Heris.[14]
Earthquakes
[edit]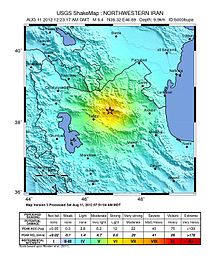
The 6.4 and 6.2 intraplate earthquakes occurred as a result of oblique strike-slip faulting in the shallow crust about 300 km east of the Eurasia-Arabian plate boundary. The two earthquakes are separated by 10 km in an east–west direction.[8]
Damage and casualties
[edit]Iran's state television reported the earthquake hit near the towns of Ahar, Heris and Varzaqan in East Azerbaijan province at 4:53 p.m. local time (12:23 GMT). "268 people, 219 women and 49 men, lost their lives in hospitals" while the rest were killed on the spot, Iran's Health Minister Marzieh Vahid-Dastjerdi said. The Iranian minister added that 3,037 people have been injured as a result of Saturday's temblors. According to the head of Iran's Rescue and Relief Organisation, access to villages has been cut and the only communication is via radio. The worst damage and most casualties were in villages near the towns of Ahar, Varzaghan and Heris.[15] In villages near Varzaqan, with most men away from home working, the many mud brick houses which collapsed trapped mainly women and children inside.[16]

Sixty-six rescue teams were sent to the affected region, along with about 200 ambulances and five helicopters. One hundred and thirty villages were 70–90 percent destroyed, and 20 were completely leveled. At least 45 people died and more than 500 were injured in Ahar, where electricity and phone lines were cut after the earthquakes.[5][17] More than 40 people died in the city of Varzaqan and 50 were killed in Heris.[4][18] The medical infrastructure in the catastrophe stricken region is not sufficient, and many heavily injured did not survive the rather long way to the nearest hospital.[19]
Most parts of Tabriz also lost electricity, and the city had a large traffic jam. Some buildings were structurally damaged.[9] Over 200 people in Varzaqan and Ahar were extricated from under the debris of collapsed buildings, and local provincial officials asked people in the region to stay outdoors during the night because of the danger of aftershocks. Some residents needed bread, tents and drinking water.[20]
Rescue teams continued searching for survivors through the night, Iranian officials[specify] said they expected the death toll to rise. Between ten and twenty villages close to the epicenter were still cut off from aid and it would take some time to reach them. The Iranian government estimated at least 16,000 people spent the first night after the quakes in emergency shelters.[5]
A day after the quakes, more than 36,000 people had been given emergency shelter, and the Iranian government had dispatched nearly 100 ambulances, 1,100 Red Crescent workers, 44,000 food packages and 5,600 tents. According to Red Crescent officials, more than 1,000 villages were affected by the disaster, and at least 5,000 people were injured. Hospitals in the region's major cities were overcrowded and struggling to cope with the large number of people waiting for treatment.[21]
Aftershocks
[edit]At least 80 aftershocks were felt. A 5.0 quake struck three hours later and a 5.1 aftershock struck 31 km southwest of Ahar on 12 August.[22][23]
On 14 August, three days after the initial quakes, another 5.1 aftershock struck the same area at a depth of 10 km.[22] An even stronger 5.3 tremor occurred on 15 August, approximately 34 km southwest of Ahar.[24]
Reaction
[edit]
Domestic
[edit]The East Azerbaijan province governor announced two days of public mourning in the province.[citation needed] Mostafa Mohammad Najjar, Minister of Interior and Marzieh Vahid Dastjerdi, Minister of Health, traveled to Tabriz and Ahar.[citation needed] The Iranian Red Crescent did not request any international assistance.[25]
International
[edit]In the first two days, the Iranian Red Crescent said they would not accept outside help.[26] Three days later, the Iranian government announced it would accept foreign help.[27]
 United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon's office issued a press release that read: "[He was] deeply saddened by the loss of hundreds of lives" and that the UN was ready to lend assistance and mobilize international support. The release said Ban "extends his sincere condolences to the Iranian government and people, particularly the families of those who have been killed or otherwise affected in this disaster."[28]
United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon's office issued a press release that read: "[He was] deeply saddened by the loss of hundreds of lives" and that the UN was ready to lend assistance and mobilize international support. The release said Ban "extends his sincere condolences to the Iranian government and people, particularly the families of those who have been killed or otherwise affected in this disaster."[28] Armenian officials said the relief aid approved by Prime Minister Tigran Sargsyan's cabinet included tents, blankets, portable beds, sleeping bags, canned food and drinking water.[29]
Armenian officials said the relief aid approved by Prime Minister Tigran Sargsyan's cabinet included tents, blankets, portable beds, sleeping bags, canned food and drinking water.[29] Azerbaijan sent an aid convoy of 25 trucks carrying 460 tents, 1,000 beds, 3,000 blankets, 20 tons of rice, 40 tons of flour and 58 tons of other food products to Ahar on 13 August.[30][31] President Ilham Aliyev expressed his condolences with regard to the earthquake.[32] The region was visited by Azerbaijani MP Ganira Pashayeva.[33]
Azerbaijan sent an aid convoy of 25 trucks carrying 460 tents, 1,000 beds, 3,000 blankets, 20 tons of rice, 40 tons of flour and 58 tons of other food products to Ahar on 13 August.[30][31] President Ilham Aliyev expressed his condolences with regard to the earthquake.[32] The region was visited by Azerbaijani MP Ganira Pashayeva.[33] The Japanese ambassador to Iran, Kinichi Komano, expressed his government's sympathy with the earthquake victims and announced Japan's readiness to provide humanitarian aid.[34]
The Japanese ambassador to Iran, Kinichi Komano, expressed his government's sympathy with the earthquake victims and announced Japan's readiness to provide humanitarian aid.[34] Pakistani President Asif Zardari and PM Raja Ashraf separately expressed condolences.[35] The government of Pakistan dispatched a C-130 loaded with relief goods including tents, flour and milk[36] on 13 August.[37]
Pakistani President Asif Zardari and PM Raja Ashraf separately expressed condolences.[35] The government of Pakistan dispatched a C-130 loaded with relief goods including tents, flour and milk[36] on 13 August.[37] Russian President Vladimir Putin expressed his condolences and offered help.[38]
Russian President Vladimir Putin expressed his condolences and offered help.[38] Syrian President Bashar al-Assad sent a cable to Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad expressing condolences, personally and on behalf of Syrians, to the victims and their families and wishing the wounded quick recoveries.[39]
Syrian President Bashar al-Assad sent a cable to Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad expressing condolences, personally and on behalf of Syrians, to the victims and their families and wishing the wounded quick recoveries.[39] Taiwan's government expressed its condolences to the families of victims and offered assistance.[40]
Taiwan's government expressed its condolences to the families of victims and offered assistance.[40] The Turkish Red Crescent sent a truck with emergency supplies to the border. The Turkish Foreign Ministry also said it was ready to help, if the need arises.[5]
The Turkish Red Crescent sent a truck with emergency supplies to the border. The Turkish Foreign Ministry also said it was ready to help, if the need arises.[5] The government of the United Arab Emirates expressed condolences and offered assistance.[41][42]
The government of the United Arab Emirates expressed condolences and offered assistance.[41][42]

 The White House Press Secretary Jay Carney released the following statement on 12 August: "The American people send the Iranian people our deepest condolences for the loss of life in the tragic earthquake in northwestern Iran. Our thoughts are with the families of those who were lost, and we wish the wounded a speedy recovery. We stand ready to offer assistance in this difficult time."[43]
The White House Press Secretary Jay Carney released the following statement on 12 August: "The American people send the Iranian people our deepest condolences for the loss of life in the tragic earthquake in northwestern Iran. Our thoughts are with the families of those who were lost, and we wish the wounded a speedy recovery. We stand ready to offer assistance in this difficult time."[43] Pope Benedict XVI, in his Sunday Angelus at the papal summer residence at Castel Gandolfo, stated: "Dear brothers and sisters, my thoughts are, at this moment ... to those of northwestern Iran, struck by a violent earthquake. These events have resulted in many victims and injured, thousands of displaced people and extensive damage. I invite you to join in my prayers for those who have lost their lives, and for all the affected people tried by these devastating disasters. These brothers and sisters need our solidarity and our support."[44]
Pope Benedict XVI, in his Sunday Angelus at the papal summer residence at Castel Gandolfo, stated: "Dear brothers and sisters, my thoughts are, at this moment ... to those of northwestern Iran, struck by a violent earthquake. These events have resulted in many victims and injured, thousands of displaced people and extensive damage. I invite you to join in my prayers for those who have lost their lives, and for all the affected people tried by these devastating disasters. These brothers and sisters need our solidarity and our support."[44]
Criticism of Iranian government and state TV's late response
[edit]The Iranian government was criticized regarding to crisis management of the earthquake. The decision to stop the search for survivors after 24 hours was based on a government assessment that all survivors had been rescued from the rubble; an unnamed local doctor disputed the likelihood of that assessment based on the remoteness of some villages. A lack of tents for the homeless was also cited by members of the Majlis.[45] The IRIB was criticised in an editorial in the Asr-e Iran newspaper for its perceived lack of news coverage of the earthquake. In a Majlis meeting on 13 August 2012, MPs from the affected region questioned President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad for not visiting the area and for not announcing public mourning.[46] That day, Iran then announced two days of public mourning.[47]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b ISC-EHB Event 604084447 [IRIS].
- ^ a b ISC-EHB Event 604846898 [IRIS].
- ^ Berberian, M. (2014), Earthquakes and Coseismic Surface Faulting on the Iranian Plateau, Developments in Earth Surface Processes (1st ed.), Elsevier, p. 592, ISBN 978-0444632920
- ^ a b Yeganeh Torbati (11 August 2012) "Two earthquakes in Iran kill 300 and injure 5,000", Reuters
- ^ a b c d Zahra Hosseinian (12 August 2012). "Two quakes in Iran kill 180 and injure 1,500". Reuters. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ "M 6.4 – 26 km SW of Ahar, Iran – Impact". 11 August 2012. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- ^ "Two deadly earthquakes hit Iran, 250 dead". Deutsche Welle. Associated Press. 11 August 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ a b ANSS: 2012a East Azerbaijan . ANSS: 2012b East Azerbaijan .
- ^ a b Shirzad Bozorgmehr; Michael Martinez (11 August 2012). "180 killed, 1,300 injured as strong quakes jolt northwestern Iran". CNN. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- ^ RFE/RL (11 August 2012). "Iranian Official Says 150 Dead in Earthquake". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- ^ Talebian, M.; Jackson J. (2004). "A reappraisal of earthquake focal mechanisms and active shortening in the Zagros mountains of Iran". Geophysical Journal International. 156 (3): 506–526. Bibcode:2004GeoJI.156..506T. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02092.x.
- ^ Allen, M.; Jackson J. & Walker R. (2004). "Late Cenozoic reorganization of the Arabia-Eurasia collision and the comparison of short-term and long-term deformation rates". Tectonics. 23 (2): n/a. Bibcode:2004Tecto..23.2008A. doi:10.1029/2003tc001530.
- ^ Moradi, A.S.; Hatzfeld D. & Tatar M. (2011). "Microseismicity and seismotectonics of the North Tabriz fault (Iran)". Tectonophysics. 506 (1–4): 22–30. Bibcode:2011Tectp.506...22M. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2011.04.008.
- ^ Hoseinpour, M.; Zare M. (2009). "Seismic Hazard Assessment of Tabriz, a City in the Northwest of Iran" (PDF). Science Information Database. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ Torbati, Yeganeh (12 August 2012). "Two earthquakes in Iran kill 250 and injure 2,000". Dubai. Reuters. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ Erdbrink, Thomas (12 August 2012). "At Least 300 Dead in Iran Earthquakes". The New York Times. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ "Rescuers dig for survivors after quakes kill 250 in Iran". 12 August 2012. Archived from the original on 13 August 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ Shirzad Bozorgmehr (11 August 2012). "Death toll rises in Iran earthquakes". CNN. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- ^ "Erdbeben im Nordwesten Irans – Mehr Opfer als befürchtet: 308 Tote nach Doppelbeben im Iran". Hamburger Abendblatt. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- ^ "Iran earthquakes kill 153 people". The News. 11 August 2012. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- ^ "UPDATE 2-Two earthquakes in Iran kill 300 and injure 5,000". Reuters. 12 August 2012. Archived from the original on 26 February 2017. Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ^ a b "Magnitude 5.1 – NORTHWESTERN IRAN". Archived from the original on 15 August 2012. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- ^ "Magnitude 5.0 – NORTHWESTERN IRAN". Archived from the original on 15 August 2012. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- ^ "Magnitude 5.3 – NORTHWESTERN IRAN". Archived from the original on 19 August 2012. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- ^ "Red Crescent on the ground following earthquakes in north-west Iran". Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ "Iranian death toll climbs in twin quakes". CBC. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- ^ "Iran U-turn opens door to foreign quake aid". The Guardian. London. 14 August 2012. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ "UN chief "deeply saddened" by deadly earthquake in Iran". Xinhua News Agency. 13 August 2012. Archived from the original on 15 August 2012. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ Hovannes Shoghikian, Lusine Musayelian (16 August 2012). "Armenia To Send Relief Aid to Iran Earthquake Victims". «Ազատ Եվրոպա/Ազատություն» Ռադիոկայան. Armenia Liberty. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ "Azerbaijan Sends Humanitarian Aid to Iran". Retrieved 13 August 2012.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Azerbaijani Humanitarian Aid Delivered to Iran". Archived from the original on 22 January 2013. Retrieved 14 August 2012.
- ^ "President Ilham Aliyev Offered Condolences to his Iranian Counterpart". Retrieved 13 August 2012.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "ЭХО – новости". Echo. Archived from the original on 21 January 2013. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ "Japan expresses sympathy with quake survivors". Islamic Republic News Agency. Retrieved 18 August 2012.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Pakistan offers quake help to Iran". Pakistan Today. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ "Pakistan to dispatch relief goods to Iran's quake-hit area". Xinhua News Agency. 13 August 2012. Archived from the original on 18 August 2012. Retrieved 9 January 2015.
- ^ "PM orders relief for Iranian quake victims". Daily Times. Pakistan. 13 August 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- ^ "روسیه برای كمك به زلزله زدگان ایران اعلام آمادگی كرد". Islamic Republic News Agency. 12 August 2012. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ "President al-Assad Condoles Iranian President over Victims of Two Earthquakes Hit North-west Iran". Syrian Arab News Agency. 12 August 2012. Archived from the original on 14 August 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- ^ "فارسی – ايرا – عملیات امداد و نجات در مناطق زلزلهزده ایران 'پایان یافت'". BBC. 12 August 2012. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ "UAE voices readiness to help Iran quake-stricken people". Islamic Republic News Agency. 12 August 2012. Archived from the original on 11 August 2024. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ "UAE ready to help Earthquake disasters in Iran". Radiofarda. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- ^ "Statement by the Press Secretary on the Earthquake in Iran". whitehouse.gov. 12 August 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2012 – via National Archives.
- ^ "Angelus, 12 August 2012 Benedict XVI". Vatican.va. 12 August 2012. Archived from the original on 27 February 2024. Retrieved 13 August 2024.
- ^ Torbati, Yeganeh (13 August 2012). "Iran government criticized over earthquake response". Reuters. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- ^ "فارسی – ايران – واکنش نمایندگان مجلس به عملکرد تلویزیون ایران در مورد زلزله". BBC. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- ^ Nasseri, Ladane; Saleh, Yeganeh (13 August 2012). "Iran Moves to Distribute Aid After Two Earthquakes Kill 306 – Businessweek". Bloomberg Businessweek. Archived from the original on 13 August 2012.
Sources
[edit]- ANSS. "2012a East Azerbaijan". Comprehensive Catalog. U.S. Geological Survey.
- ANSS. "2012b East Azerbaijan". Comprehensive Catalog. U.S. Geological Survey.
- International Seismological Centre. ISC-EHB Bulletin. Thatcham, United Kingdom.
External links
[edit]- The International Seismological Centre has a bibliography and/or authoritative data for this event.
- ReliefWeb's main page for this event.



