Operation Strike of the Sword
| Operation Strike of the Sword | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the War in Afghanistan | |||||||
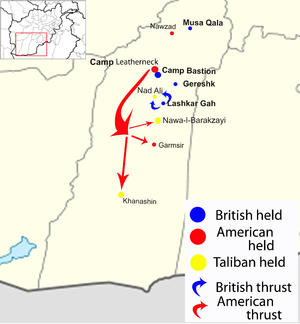 Operation Strike of the Sword in red; Operation Panther's Claw in blue | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
| Unknown | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
| At least 49–62 killed[5][6] | ||||||
Operation Strike of the Sword or Operation Khanjar was a US-led offensive in Helmand province in southern Afghanistan. About 4,000 Marines from the 2nd Marine Expeditionary Brigade as well as 650 Afghan troops were involved, supported by NATO planes. The operation began when units moved into the Helmand River valley in the early hours of July 2, 2009. This operation was the largest Marine offensive since the Battle of Fallujah in 2004.[7] The operation was also the biggest offensive airlift by the Marines since the Vietnam War.[8]
The Marines pushed into primarily three significant towns along a 75-mile stretch of the Helmand River valley south of Lashkar Gah. At least two Marine infantry battalions and one Marine Light Armored Reconnaissance (LAR) battalion spearheaded the operation. In the north, 2nd Battalion, 8th Marines (2/8) pushed into Garmsir district. In central Helmand, 1st Battalion, 5th Marines (1/5) pushed into Nawa-I-Barakzayi to the south of Lashkar Gah, 2nd Light Armored Reconnaissance Battalion (2nd LAR) entered Khanashin in the Khan Neshin district.[9][10][11]
Background
Taliban stronghold

Since 2001, Helmand province was considered to be a Taliban stronghold and had been one of the most dangerous provinces for coalition forces in Afghanistan, with British troops being locked in a stalemate since 2006. The large expanse of land made controlling the province difficult, while volunteers from across the Muslim world and hundreds of local Afghan nationals continued to join the insurgency.[12] There was a growing concern among U.S. military and intelligence officials that much of the violence that has plagued Helmand was linked to a flow of fighters and munitions particularly from Pakistan's Balochistan region.[13]
Troop surge
To help staunch the increasingly violent Taliban insurgency, President Obama, on February 18, 2009, approved an increase in US forces in Afghanistan, akin to President Bush's Iraq War troop surge of 2007.[14] By early June 2009, over 10,000 Marines had poured into southern Afghanistan, the first wave of the 21,000 troop surge.[15]
Military challenges
This section's factual accuracy may be compromised due to out-of-date information. (December 2011) |
The town of Nawzad became a clear example to Afghanistan experts of the challenges facing US forces as they sought to change the tide of the war with a limited number of troops. The town has been the scene of a stalemate since 2006. Neither British nor Estonian forces were able to dominate the region. Since taking over in March 2008, U.S. Marines too met a similar standstill.
For months, a lone company of Marines was assigned to the town. Requests for reinforcements were turned down as senior Marine commanders had to give priorities to areas with more civilians. Even though outright victory wasn't possible, the idea behind a single company of Marines "slugging it out" with the Taliban was to keep the insurgents occupied there while other units could win less battles and more hearts and more minds elsewhere.[16]
In April 2009, with three battalions in the region (3/8, 2/3, 2/14), the Marines were finally able to succeed in pushing back the front line by a few hundred yards and creating a larger buffer around the U.S. positions. A substantial number of insurgents were also believed to be killed.
However, by the end of June 2009, the town was still locked in a stalemate and the town remained a ghost town.[17]
Political pressure
In addition, the Afghanistan presidential elections, scheduled to be held on August 20, 2009, were increasingly being questioned. Critics asked how a meaningful national election could be held when Taliban militants controlled so much of southern Afghanistan.[18]
Operation goals
Adm. Michael Mullen, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, described the goal of the operation was not just driving out the Taliban from areas they control, but securing the area to allow the Afghan government to operate.[19] Brigadier General Larry Nicholson, commander of 2nd MEB, declared that the operation was aimed to improve security ahead of presidential elections, allowing voter registration where before there was none. The Marines would overwhelmingly assault and then consolidate the ISAF's hold in the region.[20]
Timeline
Military action begins
The conflict began around 1:00 a.m. local time when Marines from 1st Battalion, 5th Marines (1/5), were dropped by CH-47s and UH-60s helicopters of the 82nd Airborne Division, into dirt fields around the town of Nawa-l-Barakzayi, south of Lashkar Gah. The first shots of the operation were fired at daybreak (around 6:15 a.m.) when a Marine unit received small-arms fire from a tree-line. Cobra attack helicopters were called in and made strafing runs at the tree line from where the fire was coming from. Simultaneously, Marines from 2nd Battalion, 8th Marines (2/8), were dropped by helicopters just outside the town of Sorkh-Duz. The town of Sork-Duz lies between Nawa-l-Barakzayi and Garmsir. Temperatures reached over 100 °F (38 °C).[10][21]
-
Marines from 2/8 board helicopters at Camp Dwyer, July 2, 2009
-
Video, Operation Khanjar, Part I, "Send in the Reinforcements", United States Marine Corps with support from Afghan National Army, An additional 4,000 U.S. Marines are deployed to the Helmand province. Published July 31, 2009.
-
Video, Operation Khanjar, Part II, "Mission Launch", United States Marine Corps with support from Afghan National Army, About 25 helicopters fly back and forth dropping U.S. Marines throughout the Helmand River valley. Published July 31, 2009.
U.S. restraint
Although the operation was meant to eliminate the Taliban threat, the operation's principal focus was to win the locals' confidence and protect them from Taliban threat. To affirm this, Marine units throughout exercised military restraint when encountering enemy insurgents. Although the troops encountered roadside bombs and small-arms attacks, which resulted in the death of one Marine and several others wounded, commanders opted to mute their return fire. In the first 24 hours of the operation, the Marines did not fire artillery or call for fighter planes to drop bombs.[13]
Civilian casualties was an issue Gen. Stanley McChrystal, the U.S. Forces Afghanistan and ISAF commander, underscored prior to the operation, as it was one sure way of losing the locals' hearts and minds regardless of how many human shields the Taliban would go through on a single day. McChrystal further elaborated the need for constant surveillance to foil Taliban attempts to murder civilians while claiming US collateral damage. Though troops in similar circumstances might have called in airstrikes, Marine commanders practiced what they called "tactical patience" in a conscious effort to further minimize coalition civilian casualties in the face of strict Rules of Engagement.[22]
On the first day, July 2, Marines from 1/5 made contact with a group of about 20 militants holed up in a mud-brick compound in Nawa-l-Barakzayi. The Marines refrained from calling in a fixed-wing airstrike and instead used the 20mm guns from their AH-1W SuperCobra helicopter gunships to avoid the risk of civilian casualties. The militants managed to escape.[13][21][23][24] Though fired upon, Marines refrained from destroying many compounds because they could not confirm if civilians were inside[22]
Marine officers distributed handbills explaining their presence and talked to residents with the help of interpreters. Some Marine companies, out of respect as well as to safeguard the locals from Taliban reprisals, bedded down for the night in empty homes "with the permission of the hearts and minds of the people", instead of constructing bases with razor wire and sand-filled barriers.[13][24]
Garmsir district
Marines from 2nd Battalion 8th Marines (2/8) met little or no resistance initially.[5] On July 3, Taliban fighters in a walled compound in Garmsir engaged Marines for eight hours until an AV-8B Harrier II attack jet from VMA-214 destroyed the compound with a 500-pound bomb, killing all of the estimated 30–40 Taliban inside. No Marines were reported wounded in the action, although it delayed U.S. plans to meet with village elders and some locals.[5] Marines from 2/8 conducted joint patrols with the Afghan National Army in and around the town of Sorkh-Duz.
By July 5, elements of 2/8 were engaged in heavy fighting at Toshtay, 16 miles south of Garmsir.[25]
-
Marines from 2/8 firing on an enemy position in Garmsir, July 3, 2009
-
Video, Operation Khanjar, Part III, United States Marine Corps with support from Afghan National Army, A company of US Marines are on patrol in the village of Sorkh-Duz, in Garmsir, Helmand Province. They've been invited by the district governor. Their mission is to win over the local people. Published August 4, 2009.
Nawa-l-Barakzayi district
Hundreds of Marines from 1st Battalion 5th Marines (1/5) were lifted by helicopter into the village of Nawa-I-Barakzayi, encountering sporadic resistance. Marine commanders noted that Taliban forces seemed to have withdrawn for the time being to observe the Marines.[9][22]
On July 24, Marines from Company F, 2nd Battalion, 8th Marine Regiment, Regimental Combat Team 3, along with ANA Troops, raided a Taliban compound. Five insurgents were killed and over 270,000 lbs of poppy seed, 33 bags of opium, 13 bags of hashish, 50 barrels of precursory explosive material, 20 bolt-action rifles, 20 IED's, and 130,000 lbs of fertilizer, that could have been used for explosives charges, were seized.[citation needed]
Khan Neshin district
On July 2, 2009, approximately 500 Marines from 2nd LAR, 70-vehicle strong, arrived at Khanashin, the capital of Khan Neshin District. Khanashin had been a Taliban stronghold and coalition forces had never had a sustained presence in areas so deep into the southern Helmand River valley. The Marines halted outside the village, waiting for the village surgeon to give them permission. By the end of the day, the Marines were able to negotiate entry into the town, encountered no resistance, and began talks.[10][11][26]
Marine attack on Dahaneh
On August 12, 2009, U.S. Marines mounted a helicopter assault on the Taliban-held town of Dahaneh, it had been under insurgent control for years. The assault began before dawn, the first assault wave in Humvees and MRAPs left a Marine base at 1:00 a.m. in the town of Naw Zad, about five miles north of Dahaneh. Three CH-53E Super Stallion helicopters then picked up a platoon of Marines and dropped them behind Taliban lines in Dahaneh. These troops blasted their way into a suspected militant compound, where they arrested five men and took over the compound as a base. U.S. Marine AV-8B Harrier II jets were also involved in the battle dropping flares in a show of force. As dawn broke, insurgent rocket and mortar fire started raining down on U.S. troops. Marines entered the town as others battled militants in the surrounding mountains. The first wave of Marines was met with small arms, mortar and rocket propelled grenade fire. Insurgents were firing from house rooftops and courtyards. A heavy machine gun the Taliban was firing from one of the streets slowed the Marines' progress into the town. Militants also brought in a truck to fire heavy missiles. After militants fired volleys of rockets from a mud-wall compound, the Marines called in a missile strike which destroyed the building and killed 7–10 militants inside, according to the Marines. By sunset, the Marines had made little progress into Dahaneh beyond the gains of the initial pre-dawn assault. Since the Marines encountered stiff resistance they suspected that the Taliban knew of the attack on the town and prepared themselves. Marine forces seized about 66 pounds of opium on the first day of the battle.[27]
The second day of the fighting, Marine AH-1W SuperCobra attack helicopters fired rockets at Taliban positions in the nearby mountains where militants were believed firing at troops in the town. Later, U.S. A-10 Thunderbolt II attack aircraft fired multiple rounds into the cliffs overlooking what the Marines call "Hell's Pass", the entrance into the Now Zad valley, and U.S. surface-to-surface missiles, fired from the main Marine base, pounded the hillsides. Meanwhile, in the town, Marines came under heavy machine gun fire as they moved through the streets and alleyways. One Marine was killed. By the evening of the second day, Marine and Afghan troops had managed to take about half the town, however resistance was still continuing.[28]
On the third day, Marines launched a pre-dawn raid against a Taliban position on the southern edge of the town, storming a fortified compound and then blowing up two towers from which insurgents fired rockets and mortars at U.S. troops the day before. Marines found marijuana plants growing in the courtyard and confiscated trigger plates used to manufacture roadside bombs.
By the fourth day the battle had ended and coalition troops secured the town.
Aftermath
Pakistani concerns
On July 3, 2009, Prime Minister Yousaf Raza Gillani of Pakistan said that he was concerned with the influx of volatile strategic assets fleeing from Afghanistan into Pakistan due to the ongoing operation in Helmand, and this needs to be stopped. He urged this to a French delegation.[29]
The Pakistani army moved troops from elsewhere on its side of the Afghan border to the stretch opposite Helmand to try to stop any militants from fleeing the offensive. Both U.S. and Pakistani officials have expressed concern that stepped-up operations in southern Afghanistan could push the insurgents across the border.[22]
Effectiveness
On July 7, 2009, Afghan defense officials said that Taliban fighters and their commanders have escaped the big U.S. offensive in Helmand province and simply moved into areas to the west and north, prompting fears that the U.S. effort has just moved the Taliban problem elsewhere.[30]
Gen. Zahir Azami, speaking for the Afghan Ministry of Defense, said that since the U.S. Marines began their offensive, Taliban fighters have moved to northern Helmand province near Baghran, an area controlled by German forces, and to the eastern edge of Farah province, largely under Italy's control.[30]
Brig. Gen. Mahaiddin Ghori, the Afghan army commander in Helmand, estimated that Helmand province had roughly 500 foreign Taliban fighters and another 1,000 Afghan Taliban. Gen. Zahir Azami had no estimates of how many had moved north and west.[30]
U.S. and NATO officials acknowledged that the Taliban moved from Helmand ahead of the Marines, and U.S. officials privately said they had seen less fighting during the one-week offensive than they had anticipated.[30] General Ghori lamented the tightening of the RoE allowing up to two companies of Taliban to escape the clutches of the allied forces.
The shift of the Taliban into the areas to the west and north has prompted complaints from German and Italian commanders, whose troops shelter there, and have prompted questions about whether the United States has enough troops to pursue the insurgents while at the same time carrying out Army Gen. Stanley McChrystal's plan to "clear, hold and build" areas taken from Taliban control and simultaneously support the northern and western areas held by German and Italian forces.[30]
Casualties
During the operation 14 U.S. Marines were killed. Two Afghan soldiers and one Afghan interpreter working with the Marines were also killed.
The U.S. does not officially count the enemy dead so it is almost impossible to get an accurate number of the Taliban who died in the operation.[31] However, based on a few reports released, it can be concluded between July 2 and 4 also August 12 and 15 at least 49–62 Taliban were killed. This also however, is most likely a minimum since there is no official enemy dead count throughout the whole operation and the Taliban have a tendency to bury their dead quickly according to their religion, which makes it hard to get an accurate number of killed.
Participating units
International Security Assistance Force
- Afghan forces
- Unknown (probably includes elements of 3rd Brigade, 205th Corps which is the Helmand ANA garrison).
- British forces
- U.S. forces
- Task Force Leatherneck
- Regimental Combat Team 3
- 2nd Light Armored Reconnaissance Battalion (-)
- 2nd Marine Logistics Group
- Marine Aircraft Group 40
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 82nd Airborne Division (Task Force Pegasus)[32]
- 3rd Battalion, 82nd Combat Aviation Brigade (Task Force Talon)
Taliban forces
- Several operational and IED making cells of about 4–10 personnel each influenced by a Taliban shadow government. Quetta Shura located in Pakistan provided top Taliban leadership for Helmand province.[33]
See also
- Operation Panther's Claw – simultaneous British operation in southern Afghanistan
- Helmand Province campaign – ongoing coalition campaign to secure the province
- Battle of Now Zad – Ongoing operation by US Marines to secure Nawzad
- War in Afghanistan (2001–present)
- Civilian casualties of the War in Afghanistan (2001–present)
References
- ^ "Taliban launch 'operation' against U.S. Marines | World Military Forum – Latest Military News | Army, Navy, Air Force, Missiles". Archived from the original on 2012-03-01. Retrieved 2009-12-05.
- ^ Taliban scatter in Afghanistan, but the threat survives – TwinCities.com
- ^ ReliefWeb ť Document ť Factbox – Security developments in Afghanistan, 16 Jul 2009
- ^ Coghlan, Tom (2009-08-01). "Battle stations anatomy of an ambush by the Taleban". The Times. London. Retrieved 2010-05-20.[dead link]
- ^ a b c Chandrasekran, Rajiv (2009-07-04). "Insurgents Step Up Attacks on Marines". The Washington Post. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ Battle of Dahaneh
- ^ "Obama Launches First Major Offensive in Afghanistan". US News. 2009-07-02. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ Sheppard, Ben (July 1, 2009). "US Marines storm south in major Afghan offensive". Archived from the original on 2009-07-11. Retrieved 2009-10-04.
- ^ a b Shanker, Thom; OPPEL Jr, RICHARD A. (2009-07-03). "In Tactical Shift, Troops Will Stay and Hold Ground in Afghanistan". NY Times. Retrieved 2009-07-06.
- ^ a b c Sheppard, Ben (2009-07-03). "US Marines battle on in Afghanistan". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ a b "Operation Khanjar restores government control in Khan Neshin". ABC. 2009-07-06. Archived from the original on July 9, 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-06.
- ^ Pannell, Ian (2009-07-04). "'High Stakes Battle' for Helmand". BBC. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ a b c d "Troops push deep into Afghanistan". The Philadelphia Inquirer. 2009-07-03. Archived from the original on July 6, 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-06.
- ^ "Obama OKs Afghanistan troop surge". The Washington Times. 2009-02-18. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ "US Marines Fan out Across Dangerous Afghan South". ABC. 2009-06-08. Archived from the original on June 10, 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ Phillips, Michael M. (2009-05-23). "Stalemate in Afghanistan". WSJ. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ "Stalemate in Afghan ghost town shows task ahead". Associated Press. 2009-06-30. Archived from the original on July 3, 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ Nelson, Dean; Farmer, Ben (2009-07-02). "US Marines lead major crackdown against Taliban". London: UK Telegraph. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ "Suicide attack outside NATO base in Kandahar". Associated Press. 2009-07-06. Archived from the original on July 10, 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-06.
- ^ "US opens 'major Afghan offensive'". BBC. 2009-07-02. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ a b Straziuso, Jason (2009-07-03). "Marines suffer first casualties in Afghan offensive". Associated Press via Marine Corps Times. Archived from the original on 2009-07-09. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ a b c d "Marines exchange fire with Taliban in searing heat". Associated Press. 2009-07-03. Archived from the original on July 9, 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-06.
- ^ "U.S. Pushes Into Taliban Strongholds". The Washington Post. 2009-07-01. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
- ^ a b "Marines targeting Taliban in Afghan push". CNN. 2009-07-03. Retrieved 2009-07-06.
- ^ Farmer, Ben (2009-07-05). "US Marines face a 'hell of a fight' in Helmand". London: UK Telegraph. Retrieved 2009-07-05.
- ^ Chandrasekaran, Rajiv (2009-07-03). "Marines Meet Little Resistance in Afghan Push, page 2". The Washington Post. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ [2][dead link]
- ^ "PM Gilani rules out formation of more provinces". Dawn (newspaper). 2009-07-03. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ a b c d e "Afghans: Taliban Have Escaped Helmand and Marines". Archived from the original on 2009-07-12. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ Shapiro, Lila (2009-07-26). "US Stops Giving Militant Death Tolls In Afghanistan". The Huffington Post.
- ^ "Operation KHANJAR (SWJ Blog)". Archived from the original on 2011-01-07. Retrieved 2009-07-07.
- ^ Roggio, Bill. "Coalition strike kills senior Taliban leader in Helmand", The Long War Journal, March 23, 2009. Assessed April 23, 2010.
External links
- U.S. launches 'major operation' in Afghanistan – CNN
- Marines Move Out on New Mission – The Washington Post
- U.S. Marines Try to Retake Afghan Valley From Taliban – The New York Times
- Why Obama's Afghan War is Different – Time
- Afghans: Taliban Have Escaped Helmand and Marines – McClatchy Newspapers
- Operation Khanjar—Part 1 – July 28, 2009 – Youtube video By ISAFMEDIA – An inside look at the new U.S. troops in the Helmand province as they prepare for one of the largest operations ever to take place in Afghanistan.
- Operation Khanjar—Part 2 – July 29, 2009 – Youtube video By ISAFMEDIA – Get an inside, up-close look at the launch of Operation Khanjar. Watch as thousands of Marines are dropped by helicopter into Helmand. For more videos, check out NatoChannel.tv
- Operation Khanjar—Part 3 – August 3, 2009 – Youtube video By ISAFMEDIA – This story looks at how the US Marines on Operation Khanjar are working to win over the local people.
- Military operations of the War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) involving the United States
- Military operations of the War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) involving the United Kingdom
- 2009 in the War in Afghanistan (2001–2021)
- History of Helmand Province
- United States Marine Corps in the War in Afghanistan (2001–2021)


