Frank C. Papé
Frank C. Papé | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | Francis Cheyne Papé July 4, 1878 |
| Died | May 4, 1972 (aged 93) |
| Occupation(s) | artist, illustrator |
| Signature | |
Francis Cheyne Papé (4 July 1878 – 5 May 1972), was an English artist and illustrator whose career spanned 64 years, from 1898 to 1962. Papé's work included painting using gouache, water colour, and illustration in pen and ink.[1]
Papé illustrated many books and magazines produced in the early part of 20th century by major publishers. His work illustrated such varied writers as Homer, Suetonius, Rabelais, Spenser, Bunyon, Defoe and others.
Papé is best known for his illustrations to the books published in the 1920s by the American writer James Branch Cabell and the French writer Anatole France.
In 1921 literary critic Clement Shorter said readers of Cabell's Jurgen: A Comedy of Justice would be "enticed into the absorption of this book by the luxury of its illustration. The drawings are by Frank C. Papé and are certainly very beautiful and quaint".[2] A 1928 review said Papé was "renowned among collectors of modern first editions for his decorations in the books of Cabell and France".[3]
The growing "cult of Papé" resulted in a character in Alec Waugh's novel Kept (1925) referencing Papé's illustrations in Cabell's 1921 novel Jurgen: A Comedy of Justice - "For several minutes she remained bent over Pape’s illustrated Jurgen. 'How good they are,' she said. 'I should doubt if an artist has ever entered more completely into the spirit of the writer...' ".[4]
Cabell described Pape’s illustrations as "opulent in conceits and burgeons and whimseys" in the preface of the 1925 reissue of his Figures of Earth.[5]
During the second decade of the 20th century, Papé made extensive contributions to a number of collections of fairy, folk and other children's tales, as well as illustrating the Arabian Nights and a self-published collection of the Psalms.
Papé died 4 May 1972 in Bedford, Bedfordshire, Great Britain, 93 years old.
Early life, family and education
[edit]Papé was born in Camberwell, London, on 4 July 1878,[6] the second of Julius Eduard Paul (1848-1894) and Margaret Cheyne (née Johnston) (1853-1903) Papé's four children.[7][8][9] By the time Papé was in high school, his father was a banker in Berlin. His mother was a referenced contributor to Schwierigkeiten des englischen: Syntax (Difficulties of English: Syntax) (1904), a text book by German author Gustav Krüger.[10]
In 1901 Papé was a boarder in a London home.[11] Papé studied at The Slade School of Fine Art, completing his studies c. 1902–04.[12]
Family
[edit]Papé married Agnes Mary Stringer at St Mary's Church, Putney on 4 July 1907.[13] They had a son, Lionel Frank Papé born 15 April 1908 in Putney, Wandsworth, London, England.[14]
Stringer was a former Slade School of Fine Art student whose illustrations in Little Folks (c. 1910) magazine for children resemble Papé's early style. She did much of the coloring of his pictures. The couple collaborated on books, including the children's books Fair Folk of Many Lands published by the Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge in 1920 and The Picture Story Of Lorna Doone published by The Bodley Head in 1933. The couple lived for many years at Percy House in Royal Tunbridge Wells, Kent, England.[5][15] Papé's wife died 14 June 1955.
Early career
[edit]
Papé showed an incredible attention to detail from the outset of his career. He often developed a singular, particular style for each different book he was illustrating, sometimes using only line in a book's illustrations while other books saw Papé using soft washes of colors or shades of gray.
He also was a sly user of humor within his work. His illustration "Timothy began to dance, the booth also began to dance, the table danced" for Richard Wilson's "The Russian History Book" shows the book's characters, table, mice, cats and dishes dancing. The letters in Papé's signature are dancing as well.
Magazine illustration
[edit]
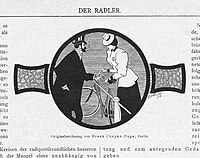
Papé's first known printed illustration work was for a Berlin magazine "Die Radler" (The Cyclist), later "Radlerin Und Radler". His work was selected by the magazine before he had turned 20 and before he had finished art school. The magazine printed his illustrations from 1898 through 1902. Papé's earliest work already exhibited many of his later seen personal techniques, including images that violated the frame of the illustration, juxtaposed patterns and a deft interplay between solid black and solid white.
Papé provided illustration for "The Wide World Magazine" during the 1910s. The primarily black and white magazine printed his work in more expensive duotone, often using a light blue second color tint to enhance Papé's work.[16]
Early art exhibitions and sales
[edit]In 1905 Papé was 27 when his work "The Life And Death Of Siegfried" sold for £157 (equivalent to $26,585 in 2023) during the Spring Exhibition at the Southport Corporation Atkinson Art Gallery in Merseyside, England.[17]
In 1908 he exhibited a diptych entitled "St. Christopher" at the 30th Southport Spring Exhibition in Southport, Merseyside, England.[18]
Book illustration
[edit]Pape's earliest book illustrations were for Emile Clement's Naughty Eric and Other Stories from Giant, Witch, and Fairyland, published in 1902, which remains extremely rare. A single copy is held by The British Library. An original pen and ink illustration from one of the stories, 'The Magic Stone', has been found in Sussex, England.[19]
Papé's next earliest illustrations are found in books for children from around 1908, including The Toils and Travels of Odysseus (1908), a translation of The Odyssey by Cyril A. Pease and John Bunyan's The Pilgrim's Progress (1910).
By 1911, Papé was a highly successful book illustrator. Papé also designed book covers for the books that contained his illustrations as well as books by other authors, including Rafael Sabatini (The Life of Cesare Borgia, 1924).
Military service
[edit]World War I brought a decline in Britain's illustrated book market, affecting Papé's livelihood. He enlisted at the age of 37 in the Royal Army Service Corps on 7 December 1915 and served on the Greco-Bulgarian front.[14][12]
Bookplate designer
[edit]Bookplates designed by Papé have become sought after by collectors. In the 1980s many volumes of author Dennis Wheatley's personal library bearing then unknown Papé bookplates were discovered on the 50p–£1 shelves at the Blackwell's bookstore in Oxford. Papé's bookplates are in most instances worth more than the book and are highly prized. One of Papé’s illustrations for the works of François Rabelais was used as a bookplate design by silent film star Louise Brooks.[20]
Collaboration with James Branch Cabell
[edit]In the 1920s Papé's career was revived due to his illustrations for books by James Branch Cabell. Early editions of many Cabell novels had been illustrated by Howard Pyle. The publishers The Bodley Head in London and Robert M. McBride & Co. in New York printed Papé's lush illustrations for Cabell's books as high quality photogravure prints, tipped into the volumes and protected by tissue overlay sheets. These editions usually included 11 or 12 of the Papé gravure prints as well as numerous incidental Papé illustrations throughout the body of the book text. Similar Papé gravure prints were included in the later Anatole France series of books he illustrated.
Jurgen obscenity trial increased public awareness
[edit]Cabell's Jurgen, A Comedy of Justice was a fantasy novel set in the Middle Ages. Jurgen, the novel's hero was a medieval pawnbroker - in his words a "monstrous clever fellow". The book recounted Jurgen's sexual liaisons with a female vampire, a goddess of fertility, and other maidens before choosing wedded bliss.
After the book was first published in 1919, the director of The New York Society for the Suppression of Vice claimed the novel was obscene, banned the book and seized the printing plates. This scandal increased public interest in Jurgen. The deluxe 1921 edition featuring Papé's illustrations increased Papé's following in the United States.[21][22]
Papé's commissions grew due to his new acclaim in the United States. Cabell's book series Biography of the Life of Manuel issued by the London publishing house The Bodley Head, included Jurgen, A Comedy of Justice (1921, originally in a limited edition), The High Place, Something about Eve and The Cream of the Jest. Papé's illustrations often closely followed the double entendres in Cabell's books.
Praised by Cabell in his novels
[edit]Cabell praised Papé's work in "A Preface To These Pictures" in the 1925 edition of his book Figures of Earth, saying in part "... most of my later writings are being commended to 'Papé collectors'. And indeed, the volume in your hands, I must perforce... regard as Mr. Papé's book, rather than my own book whensoever I I quite futilely attempt to sum up his delightful and unarithmetical additions to the text... All these fine things, and many other fine things hereinafter, stay wholly and indisputably the legal children of Frank C. Papé".[23][24]
Cabell said "The art of Mr. Papé extenuates the inadequacies of the author" in the foreword of his novel The Cream of the Jest.[25]
Cabell kept a six-page letter from Papé in his copy of Something About Eve: A Comedy of Fig-Leaves (1929) which was illustrated by Papé. The letter was found after Cabell's death. It may be seen here: Letter from Frank C. Papé to James Branch Cabell
Map of "Poictesme"
[edit]Papé's map of Cabell's mythical realm of Poictesme, based on Cabell's design, was used as the endpapers for the 1928 edition of The Silver Stallion published by Robert McBride & Company. Papé aimed to mislead readers, claiming the map was "...drawn from the yellowed parchments of Philip Borsdale, circa 1679" when in fact he had drawn it, even incorporating points of interest from Royal Tunbridge Wells where he lived in England.[26] Cabell enthusiasts purchased large format color broadside prints of the map, advertised as "suitable for framing".[27]
Illustrated Anatole France books
[edit]The success of these editions led to The Bodley Head commissioning illustrations by Papé for books of Anatole France, including The Revolt of the Angels (1924), Penguin Island (1925), Thaïs (1926) and The Well of St. Clare (1928), in addition to those for the works of Rabelais. A New York World News Service review of Penguin Island praised Papé's illustrations saying "Mr. Papé has immortality ahead if he will illustrate the full 36 (volumes)".[28]
Contemporary reviews
[edit]In 1926 The Saturday Review of Literature reviewed Papé's illustrations of France's Thaïs saying "This, like Penguin Island and others, is a beautiful book. Papé's fine draughtsmanship with its humorous diablerie, perfectly suits France's fantasies, as it has suited certain of Cabell's".[29]
Uncle Ray's Corner newspaper illustration
[edit]Circa 1925, Papé illustrated Uncle Ray's Corner, Ramon Coffman's weekly children's column syndicated in the United States by the Cleveland Plain Dealer. Papé's collaboration with Coffman included a number of book illustrations, including Uncle Ray's Story of the Stone-Age People (1936) and Coffman's The Child's Story of Science (1939).[23][30][31]
Starting in 1945, he continued his collaboration when Coffman launched Uncle Ray's Magazine. Papé contributed to this publication until the mid-1950s, first as art director, then as a staff artist.[32]
Empire Marketing Board
[edit]In 1928 Papé illustrated a series of full-color posters for the Empire Marketing Board to promote trade within the British Empire by persuading British customers to "Buy Empire" tobacco.
Later career
[edit]Economic slowdown curtailed book illustration
[edit]During the 1930s, Papé's career faltered. In July 1933 Papé wrote in an unpublished letter to a Mr. Frank House in Brooklyn, New York about the slowdown in book illustration: "As high class book work seems to be a dead horse, I have devoted most of my time to trying to get other kinds of work — for papers and what-not. There is a proverb: 'When the devil is starving he will eat flies.' "[33]
End of career and death
[edit]By the end of the 1950s, his eyesight was in serious decline, and his only known work in the 1960s was a series of children's books for Oxford University Press. His last published work was a 1968 reprint of a 1933 illustrated version of Robinson Crusoe.[34]
Papé died 4 May 1972 in Bedford, Bedfordshire, Great Britain.[35]
Career retrospective
[edit]While Papé was prolific, his illustrations are rarely seen in person and are highly collectible.
Museum holdings
[edit]An oil painting from 1908 is the single example in his file at The Courtauld Institute of Art. Another Papé work is held in an American private collection and was shown in the exhibition Fantastic Illustration and Design in Britain, 1850-1930 at the Museum of Art, Rhode Island School of Design, and the Cooper-Hewitt Museum in New York in 1979.[4]
Realized auction prices
[edit]Papé's works have been appreciated for over 120 years. His works are starting to be sold in auctions around the world, attracting the attention of collectors. Examples of realized prices at auction include:
• A single Papé illustration was sold at Christie's South Kensington facility on 7 July 1993.
• The Legend of Siegfried, signed and dated 'F.C Papé 04' and four additional panels, 36½ x 34in. (93 x 86.5cm.) signed with initials; pencil and watercolor in an embossed copper Arts and Crafts frame decorated with coats of arms, "probably designed by Papé" sold at Christie's on 16 July 1999 for £28,750 (US$ 46,575) (equivalent to $85,186 in 2023).[36]
• Reginald Thomas Cleaver's poem '"Oh break, my heart! and Death, draw near!", illustrated by a 22 year old Papé, in pencil, pen and ink and wash, heightened with white, signed and dated 'F.C.Papé 1901', 16 x 10in. (42 x 26.7cm.) sold at Christie's on 16 July 1999 for £2,300 (US$ 3,726) (equivalent to $6,815 in 2023).[37]
• Two of Papé's illustrations for George Macdonald's children's book At the Back of the North Wind, both signed 'Frank C. Papé' and both extensively inscribed with verse (on the reverse), 14 x 9¾ in (35.5 x 24.8 cm.); pencil, brown ink and watercolour, unframed, sold at Christie's on 1 December 2004 for £2,271 (US$ 3,928) (equivalent to $6,336 in 2023).[38]
Gallery
[edit]1890s
[edit]-
Illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1898).
-
Article header illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1898).
-
Illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1898).
-
Illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1898).
-
Two page spread illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1899).
1900s
[edit]-
Illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1900).
-
Illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1900).
-
Illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1901).
-
Illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1901).
-
Illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1902).
-
Illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1902).
-
Illustration by Frank C. Papé in "Radlerin und Radler" magazine. (1902).
-
Title page illustration by Frank C. Papé from "Naughty Eric" by E. Clement. (1902).
-
"A most singular woman sitting on the trunk of a tree."
Illustration # 2 by Frank C. Papé from "Naughty Eric" by E. Clement. (1902). -
"Helen went toward the fiery monster."
Illustration # 3 by Frank C. Papé from "Naughty Eric" by E. Clement. (1902). -
Illustration # 4 by Frank C. Papé from "Naughty Eric" by E. Clement. (1902).
-
"He runs... hops... skips from this terrible Frenchman."
Illustration # 5 by Frank C. Papé from "Naughty Eric" by E. Clement. (1902). -
"He nipped off one of the legs."
Illustration # 6 by Frank C. Papé from "Naughty Eric" by E. Clement. (1902).
1910s
[edit]-
"Sir Calidore overthrows the Blatant Beast"
Illustration for The Gateway to Spenser - Stories from the Faërie Queen (1910). -
"He Jumped Right Out Of The Frame"
Illustration for The Fairy of Old Spain (1912). -
Illustration for The Adventures of Samba Sall in The Wide World Magazine (1914).
-
Illustration for The Adventures of Samba Sall in The Wide World Magazine (1914).
-
Illustration for The Adventures of Samba Sall in The Wide World Magazine (1914).
-
"The Water Tsar dances"
Illustration for Russian Fairy Book (1916). -
"Falcon the Hunter"
Illustration for Russian Fairy Book (1916). -
"Nightingale the Robber fell from his nest in the old oaks"
Illustration for Russian Fairy Book (1916). -
"Diuk stooped and caught Churilo by his yellow curls"
Illustration for Russian Fairy Book (1916). -
"There passed over the boundless white plain an age."
Illustration for Russian Fairy Book (1916). -
"Oh, said the man, I am able to do everything."
Illustration for Russian Fairy Book (1916). -
"The black-browed maid stood upon the bank as the red ship ... sailed away from Novgorod"
Illustration for Russian Fairy Book (1916).
1920s
[edit]-
"Upon The Middle Chest Sat A Woman"
Illustration for James Branch Cabell's Jurgen, A Comedy of Justice (1921). -
"Smoke Empire Tobacco"
Illustration for the Empire Marketing Board (1928). -
"Tobacco Plantation in Nyasaland"
Illustration for the Empire Marketing Board (1928). -
"Tobacco Plantation in S. Rhodesia"
Illustration for the Empire Marketing Board (1928).
As illustrator
[edit]- Naughty Eric and Other Stories from Giant, Witch, and Fairyland, 1902
- The Toils and Travels of Odysseus, 1908
- Children of the Dawn - Old Tales of Greece, 1908
- The Pilgrim's Progress, 1910
- The Gateway to Spenser - Stories from the Faërie Queen, 1910
- Fifty-Two Stories of Classic Heroes, 1910
- At the Back of the North Wind, 1911
- Half a Hundred Hero Tales of Ulysses and the Men of Old, 1911
- The Golden Fairy Book, 1911
- The Ruby Fairy Book, 1911
- The Diamond Fairy Book, 1911
- Siegfried and Kriemhild: A Story of Passion and Revenge, 1912
- The Fairy of Old Spain : and other important people, 1912
- Sigurd and Gudrun: An Ancient Tale of Constancy in Love, 1912
- The Book of Psalms, 1912
- As It Is In Heaven, 1912
- The Story Without an End, 1913
- The Indian Story Book, 1914
- Robin Hood and Other Stories of Yorkshire, 1915
- The Russian Story Book, 1916
- Contes d'Autrefois. Récits adaptés des Légendes Scandinaves, c. 1920
- Tales from Shakespeare, 1923
- Tales from the Mahabharata, 1924
- For works by James Branch Cabell
- Jurgen, A Comedy of Justice, 1919
- The High Place, 1923
- Figures of Earth, 1925 [1921]
- The Silver Stallion, 1926
- Something about Eve: A Comedy of Fig-Leaves, 1927
- The Certain Hour : Dizain des poëtes, 1916
- The Cream of the Jest, 1927 [1917]
- The Way of Echben, 1929
- Domnei: A Comedy of Woman-Worship, 1930 [1913]
- For works by Anatole France
- The Revolt of the Angels, 1924
- At the Sign of the Reine Pedauque, 1924
- Penguin Island, 1925
- Thaïs, 1926
- The Well of St Clare, 1928
- Mother of Pearl, 1929
- The Complete Works of Doctor Francois Rabeleis, 1927, 2 vol.s, trans. Sir Thomas Urquhart and Peter Motteux
- also The Histories of Gargantua and Pantagruel, 1982, trans. John M. Cohen
- Suetonius' Lives of the Twelve Caesars, 1930
- The Stars, The World, and The Women, 1930, by Rhys Davies, Furnival Books No. 4.
- Old Rowley: A Private Life of Charles II, 1933
- The Picture Story of Robinson Crusoe, 1933
- Tales From the Arabian Nights, 1934
- The Naked Lady or Storm Over Adah - A Biography of Adah Isaacs Menken, 1934
- Rachel the Immortal, 1935
- Uncle Ray's Story of the Stone-Age People, 1936
From 1935 onwards Pape illustrated for the children's newspaper column Uncle Ray's Corner.
- Don Quixote Retold, 1961
Legacy
[edit]A number of Papé's original drawings, together with some of his correspondence, is preserved at Stanford University.[39]
References
[edit]- ^ Bury, Stephan (ed.). Benezit Dictionary of British Graphic Artists and Illustrators, Volume 1. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199923052.
- ^ Shorter, Clement King (17 December 1921). "A LITERARY LETTER: A Fine War Novel". The Sphere. London, England. p. 312. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ Wolf, Howard (27 October 1928). "New Rabelais is Gargantua of 1928 Books". The Akron Beacon Journal. Akron, Ohio. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ a b "LIVE AUCTION 5496 VICTORIAN PICTURES & DRAWINGS - THE PROPERTY OF A LADY - Frank Cheyne Papé (1878-1972)". www.christies.com. 6 November 1995. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ a b Peppin, Brigid; Micklethwait, Lucy (1983). Dictionary of British book illustrators : the twentieth century. London, United Kingdom: John Murray.
- ^ "England & Wales, Civil Registration Death Index, 1916-2007 for Frank Cheyne Pape". www.ancestry.com. 1972. Retrieved 22 November 2023.
- ^ "Berlin, Germany, Deaths, 1874-1955 for Paul Eduard Pape". www.ancestry.com. 1 February 1908. Retrieved 22 November 2023.
- ^ "Isabel Margareta Minna Pape in the Berlin, Germany, Births, 1874-1908". www.ancestry.com. 2 September 1883. Retrieved 22 November 2023.
- ^ "Berlin, Germany, Deaths, 1874-1955 for Max Pape". www.ancestry.com. 2 July 1889. Retrieved 22 November 2023.
- ^ Krüger, Gustav (1904). Schwierigkeiten des englischen: Syntax; nebst beiträgen zur stilistik, wortkunde und wortbildung. Greifswald, Germany: C.A. Koch.
- ^ "1901 England Census for Francis C Papé". www.ancestry.com. 1901. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ a b Cobb, Richard. Something to hold onto: Autobiographical sketches. London, United Kingdom: John Murray. ISBN 9780719545870.
- ^ "London, England, Church of England Marriages and Banns, 1754-1938 for Francis Cheyne Pape". www.ancestry.com. 1907. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ a b "Frank Pape in the UK, British Army World War I Service Records, 1914-1920". www.ancestry.com. 7 December 1915. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ "LIVE AUCTION 6422 PRINTED BOOKS". christies.com. 18 March 1994. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ Samba Sall (19 July 1926). "The Adventures of Samba Sall". Time. London, England: A. Newnes, Limited. p. 60. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ "Southport Corporation Atkinson Art Gallery". The Southport Visiter. Southport, Merseyside, England. 5 May 1905. Retrieved 28 November 2023.
- ^ "Art In Lancashire". Manchester Courier and Lancashire General Advertiser. Southport, Merseyside, England. 15 February 1908. Retrieved 28 November 2023.
- ^ Selected illustrations from Naughty Eric were published in Black & White Images magazine in 2010.
- ^ Jaffe, Lew (15 May 2014). "Confessions of a Bookplate Junkie". bookplate55.rssing.com. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ "Christian slaying Apollon". bookplate55.rssing.com. Victoria and Albert Museum. 6 January 2004. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ "Illustration for Jurgen". encyclopediavirginia.org. VIRGINIA HUMANITIES. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ a b "A SHOWER OF STONES AND SHELLS FELL ON THE MONK - FRANK C. PAPE 1878 - 1972". www.worthpoint.com. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ Cabell, James Branch (1925). Figures of Earth - A Comedy of Appearances. New York, New York: Robert McBride & Company.
- ^ Roedder, Karsten (6 November 1927). "Books on Parade". The Brooklyn Citizen. Brooklyn, New York. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ "Books". Time. New York, New York: Time Inc. 19 July 1926. p. 32. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ "The Map of PHILIP BORSDALE, circa 1679". jamesbranchcabell.org. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ Stallings, Laurence (11 November 1925). "The First Reader". The Star Tribune. Minneapolis, Minnesota. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ "The Phoenix Nest". Saturday Review of Literature. New York, New York: The Saturday Review Company, Inc. 9 October 1926. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ "England's Premiere Artist Illustrates New Weekly Feature". Wisconsin State Journal. Madison, Wisconsin. 18 December 1928. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
- ^ IBIS 1996, p.31, passim.
- ^ IBIS 1996, pp. 36–37.
- ^ Johnson, Diana L. (1979). Fantastic Illustration and Design in Britain, 1850 - 1930. Providence, Rhode Island: Museum of Art, Rhode Island School of Design.
- ^ IBIS 1996, pp. 37–38.
- ^ "England & Wales, National Probate Calendar (Index of Wills and Administrations), 1858-1995 for Frank Cheyne Pape". www.ancestry.com. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ^ "LIVE AUCTION 5496 - VICTORIAN PICTURES & DRAWINGS - LOT 112". christies.com. 6 November 1995. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ "LIVE AUCTION 8463 - ILLUSTRATED BOOKS AND ORIGINAL BOOK ILLUSTRATIONS - LOT 39". christies.com. 16 July 1999. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ "LIVE AUCTION 5503 - BRITISH AND CONTINENTAL WATERCOLOURS INCLUDING ORIGINAL BOOK - LOT 307". christies.com. 1 December 2004. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ See record on the University's website Guide to the Frank Cheyne Papé Letters and drawings , ca. 1921-1931
Sources
[edit]- "Frank C. Papé", Studies in Illustration (4), Imaginative Book Illustration Society (IBIS), Winter 1996–1997, ISSN 1474-1342
Further reading
[edit]- Horne, Alan (1994), The Dictionary of 20th Century British Book Illustrators, Woodbridge, ISBN 1-85149-108-2
External links
[edit]- Vadeboncoeur, Jim, "Frank C. Papé", www.bpib.com, archived from the original on 23 October 2000
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - Works by Frank C. Papé at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about Frank C. Papé at the Internet Archive
- Frank Cheyne Papé at Library of Congress, with 24 library catalogue records
- Frank C. Papé at the Internet Speculative Fiction Database
- 1878 births
- 1972 deaths
- People from Camberwell
- English illustrators
- British illustrators
- British children's book illustrators
- British fantasy artists
- 19th-century British illustrators
- Illustrators of fairy tales
- Magazine illustrators
- British Army personnel of World War I
- Royal Army Service Corps soldiers
- 20th-century British illustrators