Windows Media Player: Difference between revisions
Units/dates/other |
|||
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
|Windows Media Player 6.3 || [[July 17]], [[2000]] || || [[Solaris (operating system)|Solaris]] |
|Windows Media Player 6.3 || [[July 17]], [[2000]] || || [[Solaris (operating system)|Solaris]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
test |
|||
==European Commission case== |
==European Commission case== |
||
Revision as of 17:33, 20 June 2008
| File:Wmp logo for vista.png | |
| File:Windows Media Player 11 Vista.png | |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 11.0.6001.7000
/ February 4, 2008 |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Media player |
| License | Proprietary software |
| Website | Microsoft Windows Media |
Windows Media Player (WMP) is a digital media player and media library application developed by Microsoft that is used for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices. Editions of Windows Media Player were also released for Mac OS, Mac OS X and Solaris but development of these has since been discontinued.
In addition to being a media player, Windows Media Player includes the ability to rip music from and copy music to compact discs, build Audio CDs in recordable discs and synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and enables users to purchase or rent music from a number of online music stores.
Windows Media Player replaced an earlier piece of software simply called Media Player, adding features beyond simple video or audio playback.
The default file formats are Windows Media Video (WMV), Windows Media Audio (WMA), and Advanced Systems Format (ASF), and supports its own XML based playlist format called Windows Playlist (WPL). The first generation Zune software (but not the current second generation software) which actually is a modified version of Windows Media Player, additionally supports AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) audio, MPEG-4 and H.264 video formats out-of-the-box. The player is also able to utilize a digital rights management service in the form of Windows Media DRM.
History
Windows has had a media player since the year 1991, when Windows 3.0 with MultiMedia Extensions was released. The original Media Player application used MCI to handle media files. In 1996 Microsoft released ActiveMovie, a new way of dealing with media files and streaming media (which the original Media Player couldn't handle). A wrapper was provided for users in the form of the ActiveMovie Control, allowing users to play media files on their computer.
ActiveMovie morphed into DirectShow and a new Media Player was created, known internally as Media Player 2. This player was an evolution from the ActiveMovie Control, providing a richer and more intuitive user interface. Media Player 2, like its predecessor, was also a wrapper—this time around DirectShow. Version 5.2 was the first version of this new Media Player, with version 6.x becoming widespread.
Version 6.4 was the final version of Media Player 2, by now known as Windows Media Player. Version 6.4 was included with Windows Me, Windows 2000 and Windows XP, but was dropped in Windows Vista.
There was another large revamp in Windows Media Player version 7, with the release of Windows Me, with a new user interface, visualisations and increased functionality. WMP7 came with the WMA and WMV codecs.
Features
- Allows the user to connect, share and sync data with portable handheld devices and game consoles. Media can be optionally transcoded to a format better suited for the target device, automatically, when synchronizing.
- Playback of audio, video and pictures, along with fast forward, reverse, seek and time compression and dilation.
- Supports local playback, streaming playback and progressive downloads.
- Support for any media codec and container format using specific DirectShow filters.
- Full media management, via the integrated media library, which offers cataloguing and searching of media. Media can be arranged according to album, artist, genre, date et al.
- Video Smoothing which upscales frame-rate by interpolating added frames, in effect giving a smoother playback on low-framerate videos.
- Includes a 10-band graphic equalizer and SRS WOW audio post-processing system. Windows Media Player can also have attached plug-ins which process the output audio or video data.
- Features a taskbar-mounted Mini mode in which the most common media control buttons are presented as a toolbar on the Windows taskbar. Flyout windows can display media information, the active visualization or the video being played back.
- Can use video overlays or VMR surfaces, if the video card supports them. In Windows XP, it uses VMR7 by default, but can also be made to use the more advanced YUV mixing mode by enabling the "Use high quality mode" option in Advanced Performance settings. This turns on deinterlacing, scaling and improved color accuracy. [1]
- Version 11 introduced improved support for DirectX accelerated decoding of WMV video (DXVA decoding)
- Features integrated CD-burning support for audio as well as data CDs. Data CDs can have any of the media formats supported by the player. While burning Data CDs, the media can, optionally, be transcoded into WMA format.
- Audio CDs can be ripped as WMA or WMA 10 Pro at 48, 64, 96, 128, 160 and 192 kbit/s, WMA lossless (470 to 940 kbit/s), WMA variable bitrate (from 40-75 kbit/s up to 240-355 kbit/s), MP3 at 128, 192, 256 and 320 kbit/s, or uncompressed WAV. 24 bit high-resolution CDs are also supported, if capable audio hardware is present.
- Includes intrinsic support for Windows Media codecs which support multichannel audio at up to 24-bit 192 kHz resolution.
- Supports subtitles and closed-captioning, if present in the media.
- Features "Synchronized Lyrics", by which different lines of lyrics can be time-stamped, so that they display only at those times.
- Windows Explorer shell integration to add files and playlist to the Now Playing and other playlists can be controlled from the Windows Explorer shell itself, via right-click menu.
- Provides an embeddedable ActiveX control for Internet Explorer so that developers can play Windows Media on web pages.
Other versions
Microsoft has also released versions of Windows Media Player for other platforms including Windows Mobile, Mac OS, Mac OS X, Palm-size PC, Handheld PC, and Solaris. Of these, only the Pocket PC / Windows Mobile edition continues to be actively developed and supported by Microsoft. Version 1 of the Zune software was also based on Windows Media Player, later versions are not.
Windows Mobile
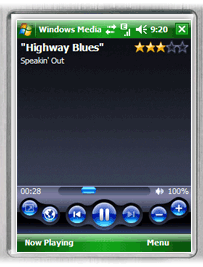
Windows Media Player for Pocket PC was first announced on January 6 2000, and has been revised on a schedule roughly similar to that of the Windows version.[2] Currently known as "Media Player 10 Mobile", this edition (released in October 2004) closely resembles the capabilities of the Windows version of WMP 10, including playlist capabilities, a media library, album art, WMA Lossless playback, support for DRM-protected media, video playback at 640x480 with stereo sound, and the same Energy Blue interface aesthetics also seen in recent versions of Windows XP Media Center Edition. It also supports synchronization with the desktop version of WMP 10, and additionally supports synchronizing and transcoding of recorded television shows from Media Center. Media Player 10 Mobile is not available as a download from Microsoft; distribution is done solely through OEM partners, and is typically included on devices based on Windows Mobile.
Windows Mobile 6.0 includes a copy of Windows Media Player 10 Mobile but with a similar (but not quite identical) theme as Windows Media Player 11.
Mac OS X
Version 9 was the final version of Windows Media Player to be released for Mac OS X before development was canceled by Microsoft. WMP for Mac OS X received widespread criticism from Mac users due to poor performance and features. Developed by the Windows Media team at Microsoft instead of the Macintosh Business Unit and released in 2003, on release the application lacked many basic features that were found in other media players such as Apple's iTunes and QuickTime.[citation needed] It also lacked support for many media formats that version 9 of the Windows counterpart supported on release 10 months earlier.
The Mac version supported only Windows Media encoded media (up to version 9) enclosed in the ASF format, lacking support for all other formats such as MP4, MPEG, and Microsoft's own AVI format. On the user interface front, it did not prevent screensavers from running during playback, it did not support file drag-and-drop, nor did it support playlists. While Windows Media Player 9 had added support for some files that use the WMV9 codec (also known as the WMV3 codec by the FourCC), in other aspects it was seen as having degraded in features from previous versions.
On January 12, 2006 Microsoft announced it had ceased development of Windows Media Player for Mac.[3] Microsoft now distributes a third-party plugin called WMV Player (produced and maintained by Flip4Mac) which allows some forms of Windows Media to be played within Apple's QuickTime player and other QuickTime-aware applications.[4] Mac users can also use the free software media player VLC, which is also able to play WMV-3 / WMV-9 / VC-1 Windows Media files
Release history
| Version | Original release |
Latest build |
OS Compatibility | Codename |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | ||||
| Windows Media Player 11 | October 30, 2006 | 11.0.6001 | Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista Windows XP SP2 |
Polaris (Windows XP) Aurora (Windows Vista) |
| Windows Media Player 10 | October 12, 2004 | Windows Server 2003 SP2 Windows XP |
Crescent [5] | |
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | January 27, 2003 | Windows XP Windows 2000 Windows Me Windows 98 SE |
Corona | |
| Windows Media Player for Windows XP (Version 8) |
October 25, 2001 | Windows XP | ||
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 16, 2001 (98, Me and 2000) | 7.1 | Windows 98 Windows Me Windows 2000 |
|
| Windows Media Player 7.0 | July 17, 2000 (9x, NT and 2000) September 14, 2000 (Me) |
7.0 | Windows 95 Windows 98 Windows Me Windows NT 4.0 Windows 2000 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.4 ( mplayer2 for 2000 and XP) |
November 22, 1999 | Windows 95 Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 2000 Windows XP |
||
| Windows Media Player 6.1 | June 25, 1998 | Windows 95 | ||
| Windows CE / Windows Mobile / Pocket PC / Other handheld devices | ||||
| Windows Media Player | April 2000 | Handheld PC | ||
| Windows Media Player 1.2 | July 2000 | Palm-size PC | ||
| Windows Media Player 7 | December 12, 2000 | Pocket PC | ||
| Windows Media Player 8 | June 2002 | Pocket PC (version 2002 and Smartphone) |
||
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | June 23, 2003 | Windows Mobile 2003 | Corona | |
| Windows Media Player 10 | May 9, 2005 | Windows Mobile 5.0 Windows Mobile 6.0 |
||
| Windows Media Player 11 | 2008 | Windows Mobile 6.1 Windows Mobile 7 |
||
| Mac OS | ||||
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | Mac OS 7 Mac OS 8 |
||
| Windows Media Player 7 | July 24, 2001 | 7.0.1 | Mac OS 8 Mac OS 9 |
|
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | November 7, 2003 | Mac OS X | Corona | |
| Solaris | ||||
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | Solaris | ||
test
European Commission case
In March 2004, the European Commission in the European Union Microsoft antitrust case fined Microsoft €497 million and ordered the company to provide a version of Windows without Windows Media Player, claiming Microsoft "broke European Union competition law by leveraging its near monopoly in the market for PC operating systems onto the markets for work group server operating systems and for media players". The company has made available a compliant version of its flagship operating system under the negotiated name "Windows XP N", though the product has not been very successful.[6] Windows Vista is also available in "N" editions. Still, with these editions it is possible to either install Windows Media Player (XP/Vista) or the Media Restore Pack through Windows Update (Vista) to gain the media player functionality back.
See also
- List of media players
- Comparison of media players
- Media Transfer Protocol
- Windows Media Encoder
- Windows Media Services
References
- ^ Windows Media Player 10 additional documentation
- ^ "Microsoft Unveils Windows Media Player for Palm-Size and Pocket PCs". Microsoft PressPass. Microsoft. January 6 2000. Retrieved 2006-05-14.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help)CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ Fried, Ina (2006-01-12). "Music stops for Mac Windows Media Player". CNET. Retrieved 2006-12-21.
- ^ "Windows Media Components for QuickTime". Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-03-30.
- ^ Media Transfer Protocol presentation
- ^ Marson, Ingrid (2005-11-18). "Still 'no demand' for media-player-free Windows". CNET. Retrieved 2006-12-21.
External links
- Microsoft Windows Media home page
- No Picture in Windows Media Player Error Message
- A Little Windows Media Player History
- Windows Media Player Support
- Microsoft ports Windows Media to Linux (10 April 2003, vnunet.com)
- Error Messages in Windows Media Player 10
- Error Messages in Windows Media Player 9
- Flip4Mac- official codec provider for Mac OS X users for WMP 9
- Audio and Video Codecs for Windows Media Player
- Windows Media Player plug-ins and skins
- List of default codecs in Windows XP SP2 and WMP 9 and 10
- MSDN How To Embed Windows Media Player in a HTML Web Page (For Webmasters)
- Creating A Windows Media Custom Experience (For Webmasters)
- Older versions of Windows Media Player
