Windows 3.0
| Version of the Windows operating system | |
 | |
 Windows 3.0 screenshot | |
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Windows |
| Source model | Closed source |
| Released to manufacturing | May 22, 1990 |
| Latest release | 3.00a with Multimedia Extensions / October 20, 1991 |
| License | Commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows 2.1 (1988) |
| Succeeded by | Windows 3.1 (1992) |
| Support status | |
| Unsupported as of December 31, 2001 | |
Windows 3.0 is the third major release of Microsoft Windows, launched on May 22, 1990. It introduces a new graphical user interface (GUI) that represents applications as clickable icons, instead of the list of file names in its predecessors. Later updates expand capabilities, such as multimedia support for sound recording and playback, and support for CD-ROMs.
Windows 3.0 was the first version of Windows to perform well both critically and commercially, and was considered a major improvement over its previous Windows 2.0 offering. Its GUI was considered a challenger to those used and popularized by Apple Macintosh and Commodore Amiga.[1] Other praised features are the improved multitasking, customizability, and especially the utilitarian memory management that troubled the users of Windows 3.0's predecessors.
The software was a major success, achieving 10 million sales. However, Microsoft was criticized by third-party developers for bundling its separate software with the operating environment, which they viewed as an anticompetitive practice. It was succeeded by Windows 3.1 in 1992. Support for Windows 3.0 ended on December 31, 2001.
Development history
[edit]Before Windows 3.0, a partnership bundled IBM's personal computers with Microsoft's MS-DOS since 1981. Microsoft had previous attempted to develop a successful operating environment called Windows,[2] which IBM declined for its product line.[3] As MS-DOS's fifth iteration approached, IBM demanded a version that could run in "protected mode", to allow multiple programs at once, among other benefits. MS-DOS was originally designed to run in real mode and run only one program at a time, due to the limitations of the Intel 8088 microprocessor. Intel had later released the Intel 80286, supporting such multitasking efficiently (with several different hardware features, including memory protection, hardware task switching, program privilege separation, and virtual memory, all absent on the earlier Intel x86 CPUs) and which could be directly connected to 16 times as much memory as the 8088 (and 8086). The two companies developed the next generation beyond MS-DOS, called OS/2. Early OS/2 software is not encumbered with MS-DOS compatibility, giving IBM a technological advantage.[4]
In late 1987, Windows/386 2.0 introduced a protected mode kernel that can multitask several MS-DOS applications using virtual 8086 mode, but all Windows applications still run in a shared virtual DOS machine. As the rest of the Microsoft team moved on to the OS/2 2.0 project, David Weise, a member of the Windows development team and a critic of IBM, believed that he could restart the Windows project. Microsoft needed programming tools to run in protected mode, so it hired Murray Sargent, a physics professor from the University of Arizona who had developed a DOS extender and a debugging program that works with protected mode applications.

Windows 3.0 originated in 1988 as an independent project by Weise and Sargent, using Sargent's debugger to improve the memory manager and run Windows applications in separate protected memory segments.[6] In a few months, Weise and Sargent cobbled together a rough prototype to run Windows versions of Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, then presented it to company executives, who were impressed enough to approve it as an official project. When IBM learned of Microsoft's upcoming project, their relationship was damaged, but Microsoft asserted that it would cancel Windows after its launch and that it would continue to develop OS/2.[7]
Windows 3.0 was officially announced worldwide on May 22, 1990, in the New York City Center Theater. The event had 6,000 attendees, and it was broadcast live in the Microsoft social fairs of seven other North American cities and twelve major cities outside. Microsoft spent US$3 million to host the festivities, which co-founder Bill Gates referred to as the "most extravagant, extensive, and expensive software introduction ever".[8] Microsoft did not offer free runtime licenses of the software to applications vendors, because runtime versions of Windows lack multitasking.[9] Instead, the company offered upgrades for both full and runtime previous versions of Windows at a cost of US$50 (equivalent to $117 in 2023)—considerably lower than the full license's suggested retail price of $149.[10] The software was bundled by computer hardware manufacturers. The first were Zenith Data Systems, Austin Computer Systems, and CompuAdd, followed by more than 25 others, not including IBM.[11]
Microsoft's "Entry Team" was assigned to make Windows 3.0 generally appealing to the public, and was concerned that the public might perceive it as no more than a tool for large enterprises, due to high system requirements. Major game publishers did not see it as a potential game platform, instead sticking to MS-DOS. Microsoft's product manager Bruce Ryan compiled games that the Windows team had designed in its spare time to create Microsoft Entertainment Pack, which includes Tetris and Minesweeper. There was little budget, none spent on quality testing. Nevertheless, the Entertainment Pack was sold as a separate product, and it became so popular that it was followed by three other Entertainment Packs.[12]
On December 31, 2001, Microsoft dropped support for Windows 3.0, along with previous versions of Windows and Windows 95, Windows for Workgroups, and MS-DOS versions up to 6.22.[13][14]
Features
[edit]Windows 3.0 features a significantly revamped graphical user interface (GUI), which was described as having a three-dimensional look similar to the Presentation Manager, rather than the flat look of its predecessor, Windows 2.1.[15][16] It also includes technical improvements to the memory management to make better use of the capabilities of Intel's 80286 and 80386 processors. Dynamic Data Exchange is a multitasking protocol whereby multiple running applications dynamically exchange data with one another, i.e., when data in one application changes, so does the data in another. This feature had appeared in Windows previously, but until Windows 3.0, due to memory constraints, users were unable to use the protocol. These users instead had to exit to DOS to run one application, close it, and open another to exchange data.[17][18] Due to its support for the 386 and later processors, Windows 3.0 can also use virtual memory, which is a portion of a hard disk drive that is substituted for memory by the processor in the event that its own memory is exhausted.[19][20] Like its predecessors, Windows 3.0 is not an operating system per se, but rather an operating environment that is designed for DOS and controls its functions.[10][21]
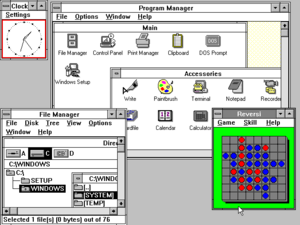
The MS-DOS Executive file manager was replaced with Program Manager, the list-based File Manager, and Task List.[22] Program Manager is a graphical shell composed of icons, each with an underlying title. They can be moved and arranged in any order, and the icons' titles can be renamed. When double-clicked on, these icons open corresponding applications or smaller windows within the Program Manager window called group windows. These group windows contain such icons and can be minimized to prevent cluttering of the Program Manager window's space.[23] File Manager is another shell used to access or modify applications, but displays them as files contained in directories in a list format. Its purpose as an alternative to using DOS commands is to facilitate moving files and directories.[24] Task List displays all running applications and may also be used to terminate them, select a different program, cascade or tile the windows, and arrange minimized desktop icons.[25] The Control Panel, where users can change settings to customize Windows and hardware, was also redesigned as an icon-based window.[22][26]
The drivers bundled with Windows 3.0 support up to 16 simultaneous colors from EGA, MCGA or VGA palettes, as opposed to the previous maximum of eight colors,[27] though the operating environment itself supports graphics adapters that offer resolutions and the number of colors greater than VGA.[28] Windows 3.0 also introduced the Palette Manager, a set of functions that allow applications to change the lookup palette of graphics cards displaying up to 256 colors to use needed colors. When multiple displayed windows exceed the 256-color limit, Windows 3.0 prioritizes the active window to use that application's colors, without resorting to dithering and then filling in areas.[29][30]
Windows 3.0 retains many of the simple applications from its predecessors, such as the text editor Notepad, the word processor Write, and the improved paint program Paintbrush. Calculator is expanded to include scientific calculations.[15][31] Recorder is a new program that records macros, or sequences of keystrokes and mouse movements, which are then assigned to keys as shortcuts to perform complex functions quickly.[15][32] Also, the earlier Reversi game was complemented with the card game Microsoft Solitaire,[33] which would eventually be inducted into the World Video Game Hall of Fame in 2019.[34] Another notable program is Help. Unlike DOS applications, which may have help functions as part of them, Windows Help is a separate and readily accessible application that accompanies all Windows programs that support it.[15][35]
Memory modes
[edit]Windows 3.0 was the only version of Windows that could be run in three different memory modes:
- Real mode, intended for older computers with a CPU below Intel 80286, and corresponding to its real mode;
- Standard mode, intended for computers with an 80286 processor, and corresponding to its protected mode;
- 386 Enhanced mode, intended for newer computers with an Intel 80386 processor or above, and corresponding to its protected mode and virtual 8086 mode.[36]
Real mode primarily existed as a way to run Windows 2.x applications. It was removed in Windows 3.1. Almost all applications designed for Windows 3.0 had to be run in standard or 386 enhanced modes. (Microsoft Word 1.x and Excel 2.x would work in real mode as they were actually designed for Windows 2.x). However, it was necessary to load Windows 3.0 in real mode to run SWAPFILE.EXE, which allowed users to change virtual memory settings. Officially, Microsoft stated that an 8Mhz turbo 8086 was the minimum CPU needed to run Windows 3.0. It could be run on 4.77 MHz 8088 machines, but performance was so slow as to render the OS almost unusable. Up to 4 MB of expanded memory (EMS) is supported in real mode.
Standard mode was used most often as its requirements were more in-line with an average PC of that era — an 80286 processor with at least 1 MB of memory. Since some PCs (notably Compaqs) did not place extended memory (XMS) at the 1MB line and instead left a hole between the end of conventional memory and the start of XMS, Windows could not work on them except in real mode.
386 Enhanced mode was a 32-bit virtual machine that ran a copy of 16-bit Standard mode, and multiple copies of MS-DOS in virtual 8086 mode.[37] 386 enhanced mode uses virtual 8086 mode to allow multiple DOS programs to run (each DOS session takes 1MB of memory) along with being windowed and allowing multitasking to continue. Virtual memory support allows the user to employ the hard disk as a temporary storage space if applications use more memory than exists in the system.
Normally, Windows will start in the highest operating mode the computer can use, but the user may force it into lower modes by typing WIN /R or WIN /S at the DOS command prompt. If the user selects an operating mode that cannot be used due to lack of RAM or CPU support, Windows merely boots into the next lowest one.
Updates
[edit]There are two updates known to have been published for Windows 3.0. One of them is Windows 3.0a, released in December 1990. It modified Windows' DOS extender—a program that enables DOS applications to access extended memory—to prevent errors caused by software calling into real-mode code when Windows is loaded in standard mode. It also simplified the installation process and alleviated crashes associated with networking, printing, and low-memory conditions.[38][39]
Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions
[edit]Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions 1.0 (MME) was released to third-party manufacturers in October 1991.[40][41] The application programming interface introduced Media Control Interface, designed for any media-related device such as graphics and audio cards, scanners, and videotape players.[42][43] It also supported recording and playing digital audio,[44] MIDI devices, screensavers and analog joysticks,[42] as well as CD-ROM drives, which were then becoming increasingly available.[45] Other features included additional applets such as an alarm clock and Media Player, used to run media files.[46] MME supports stereo sound[47] and 16-bit audio bit depth and sampling rates of up to 44.1 kHz.[48]
System requirements
[edit]The official system requirements for Windows 3.0 and its substantial update, Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions:
| Windows 3.0[49] | Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions[50] | |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | 8086/8088 processor | 80286 processor running at 10 MHz |
| RAM | 1 MB of memory (640 KB and 384 KB of conventional and extended memory, respectively) (Work with only 640Kb - Real Mode) | 2 MB of memory |
| Storage | Hard drive with 6–8 MB of free space | Hard drive with 30 MB of total space |
| Medium | At least one floppy drive for the installation disks | A CD-ROM drive is essential for performing numerous multimedia operations.[51] |
| Video | Windows 3.0 supports a large array of graphics cards and computer monitors, and will try to use one of its generic drivers in the event that no driver exists to support the hardware. However, because the user interface is designed to be displayed at resolutions relatively high by 1990's standards, an EGA, MCGA or VGA display was recommended. (work with CGA and Hercules) | VGA graphics card |
| OS | MS- or PC DOS version 3.1 or higher | |
| Mouse | A Microsoft-compatible pointing device is recommended. | A mouse is required to perform many of the multimedia operations.[47] |
The processor and memory minimum requirements for the original version are those needed to run Windows in real mode, the lowest of the three operating modes.[21] This mode severely limits the multitasking capabilities of Windows,[52] although it can still use expanded memory, which is memory that is added by installing expanded memory boards or memory managers.[53] However, it also provides backward compatibility with as many hardware and software designed for DOS as possible, and it may be used to run DOS applications and older Windows applications not optimized for Windows 3.0 if running them in higher operating modes is not possible. Standard mode requires at least an 80286 processor, and although the memory required is unchanged, the mode does allow the processor to use extended memory for running applications. 386 enhanced mode requires at least an 80386 processor and two megabytes of memory.[52] While the other modes can run DOS applications in full-screen only and must suspend DOS applications to run Windows programs and vice versa, the DOS applications in 386 enhanced mode can be run windowed and concurrently with the Windows applications.[54] Unlike the other modes, this one cannot be used to run DOS applications that use DOS extenders incompatible with DPMI specifications.[52] Normally, Windows will start in the highest operating mode the computer can use, but the user may force it into lower modes by typing WIN /R or WIN /S at the DOS command prompt. If the user selects an operating mode that cannot be used due to lack of RAM or CPU support, Windows merely boots into the next lowest one.[55]
Reception
[edit]Windows 3.0 is considered to be the first version of Windows to receive critical acclaim.[2] Users and critics universally lauded its icon-based interface and the ensuing ease of performing operations,[15][16][27][56] as well as the improved multitasking and greater control over customizing their environments.[22][56][57] Computerworld considered the software to share the same benefits as OS/2 and Unix.[15] Garry Ray of Lotus considered this version of Windows the first of the environment to bear "serious long-term consideration."[16] Bill Howard of PC Magazine found its user interface to be easy to use, though not quite as intuitive as Macintosh.[56] The editor of InfoWorld, Michael J. Miller, had faith that PC users would fully transition from the preceding text-only environment to the GUI with Windows 3.0 as their primary choice.[58]
One critical aspect of Windows 3.0 is how it managed memory. Before its release, users of previous versions of Windows were burdened with trying to circumvent memory constraints to use those versions' touted capabilities. The Windows software occupied a large amount of memory, and users regularly experienced system slowdowns and often exceeded memory limits. Windows 3.0 also had relatively high memory requirements by 1990's standards, but with the three memory modes, it was praised for using memory more efficiently, removing the 640–kilobyte limit that had existed in computers running on Microsoft software since DOS, and supporting more powerful CPUs.[15][16][56][58]
Ted Needleman of the computer magazine Modern Electronics called Windows 3.0's GUI "state-of-the-art" and compared Microsoft's previous attempts to produce such a GUI to Apple Lisa, Apple's early such attempt and the predecessor to its far more successful Macintosh. He cautioned about the seemingly cheap upgrade cost of US$50 when the system requirements and the need to upgrade any installed applications for compatibility are considered. He also cautioned that the software's advantages could be taken only by running Windows applications.[10] However, in February 1991, PC Magazine noted a vast array of applications designed specifically for Windows 3.0, including many that had yet to be available for OS/2. It also cited two other factors leading to the operating environment's success: one of them was the inexpensive cost of the hardware needed to run it compared to the Macintosh, and the other was its focus on fully utilizing hardware components that were relatively powerful by its time's standards.[59]
Amid the unprecedented success of Windows 3.0, Microsoft came under attack by critics as well as the United States Federal Trade Commission, who alleged that the company had attempted to dominate the applications market by luring its competitors into developing software for IBM's OS/2 while it was developing its own for Windows.[60] At the time of Windows 3.0's release, Microsoft had only 10 and 15 percent of the market shares on spreadsheets and word processors, respectively, but those figures had risen to over 60 percent in 1995,[61] overtaking previously dominant competitors such as Lotus Development Corporation and WordPerfect.[62] Microsoft did indeed suggest developers to write applications for the OS/2, but it also intended Windows 3.0 to be a "low-end" alternative to the latter, with Gates referring to the OS/2 as the operating system of the 1990s. The Windows brand was also intended to be canceled after this version's release.[63] The investigations into—and the eventual subsequent suing of—Microsoft led to a settlement on July 15, 1994, where Microsoft agreed not to bundle separate software packages with its operating products.[64] It marked the first time that the company had ever been investigated for anticompetitive practices.[60]
Sales
[edit]Windows 3.0 is also considered the first Windows to see commercial success.[2] At the time of release, of the 40 million personal computers installed, only five percent used either previous version of Windows,[65] but within its first week of availability, it rose as the top-selling business software.[66] After six months, two million copies were sold.[60] Its success was interdependent with the PC industry, exemplified by an explosion of demand for and subsequent production of Intel's more powerful microprocessor, the 80486.[67] Windows became so widely used in businesses that Brian Livingston of InfoWorld wrote in October 1991 that "a company with no PCs that run Windows is almost like a company without a fax machine."[68] Microsoft had spent a total of $10 million in its marketing campaign for the software, including the $3 million for its release.[69] When its successor, Windows 3.1, was released, sales totaled about 10 million copies,[2] and a year later the Windows series would overtake DOS as the bestselling application of all time.[62]
Windows 3.0 is regarded in retrospect as a turning point in the future of Microsoft, being attributed to its later dominance in the operating system market and to the company's improved applications market share.[61] The company used to have close ties with IBM since the former's inception,[70] but the unexpected[60] success of its new product would lead to the two companies recasting their relationship, where they would continue to sell each other's operating products until 1993.[70] After the fiscal year of 1990, Microsoft reported revenues of US$1.18 billion, with $337 million appearing in the fourth quarter. This annual statistic is up from $803.5 million in fiscal 1989, and it made Microsoft the first microcomputer software company to reach the $1 billion mark in one year. Microsoft officials attributed the results to the sales of Windows 3.0.[71]
References
[edit]- ^ Reimer, Jeremy (November 29, 2019). "Half an operating system: The triumph and tragedy of OS/2". Ars Technica. Retrieved November 18, 2024.
- ^ a b c d Lendino, Jamie (November 20, 2015). "Microsoft Windows turns 30: A brief retrospective". ExtremeTech. Archived from the original on December 23, 2019. Retrieved December 22, 2019.
- ^ Edstrom & Eller 1998, p. 60.
- ^ Edstrom & Eller 1998, pp. 74–76.
- ^ "Windows 3.0 build 14". BetaWiki. Retrieved December 13, 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Sinofsky, Steven (February 7, 2021). "Klunder College". Hardcore Software. Archived from the original on February 28, 2021. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ Edstrom & Eller 1998, pp. 87–95.
- ^ "Vision for the Future". The Making of Microsoft: How Bill Gates and His Team Created the World's Most Successful Software Company. Prima Publishing. 1991. p. 239. ISBN 1-55958-071-2. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
- ^ InfoWorld, May 1990, p. S46.
- ^ a b c Needleman, Ted (September 1990). "The Real Windows Finally Arrives". Modern Electronics. Vol. 7, no. 9. CQ Communications. pp. 64–65, 68. ISSN 0748-9889. Retrieved January 4, 2020.
- ^ von Simson, Charles (May 28, 1990). "Microsoft leads DOS revival". Computerworld. Vol. 24, no. 22. p. 116. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved February 2, 2020.
- ^ Weinberger, Matt (August 17, 2015). "Bill Gates was so addicted to Minesweeper, he used to sneak into a colleague's office after work to play". Business Insider. Retrieved January 13, 2020.
- ^ "Pulling the Plug". PC Magazine. Vol. 20, no. 11. June 13, 2001. p. 73. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved December 16, 2019.
- ^ Cowart, Robert (2005). Special edition using Microsoft Windows XP home. Brian Knittel (3 ed.). Indianapolis, Ind.: Que. p. 92. ISBN 0-7897-3279-3. OCLC 56647752. Archived from the original on June 4, 2022. Retrieved April 19, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Windows 3.0 ends the wait". Computerworld. Vol. 24, no. 31. July 30, 1990. p. 33. Retrieved December 25, 2019.
- ^ a b c d Ray, Garry (July 1990). "Microsoft Windows 3.0". Lotus. Vol. 6, no. 7. IDG. pp. 88–89. Retrieved December 25, 2019.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, pp. 199–200.
- ^ InfoWorld, May 1990, p. S26.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, p. 405.
- ^ InfoWorld, May 1990, p. S3.
- ^ a b Windows 3 Companion 1990, p. 3.
- ^ a b c InfoWorld, May 1990, p. S7.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, pp. 101–102.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, pp. 121–122.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, pp. 26–27.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, p. 43.
- ^ a b InfoWorld, May 1990, p. S4
- ^ Poor, Alfred (June 25, 1991). "High Resolution And High Speed". PC Magazine. Vol. 10, no. 12. pp. 103–104. Archived from the original on April 7, 2022. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, p. 49.
- ^ PC Magazine, February 1991, pp. 375–376.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, p. 365.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, p. 317.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, p. 387.
- ^ Williams, David (May 3, 2019). "Microsoft Solitaire has been clicked and dragged into the World Video Game Hall of Fame". CNN Business. Archived from the original on December 22, 2019. Retrieved December 21, 2019.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, p. 87.
- ^ "Windows 3.0". Human Computer Interaction Lab of the University of Maryland. Retrieved August 20, 2013.
- ^ Chen, Raymond (May 17, 2010). "If Windows 3.11 required a 32-bit processor, why was it called a 16-bit operating system?". Archived from the original on June 5, 2010. Retrieved January 21, 2017.
- ^ Johnston, Stuart J. (November 26, 1990). "Windows Update Will Fix Bugs, Simplify Use". InfoWorld. Vol. 12, no. 48. p. 5. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved January 26, 2020.
- ^ Daly, James (April 29, 1991). "Windows 3.0A tackles UAE bug". Computerworld. 25 (17): 41. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved October 23, 2014.
- ^ InfoWorld, October 1991, p. S90
- ^ "Windows Version History". Microsoft Support. July 19, 2005. Archived from the original on January 3, 2018. Retrieved January 21, 2017.
- ^ a b Multimedia Guide 1991, p. 1-2.
- ^ Bright, Peter (October 21, 2012). "Turning to the past to power Windows' future: An in-depth look at WinRT". Ars Technica. p. 2. Archived from the original on January 26, 2020. Retrieved January 26, 2020.
- ^ Multimedia Guide 1991, p. 6-1.
- ^ InfoWorld, October 1991, p. S100.
- ^ Multimedia Guide 1991, p. 9-3.
- ^ a b InfoWorld, October 1991, p. S95.
- ^ InfoWorld, October 1991, p. S104.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, p. 3–4.
- ^ Multimedia Guide 1991, p. 1-3.
- ^ Multimedia Guide 1991, p. 4-1.
- ^ a b c Windows 3 Companion 1990, pp. 406–408.
- ^ InfoWorld, May 1990, p. S12.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, pp. 202–203.
- ^ Windows 3 Companion 1990, p. 6.
- ^ a b c d Venditto, Gus (July 1990). "Windows 3.0 Brings Icons, Multitasking, and Ends DOS's 640K Program Limit". PC Magazine. Vol. 9, no. 13. pp. 33–35. Archived from the original on February 25, 2021. Retrieved December 21, 2019.
- ^ InfoWorld, May 1990, p. S1.
- ^ a b InfoWorld, May 1990, p. S12
- ^ PC Magazine, February 1991, p. 102.
- ^ a b c d Edstrom & Eller 1998, p. 97–98.
- ^ a b Edstrom & Eller 1998, p. 95.
- ^ a b Wallace, James (1997). "The Road Ahead". Overdrive: Bill Gates and the Race to Control Cyberspace. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 24. ISBN 0-471-18041-6. Retrieved January 19, 2020.
- ^ Edstrom & Eller 1998, p. 94.
- ^ Department of Justice (August 21, 1995). "Final Judgment" (PDF). Archived from the original on January 19, 2020. Retrieved January 19, 2020.
- ^ InfoWorld, May 1990, p. 41.
- ^ Venditto, Gus (August 1990). "Pipeline". PC Magazine. Vol. 9, no. 14. p. 63. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved December 22, 2019.
- ^ Yu, Albert (1998). Creating the Digital Future. The Free Press. p. 145. ISBN 0-684-83988-1. Retrieved February 5, 2020.
- ^ InfoWorld, October 1991, p. S83.
- ^ Tremblay, Victor J.; Tremblay, Carol Horton (2007). Industry and Firm Studies (4th ed.). M.E. Sharpe. ISBN 978-0-7656-1723-1. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved February 5, 2020.
- ^ a b Edstrom & Eller 1998, p. 99.
- ^ Johnston, Stuart J.; Flynn, Laurie (July 30, 1990). "Microsoft Tops $1 billion in 1990". InfoWorld. Vol. 12, no. 31. p. 8. Archived from the original on February 27, 2021. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
Bibliography
[edit]- Lorenz, Lori L.; O'Mara, R. Michael (September 1990). Windows 3 Companion. Microsoft Press. ISBN 0-936767-19-7. Retrieved December 20, 2019.
- Edstrom, Jennifer; Eller, Marlin (1998). Barbarians led by Bill Gates. Henry Holt and Company. ISBN 0-8050-5754-4. Retrieved December 29, 2019.
- "InfoWorld". Vol. 12, no. 22. May 28, 1990. Archived from the original on August 14, 2021. Retrieved December 21, 2019.
- "PC Magazine". Vol. 10, no. 4. February 26, 1991. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- "Microsoft Windows Multimedia Authoring and Tools Guide". Microsoft Press. 1991. ISBN 1-55615-391-0. Retrieved January 26, 2020.
- "InfoWorld". Vol. 13, no. 42. October 21, 1991. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved January 2, 2020.
External links
[edit]- Windows history: Windows 3.0 takes off Archived January 11, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, an article detailing a brief history of Windows 3.0
